From this article you will learn about the types of polyarthritis, what kind of disease it is, what causes it. Symptoms and treatment, signs, diagnosis of pathology.
Author of the article: Nivelichuk Taras, head of the department of anesthesiology and intensive care, work experience 8 years. Higher education in the specialty “General Medicine”.
Article publication date: 06/25/2019
Article updated date: November 29, 2019
Polyarthritis is simultaneous inflammation of at least 5 joints. There are different types of polyarthritis (rheumatoid, psoriatic, gouty), their common symptom is pain in different joints.
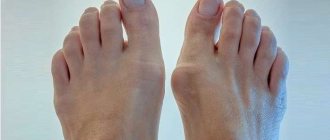
Types of polyarthritis using the example of hand joints. Click on photo to enlarge
The changes that occur in the body during polyarthritis, their danger and the prognosis for recovery depend on the type of pathology (the cause of inflammation of many joints), as well as on the degree of its severity.
- Some types of polyarthritis (for example, if the cause of the disease is the body’s reaction to a viral infection) can be cured completely, or even such pathology goes away completely on its own.
- Others, such as gouty arthritis, can be successfully treated into stable remission.
- Rheumatoid and psoriatic polyarthritis are incurable and require lifelong therapy.
Depending on the type of pathology, rheumatologists and traumatologists can treat it.
Polyarthritis of the joints - symptoms and treatment. Detailed information and useful tips
Polyarthritis, or simultaneous damage to several groups of joints, is not a separate disease, but the result of other pathologies. With polyarthritis, the entire structure of the joint suffers, namely the vessels, nerves, muscles, ligaments, capsules, menisci and most importantly: cartilaginous plates. Under the influence of a certain factor, an inflammatory agent and concomitant pathologies in the joints, the mechanism of an infectious-inflammatory process is initiated, which leads to the destruction of bone and cartilage tissue, limiting the biomechanics of the organ. This pathology is common to absolutely all people, regardless of gender or age. Therefore, all sane people should know everything about polyarthritis of the joints, symptoms and treatment.
Rheumatoid polyarthritis develops against the background of:
- autoimmune reaction,
- genetic predisposition,
- inflammatory processes that are already occurring in the body (sore throat, flu, sinusitis, otitis media, etc.),
- allergic reaction.
Crystalline polyarthritis develops against the background of metabolic disorders, for example, with gout or diabetes. The crystalline form of salts deposited in joints damages tissues, leading to deformation.
For unknown reasons, psoriatic polyarthritis develops against the background of psoriasis. It can develop in those whose relatives suffered from psoriasis or psoriatic polyarthritis.
Post-traumatic polyarthritis develops against the background of various bruises, dislocations, cracks, and minor injuries. There is a separate reason here - monotonous constant movements of the joints.
Reactive polyarthritis develops after suffering from various infectious and inflammatory diseases:
- cystitis,
- urethritis,
- endometritis,
- pharyngitis,
- bronchitis,
- prostatitis,
- gastritis,
- labyrinthitis,
- pneumonia, etc.
go to top
Classification, list of reasons
Multiple unusual damage to joints of an inflammatory nature or polyarthritis of the joints has its own special feature, namely, several joints from different areas of the locomotor system become inflamed simultaneously or gradually, and not in pairs, as usually happens with arthritis, arthrosis, or deforming arthritis-arthrosis. The etiology and pathogenesis of polyarthritis are identical to arthritis, that is, the structure of the articular structure is disrupted through abrasion of the cartilaginous plate, the appearance of bare bones with osteophytes + false joints. Next, the muscular-ligamentous corset is involved, plus partial or complete restriction of the motor function of the joints occurs. For the most complete concept, a photo is attached of polyarthritis of the joints.
Important! The clinical picture of arthritis manifests itself in several joints, and this is fraught with disability. At the first signs of the disease, immediately contact a traumatologist or rheumatologist.
Classification of polyarthritis according to the type of factors causing pathology:
Attention! The cause of polyarthritis is viral infections such as ARVI. Food poisoning also causes inflammation of multiple joints (most often the lower and upper extremities). After the cessation of the disease, all symptoms of polyarthritis disappear.
Which type affects the body is determined by diagnostics, that is, laboratory plus instrumental studies carried out after a general examination by a traumatologist, surgeon or rheumatologist.
Complications of polyarthritis
Typical consequences of a progressive disease can be deforming polyarthrosis, in which the process of ossification of scar tissue occurs, which leads to limitation of motor activity and the development of contractures.
Surgery in some cases can correct the situation, but this method of treatment cannot always be used. Such exceptions include children under 12 years of age, elderly patients, and people suffering from heart disease.
As a result, this category of patients, as a rule, is forced to change their usual lifestyle due to partial loss of full use of their limbs. Due to the difficulties in conducting independent active activities, a natural step in such a situation is to register a disability.
With rheumatoid polyarthritis, a number of complications may occur. Thus, inflammatory processes in the joints over time can provoke the appearance of damage to the eyes, skin, lungs, blood vessels, heart, and other organs. In addition, medications prescribed for the treatment of polyarthritis can also have some side effects.
Rheumatoid nodules can also appear in the heart and lungs. As a complication of the disease, a rash and other skin problems may appear. This can be either a consequence of the disease or a side effect of medications taken. Polyarthritis can cause eye diseases. Thus, patients sometimes develop inflammation of the episclera, scleritis.
And if the first disease is quite mild, then the second can even provoke vision loss. Sjögren's syndrome, which also occurs as a complication of polyarthritis, causes dryness and irritation in the eyes. If timely treatment is not started, scars may appear on the conjunctiva.
A rare and particularly severe complication is vasculitis, which affects small blood vessels. In most cases, patients have a decrease in the number of red blood cells, resulting in anemia with all the accompanying symptoms. Rarely, with polyarthritis, Felty's syndrome manifests itself - an increase in the size of the spleen.
In turn, this syndrome greatly increases the risk of lymph node tumors. When rheumatoid nodules form in the lungs, they, as a rule, do not affect the patient’s condition. However, sometimes they provoke lung collapse, infection, and accumulation of fluid between the membranes in the lungs. People with rheumatoid arthritis are much more susceptible to infections. Proper treatment of the disease and constant monitoring by the attending physician will help avoid such problems in the future.
Symptomatic picture
Each type of polyarthritis has its own individual symptoms. It depends on the underlying type or on the somatic disease. Therefore, each type is symptomatically characterized individually, namely:
- Polyarthritis against the background of rheumatism is manifested by migrating pain sensations, that is, sharp pain in one joint may subside, and in another it may begin, and so on the chain will continue. The manifestations of polyarthritis directly depend on the type of pathology. In addition to pain (which develops at night), patients experience complete or partial paralysis of movement in deformed or swollen joints. As the disease progresses, the pain intensifies, the general condition worsens, plus neurological signs are added to this; burning, numbness + chilliness. In addition to damage to the joints with rheumatism, damage to other systems is observed: cardiovascular, urinary and digestive. Therefore, such patients have hypertension, arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation, cardiac pain radiating to the left shoulder, as well as pain in the epigastric abdominal area, gastrointestinal disorders, and dysuric dysfunction.
- Multiple infectious arthritis (most often affecting the knee and shoulder joints) is clinically characterized by the following symptoms: pain, slight swelling and partial impairment of movement. All symptoms disappear after a full course of treatment. Polyarthritis of this type of joints consists of inpatient or outpatient treatment under the supervision of a physician.
- The crystalline form of joint pathologies is characterized by symptoms such as: severe pain in the joints of the feet, hands, and less often the knees or spine. Joints are swollen and painful. Some conglomerates (tophi) are visible around the joint. Biomechanics are completely disrupted. Movements are difficult and very painful. Sick locomotor organs react to changing weather. If the disease is advanced, then the microbial flora with fever, nausea, gag reflex, and suppuration of the joint joins the destruction.
Patients with diseases of the locomotor system, regardless of the stage and type of disease, are interested in: polyarthritis of the joints, drug treatment. After familiarization, as well as detection of certain symptoms, it is recommended to be examined in specialized centers.
https://youtu.be/H2zQhC7GJtU
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is based on the following indicators:
If symptoms of polyarthritis persist for one year or longer, x-rays of the hands and feet should be performed.
- Anamnesis collection. The doctor asks the patient whether he has chronic diseases or a hereditary predisposition to joint diseases.
- Examination of the patient. During examination, the doctor determines specific types of deformation.
- Laboratory research. A blood test will show high levels of white blood cells, C-reactive protein and rheumatic factor.
- X-ray. The simplest and most accessible procedure to determine the degree and activity of the disease.
- Ultrasound. Manipulation is carried out to identify complications.
Treatment technique
Before prescribing therapy, it is necessary to perform diagnostic tests, both laboratory and instrumental, to determine the cause. To diagnose multiple arthritis, a test analysis is performed to detect rheumatoid factor. According to statistics, in about 30% of cases in the patients studied, tests show the presence of the factor; antibodies of antinuclear origin are detected in the blood. This may be seropositive multiple rheumatoid arthritis, it refers to a severe form of the disease. In gout, a high concentration of purines is detected, and in infectious, a large titer of leukocytes, toxins and enzymes of the inflammatory process.
Based on the results of the examination, individual treatment is prescribed.
The treatment regimen for polyarthritis includes the following medications:
- drugs that relieve pain: Analgin, Baralgin, even narcotic medications, depending on the intensity of the pain;
- non-steroidal drugs: Diclofenac, Dikloberl, Ibuprofen, Movalis, Voltaren, Metindol, Butadione, Naproxen;
- medications of the COX1 or COX2 group (non-selective enzyme inhibitors) are prescribed;
- antispasmodics: No-Shpa, Spazmalgon;
- muscle relaxants with peripheral and central effects: Papaverine, Sirdalud Mydocalm, Baclofen;
- chondroprotectors: Chondrolon, Chondroxide, Alflutop, Rumalon, Chondrotin + Glucosamine;
- vitamins: B12, B1, B6, A, D, PP;
- antioxidant drugs: vitamin C;
- drugs that enhance immunity: Interferon Alpha;
- intra-articular blockades: Novocaine, Kenalok or Hydrocortisone;
- desensitizers: Tavegil, Suprastin, Diphenhydramine;
- massage and exercise therapy.
The crystalline type of polyarthritis pathology to the specified list is subject to adjustment of the level of salts, micro and macroelements, as well as uric and oxalic acid. Allopurinol and Urodan are added to the therapeutic regimen. Plus, an item is added to the scheme: detoxification therapy. All types of polyarthritis include adjusting the nutritional diet, excluding peppery, fatty, fried, spicy and bitter foods, as well as sour, sweet, alcohol and all carbonated drinks.
Important! In case of multiple hand arthritis with a rheumatoid component, modulation of immune reactions is performed using cytostatics (anticancer cytostatics), immunosuppressive group (chemical immunosuppressants).
The method of monoclonal antibodies is also used (the newest technique in therapy). If there is complete deformation of the fingers and hands, endoprosthetics of all affected joints is performed.
General approach to the treatment of inflammatory joint diseases
To get rid of inflammatory joint disease, you need to choose the right treatment tactics and adjust your lifestyle.
To achieve complete recovery, you need to adhere to the following principles:
- Treatment with disease-modifying anti-inflammatory drugs (DMARDs) should begin as early as possible;
- Medicines should be as active as possible. It is advisable to review the treatment regimen every 2-6 months;
- Therapeutic measures depend on the clinical manifestations and disease activity;
- Factors that can lead to exacerbation of the disease should be avoided: smoking, alcohol, poor diet, excessive physical activity;
- Ideal body weight should be maintained.
