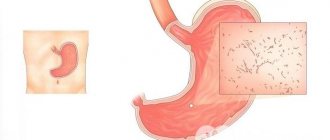
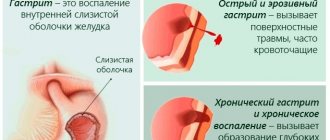
Gastritis refers to all inflammatory diseases of the stomach. The process is localized on the mucous membrane and occurs as acute or chronic inflammation. As a result of prolonged, poorly treated gastritis, the cells are destroyed and the organ ceases to participate in digestion. Hyperacid gastritis refers to pre-ulcerative conditions of the stomach.
The disease has many varieties. The ability to examine the mucosa using fibrogastroscopy contributes to an accurate diagnosis. Classifications have appeared taking into account the type and location of inflammation. However, for practitioners, one of the main fundamental distinguishing principles remains the ability of the stomach to produce juice.
The main component of gastric juice is hydrochloric acid. Depending on its level, gastritis is distinguished with high or low acidity. We will look at the connection between inflammation and increased acidity, and the clinical signs of these disorders.
Where is acid produced and what affects it?
The body of the stomach contains the main secreting glandular cells. Among them there are “main” (40%), which synthesize enzymes. Pepsinogen is of greatest importance. Others, parietal (account for 12%), secrete chloride salts and a substance called intrinsic Castle factor. It ensures the absorption of vitamin B12 in the small intestine.
Chlorides combine with hydrogen ions in the lumen of the glands, resulting in the formation of hydrochloric acid. Role of acid:
- activate pepsinogen so that it turns into pepsin;
- maintain an optimal level of acidity (in diagnostics it is called pH) for the functioning of the enzyme systems of the stomach;
- provide initial chemical processing of food;
- using a bactericidal effect, protect the gastric mucosa from pathological microorganisms.
The glands of the lower stomach (antrum) produce an alkaline secretion. It is designed to prevent acid from entering the duodenum.
Normal fluctuations in acidity throughout the day are ensured by the coordinated work of the antral and fundic glands
In order for acidity to increase, one of the conditions is necessary: either a sharp increase in the production of gastric juice in the body, or blocking the alkalization process. Normally, the balance is controlled by the nervous and endocrine systems (hypothalamus, pituitary gland). This explains the influence of stress and nervous tension on the secretion mechanism in the stomach.
Gastrin is considered one of the main hormones. It is produced by G cells in the antrum of the stomach and is capable of both stimulating and blocking digestion. In practice, its ability to activate the activity of parietal cells and increase acidity is important.
Some scientists reject the existence of hyperacid gastritis. Their main argument: an inflamed stomach cannot function stronger than a healthy one.
Others explain the mechanism by damage to the antrum by irritation of G-cells, an increase in secreted gastrin and subsequent stimulation of the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the unaffected fundus. Even if the inflammation of the fundus of the stomach is captured by inflammation, the decrease in acidity begins only when the process reaches the submucosal layer.
Classification of drugs for gastritis
Drugs designed to relieve gastritis must be selected taking into account the symptoms:
- tablets for high acidity - taken when there is increased production of gastric juice and, as a result, a high concentration of hydrochloric acid in its composition;
- medications for low acidity - if the stomach does not produce enough juice, food begins to ferment and decompose, so it is necessary to take medications to increase the acidity level;
- antacids - means to protect the mucous membranes from irritants, which are used to normalize acidity, get rid of belching, abdominal pain, etc.;
- adsorbents - designed to remove allergens from the body that provoke exacerbation of gastritis and accompanying symptoms (pain, heaviness, heartburn);
- bismuth preparations - the medicine is required to be taken for gastritis and peptic ulcers if the test for the bacteria Helicobacter pylori is positive;
- antibiotics - if gastritis is in the acute stage, you need to take the penicillin group, in the chronic form - macrolides.
Important!
Gastritis requires urgent treatment. Therapy often includes auxiliary drugs, such as electrolytes, antispasmodics, anesthetics, and antiallergic drugs.
Causes
The following reasons are important for the development of gastritis with high acidity:
- external (exogenous);
- internal (endogenous);
- hereditary-constitutional.