Only a doctor can prescribe the correct treatment for polyarthritis
To eliminate polyarthritis, drug therapy is most influential. Drug treatment is aimed at correcting various pathological processes in the human body.
Elimination of pain is the primary goal of treating joint inflammation of any origin.
Traditional medicine: recipes
Treatment of polyarthritis of the joints with folk remedies along with drug therapy will bring great benefits in curing the disease:
- Tincture of spruce needles : thoroughly crush 200g of needles and pour in 500ml of vodka. Leave for 7-10 days. Rub this tincture on sore joints.
- Rubbing propolis and vodka : 50g propolis + 100ml vodka. Infuses for 7 days. Rub your joints 3-5 times a day. Treatment course: until complete recovery.
- Garlic tincture with alcohol and honey : 150g chopped garlic + 100g honey + 50-100ml medical alcohol. Leave for 10 days. Rub the sore areas 2 times a day. After rubbing, place a small bag on top and leave for an hour.
- Caucasian hellebore ointment : one spoon of hellebore powder + a spoon of bee honey + a spoon of mustard powder and rendered lard. Stir thoroughly and leave in a warm and dark place for 10 days. Then use it as an ointment.
- Birch bud tincture : 200g of dry birch bud powder, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave for 24 hours. It is recommended to drink 50 ml once or twice a day before meals.
- Burdock root + honey : crushed root is poured into a liter of vodka and infused for a month. This tincture is used to wipe the joints.
Read also: Nutrition for rheumatoid arthritis
Before using folk tinctures or ointments, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
https://youtu.be/L-ofxWQAJdA
Joint disease, that is, the simultaneous damage of several different groups, is a serious challenge. Timely identification of the cause and its elimination will help to avoid many complications of the musculoskeletal system with damage to other vital organs and systems. Plus, armed with the necessary information, the patient will not allow the disease to progress to the chronic stage and be assigned a disability group.
Polyarthritis in children
Diagnosing polyarthritis in children is quite difficult, since they cannot talk about their feelings and adequately assess their condition (especially young children). Therefore, they become moody, sleep poorly, refuse to eat and stop moving. However, there are symptoms that can help identify polyarthritis in children. For example, a child stops walking, prefers to lie down, and if he is forced to move, he becomes capricious and cries. Also one of the symptoms is stiffness of movement in the morning and lameness in the child.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of joint diseases in children and, as in adults, each type of arthritis has its own reasons for development. However, the main reasons for the development of the disease in children are:
- hypothermia;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- injuries;
- hereditary factor;
- avitaminosis;
- metabolic disease;
- previous infection;
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune system.
The disease in children manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- dysfunction of the joint (the child has difficulty moving);
- pain that intensifies during and after movement;
- lameness;
- loss of appetite;
- capriciousness (usually a cheerful and cheerful baby becomes capricious and whiny);
- lethargy and fatigue;
- loss of body weight.
During an acute attack of polyarthritis, the joints become purple and may become deformed. Effective treatment of arthritis depends on identifying the cause of the disease. If diagnosis is successful, treatment is prescribed, which is complex and quite long-term (in some cases several years). Treatment is carried out both in the hospital and on an outpatient basis. It consists of taking anti-arthritic medications, physiotherapy, physical therapy, massage, diet and spa treatment. If treated incorrectly and untimely, the disease becomes chronic and accompanies the child for life. In addition, during the period of acute exacerbation, it is recommended to wear splints, bandages and orthoses to temporarily restrict movement and fix the joint in a certain position. In severe cases, surgical treatment is performed. It is important to remember that polyarthritis is a disease that is difficult to diagnose at an early stage, but its consequences have a great impact on the quality of life and health of the child.
How to treat polyarthritis
Joints are the part of the musculoskeletal system that connects the bones and provides movement throughout the human body. Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joint, which can occur for various reasons. Polyarthritis is multiple inflammation of the joints. Today we will talk about the treatment of polyarthritis.
What kind of disease polyarthritis is and how to treat it is of interest to many patients. Joint inflammation is a serious pathology that can lead to disability and chronic joint pain. For this reason, polyarthritis must be treated correctly, under the supervision of an experienced doctor.
Main symptoms
https://youtu.be/Wqry8B-d9ow
Regardless of the disease that led to polyarthritis, the following clinical signs will always be distinguished:
- joint pain;
- restriction of movement in them;
- swelling in the affected area;
- increase in local temperature over the affected area;
- deformation of the articular surfaces with the possible development of persistent contractures (inability to straighten or bend the limb).
These types of symptoms can occur together or follow one another.
Which doctor treats polyarthritis?
The first question that arises among patients is which doctor treats polyarthritis of the joints. If the patient experiences symptoms such as joint pain in the morning or when moving, swelling around the affected joint, redness of the skin and impaired motor activity, then you should consult a therapist as soon as possible.
The fact is that polyarthritis is a whole complex of pathologies that arise for a variety of reasons, and depending on the type of disease, different specialists will deal with its treatment.
A general practitioner will be able to take an anamnesis and evaluate the patient’s complaints, and prescribe blood and urine tests. Based on such an examination, the specialist will refer the patient to the specialist who is needed in a particular case.
If joint pain is associated with injury, the patient will be referred to a traumatologist or surgeon. In case of gout, treatment will be carried out by a rheumatologist, and the patient will also need to consult a nutritionist and endocrinologist. For rheumatoid arthritis, the patient will be advised to consult a rheumatologist and immunologist.
Signs of polyarthritis
Since polyarthritis occurs for multiple reasons, the symptoms and course of the disease, as well as its treatment methods, differ in polymorphism. Therefore, for each patient suffering from polyarthritis, the disease progresses individually and in its own way. A common symptom that unites all types of polyarthritis is inflammation of the joint tissue (synovium) that surrounds it.
Thus, the symptoms of polyarthritis depend on its type and the cause that caused it. For example, rheumatoid polyarthritis is characterized by a sluggish onset. Symptoms appear only when the weather changes: joints become slightly swollen, fatigue and sweating appear. With infectious polyarthritis, swelling and redness of the skin over the affected joint and limited mobility are observed. Sometimes there is loss of appetite and weight loss, as well as an increase in body temperature. In some cases, polyarthritis leads to a strong increase in temperature, which is accompanied by fever and leads to damage to internal organs. Post-traumatic polyarthritis is manifested by limited movement, aching dull pain in the joints and muscles, as well as crunching in the joints. Complications of this form of arthritis can be an abscess, erysipelas, or furunculosis.
Metabolic polyarthritis is accompanied by the deposition of sodium urate in the articular cartilage, which damages them, makes them rough, with cracks and ulcers. It mainly affects the big toe, which becomes swollen and red. The attack is accompanied by severe pain and high fever. Over time, tophi appear, which is a classic manifestation of gouty arthritis.
Reactive polyarthritis develops as a result of a genitourinary infection. As a rule, it begins violently with high fever and severe pain. The joint swells, the skin over it turns red, and mobility is limited. With adequate treatment, the disease goes away quickly and without consequences.
Since each type of polyarthritis has its own manifestations, the main symptoms for all forms can be identified:
- joint pain;
- deformation of joint tissues;
- skin pigmentation on the inflamed joint;
- jumps in body temperature;
- burning and numbness of the limbs;
- morning stiffness of joints;
- flying pains that can “wander” from joint to joint.
The entire spectrum of symptoms can be divided into three types:
- acute form;
- subacute;
- chronic.
The acute form of the disease is manifested by severe pain and is permanent. Joint dysfunction, swelling and redness are also observed. The subacute form does not have pronounced manifestations, and in the chronic course of the disease, pain is observed only during the period of exacerbation. In addition to damage and deformation of the joints, with polyarthritis, muscle atrophy and a decrease in muscle mass are observed.
Which clinics treat polyarthritis?
We figured out which doctor treats polyarthritis of the fingers and other joints, but the question remains open, which hospital can you go to for quality treatment. You can check your joints at any local clinic completely free of charge under your compulsory medical insurance policy. To do this, you need to visit a therapist who will give you a referral to other specialists.
If the patient does not want to wait his turn at the municipal clinic, he can undergo examination and treatment for polyarthritis for a fee. Paid services are provided in both clinics and private clinics, but before contacting an unknown private clinic, it is recommended to make sure of the professionalism of the doctors.
Effective treatment of polyarthritis is also carried out in clinics abroad, Israel, Germany and other countries with a high level of medicine. In order to undergo treatment in a foreign clinic, you need to choose a medical institution, contact the doctor and agree on treatment.
In Israel, polyarthritis is treated in clinics such as Assuta, Hadassah, etc. These medical institutions are known all over the world; they employ experienced specialists who provide the highest level of medical care.
Life forecast
The prognosis for life is favorable when treating any type of polyarthritis. Although the disease is not curable, it is well controlled, preventing exacerbations. How long do people live with polyarthritis? All life. The disease is not fatal, but it has its complications if the patient is not treated:
- Focal nephritis.
- Heart diseases.
- Respiratory diseases.
- Skin diseases.
- Amyloidosis.
- Impaired liver and kidney function.
- Bursitis with the formation of abscesses and furunculosis.
- Tenosynovitis.
Here it is important not only to treat your illness constantly, but also to carry out prevention:
- Avoid traumatic situations;
- Eat well;
- Treat all specific infectious diseases;
- Perform moderate exercise;
- Strengthen immunity;
- Avoid hypothermia;
- Contact a doctor at the first symptoms.
How to treat polyarthritis at home
Polyarthritis requires complex and long-term treatment, but most often therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis if there is no need for surgical intervention. How to treat polyarthritis of the joints on the fingers, glenohumeral polyarthritis and its other types, the doctor must decide, since it is first necessary to make a correct diagnosis.
Therapy for polyarthritis is very different, depending on its type, let's look at how polyarthritis can be treated with medications:
- To relieve pain and inflammation, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, for example, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Nise, etc. Such drugs effectively relieve pain and reduce inflammation. These drugs are used in the form of tablets and ointments on the affected area.
- Corticosteroids are prescribed for severe pain and inflammation, most often in advanced stages of polyarthritis. The drugs are injected into the joint cavity, which helps to quickly relieve the symptoms of the disease.
- If polyarthritis is associated with metabolic disorders, as happens with gout, then drugs are prescribed that remove uric acid from the body.
- If polyarthritis is associated with infection, then antibiotics and antiviral drugs are prescribed.
- For rheumatoid polyarthritis, taking basic medications is indicated.
- In cases where destruction of cartilage tissue is observed, vitamins and chondroprotectors are prescribed.
The doctor treating polyarthritis must prescribe rest to the patient during the period of exacerbation of the disease. It is forbidden to load the affected joints; this is necessary in order to prevent the destruction of cartilage tissue. Physiotherapeutic treatment is indicated to relieve inflammation and pain in polyarthritis.
After relieving inflammation and pain, patients are recommended to engage in physical therapy, undergo massage, and balneotherapy, that is, treatment with mineral waters, is also very effective for polyarthritis. Following all the doctor’s recommendations will help avoid relapses of the disease and extend the life of the joints.
Polyarthritis and its types
What happens in the body during polyarthritis? It is well known that around the tissues that surround the membranes of the joints there are a huge number of blood vessels and nerve endings. When an infection occurs in the body, it spreads through the bloodstream, entering the joint, causing its inflammation and destruction. This is how polyarthritis develops.