The external group includes:
- violation of the regime and quality of nutrition, long breaks in food, starvation diets, overeating heavy foods, refined foods (sweets), which reduce the binding of excess hydrochloric acid in the gastric juice;
- hard work, stress;
- taking medications with a negative effect on the stomach (salicylic acid derivatives, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, sulfonamides);
- lack of substances in food that ensure the restoration of damaged cells of the gastric mucosa and glandular epithelium (vitamins, iron, protein, microelements).
Studies have shown that in areas with unfavorable environmental conditions, 3 times more pathologies of the stomach and duodenum are detected. Among internal factors, the main importance is given to mechanisms for:
- neuro-reflex effect on the gastric mucosa of other pathologically altered organs of the digestive system (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, intestines), this leads to a breakdown in control of secretory activity and gastric motility;
- increased production of histamine;
- disruption of microcirculation of blood flow in the stomach area up to chronic thrombohemorrhagic syndrome.
This is possible with long-term smoking, alcoholism, and endocrine diseases. As a separate reason, we present opinions regarding Helicobacter pylori infection. Inflammation occurs even with normal acidity. Regenerative processes are blocked, and the urease enzyme creates a protective layer around the bacterium itself.
Helicobacter penetrates the mucus layer, attaches to epithelial cells, and moves inside the crypts and glands of the stomach. In this way, the protective layer is destroyed and free access of hydrochloric acid to the tissues is opened.
Some researchers do not recognize the leading role of Helicobacter infection. More than 140 strains with varying degrees of infectivity and sensitivity to antibacterial agents have already been isolated. Scientists believe that combinations of infectious agents are possible.
Treatment of gastritis with high acidity
The tactics for providing assistance are as follows:
- relief of exacerbation;
- elimination of pain and dyspeptic disorders;
- eradication of Helicobacter pylori.
Therapy will be aimed at reducing the increased impact of aggressive factors (increased acidity), as well as neutralizing acid in the lumen of the stomach and normalizing the evacuation function. An important stage is increasing the protective qualities of the inner shell (increasing the secretion of mucus, bicarbonates, increasing trophism, stimulating regeneration).
Conservative therapy
The essence of the method is to prescribe a special diet with the complete exclusion of substances that provoke exacerbations (table No. 1). Meals should be fractional - at least 5-6 times a day. The temperature for serving food is warm. It is strictly forbidden to consume cold or hot foods during treatment.
Drug therapy
The most important stage of treatment is the elimination of Helicobacter pylori, which is the main cause of gastritis and excess stomach acidity. For this purpose, three-component therapy can be prescribed:
- proton pump inhibitors – Omez;
- antibacterial agents: Calirthromycin and Amoxicycline.
All medications are taken 2 times a day for 1 week. If, according to the results of the examination after completing the course of treatment, there are no signs of improvement, then a quadruple therapy regimen is prescribed:
- proton pump inhibitors – Omeprazole;
- antibacterial agents: Calirthromycin and Amoxicycline;
- enveloping agent – Bismuth subcitrate.
Expert opinion
Tsareva Nadezhda
General practitioner, hepatologist, site expert
After the entire therapy (7 days), omeprazole should be taken for another 1 week for preventive purposes.
All other drugs are prescribed symptomatically:
- decreased contractile activity of the smooth muscles of the stomach - Buscopan.
- antacids - for severe heartburn or pain. Almagel and Maalox have proven themselves well.
- cytoprotectors - substances that protect the mucous membrane (De-Nol, Ventrisol).
- normalization of motor activity – prokinetics. The drug of choice is Domperidone.
The duration of treatment is 3-4 weeks after the end of the eradication stage of treatment.
Drugs for the treatment of gastritis with high acidity
| Drug name | Pharmacological group | Mode of application | Brief description of the action | average price |
| Omeprazole | Proton pump inhibitor. | 20 mg 2 times a day – 7 days | Blocks the synthesis of hydrochloric acid | 150 rubles |
| Clatrithromycin | Broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent. | 0.5 2 times a day – 7 days. | Destroys Helycobacter Pylori bacteria and other bacterial agents. | 350 rubles |
| Amoxicillin | Broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent. | 0.5 2 times a day – 7 days. | Destroys Helycobacter Pylori bacteria and other bacterial agents. | 100 rubles |
| Domperidone | Prokinetic. | 0.02 2 times a day – 3 weeks. | Increases the number of peristaltic contractions of smooth muscles due to the block of dopamine receptors. | 75 rubles |
| Bismuth subcitrate | Gastroprotector. | 0.5 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals for 3-4 weeks. | Creates a protective film of bicarbonates on the surface of the mucous membrane. | 450 rubles |
| Almagel | Antacid. | 3-9 ml 3-4 times a day during the entire treatment period | Neutralizes hydrochloric acid, pepsin and other digestive enzymes, eliminating their adverse effects on the mucous membrane. | From 400 rubles |
List of permitted and prohibited products
The point of diet No. 1 is maximum sparing of the mucous membrane. The daily diet should contain the following components:
- fats – less than 120 grams;
- proteins – 110 grams;
- carbohydrates – from 450 to 500 grams;
- liquid – 1.5-1.8 liters;
- sodium chloride (table salt) – up to 6 grams.
The energy value should not fall below 2800 kcal. Food should be steamed, boiled or pureed. The ideal serving temperature is 45 degrees.
| Product group | Can | Forbidden |
| Flour products | White bread, dry crackers. | Rye bread, sweet products. |
| Meat | Low-fat varieties of pork, rabbit, chicken). | Meat products with a lot of fat. |
| Fish | Low-fat types, pureed, salmon caviar. | Fatty types, as well as smoked or fried fish. |
| Eggs | Soft-boiled, fried eggs. | Hard-boiled, raw egg whites. |
| Dairy | Milk, low-fat cottage cheese. | Highly acidic foods, cheeses. |
| Fats | Butter, olive and sunflower oils. | All other types of fats. |
| Cereals | Porridge with milk or water - rice, semolina, rolled oats. | Millet and barley porridge, legumes and pasta. |
| Soups | Puree soups from well-mashed vegetables, dairy or cereal. | Meat broths, mushroom and strong broths on vegetables, cabbage soup. |
| Vegetables | Potatoes, beets, carrots, green peas (preferably in the form of a soufflé or puree). | All other vegetables |
| Fruits | Everything that is not prohibited. | Sour and unripe fruits and berries, dried fruits. |
| Beverages | Weak tea with added cream and milk, berry and fruit juices | Kvass, strong coffee, juices from sour fruits and berries. |
Example menu
| Breakfast | 2 boiled eggs, 200 ml of rice porridge with milk, weak tea with cream. |
| Breakfast 2 | Baked apple, rosehip jelly. |
| Dinner | Carrot puree – 350 ml, steamed rabbit meat cutlets – 2 pcs., watermelon jelly – 250 g. |
| Afternoon snack | Dried white bread up to 400 g, berry compote – 200 ml. |
| Dinner | Boiled lean fish – 90 g, zucchini puree with olive oil – 200 g, weak tea with cream – 200 ml. |
What types of gastritis are known, accompanied by increased acidity?
One of the classifications proposes to distinguish gastritis by type and type, depending on the causes, and include them in the formulation of the diagnosis. This applies to any inflammation of the stomach, regardless of acidity.
Why does my stomach hurt immediately after eating?
Fundal (type A) - affects the body of the stomach, most often caused by a genetic predisposition and the production of autoantibodies. The glands of the fundus atrophy, so there is no increase in acidity.
Antral (type B), bacterial - caused by infection, including Helicobacter, inflammation overirritates G-cells, they increase gastrin synthesis. In response, the “healthy” fundus produces an increased volume of hydrochloric acid, and acidity increases. In the later stages, stomach cells become depleted and acidity drops.
Chemotoxic (type C) - diagnosed if the provoking factors were medications, alcohol, or ingestion of toxic substances. Divided by:
- reflux gastritis - is formed due to impaired motility and inflammation of the gallbladder or duodenum, reflux of bile acids into the stomach occurs, which is tantamount to a chemical burn of the mucous membrane;
- medicinal.
Prevention
Prevention of the development of gastritis with high acidity includes two areas.
- Preventing Helicobacter pylori infection. To do this, it is necessary to carefully observe personal hygiene measures (washing hands before eating, drinking only high-quality, purified water, washing fruits and vegetables).
- Proper nutrition. You should eat food at least 3-4 times a day. The diet must be balanced in the content of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, and contain all the necessary microelements and vitamins. It is necessary to give up dry meals, snacks on the go, abuse of carbonated and alcoholic drinks, and coffee.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
How do the main symptoms appear?