The following types of polyarthritis are distinguished:
- Infectious polyarthritis develops due to infection. This type of disease is quite easy to treat, but only if the disease is detected in a timely manner, correctly diagnosed and an adequate treatment regimen is selected. If the symptoms are ignored, infectious polyarthritis can lead to serious consequences in the form of joint dysfunction.
- Rheumatic (rheumatoid) polyarthritis does not develop due to infection. This type of polyarthritis is much more dangerous, since in addition to joints it also affects connective tissue, and can also quickly spread to other tissues and organs. It is necessary to begin treatment immediately after detection of the disease, since advanced stages are difficult to cure. As a result of medical statistics according to the international classification code (rheumatoid arthritis ICD), 60% of people (after 50 years) suffer from this disease.
- Psoriatic polyarthritis causes inflammation of those joints, the skin over which is affected by psoriasis. For example, skin lesions on the ankle provoke damage to the ankle joint. In the absence of adequate treatment, the disease can spread to other joints.
- Reactive polyarthritis develops as a result of infections of the genitourinary system (cystitis or urethitis). This type of arthritis is very dangerous because other diseases can occur against its background: polyneuritis, conjunctivitis, colitis.
- Metabolic polyarthritis (crystalline) occurs due to metabolic disorders. When purine metabolism is disrupted, the body releases a large amount of uric acid, which is deposited in the joints, causing gout attacks. A striking example of metabolic polyarthritis is gouty arthritis. Over time, degenerative changes in the articular cartilage occur, which are accompanied by sclerotic and fibrinous changes in the synovial membrane of the joint.
- Post-traumatic polyarthritis occurs after an injury: joint fracture, bruise, dislocation or subluxation. This arthritis is dangerous due to possible complications: inflammation of the mucous membranes of the joint and the development of watery edema around it.
How to treat rheumatoid polyarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis requires special attention, as it is a complex autoimmune pathology that is not so easy to get rid of. The disease is called polyarthritis if five or more joints are inflamed.
In general, the answer to the question of how to treat seropositive rheumatoid arthritis is simple; the prescriptions usually coincide with the treatment of ordinary polyarthritis. Patients are prescribed anti-inflammatory and painkillers, vitamins, and therapeutic treatment. An exception is the use of special basic medications, which are necessary to suppress the body’s autoimmune reaction and stop the destruction of joints.
Depending on the age and condition of the patient, the stage of the disease, the doctor prescribes the following basic drugs:
- gold preparations;
- immunosuppressants;
- antimalarial drugs;
- sulfonamides;
- d-pennicylamine.
All these medications are taken only as prescribed by a doctor, as they have serious side effects. Uncontrolled use of basic drugs can lead to serious complications and even death.
An important part of the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis is a special diet. It has been noted that some foods can provoke exacerbation of polyarthritis, these include milk, pork, corn, citrus fruits, wheat and oatmeal. The consumption of these products should be reduced to a minimum, or better yet completely excluded from the diet.
What is the difference between polyarthritis and polyarthrosis?
No less important points are the distinctive features of polyarthritis from polyarthrosis. What is the difference?
Polyarthrosis is a joint disease associated with age-related degenerative (destructive) changes in them. It occurs in the older age group and most often affects large articular surfaces - knees, shoulders, pelvic joints. Polyarthrosis is a pathology that affects exclusively the joints. At the same time, their defeat due to polyarthritis is only the “tip of the iceberg.” In addition to the articular surfaces, the pathological process can also involve vital organs - the heart, liver, kidneys, blood vessels and others. This condition can be activated by any infectious agent (microbe, virus, fungus, etc.), mechanical injuries, disturbances in metabolic processes (for example, purine metabolism in gout), or by one’s own body, when, due to failures in the immune system, antibodies are produced against joint cells (autoimmune damage). ). The incidence of polyarthrosis directly correlates with age. After reaching the age of 65, this pathology is observed in every second person. In total, about 5 - 7% of the world's population suffers from polyarthritis, and more than 20% suffer from polyarthrosis.
By 2030, according to various forecasts, more than 65 million people will suffer from various types of arthritis.
How to treat rheumatoid arthritis at home
It is not recommended to treat rheumatoid polyarthritis at home, as there is a need to take basic medications. During the period of exacerbation, the doctor must monitor the patient’s condition in order, if necessary, to cancel the prescribed drug and replace it with another.
Read also: Treatment for arthritis
After consultation with a doctor, you can be treated on an outpatient basis; in this case, the specialist prescribes therapy for the patient and recommends regular examinations to assess the dynamics of the body’s condition.
For rheumatoid arthritis, traditional medicine recipes can be used, but it is worth remembering that they are not a panacea and will not get rid of the cause of the pathology, but will only slightly alleviate the symptoms of polyarthritis.
Prevention and prognosis
There are many root causes of the disease, so first of all, it is important for a person to monitor his health, not skip routine medical examinations, and consult a doctor at the first symptoms. It is also important to eat right, exercise as a preventive measure, and protect your joints from injuries and bruises. If you are predisposed to polyarthritis, it is important to always be in touch with your doctor. When the pathology is diagnosed in the initial stages, the prognosis for recovery is favorable, otherwise joint deformation is inevitable, which entails complications and negative consequences.
https://youtu.be/jQwF3sWDnbA
Treatment of polyarthritis with folk remedies
Many patients prefer traditional medicine recipes, so let’s look at how to treat polyarthritis of the fingers with folk remedies so that the therapy is as effective and safe as possible. First of all, you need to make sure that you are not allergic to the components of the product, and also be sure to consult a doctor.
For various types of polyarthritis, the following folk recipes will help relieve inflammation and pain:
- Mineral and salt baths are good for polyarthritis; they are carried out during periods of exacerbation of the disease and for prevention. Instead of baths, you can make lotions with saline solution; for this, sea salt is dissolved in hot water and a clean cloth is soaked in it.
- A compress made from cabbage leaves and honey has an anti-inflammatory effect. To prepare it, you need to crush a leaf of white cabbage with a rolling pin and grease it with natural honey, apply it to the sore joint overnight.
- Tea made from rose hips and currants is very useful for polyarthritis. To prepare it, rose hips are poured into a thermos and poured boiling water, left for 8 hours, then filtered and grated currants are added to it. The resulting drink should be drunk throughout the day instead of black tea.
- Many patients are interested in how to treat polyarthritis with an Adam's apple. A medicinal rub is prepared with this fruit, which helps reduce joint pain. The Adam's apple needs to be washed and grated, the pulp should be placed in a liter jar and filled with 200 grams of alcohol. Cover the product with a lid and leave for 2 weeks in a dark place, shaking occasionally. Rub the product onto your joints twice a day for two weeks.
Treatment methods
The prognosis for recovery from polyarthritis depends on what disease it is caused by.
If inflammation of 5 or more joints is caused by the body's response to a viral infection, the patient's condition improves on its own within 6 weeks.
But rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic and constantly progressive disease that cannot be completely cured.
An accurate answer to the question of how to treat polyarthritis will only be possible after determining the exact cause of its occurrence.
Only a doctor who has established and confirmed the diagnosis can prescribe appropriate conservative or surgical treatment.
Drug treatment
Treatment for almost all types of polyarthritis involves taking medications that reduce inflammation.
Doctors may prescribe drugs from the following groups.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Examples of drugs: aspirin, naproxen, ibuprofen, diclofenac and others. They reduce the activity of the inflammatory process and also help relieve pain.
The action of NSAIDs develops quickly. Side effects of these drugs include upset stomach, ulcers, and gastritis.
Corticosteroids
Examples of medications: prednisolone, hydrocortisone, dexamethasone. They reduce inflammation by suppressing the body's immune system.
Corticosteroid drugs to reduce inflammation in polyarthritis. Click on photo to enlarge
This treatment is most effective if polyarthritis is caused by autoimmune diseases - for example, systemic lupus erythematosus.
Corticosteroids may increase the risk of osteoporosis, obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and impaired immunity.
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs
These are methotrexate, cyclosporine, azathioprine. This group of drugs is used to treat polyarthritis: rheumatoid, psoriatic, and also caused by ankylosing spondylitis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
They reduce inflammation and relieve pain, reduce or prevent joint damage, and help maintain joint structure and function. The action of these drugs is based on the suppression of the body's immune and inflammatory systems.
The effects of these drugs take several weeks to develop, so disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs are not used to quickly relieve the symptoms of polyarthritis - NSAIDs or corticosteroids are used for this purpose.
Because antirheumatic drugs suppress the immune system, patients may develop infections.
TNF (tumor necrosis factor) inhibitors
TNF inhibitors are molecules that can suppress the activity of substances that cause inflammation.
Examples of drugs in this group: infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept. Tumor necrosis factor causes inflammation in various types of polyarthritis, and the use of TNF inhibitors suppresses this reaction.
They are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis.
The main side effects are intolerance reactions, fever, chills, headaches, increased susceptibility to infectious diseases.
Non-drug treatment
If a person develops signs of polyarthritis, several doctors may be involved in his treatment. But the recovery process largely depends on the patient himself.
Every patient with polyarthritis (of any type) needs:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Eat properly and balanced.
- Stay physically active.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Dealing with the emotional and psychological consequences of an existing health problem may require support from relatives, friends, and colleagues.
Positive changes can be motivated by knowledge of what polyarthritis is, how to deal with this disease, what its symptoms and treatment are.
Your doctor can help you plan for any changes you need to make in your lifestyle, activity, diet, and work life.
Simple changes to help cope with polyarthritis:
| Change | Description |
| Stay Organized | Take some responsibility for your treatment by noting your symptoms, their intensity, and how they relate to your medications. Monitor side effects of your medications This information will help doctors decide on further tactics. |
| Control pain and fatigue | It is important not to let pain and fatigue become overwhelming To relieve pain, you can combine medications with non-drug methods of pain relief. To combat stress, use various relaxation techniques, physical activity, meditation and other methods. |
| Stay physically active | Exercise is good for joints and overall health They help strengthen muscles, maintain and increase mobility, improve sleep quality, improve mood and reduce weight. |
| Balance physical activity with rest | Rest is important if the disease is in the acute stage, i.e. any movements in the affected joints are sharply painful and limited |
| Follow the rules of a healthy and nutritious diet | A healthy diet helps maintain normal body weight and control inflammation Limit your consumption of refined and highly processed foods Choose plant-based foods that are rich in antioxidants and have anti-inflammatory properties. |
| Improve your sleep | Make your bedroom dark, cool and quiet In the evening, avoid caffeinated foods and drinks, avoid strenuous physical activity, take a warm bath |
Folk remedies
Many patients give preference to folk remedies for the treatment of polyarthritis of the joints, believing in their safety and effectiveness. For this purpose, use:
- Alcohol tincture of chestnuts.
- Decoction of bay leaves.
- Tincture of aspen buds.
- A solution for external use made from turpentine, egg yolk and vinegar.
- Grinding from radish juice, honey and vodka.
Alcohol tinctures from chestnuts for the treatment of polyarthritis
Recipes of folk remedies, dosage, duration of use.
Let's look at examples of preparing two recipes:
Alcohol tincture of chestnuts
- Take 50 g of chestnut skins, finely chop.
- Add 500 ml of 40% vodka.
- Leave in a dark, dry and cool place for 2 weeks.
Take 30 drops for 1 week, dissolving in water (100 ml) 3 times a day before meals.
Decoction of bay leaves
- Take 5 crushed bay leaves.
- Add 300 ml boiling water.
- Soak in a water bath for 5 minutes.
- Leave in a thermos for 5 hours.
Drink the entire prepared broth within 12 hours in small portions (no more than 50 ml at a time). The course of treatment is 3–5 days.
For more detailed prescriptions, you need to look at the specific disease, when and what is suitable.
Before using any homemade product, you should consult your doctor.
What kind of disease
The disease develops due to injury or infection of tissues by harmful bacteria. Since inflammation affects several joints at once, the cause in most cases is infection. The disease can develop quickly or affect the joints gradually. The joint contains a large number of nerve endings and blood vessels.
With polyarthritis, the tissue and synovium become inflamed. It is extremely difficult to make a diagnosis, since the disease has similar symptoms to other diseases. Inflammation causes severe and unbearable pain, limiting a person’s movements and significantly complicating his life.
Many viruses can trigger the development of the disease, most often the pathology develops against the background of rubella or mumps. In some cases, the disease may be a harbinger of hepatitis B. Polyarthritis of the joints is a serious and unpleasant disease, but it can be cured. You need to seek help from a specialist in a timely manner. Treatment of the disease occurs much faster if the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations.
What types of pathology are there?
Considering the reason why the disease began to develop, there are the following types of polyarthritis:
- Infectious specific. It appears after the body is infected with pathogens that provoke tuberculosis, gonorrhea, brucellosis, and dysentery. Inflammation is localized in the area of a single joint or spreads to several joints.
- Infectious nonspecific. In this case, it is impossible to name the exact cause of the pathology. But traditional medicine suggests that the impetus for the development of the disease is the body’s immune response to an allergic irritant, as a result of which the erosive process progresses on the joint structures.
- Exchangeable or crystalline. Inflammatory complications develop as a result of disturbances in metabolic functions in the body. As a result, salt formations appear on the articular surfaces, which gradually destroy and deform the joint.
- Psoriatic. The factors that provoke this type of polyarthritis are still unknown. A destructive autoimmune process provokes inflammation of the synovial membrane, and soft structures - ligaments and tendons - can be damaged.
- Post-traumatic. The first symptoms of polyarthritis in this case begin to appear after a bruise, trauma, fracture, crack or microtrauma.
- Reactive. The main root cause is infection with bacterial, chlamydial, fungal and viral microorganisms. Also, the development of pathology can be affected by infection of the genitourinary system, gastrointestinal tract, and respiratory tract. Even if the pathogen penetrates the eyes, and the person does not carry out adequate treatment, it can spread throughout the body and begin to affect the joint structures.
Other varieties
The disease can be localized on the toes.
There is also a classification based on location. In this case, polyarthritis of the toes and hands, spine, wrist, knee, ankle, and hip joints are distinguished. The cervical spine is also affected. According to the nature of the flow they are distinguished:
- Acute polyarthritis. Signs of pathology are clearly expressed; if therapy was carried out adequately, this helps prevent negative consequences.
- Chronic polyarthritis. It is characterized by a sluggish inflammatory process, as a result of which irreversible degenerative disorders develop in the joint structures.
Classification
- Rheumatoid can cause damage to several joints at the same time. The connective tissue is the first to suffer. Polyarthritis of this type quickly develops in all other joints of the body; it is timely consultation with a doctor that can reduce the negative consequences of this fleeting disease;
Dr. Bubnovsky: “Penny product No. 1 for restoring normal blood supply to the joints. Helps in the treatment of bruises and injuries. Your back and joints will be the same as when you were 18 years old, just apply it once a day. »
- Infectious develops as a complication of tuberculosis or gonorrhea. Pathogens penetrate the joints in most cases, but timely medical care can effectively and quickly cope with the infection;
- Metabolic are found in those people who have metabolic disorders. Hence its name. If a person’s body suffers from excessive salt deposition, then the likelihood that he will develop this particular type of polyarthritis is very high;
- Reactive develops as a result of infection in the human genitourinary system; less commonly, the cause may be an infection of the upper respiratory tract. With this type of disease, patients experience conjunctivitis or colitis;
- Psoriatic has an autoimmune nature; the patient has skin rashes in the form of psoriasis. It mainly affects young and middle-aged people. It can occur in both men and women. Fortunately, children do not suffer from this type at all;
- Brucellosis occurs after infection with the bacterium brucellosis occurs. It is transmitted from a sick animal to a person through direct contact. In addition, the pathogen may be on poorly processed food. The disease most often affects the large and medium joints of a person, usually the hip or shoulder;
- Gonorrheal can occur after gonorrhea or in the presence of chronic prostatitis;
- Syphilitic often occurs as a complication of syphilis. Treponema pallidum spreads throughout the body, affecting human joints. The patient experiences acute pain, especially at night;
- Dysenteric is a consequence of the fact that a person has had dysentery. At the same time, the patient’s body temperature rises. The patient feels aches and general weakness.
Doctors note the fact that most often polyarthritis affects a person’s hands and fingers. According to studies, finger pathology occurs in many people, approximately 60% of all patients. The joints of the fingers become deformed and take on an unnatural shape. In addition to external signs, there are a number of negative consequences, including loss of hand functionality.
Polyarthritis of the legs is also often noted by doctors. The inflammatory process occurs as a result of bruise or hypothermia. The foot becomes immobile and increases in size. The person cannot stand on his own two feet and becomes completely helpless.
Symptoms and treatment of polyarthritis of the joints depend on what type of inflammation affects the person. Swelling, discoloration of tissues and lack of movement indicate that polyarthritis is caused by infection.
Rheumatoid polyarthritis has no clear symptoms. With this type of disease, there may not be any external signs such as swelling or redness of the skin in the knee area. However, a person experiences pain when there is a sudden change in weather. Sick people become indifferent to food, as a result of which they lose a lot of weight. Some experience high fever and general weakness.
Polyarthritis of the hands is accompanied by a sharp pain syndrome, especially when moving the hands. The skin at the site of inflammation turns red and swells. The person’s temperature increases, and the fingers become immobilized.
Read also: Is arthritis curable?
The disease can cause various complications in the human body. Patients often experience inflammation of tendons, ligaments and muscles. This condition in scientific language sounds like periarthritis. Periarthritis can occur in any joint in a person, but is more common in the shoulder. Scapulohumeral periarthritis is characterized by localization of inflammation directly in the scapula.
Less frequently, but still, pathology of the jaw joint occurs. Patients are unable to open their mouth wide and chew food. The pain radiates to the temple and back of the head, bringing unbearable discomfort.
The disease can be caused by various reasons. The most common ones are:
- The presence of acute infectious processes in the body, for example, sore throat or pneumonia. The causative agent of sore throat is delivered to human joints through the bloodstream;
- Insufficient blood supply;
- Chronic inflammation;
- Due to mechanical damage. For example, in case of a blow or bruise;
- Autoimmune diseases;
- Allergy;
- Prolonged exposure to cold;
- Obesity;
- Failure of the endocrine system;
- Bad habits;
- Poor nutrition.
Regardless of what type of polyarthritis affects the human body, there are common symptoms characteristic of any type of disorder.
- The pain is located directly in the joint. It especially increases during movement;
- In the place where there is an inflammatory process, the soft tissues turn red and swell;
- There is no sensitivity in the limbs;
- Body temperature rises;
- Functions such as flexion and extension are completely absent;
- In later stages, significant deformation is observed. It is especially clearly visible on the patient’s arms and legs.
Characteristic features of the disease
The development of the disease can be triggered by infection, endocrine disorder, and various forms of arthritis in children and adults. Polyarthritis affects almost all structural elements of the joints. The inflammatory process involves capsules, synovial membranes, ligamentous-tendon apparatus, and nearby periarticular tissues. In the absence of medical intervention, complete fusion of the joint spaces and the development of ankylosis are possible. Polyarthritis can be either an independent pathology or a consequence of other diseases of the joints or internal organs. The severity of symptoms and the prognosis for recovery depend on the factors that provoke its development. The functional activity of several joints may decrease for two reasons:
- pain, to eliminate which a person deliberately limits movement;
- pathological changes in soft, cartilage, bone tissues.
The pain syndrome has a wave-like character. Its intensity increases with physical exertion, increased physical activity, and at night and in the morning. With timely diagnosis of the acute form of polyarthritis and its immediate treatment, the prognosis for complete recovery is favorable. Chronic disease is also treatable to one degree or another, but leaves behind irreversible consequences. Most often, patients are diagnosed with rheumatoid, infectious, reactive polyarthritis.
Less commonly diagnosed is gouty pathology, provoked by the deposition of crystallized uric acid salts in the joints and periarticular tissues. The clinical picture of psoriatic polyarthritis combines signs of damage to the joints and skin. The reasons for the development of these two forms of arthritis have not yet been established.
Rheumatoid polyarthritis
This is an independent systemic pathology that affects connective tissue joint structures. Rheumatoid polyarthritis is still a completely incurable disease that causes disability in 70% of patients. It is diagnosed much more often in women of fertile age than in men. The reasons for the development of polyarthritis have not been established, but the presence of special genes has been revealed to be of no small importance in the pathogenesis. Under the influence of certain factors (relapse of a chronic disease, infection, severe hypothermia, stress), the functional activity of the immune system decreases. It begins to produce antibodies that destroy the body's own cells.
The clinical picture of rheumatoid polyarthritis includes articular and extra-articular signs. The articular-visceral form, considered the most severe, is characterized by damage to the joints simultaneously with the organs of the cardiovascular, respiratory, and nervous systems. And with Felty's syndrome, pathological changes are observed in the spleen. But all forms of rheumatoid polyarthritis have many common clinical manifestations:
- symmetry of inflammatory damage to joints;
- morning stiffness in the joints, usually at an early stage of the pathology;
- arthralgia of a wave-like nature;
- feeling of numbness, stiffness;
- muscle atrophy;
- decreased tactility;
- deformation of the joints, their increase in size.
https://youtu.be/EzlgImwVUfw
The general health of a person gradually deteriorates. During the day, the temperature may rise several times, chills, fever, cold sweat, and fatigue may occur. As polyarthritis progresses and damages internal organs, the severity of symptoms increases. The course of the disease is often complicated by vasculitis, atherosclerosis, pericarditis, heart disease, pleurisy, ulcerative keratopathy, and keratoconjunctivitis. If the pathology affects the nervous system, then the clinical picture is supplemented by cervical myelitis, multiple mononeuritis, and sensory-motor neuropathy.
Reactive polyarthritis
One of the reasons for the development of reactive polyarthritis is infection with pathogenic bacteria, fungi or viruses. But it is not the activity of pathogenic microorganisms that leads to the inflammatory process in the joints, but the inadequate response of the immune system. The protein structures of infectious agents and cells of connective tissue joint elements are quite similar. Therefore, immunoglobulins produced by the immune system begin to attack the synovial capsules and their membranes, elements of the ligamentous-tendon apparatus. For example, rheumatoid arthritis occurs after a person is infected with beta-hemolytic streptococci. The breakdown of tissue provokes inflammation, further damaging the joints. The following symptoms are characteristic of the reactive form of polyarthritis:
- hyperthermia, chills, general malaise;
- hyperemia of the skin over the site of inflammation;
- swelling of the joint, pain, increasing with movement and palpation.
Extra-articular signs include redness of the eyes, lacrimation, burning, frequent urination, inflammation of the oral mucosa, accompanied by damage to the surface layer and the formation of erosions.