Symptoms of gastritis with high acidity have common symptoms of all gastritis and their own specific characteristics. Doctors “recognize” them if the patient complains of:
- a feeling of heaviness, fullness in the stomach 20–30 minutes after eating, pain of a dull or aching nature, intensifies on an empty stomach, with a long break in food, when the stomach is empty;
- belching with sour contents;
- heartburn - caused by the backflow of gastric juice into the lower part of the esophagus;
- tendency to constipation;
- short-term colic along the intestines;
- nausea after eating;
- sometimes vomiting with sour contents, which improves the general condition;
- change in appetite - a decrease is due to fear of pain, and an increase is due to an improvement in the condition when binding acid to food.
Upon examination, the doctor discovers: a bright red tongue with a white or gray coating, moderate pain in the epigastrium in the superficial form and severe in the case of severe disease; patients usually do not lose weight. Patients experience astheno-neurotic syndrome.
Patients are bothered by constant bloating
These are signs of damage to nervous regulation: emotional instability, laughter is replaced by anxiety, crying, increased irritability, a tendency to lower blood pressure, bradycardia (lower heart rate), arrhythmias, increased sweating; when running a blunt spatula over the skin, the doctor sees the appearance of red stripes (red dermographism - a sign of impaired vascular tone).
General clinical picture
Hyperacid gastritis has symptoms that are similar to manifestations of other disorders of the gastrointestinal tract:
- Aching pain in the epigastric region. Discomfort is localized in the left hypochondrium. In the antral form, the pain is localized in the right area.
- Early saturation. Almost immediately after starting to eat, the patient experiences satiety, which does not depend on the volume of food eaten.
- Feeling of fullness after eating. It is regarded as discomfort that occurs due to prolonged presence of food in the stomach area.
- Heartburn. With increased acidity, the patient experiences a characteristic burning sensation, which worsens the standard of living. Heartburn, as a symptom of gastritis with high acidity, appears mainly when the body bends forward.
- Sour belching. A distinctive symptom for a disease in which the secretion of gastric juice increases. With the development of gastritis with low acidity, rotten belching occurs.
- Nausea accompanied by vomiting. Nausea occurs mainly on an empty stomach, when there are long breaks in food. Vomiting is characteristic of eroded gastritis when consuming large amounts of acidic foods.
- Flatulence. It occurs due to constipation, which develops against the background of fermentation.
- Decreased or increased appetite. With a superficial course of the disease, after eating, a decrease in acidity occurs, which helps to improve the patient’s condition and increase appetite.
- Hunger and night pain. When there is no food inside, severe discomfort develops, which worsens the general condition and disrupts sleep at night.
- Limited pain in the epigastric region upon palpation. At the same time, the anterior abdominal wall is soft.
As the pathological process progresses, inflammation spreads to other parts of the stomach. The disease becomes diffuse and is accompanied by secretory deficiency and atrophy of the mucous membrane.
Signs of chronic hyperacid gastritis are not pronounced. Periods of exacerbation occur after overeating and long breaks between meals. Relapses are typical for people who drink large quantities of alcohol and after food poisoning. The cause of exacerbation can be severe stress, smoking and eating poor-quality food (too cold or hot foods, fatty or spicy foods). Symptoms of exacerbation of gastritis also appear with heavy food intake.
We recommend: Gastritis in children: symptoms and signs
It is imperative to pay attention to the presence of so-called alarm symptoms or “red flags”, the detection of which requires a thorough diagnostic search in order to identify a more serious organic disease. They are listed below:
- unmotivated weight loss;
- dysphagia and fever;
- black tarry stools;
- vomiting blood and anemia;
- increased ESR and leukocytosis.
How does chronic gastritis differ from acute gastritis?
Gastroenterologists at the present stage of diagnosis do not focus on patient complaints, data on the secretory function of the stomach and fluoroscopy. Objective signs of gastritis with high acidity are accurately characterized only after studying a biopsy of the mucous membrane.
Among the morphological changes, the following should be identified: a reduced or preserved number of glandular cells in the corresponding part of the stomach, round cell infiltration, epithelial degeneration, replacement of gastric gland tissue with intestinal epithelium (metaplasia), areas of scar tissue.
Until the results of endoscopic and histological studies are received, international associations of gastroenterologists recommend using the term “non-ulcer dyspepsia.”