Reactive polyarthritis is diagnosed after salmonellosis, shigellosis, cystitis, prostatitis, pyelonephritis. With a sharp decrease in immunity, the cause of pathology is pneumonia, sinusitis, acute tonsillitis, bronchiolitis, and pharyngitis. Its development is predisposed by increased physical activity, the presence of chronic infectious foci in the body, and injuries complicated by a violation of the integrity of the skin.
Infectious polyarthritis
This is one of the few forms of polyarthritis with a benign course. With timely diagnosis and adequate therapy, the prognosis for complete recovery is favorable. The cause of the development of infectious polyarthritis is infection with syphilis, gonorrhea, and the penetration of pathogens of dysentery, brucellosis, and tuberculosis into the body. The inflammatory process in the joints develops at the acute stage of the underlying disease. Polyarthritis is characterized by damage to several joints (oligoarthritis). The severity of symptoms and specificity of signs depend on the type of infectious agents:
- with syphilis, large joints are involved in the pathological process: hips, ankles, knees, shoulders, elbows. Polyarthritis immediately manifests itself acutely - intense pain, intensifying at night, rapid deformation of joints with gummas (painless nodes located in the subcutaneous tissue);
- Gonorrheal polyarthritis occurs approximately a month after infection. It is characterized by a sudden onset with hyperthermia and acute, piercing pain. With the development of a purulent process, there is a high probability of ankylosis (immobilization) as a result of fusion of the joint space;
- dysenteric polyarthritis occurs during the recovery stage, affecting several joints. Clinically, the pathology is manifested by pain and low-grade fever.
Brucellosis polyarthritis is the most severe and quickly becomes chronic. When visiting a doctor, the patient complains of constant aching, pressing pain, limited mobility, and severe swelling. During relapses, the joints swell, the lymph nodes become enlarged, the body temperature repeatedly rises throughout the day, and hepatosplenomegaly is observed (an increase in the size of the liver and spleen).
Establishing diagnosis
At the first manifestations of pain, you should seek help from a doctor. The main thing during the consultation is to tell everything in detail and accurately. For example, the slow course of the disease, starting with damage to one joint and gradually spreading to others, is characteristic of rheumatoid polyarthritis. The presence of psoriasis on the patient's skin indicates that the joints are affected by the psoriatic form. In order to make an accurate diagnosis, you will have to undergo a lot of research. Most often, diagnostics are prescribed using:
- Ultrasound;
- X-ray;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT scan;
- Puncture of joint fluid to determine the causative agent of infection;
- A blood test that determines creatinine and AST;
- Urine testing for rheumatoid factor.
During standard pathology tests, the patient may be required to undergo a full body diagnostic. This includes ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs and an electrocardiogram of the heart. It may be necessary to consult other specialists, for example, a phthisiatrician or an infectious disease specialist, to exclude specific polyarthritis. They, in turn, can prescribe special tests, such as the Wasserman test, bacterioscopy and enzyme immunoassay.
Treatment of any type of ailment involves an integrated approach. First of all, the doctor prescribes drugs that can relieve acute pain, thereby alleviating the patient’s condition. Next, drugs are selected that can restore lost functions. Most often, doctors use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that can reduce discomfort and relieve inflammation from tissues.
In addition, if tests of synovial fluid show the presence of infection, then broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are prescribed. Gels and ointments with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects are used as auxiliary agents. For example, ointment with diclofenac. The administration of diclofenac in the form of injections is justified.
In medical practice, a situation often occurs when a person develops osteoporosis against the background of polyarthritis. Therefore, patients are advised to review their diet and enrich it with foods high in calcium. You should eat more dairy products, such as cottage cheese and milk.
Add more fresh vegetables, fruits and fish to the menu. It is necessary to avoid excessively fatty and salty foods. Sweets, fresh baked goods, coffee and alcohol are strictly prohibited. The doctor can also prescribe multivitamin complexes containing calcium and vitamin D.
Physiotherapy is performed for recovery. Usually prescribed:
A course of physical therapy and massage is provided. To normalize blood circulation in the affected joint, compresses with dimexide are used. Medications may include analgesics, corticosteroids and antihistamines. In particularly advanced cases, surgery may be required. Reflexology and acupuncture are indicated for patients. Treatment with mud wraps would be useful.
Diagnosis of polyarthritis
When diagnosing polyarthritis, special attention is paid to collecting anamnesis, complaints and features of the clinical picture of the disease. For correct diagnosis, the following clinical studies are carried out:
- complete blood count (the test for erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is important;
- biochemical blood test (determining creatine level and ACTA level);
- analysis for rheumatoid factor (RF);
- Analysis of urine;
- examination of synovial fluid.
Instrumental research:
- radiography;
- Ultrasound of joints;
- scintigraphy;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Computed tomograph (CT).
One fact should be taken into account: a negative test for rheumatoid factor does not mean that a person does not have arthritis, since rheumatoid factor is not detected in seronegative rheumatoid polyarthritis (and this is what we are talking about). To identify this form, the patient is prescribed additional ultrasound and ECG studies. To diagnose metabolic polyarthritis, a study of synovial fluid is prescribed. If there is a suspicion of infectious polyarthritis, consultations with related specialists are prescribed: a venereologist, a phthisiatrician, an infectious disease specialist, and some additional tests are also carried out.
Traditional methods
Therapy can be supplemented with treatment with folk remedies. Do not forget that home recipes can only help if the person strictly follows the recommendations of his doctor. The most popular methods are:
- Ointment based on pumpkin oil. Crushed pumpkin seeds are mixed with a small amount of vegetable oil with the addition of black pepper. The resulting mixture is applied to the sore joint, preferably at night;
- Eucalyptus oil can effectively eliminate pain; just rub it in at least 3-4 times a day. Eucalyptus oil is sold in any pharmacy, its price is usually not high;
- A lotion made from radish juice and honey has many positive reviews. It won't be difficult to prepare it. Radish juice and honey are mixed in equal parts, then two tablespoons of salt are added. The components are mixed until a homogeneous consistency is obtained and applied to the affected area;
- Decoction of bitter wormwood. The leaves of wormwood are poured with boiling water and left for half an hour. After this, the herbal decoction is filtered, moistened with a clean cloth and applied to the sore spot.
It is important to understand that traditional medicine recipes cannot replace classical drug treatment. Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner can lead to serious and irreversible consequences. In addition to the advice of traditional medicine, a person suffering from a chronic form must radically change his attitude towards his lifestyle. The best solution is to eat healthy foods and engage in physical activity.
https://youtu.be/IUBBHONn5AE
Baths and applications for the treatment of illness
Polyarthritis can be treated at home using baths and applying special masks to the areas where the joints are affected. Good results are demonstrated by herbal baths, which should be taken for a whole week without breaks, and then stop the procedures for 5 days and repeat the course again. To prepare them, you need to take 20 tbsp. l. sage (dried) and pour 5 liters of boiled water over it. The herb should be infused for 3 hours, and after this time, the product is added 1 liter to the solution prepared for bathing.
You can make a bath that has a positive effect from straw (dry), which will require 250 g. The substance is poured into 5 liters of boiled water and kept over medium heat for 30 minutes. After this, the hands and feet are immersed in the broth (you need to wait until the product cools down to 37°C). This treatment is required for 10-12 days. Add 5-10 drops of fir oil to the bath, and then lower the areas affected by the disease into it.
How to treat polyarthritis with applications? To do this, you need to take blue clay, dilute it with water and apply it to your hands. The thickness of one cake should be 2 cm. When there is enough product, wrap the sore spot with cling film and wrap it with a woolen scarf. This application must be kept for 2 - 3 hours. If blue clay is not available, it can be replaced with green or any other clay.
If pain appears in your hands, you can take ordinary unnecessary mittens, soak them in a salt solution, and then hold them on your palms for 2 hours. This treatment method is often done at night. To do this, wrap cling film over the mittens or put on plastic bags. Saline solution is prepared from 1 tbsp. l. substances and 250 ml of water. In addition, taking pine baths, which are created from pine branches and cones, is considered beneficial.
Causes
Doctors cannot discover the exact causes of the disease. There are suggestions about the relationship of the disease with genetic predisposition. If a patient has certain antigens and a bacterial infection, then antibodies of a specific nature are formed. When antibodies combine with blood plasma proteins, the membranes of the joints are affected.
Rheumatoid polyarthritis is the result of a malfunction of the immune system. The following reasons can lead to such a result:
- hypothermia of the body;
- influence of toxins and allergens;
- stress;
- previous injuries;
- presence of infection or viruses;
- disruptions in the hormonal system.
https://youtu.be/svEZwtQTYks
Main symptoms and treatment methods for polyarthritis of the shoulder joint
Unobtrusive shoulder pain is not as harmless as it might seem at first glance. Perhaps this is the initial stage of a serious illness that requires immediate action. We will look at it in detail in this article, the topic of which is polyarthritis of the shoulder joint: symptoms and treatment.
Description of the disease
Arthritis is inflammation of a joint. It leads to the destruction first of the cartilage and the synovial membrane lining the inner surface of the articular capsule, then of the ligaments and tendons. Accordingly, shoulder polyarthritis is an inflammatory process in the shoulder joint. The prefix "poly" means that the disease affects both shoulder joints, but not necessarily at the same time.
Pathology can develop sequentially, first on one side, then on the other. As a result of tissue destruction, joint mobility is limited; if left untreated, the disease leads to disability.
Polyarthritis of the shoulder joint occurs more often in people over 40 years of age, but is possible at any age. There are 4 stages of the disease:
- Simple shoulder polyarthritis. Characterized by mild pain in the shoulders, especially when performing manual activities that require effort.
- Acute humeroscapular. I am worried about severe pain, especially when trying to raise my arm up.
- Chronic humeroscapular. Acute polyarthritis progresses to the chronic stage in the absence of treatment. The pain weakens, but becomes constant or regular, often leading to sleep disturbances.
- Shoulder capsulitis (“frozen shoulder”). Individual areas of the joint capsule stick together, so that the joint loses mobility.
The inflammatory process ends with the fusion of tissue remnants, which leads to loss of joint mobility.
https://youtu.be/i8HqGF3hwOE
Causes of shoulder polyarthritis
Depending on the cause, the disease is classified as follows:
- Rheumatoid polyarthritis. Its exact cause has not been established; it is suspected to be an autoimmune disease. It is chronic and always affects joints on both sides of the body. Advanced rheumatoid polyarthritis is difficult to cure, so it is important to identify it at an early stage and begin treatment immediately.
- Post-traumatic. Occurs with severe trauma - fractures, dislocations or bruises of the shoulder joint.
- Exchange (crystalline). It occurs as a result of the irritating effect of salt deposits on the joint capsule.
- Infectious. Caused by pathogenic viruses and microbes that have entered the joint. Frequent pathogens are tubercle bacilli, bacteria of the genus Brucella (brucellosis) and gonococci (causative agents of gonorrhea).
- Reactive. This is a secondary polyarthritis that develops against the background of an infectious disease. It is often provoked by conjunctivitis, polyneuritis, cystitis or colitis.
- Psoriatic. It occurs as a consequence of skin psoriasis, but with a significant delay: the joints become inflamed six months after the skin is cleared of growths as a result of treatment.
- Osteoarthritis. Caused by disorders in joint tissues and weakened immunity as a result of senile degradation.
In addition, shoulder arthritis can be caused by:
- Excessive loads. This is especially true for athletes, but an ordinary person can also suffer if he rashly takes on unusually hard work.
- Intervertebral hernia in the cervical spine. It leads to pinching of the nerves innervating the joints, as a result of which inflammation occurs in the latter due to lack of blood supply and other disorders.
- Amputation of the mammary gland due to a cancerous tumor that has developed in it. Changes the blood circulation pattern in the shoulder area so that it enters the joint in a smaller volume. Lack of blood supply provokes inflammation.
- Myocardial infarction. In this case, the blood supply to the joint is limited due to vasospasm.
Shoulder polyarthritis: symptoms and treatment
The disease is accompanied by the following phenomena:
- Pain in the joint increases over time with a gradual limitation of its mobility; at first the discomfort is almost unnoticeable, but soon the patient, due to severe pain, can no longer raise his arm or place it behind his back;
- Crunching in the joint during physical activity;
- Swelling, redness;
- Temperature increase;
- Decreased general tone, rapid fatigue.
Depending on the location of pain, the following types of polyarthritis are distinguished:
- Scapulohumeral: shoulder pain in the back;
- Acromioclavicular: pain in the front;
- Right-handed;
- Left-handed.
Shoulder polyarthritis is diagnosed using conventional methods:
- Anamnesis (questioning the patient regarding symptoms);
- Palpation (feeling the sore spot with your fingers);
- X-ray examination;
- Ultrasound diagnostics.
The absence of complex special techniques should not be misleading: the patient is not able to independently identify polyarthritis, much less choose a course of treatment. You should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Treatment usually includes:
- For secondary polyarthritis: therapy to cure the main infection - colitis, cystitis, etc.
- Taking universal antibiotics and non-steroidal drugs with immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects. The latter include, for example, Ibuprofen and Diclofenac. These drugs have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract, so for diseases of the latter, Celecoxib or Nimesil are used instead.
- Use of external preparations: rubbing ointments with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, compresses, rubbing, lotions.
- If there is a lack of blood supply: taking vascular medications.
- Taking chondroprotectors. These drugs activate the process of cartilage tissue restoration.
- In difficult cases: injections of corticosteroid hormones into the joint (blockade) or intramuscularly.
- Taking analgesics (to relieve pain).
- Performing special exercises to improve blood circulation and develop mobility. Gymnastics are prescribed after inflammation has been relieved. Loads are contraindicated - only physical activity.
- Surgical intervention.
The latter method is used in advanced cases or when other treatment methods are ineffective.
The following types of operations are performed:
- Resection of the shoulder joint;
- Arthroscopy: involves making two small incisions;
- Endoprosthetics: replacement of a joint with a prosthesis.
Physiotherapeutic effects have a beneficial effect on the healing process:
- Barotherapy;
- Massage;
- Mineral and mud baths;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Laser therapy;
- Ultrasound treatment;
- Phonophoresis (ultrasound + medication): in this case, hydrocortisone is used.
Physiotherapy methods increase blood and lymph circulation in the joint and thereby eliminate congestion.
Lifestyle and diet
To speed up recovery, the patient must provide himself with comfortable conditions and eliminate harmful factors. Dampness, cold, alcohol and nicotine, and stress on sore joints are contraindicated.
A nutritious diet is important. It should primarily include sources of protein and foods rich in calcium, vitamins and fiber. These include:
- Fish and other seafood;
- Beef and pork meat, poultry;
- Dairy products, especially concentrated: cottage cheese and cheese;
- Nuts, pumpkin and sunflower seeds;
- Mushrooms;
- Fruits, vegetables, herbs;
- Eggs;
- Ground eggshells (rich in calcium).
Fatty and spicy foods, sweets and baked goods should be avoided.
https://youtu.be/NydmSvbOS5o
ethnoscience
It is useful to use the following products from the “natural first aid kit” together with pharmacological drugs:
- Cabbage leaf and honey. The sheet is rolled with a rolling pin (to release the juice) and smeared with honey, then applied to the sore joint. Polyethylene and something warm, for example, a scarf (compress), are placed on top. The dressing is changed every two hours. It effectively relieves swelling and soothes pain.
Burdock leaf is also used. Roll it with a rolling pin until the juice appears and apply it to the joint, wrapping a warm scarf on top. Remove the bandage after a few hours.
The root of the plant is also used. It is crushed and in the amount of 1 tbsp. spoons are poured into the bottle. 3 crushed pods of hot pepper with lilac flowers (3 tablespoons) are also placed there and then filled with alcohol in a volume of 0.5 liters. After rubbing for 5 days in a dark place, it is rubbed into the joint twice a day.
Characteristic symptoms and how to treat polyarthritis of the shoulder joint, diagnosis of pathology
Polyarthritis is a pathology in which several joints are affected. A common disease is polyarthritis of the shoulder joint. Symptoms and treatment of the disease have characteristic features. The danger of polyarthritis is that it is very difficult to diagnose in the initial stages, when the prognosis for recovery is very high. This is due to the fact that at these stages the pathology occurs without severe symptoms.
Causes of inflammation
With shoulder polyarthritis, inflammatory changes in the joints are diagnosed. This affects the cartilage, synovial membrane and ligaments. Pathology can simultaneously occur in both joints or move from one to the other. As a result of the development of pathology, complete immobility of the joint may occur.
Among other things, polyarthritis tends to become chronic, in which relapses often occur. In this case, destruction of the joint occurs. Rheumatoid arthritis and periarthritis can result in complete immobility of the joint.
The main factors that can cause the disease include:
- Shoulder joint injury. A fall or impact can cause damage to the joint and periarticular tissues.
- Great physical activity. Arthritis often occurs in insufficiently physically developed people who perform prolonged and heavy workloads. The pathology is also observed in athletes whose shoulder is under constant load.
Exercise can cause shoulder damage
- Hernias. The pathology is accompanied by pinching of nerve trunks. Damage to the roots leads to disruption of the blood supply to the articulation area. As a result, inflammation occurs and develops.
- Operations. During surgery on the chest, a redistribution of blood flow occurs. As a result, the blood supply to the joint capsule is reduced, which leads to polyarthritis. Often these factors include removal of the mammary gland for cancer.
- Myocardial infarction. The phenomenon is accompanied by spasm of the blood vessels in the hand, which can lead to disruption of blood flow and the occurrence of illness.
Polyarthritis often appears in middle-aged people. This is due to the fact that for one reason or another they are more susceptible to degenerative processes. Young people are no exception. Patients with post-traumatic syndrome are at particular risk.
Symptoms
At the initial stage, it is very difficult to determine the presence of the disease. This is due to the fact that it occurs with mild symptoms. As a result of the development of periarthritis, the pain syndrome increases. The pain becomes more intense and worsens with arm movements. Depending on the location, polyarthritis is divided into scapulohumeral and acromioclavicular. In such forms, the pain is unbearable and limits the movement of the joint.
Impaired blood supply to the limb leads to swelling. In addition, characteristic manifestations of polyarthritis include:
- redness of the skin;
- general weakness and fatigue;
- characteristic crunch in the joint;
- insomnia;
- at an advanced stage - fever.
When shoulder polyarthritis appears, symptoms and treatment should be started as early as possible. First you need to contact a specialist. Based on the research, effective treatment is prescribed. The earlier the diagnosis is made, the greater the chances of a quick recovery.
Polyarthritis is accompanied by pain of a different nature
Important! Treatment is prescribed and carried out under the close supervision of a doctor. Self-medication may not only not give the desired result, but also cause complications.
How to treat shoulder inflammation
If treatment for periatritis is not started in a timely manner, it can become chronic. This means that pain and limited mobility of the joint joint will become the patient’s companions. This can be avoided through complex therapy, which includes the following treatment methods:
- physiotherapy;
- gymnastics;
- diet;
- folk remedies.
Regardless of which method is used, it is prescribed by a doctor after an examination and an accurate diagnosis. Taking medications is combined with other methods of treatment.
Physiotherapy
Treatment of periarthritis is impossible to imagine without physiotherapy. It is aimed at eliminating symptoms such as lack of mobility, pain and swelling. It is worth considering that some methods are not used during an exacerbation of the pathology. On the other hand, physical therapy can reduce inflammation. Among the popular treatment methods it is worth highlighting:
- X-ray therapy. The technique has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. During the procedure, a local effect is applied to the affected area. During irradiation, the immune system is suppressed, which helps relieve inflammation.
- Swimming. Going to the pool provides an opportunity to improve shoulder mobility. In water, the joint does not experience serious loads.
- Treatment with leeches. Worms secrete a substance that has an analgesic effect and helps thin the blood. Hirudotherapy helps eliminate congestion.
- Acupressure. With its help, muscle spasm is relieved and shoulder mobility is restored. Manual therapy and acupuncture are also used to treat polyarthritis. All procedures must be carried out by a specialist. It is possible to use essential oil.
Gymnastics
Performing certain exercises allows you to resume full mobility of the joint and also speed up recovery. It should be borne in mind that the loads should not be large. Classes are held according to the following scheme:
- Exercises for healthy joints. Perform in a lying or sitting position. Classes last approximately 5 minutes.
- Complex exercises for healthy and affected joints. In this case, it is possible to use projectiles. Intense exercises last no more than 10 minutes.
- Walking and exercise equipment. If health allows, it is recommended to increase the load. The duration of strength exercises should not exceed 5 minutes.
- Classes end with a set of exercises in a sitting position.
Exercises can improve joint mobility.
With polyarthritis, movements should be slow and smooth. This will prevent severe pain and further damage to the joint.
Diet
To increase the effectiveness of therapy, the patient must adhere to a special diet. You should completely or partially remove foods such as salt, spices, sweets, smoked meats and pickles from your diet. Experts also recommend avoiding drinking strong coffee and tea, lemonade, citrus fruits and exotic fruits.
Instead, you should include the following foods in your diet:
- fruits and vegetables;
- lean meat and fish;
- porridge;
- berry compote and herbal tea;
- infusions of medicinal herbs.
Fermented milk products will also be irreplaceable. They contain lacto- and bifidobacteria, which ideally fight pathogenic intestinal microflora.
Folk remedies
To reduce pain and eliminate inflammation, folk remedies are widely used. Among the popular traditional home recipes it is worth highlighting:
- Alcohol infusion of lilac, pepper and burdock. At night, rub it on the affected area.
- Vinegar compress. Add vinegar to 500 ml of water. A piece of cloth is soaked in the solution and applied to the joint. Cover with a scarf and leave overnight.
- Herb tea. For cooking you will need 1 tbsp. l. cinquefoil and 2 tbsp. l. horsetail. Pour 1 liter of boiling water. Use throughout the day. Course of treatment – 1 month.
Folk remedies are widely used for polyarthritis of the shoulder.
Polyarthritis requires timely and comprehensive treatment. Therefore, when the first signs occur, you should consult a doctor. Based on the diagnosis, appropriate treatment is prescribed. During therapy, you should strictly follow the doctor’s instructions and the conditions of the procedures.
https://youtu.be/ig-FPbkXKPg
Sources: https://sustavbol.ru/artrit/simptomy-i-lechenie-poliartrita-plechevogo-sustava-918/ https://xn--h1aeegmc7b.xn--p1ai/zabolevaniya/plechevoy-poliartrit https://artritu .net/poliartrit-plechevogo-sustava https://mysustavy.ru/osnovnye-simptomy-i-metody-lecheniya-poliartrita-plechevogo-sustava/ https://sustaved.ru/metody-lecheniya-poliartrita-plechevogo-sustava/ https://lechisustavv.ru/vospalitelnyie-i-infektsionnyie-zabolevaniya/artrit/3816-simptomyi-i-lechit-poliartrit-plechevogo-sustava.html https://ortocure.ru/kosti-i-sustavy/artrit/postizometricheskaya -relaksatsiya-pri-periartrite.html
What is polyarthritis
Inflammatory processes that affect several joints at once (5 or more) are diagnosed as polyarthritis. In most patients, the disease affects the joints of the limbs;
- knee;
- hip;
- phalanges of the toes;
- brachial;
- elbow;
- phalanges of the fingers.