Provoking factors
Erosive gastritis with high acidity is not the norm. The acidic environment has a negative effect on the mucous membrane, which leads to the development of the disease.
Secretion secretion increases against the background of exogenous (external) factors. We are talking about the penetration into the body of substances that increase the level of acidity:
- eating very cold or hot foods;
- inappropriate chewing of food;
- inclusion of fried and spicy foods in the diet;
- alcohol abuse and smoking;
- uncontrolled use of medications.
The secretory functions of the gastrointestinal tract can be disrupted due to polluted environment and regular ingestion of harmful substances or dust, for example, when working in hazardous industries.
Internal reasons
Among the endogenous development factors, the following should be highlighted:
- Heredity. According to the results of ongoing research, if immediate relatives suffered from gastritis, then the risk of developing the disease in the younger generation is high.
- Poor lifestyle and regular stressful situations.
- Lack of vitamins in the body and disruption of metabolic processes.
- Dysfunction of organs involved in digestive processes.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system and respiratory organs. Against the background of hypoxia of cellular structures, a violation of secretory functions occurs.
The cause of the development of a pathological process with increased secretory function is the effect of Helicobacter pylori bacteria on the mucous membrane. Pathogenic microorganisms produce catalase to suppress human immunity and urease to protect against the effects of gastric juice. Helicobacter pylori activates the inflammatory process, releases toxins that poison the body, and have a negative effect on the functions of the stomach, which impairs its functioning.
We recommend: Symptoms of exacerbation of gastritis
Experts in the field of gastroenterology have been able to establish a close relationship between Helicobacter pylori and gastritis with high acidity. That is why, when primary symptoms appear, the patient is first referred for diagnosis of this pathogenic microorganism.
What examination needs to be done?
In clinical tests, no specific changes should be expected; only confirmation of the presence of an inflammatory process in the body (slight increase in leukocytes, ESR) is possible. Biochemical tests indicate concomitant damage to the liver and pancreas.
If erosions appear on the gastric mucosa, bleeding can be detected by the reaction of feces to occult blood (Gregersen). To identify Helicobacter, the following are carried out: urease breath test, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, polymerase chain reaction method.
Bacteria can be seen when examining biopsy material. The esophagus, all parts of the stomach and the duodenum are examined using a fibrogastroscopic method. The diagnosis includes a type of inflammation. pH-metry - stands for hyperacidity when the value is less than 1.5.
There are several ways to measure gastric pH
To measure pressure fluctuations in the stomach cavity and the possibility of reflux from the duodenum, electrogastroenterography is indicated. Ultrasound and computed tomography are auxiliary methods for diagnosing diseases of other abdominal organs with possible secondary inflammation of the stomach.
Tablets to neutralize hydrochloric acid (Antacids)
These are the most effective drugs for gastritis, neutralizing hydrochloric acid contained in gastric juice. Available without a prescription, it can be taken even by children who complain of heartburn or discomfort in the stomach. They differ from other drugs in their longer-lasting therapeutic effect, neutralize acid, and are also cheaper than their analogues.
Maalox
Coating agent, antacid, the active substances of which are: aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide. Prescribed for exacerbation of gastritis, chronic gastritis with high and normal acidity, peptic ulcer. Helps with overeating, stomach discomfort from taking medications or alcohol abuse.
Drink after meals, chewing or dissolving 1 tablet every 1.5 hours. But, no more than 12 tablets per day.
Side effects include diarrhea, constipation, and skin rashes.
Reviews say that the drug is a salvation for heartburn. One sachet is enough to neutralize the unpleasant sensations.
Talcid
This is an antacid drug used in the treatment of gastritis with high acidity and gastric ulcers. The active ingredient of the drug is hydrotalcite. Excipients include magnesium stearate, corn starch, mannitol, peppermint flavor.
The tablet can be chewed and washed down with water. Acute, chronic gastritis - 500 mg 2 hours after meals and before bedtime. Ulcer - 1000 mg 4 times a day after meals. The duration of treatment is 4 weeks, and ends when the symptoms disappear.
In case of overdose, relaxation of the stool may occur. During pregnancy, take only after consulting a doctor.
Gastal
A combined agent that reduces acidity and does not have a stimulating effect on the secretion of gastric juice. The drug is used for acute and chronic gastritis, irritation of the gastric mucosa, and heartburn.