The location of pain and discomfort is constantly changing. For example, today the shoulder, hip, and knee joints hurt, and the next day - the elbows and toes. There is no consensus in medicine regarding the root cause of the disease. There is a theory that the immune system malfunctions. It begins to identify healthy cells of the body as foreign and starts the process of their destruction. According to other experts, polyarthritis occurs against the background of severe stress, severe hypothermia, and serious hormonal imbalance.
Symptoms
Timely diagnosis of the disease is the key to recovery, and therefore it is important to seek help from a doctor if the patient exhibits the following symptoms:
- swelling in the joint area - the rheumatic type of polyarthritis affects small joints of the hands or feet, moving to larger ones - elbows or knees, ankles;
- the patient feels stiffness in the joints (especially in the morning), which is observed in the first couple of hours after waking up, and goes away after warming up. This is the most striking and characteristic symptom of pathology, along with dystrophic changes in the joints;
- formation of a painful protrusion over the affected joint;
- pain at the very beginning of the development of the pathological process is periodic, gradually acquiring a permanent character. If the pathology is in an advanced form, the patient feels such a severe attack of pain that he is unable to move, and eventually becomes disabled, bedridden;
- deformation of the affected joint resulting from the destruction of cartilage tissue. This process is accompanied by stiffness of movement and low joint mobility, atrophic processes affecting the muscles, less often (in advanced form) polyarthritis can manifest itself as constant dislocations (see photo above).
It should also be noted that among all existing forms of rheumatic polyarthritis, doctors distinguish the nodular form into a separate group of pathological processes.
The symptoms of this type of pathological process are characterized by the formation of painful nodular neoplasms in the subcutaneous tissue .
Such nodular neoplasms can appear and disappear on their own, without medical intervention.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy is the main method of combating polyarthritis. As a rule, patients are prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids, the action of which is aimed at relieving pain and eliminating manifestations of an inflammatory nature.
Treatment of infectious polyarthritis involves the use of antibiotic drugs aimed at suppressing pathogens. Infectious-allergic polyarthritis most often requires the prescription of antihistamines that eliminate allergic manifestations. In some situations, patients are prescribed a course of hormone therapy.
Since in most cases polyarthritis develops against the background of a weakened immune system, the patient is required to be prescribed vitamin and mineral complexes and immunomodulatory drugs. When treated with corticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, patients are additionally prescribed antirheumatic drugs that help suppress immune system factors.
Patients are often prescribed so-called anti-TNF drugs, the action of which is aimed at suppressing necrotic factors of tumor growth that can provoke various forms of joint lesions.
We emphasize that only the attending physician should prescribe any medications, determine their dosage and the duration of the therapeutic course, exclusively on an individual basis.
Rehabilitation
The most important condition for the rehabilitation of the disease is the absence of exacerbation, which is treated with medication.
Only in the “cold” stage is spa treatment recommended, which brings a very good effect:
- peloid therapy (use of therapeutic mud);
- thalassotherapy (sea bathing);
- climatotherapy (air and sun therapy in some cases leads to complete recovery, for example, with psoriatic arthritis);
- drinking alkaline mineral waters (indicated for gout).
Traditional medicine in the fight against disease
Many patients, if they experience polyarthritis of the arms and legs, prefer to use primarily traditional methods of treatment. Moreover, the list of such recipes may even outstrip those offered by traditional medicine. First of all, we are talking about all kinds of herbal preparations and decoctions. Polyarthritis has been treated with folk remedies of this type since time immemorial through trial and error. As a result, today we have come to know a large number of different recipes, which are happily used by those who do not like to take pills, or indeed seek help from doctors.
One of the most popular collections consists of blackthorn and black elder flowers mixed with warty birch and stinging nettle leaves. In this case, the ratio of all ingredients should be equal. Next, you need to take 1 tablespoon of the resulting mixture and add 250 ml of water. After this, the mixture must be boiled for about 10 minutes. The resulting broth must be filtered through cheesecloth. In the future, it should be consumed on an empty stomach, several glasses a day.
Another decoction is prepared by mixing equal amounts of horsetail and hernia grass, parsley seeds and juniper fruits, as well as buckthorn bark. The resulting mixture (1 tablespoon) must be poured with a glass of water and simmered over low heat for 15 minutes, strain through cheesecloth, and then drink half a glass 2 times a day.
Traditional medicine is rich in not only decoctions. Her recipes include many for external use. For example, it is recommended to make an ointment from the following ingredients: 1 chicken egg yolk, 1 tablespoon of vinegar and 1 teaspoon of turpentine. In the future, this ointment must be rubbed onto the skin over the affected joint.
Currently, it is quite common to use lotions rather than ointments as external agents. One of the most popular folk recipes recommends using honey, vodka, salt and radish juice to prepare them. In this case, for 2 glasses of radish juice you need to take 100 ml of vodka, half a glass of honey and 1 tablespoon of table salt. Many note that if polyarthritis of the hands has developed, treatment with such lotions often helps no worse than with proprietary anti-inflammatory ointments.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of nonspecific polyarthritis, increased attention should be paid to physical education and hardening. It is necessary to avoid hypothermia, dampness, drafts, overheating; overwork, severe stress, anxiety. If you experience joint pain or stiffness of movement, you should seek medical help and begin treatment for the disease in the early stages.
It is recommended to undergo regular examinations by doctors. If chronic infectious diseases are detected, it is worth promptly starting treatment until complete recovery. You must strictly follow the doctor's recommendations. Diseases should not be ignored or left untreated. To prevent relapses, a course of Rezokhin, Bicillin, and Aspirin is prescribed 1-2 times a year.
Therapeutic diet
Dietary nutrition is included in the comprehensive treatment of polyarthritis.
Food should be prepared with a minimum amount of salt and sugar. Drinking enough fluid is a must. You can drink not only water, but also herbal decoctions, dried fruit compote, jelly, and green tea. It is necessary to include fresh and boiled vegetables, herbs, and fruits in the diet. Jellied meat has a beneficial effect on the condition of cartilage tissue. But it should not be an everyday food because it has a high cholesterol content. Completely remove spicy, fatty foods, smoked and rich foods from your diet. On the contrary, add the consumption of milk and low-fat dairy products, lean meat, fish, and cereals.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/lw-Oqj_zlRk
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/svEZwtQTYks
Good:
Treatment of polyarthritis with folk remedies at home is an indispensable part of complex joint therapy. This treatment is aimed at eliminating painful symptoms and improving the patient’s overall well-being.
It is important to use traditional recipes correctly so as not to harm your health.
Stages of development of infectious polyarthritis
There are several stages of disease progression:
- the initial stage is characterized by thinning of the cartilage and a decrease in the distance between the bones. It is accompanied by an inflammatory process of the synovial membrane, swelling of the affected area, and painful sensations during intense physical activity. There are no signs of infectious polyarthritis on x-ray. Doctors note an increase in synovial fluid, a local increase in temperature;
- the second stage occurs with severe painful sensations and the formation of ulcerative lesions. Limitation of mobility of the affected joints and absence of deformities are noted. When the weather changes, painful sensations develop. In the morning, stiffness is noted, which disappears after performing gymnastics;
- the third stage is manifested by severe pain and contracture, the cartilage practically becomes thinner, and osteophytes form. On radiography, swelling of the soft tissues is noticeable;
- the final stage of the disease involves the disappearance of the lubricating fluid; treatment requires surgical intervention. Conservative methods of therapy are ineffective. The painful sensations become chronic and disturb the patient during rest.
Causes of joint inflammation
The cause of the development of inflammation of the joints of an infectious specific type is the penetration of infection into areas of gonorrhea, tuberculosis, dysentery, brucellosis, etc.
- Brucellosis polyarthritis develops due to contact with sick animals or people, as well as by eating food contaminated with Brucella.
- Gonorrheal polyarthritis develops against the background of gonorrhea, prostatitis, and chronic gonorrheal urethritis.
- Dysenteric polyarthritis occurs after the patient has been cured of dysentery.
- Syphilitic polyarthritis develops at the late stage of syphilis.
Read also: How to treat polyarthritis
go to top
Joint damage due to various infectious diseases
Inflammation of several joints at once can be observed in some skin diseases, for example, syphilis. The causative agent of syphilis is Treponema pallidum. Inflammation of the joints occurs in the tertiary period of the disease. The main manifestations are:
- pain in the joints;
- deformation of the affected joint;
- minor dysfunction;
- swelling.
Read also: Causes of arthritis
With syphilis, bilateral inflammation often occurs. In one case, the synovial membrane is affected, and in the other, cartilage and bone tissue. The largest joints (knees, elbows) almost always become inflamed. The cause of infectious polyarthritis can be dysentery. Polyarthritis occurs during the patient’s recovery, less often 1-2 months after treatment. Additional symptoms include high body temperature. A blood test reveals a high ESR and slight leukocytosis. Diagnosis does not present much difficulty if the history indicates dysentery.
Brucellosis can also cause joint inflammation. The symptoms are pronounced. These include pain, swelling, and limited mobility. At the same time, against the background of the disease, the spleen and lymph nodes may enlarge, and the body temperature may rise. The nervous system is often affected. This manifests itself in the form of neuritis and neuralgia. In some cases, inflammation is localized in the lumbar joint.
Polyarthritis of gonorrheal nature is characterized by a sudden onset and acute pain. Sometimes suppuration may occur followed by the development of ankylosis. Extra-articular symptoms include weakness, increased body temperature, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and weight loss of the sick person.
Treatment of polyarthritis at the Paramita clinic
The clinic’s specialists are deservedly famous for their many years of experience and high qualifications. We treat polyarthritis without the use of drugs or surgery, using only reliable and proven methods. After completion of treatment, we give recommendations on prevention and maintaining your health in good shape.
In most cases, we were able to slow down the course of the chronic form of a disease such as polyarthritis. The specialists of our clinic will help to significantly improve the quality of life of patients by strengthening the immune system and improving the functional activity of the joints.
https://youtu.be/4ND_56IQ_FY
https://youtu.be/yxO-roGRF4E
Diagnostic and therapeutic measures
Diagnostics involves interviewing the patient, external examination, laboratory tests (blood tests), and instrumental research methods (radiography, CT or MRI). For polyarthritis of a specific nature, special laboratory tests may be required. For example, to confirm the syphilitic nature of the disease, the Wasserman reaction is performed, and for brucellosis, the Wright reaction is performed.
Treatment should be aimed at the underlying disease. The doctor may prescribe antibacterial drugs depending on the type of pathogen, painkillers from the NSAID group, and antihistamines. In addition, treatment includes physical therapy and compresses. Sometimes treatment involves puncture of the affected joint. Thus, polyarthritis of infectious origin develops against the background of another somatic pathology and is one of its manifestations or complications.
Clinical picture
The symptoms of specific and nonspecific infectious polyarthritis have much in common. Diseases differ in the duration of the infectious period. Nonspecific pathology develops after acute respiratory viral infection, influenza, and intestinal infection during the recovery stage. Inflammation caused by gonococci or treponema occurs in the most acute stage. For example, polyarthritis of syphilitic origin clinically manifests itself in the tertiary period. The pathology affects the largest joints in the human body. It is diagnosed in the knees, ankles, elbows, and shoulders. The following symptoms are characteristic of infectious polyarthritis:
- long incubation period and acute onset;
- pain that worsens at night;
- pain when palpating the joint;
- the formation of edema localized in the affected area;
- redness of the skin.
Polyarthritis provoked by gonorrhea pathogens clinically manifests itself 3-4 weeks after infection. The disease is accompanied by strong, sharp painful sensations. Purulent exudate accumulates in the joint cavity, and ankylosis develops. The immobility of the joint increases as a result of the formation of bone, cartilage or fibrous fusion of bones. Symptoms of dysenteric polyarthritis occur during the recovery stage of a person. One or more joints are affected. The disease is highly treatable and causes virtually no complications. Like all infectious pathologies, polyarthritis can be accompanied by signs of general intoxication of the body:
- an increase in temperature above subfebrile levels;
- neurological disorders in the form of dizziness and headaches;
- nausea, vomiting, increased gas formation, lack of appetite.
Brucellosis polyarthritis is the most severe. It often takes a chronic form, which is dangerous due to frequent painful relapses. During the exacerbation phase, a feverish state occurs, the lymph nodes become greatly enlarged, and the range of motion in the joints is limited.
In the absence of qualified medical care for syphilitic polyarthritis, gummas quickly form - chronic infiltrates in the form of nodes prone to decay and ulceration. This causes irreversible deformation of the inflamed joint.
Advice from healer Clara Doronina
How to treat polyarthritis at home in order to restore the function of damaged joints in a short time, says Klara Doronina. The following recommendations will help relieve inflammation and eliminate pain:
- Cleanse the body with medications or folk remedies;
- Drink 200 ml of infusion of raw potato skins 3 times a day - 10 tablespoons per liter of boiling water;
- Every day before meals, drink the prepared mixture - a spoonful of buckwheat, 2 slices of dried apricots, 10 raisins, a slice of lemon, 2 nuts, a spoonful of crushed eggshells, 6 spoonfuls of water and a spoonful of honey. Consuming the mixture in the morning is an excellent vitamin set of useful components for the whole body. Duration – 2 months. After that - a break for six months;
- Instead of tea, take a decoction of cinquefoil - pour a liter of boiling water over four tablespoons of the raw material, boil for 5-10 minutes, take 100 ml three times a day after cooling.
Thus, Clara Doronina managed to alleviate the symptoms of severe acute polyarthritis of the joints. She also recommends doing clay wraps - dilute the mixture with warm water, apply to the sore spot, remove the composition for 30 minutes. At the initial stage of the disease, this method can achieve stable remission for a long period.
Symptoms of polyarthritis
The general signs of the disease undoubtedly include pain in the area of the affected joints, their pronounced deformation, and limited joint mobility. The main symptoms of polyarthritis also include:
- Changes in the shade of tissues adjacent to the joints.
- Temperature increase.
- Wave-like nature of the pain: the most severe pain occurs in the morning or night hours.
- In its acute form, polyarthritis causes severe limitations in joint mobility, noticeable swelling, and redness of the skin.
- Difficulty in vitality due to the inability to use the affected limb in the chronic form of the disease.
Types of infectious arthritis
Infectious polyarthritis
After some illnesses such as gonorrhea, tuberculosis, syphilis, brucellosis, dysentery, the patient develops infectious polyarthritis, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain and limitation of movement, which are observed after a long period of rest or severe physical activity;
- deformation of the affected pair of joints;
- increased body temperature;
- swelling, redness of the affected joints;
- enlargement of nearby lymph nodes.
There are many classifications of infectious arthritis, depending on the etiology, nature and location of inflammation.
Depending on the etiology
Different pathogens can form and develop the inflammatory process in different ways. But all arthritis that is not completely cured brings one result - restriction or deprivation of the functionality of the joint.
Bacterial
Together with the bloodstream, bacteria enter the joints, where they accumulate on the tissues. This type mainly affects children and the elderly.
Bacterial arthritis almost always increases body temperature, and aching pain is felt in the joints (see how to relieve joint pain).
The skin in the joint area takes on a red tint. Treatment necessarily includes the use or intravenous administration of antibacterial drugs (Ceftriaxone, Ampicillin, Tseporin, etc.
).
The course of treatment can last from 1 to 3 weeks, depending on the nature of the pathogen.
Viral
Hepatitis, rubella, mumps and other viral diseases can cause pyogenic arthritis. Often this type occurs as polyarthritis. If the cause of the disease is hepatitis, the arthritis will go away on its own.
Treatment occurs by getting rid of the viral disease that caused the arthritis infection. Anti-inflammatory drugs are also prescribed. Treatment lasts up to 2 months. If arthritis is detected in time, then a 2-week course of treatment may be quite sufficient for recovery.
Fungal
If pyogenic arthritis is fungal in nature, hospital treatment is required. After some time, the patient may be prescribed antifungal drugs (gold-based products, Nystatin, Terbinafine) to take home at a medical facility. In this case, it is extremely important to follow the instructions of your doctor and complete the course. Otherwise, surgery may be required.
Parasitic
Acute forms of diseases such as opisthorchiasis, hookworm, onchocerciasis and others can cause parasitic arthritis. Polyarthritis often occurs. Small joints are most often affected. A rash, itching, and irritation appear on the skin at the site of inflammation.
The course of treatment consists of antiparasitic drugs and symptomatic drugs.
Reactive
A common type of disease that is systemic in nature. Diagnosis is quite difficult, since pathogenic microorganisms are not detected during culture collection. The cause of inflammation can be infections that are localized in the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary tract.
Harmful organisms can remain in cells for a long time without causing a response from the immune system.
Rheumatoid
One type of chronic arthritis is rheumatoid. Appears mainly in older people. The infection progresses slowly, gradually deforming the joints, leading to pain and swelling. A deformed joint can no longer be returned to its original form without leaving a trace.
The etiology may be viral or hereditary.
https://youtu.be/uQtGbDZWVDU
Surgical assistance
In the event that the patient cannot be helped through the use of medications or physiotherapeutic techniques, an operation has to be performed to overcome polyarthritis, the symptoms and treatment of which we describe. The joint that has undergone the most pathological changes should be operated on first. In some cases, in order for the patient to stop experiencing severe pain in the joint area, quite serious surgical operations have to be performed. Sometimes the only solution is to immobilize the joint.
Choosing a method to combat the disease
A lot here depends on how long ago the disease arose. Polyarthritis of high degrees of development, when the patient experiences severe pain and is practically unable to move, is most often treated surgically. As for this disease, identified in the early or intermediate stages of its development, therapists and physiotherapists are involved in the fight against it. As a result, it is very important to conduct a full examination of the affected joints before treating polyarthritis.
The performance of surgical operations may be hampered by the poor general condition of the patient, as well as the presence of significant chronic cardiac or respiratory failure.
Complications and prognosis
As doctors note, the outcome of treatment when a diagnosis of “rheumatic polyarthritis” is made and an effective course of treatment is prescribed is very favorable. Timely identified pathology and prescribed treatment can relieve the manifestation of negative symptoms from the first days.
If the disease is advanced and proceeds in a severe form, involving healthy tissues surrounding the joint in the process, the outcome is unfavorable. Regarding the latter, doctors say that the risk of developing deformation in the joints is very high, and accordingly, their functionality is impaired.
If during the course of dystrophic, destructive processes the nerve endings are affected, the patient may be bothered by the manifestations of chilliness and coldness in the area of the affected joint, “running goosebumps” in the limbs. In the absence of timely treatment, or if it was chosen incorrectly, the pathology enters the chronic stage, with periodic exacerbations in the autumn-spring months.
Rheumatic arthritis is a very dangerous pathology that poses a serious threat to human health and normal, everyday life. It is for this reason that it is so important to consult a doctor in a timely manner and undergo examination and treatment.
Compliance with the doctor’s recommendations and prevention of relapse is the key to a long and active life.
https://youtu.be/k4G3N4—rLU
Infectious specific polyarthritis: symptoms
This form of polyarthritis occurs due to infectious diseases such as gonorrhea, tuberculosis, dysentery, brucellosis and, less commonly, under the influence of other types of infections on the body. As a rule, changes in the joints form during a pronounced period of manifestation of the underlying disease. Inflammation is concentrated in the area of a single joint or affects several joints.
Brucellosis polyarthritis
In this form, joint disease most often manifests itself in a chronic form, and many systems and organs in the body are affected. The disease affects people who have had contact with an animal infected with brucellosis or people who have eaten food contaminated with the causative agent of brucellosis. Such products include cheese, raw milk, cottage cheese, etc.
Brucellosis polyarthritis of joints: symptoms
Mostly large joints are affected. Characteristic manifestations are acute pain that occurs in the joints, as well as their swelling in combination with limited mobility in them. This polyarthritis is also characterized by the appearance of undulating fever and enlargement of the spleen, lymph nodes and liver. In addition, neuralgia and neuritis often occur. The inflammatory process is also concentrated in the area of the lumbar vertebral region, including in the area of the sacroiliac joints. Accurate diagnosis is ensured by using the Wright and Heddleson reaction, as well as the Burnet test and several other effective options that provide differential diagnosis of this type of polyarthritis from nonspecific infectious polyarthritis, rheumatic and others.
Gonorrheal polyarthritis
The development of the gonorrheal form of the disease occurs, as a rule, during the first month of gonorrhea. Meanwhile, with prostatitis or chronic gonorrheal urethritis, the timing may be slightly increased.
Gonorrheal polyarthritis of joints: symptoms
The development of the inflammatory process in the joints is characterized by a sudden onset in combination with extremely pronounced pain. Mostly the large joint is affected. When the process is purulent, its completion is marked by complete articular ankylosis (that is, complete immobility of the joint). A characteristic manifestation of the disease is also high fever, weakness, weight loss, and an increase in ESR in the blood (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). To differentiate this form of the disease, it is enough to diagnose gonorrhea; in parallel, the Berde-Giangou reaction is used - in this case it is positive.
Dysenteric polyarthritis
The development of this form of polyarthritis occurs in patients with dysentery, usually during the recovery stage, in rare cases - 1-2 months after the end of the disease.
Dysenteric polyarthritis of joints: symptoms
Inflammation occurs in one or several joints, and at the same time a high temperature appears. A blood test determines the moderation of leukocytosis, as well as acceleration in ESR. As a rule, the course of this form of the disease is characterized by its own benign quality, and due to adequate therapy it is possible to completely get rid of articular manifestations. Differentiation of the disease is required from its infectious or rheumatic form. The presence of dysentery in the patient's history helps to determine, accordingly, dysenteric polyarthritis, which is also accompanied by the determination of the lack of effectiveness in the antirheumatic treatment used.
Syphilitic polyarthritis
In this case, joint disease occurs when the tertiary form of syphilis (that is, its late form) is relevant.
Syphilitic polyarthritis of the joints: symptoms
The development of the inflammatory process occurs in acute or subacute form, characteristic pain occurs, especially intensifying at night. In general, the patient’s condition is little subject to any changes. There is no pain in the specific form of its manifestations when trying to determine it during palpation. Most often, the large joint (shoulder, knee, elbow or ankle) is affected. With the development of the gummous process in the joint, its rapid deformation is formed, but its functionality is little affected, which is unusual for other forms of manifestation of polyarthritis. This form of polyarthritis can be differentiated by a history of syphilis, which, in turn, is determined by a positive Wasserman reaction and other specific techniques.