Ingredients: aluminum hydroxide carbonate, magnesium hydroxide, corn starch, sorbitol, talc, mannitol, lactose monohydrate.
Adults: 2 tablets at least 4 times a day, 1.5 hours after meals and before bedtime. Children over 6 years of age receive half the adult dose. Dissolve the tablet, do not swallow it whole.
Overdose may cause nausea, constipation or diarrhea. Allergies, colitis, and dermatitis rarely occur. Not recommended for children under 6 years of age.
Customer reviews indicate that the drug copes well with heartburn and bloating. It has a beneficial effect on the gastric mucosa; the result after taking it does not appear instantly, but gradually.
Phosphalugel
The composition of this medicine (20 g sachet) includes purified water, calcium sulfate, pectin, aluminum phosphate, potassium sorbitol, agar-agar, sorbitol, orange flavor. The drug has an adsorbing, enveloping effect, neutralizes acidity levels, reduces the activity of pepsin, and protects the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Indications for use: gastritis with normal or increased secretory function, stomach and duodenal ulcers, heartburn, colon diseases, gastroesophageal reflux, intoxication disorders.
Dosage regimen for adults: 2 sachets an hour before meals, 3 times a day, also at night. For children under one year old, ¼ packet (1 tsp) after each meal, over one year old, ½ packet (2 tsp) after each feeding. Can be taken pure or diluted with water.
Contraindications: kidney disease, sensitivity to the drug.
Reviews say that the drug solves several problems at once, relieves pain, eliminates belching, heartburn, and restores intestinal function. I like that the packaging is convenient (single dose), you can take it anywhere and squeeze it directly into your mouth. Has a pleasant citrus taste.
How to treat gastritis with high acidity?
Treatment of gastritis with high acidity requires compliance with the following basic goals:
- normalize acidity;
- relieve the patient’s stomach from the effects of Helicobacter pylori;
- carrying out optimal anti-inflammatory therapy;
- restoring the ability of cells to regenerate;
- strengthening immune defense.
In case of acute catarrhal form and mild exacerbation of chronic gastritis, patients can be treated on an outpatient basis. In the case of more complex types, protracted course, hospitalization in a specialized department is recommended. Smoking, drinking alcohol, and carbonated water are strictly prohibited.
Diet
The treatment regimen must include dietary nutrition. Food for patients should be prepared only steamed or boiled or stewed. Frying methods are excluded. The feeding schedule becomes more frequent up to 5–6 times. This is necessary for the constant binding of hydrochloric acid. The total volume for each meal is reduced.
Dietary table No. 1 is assigned. The patient should not cook spicy, smoked, or highly salty foods. Pickled vegetables, sour fruit and berry juices, fermented milk products, legumes, mushrooms, cabbage, onions and garlic, other hot seasonings, cucumbers, and radishes are excluded.
You cannot eat nuts, cakes with cream, sweets (jam), sour apples, lemon. Sweet fruits are allowed fresh and in juice (grapes, peeled apples, melon). All dishes should be well-cooked and chopped as much as possible in order to relieve the stomach.
Boiled porridges (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal) are recommended. Patients benefit from porridge with pumpkin and pumpkin juice. Pearl barley, wheat and barley are prohibited. You can cook pasta. A liquid puree is prepared from potatoes, stewed together with carrots and zucchini.
Broccoli allowed
Soups made from meat and fish should not be rich. Canned meat and fish, and fatty pork are prohibited. Recommended are chicken, skinless turkey, beef in the form of meatballs, steam cutlets, slimy soups with boiled oatmeal. If tolerated well, you can drink whole milk, coffee with milk, weak black and green tea, and rosehip decoction.
It is recommended to use sweet berry jelly, compotes, and oatmeal jelly. It is better to refrain from eating pears and plums. Pears have a strengthening effect, plums weaken. They contain coarse fiber, which is not good for the stomach during the inflammation stage.
Butter or olive oil is added to main courses, puree soups, and is recommended to be taken on an empty stomach. How long to follow a diet for acute gastritis should be decided with your doctor. Chronic patients will have to adhere to restrictions throughout their lives.
Treatment with medications
Drug treatment includes drugs from different groups. For the treatment of acute gastritis, antispasmodics (No-shpu, Drotaverine, Papaverine) are used to reduce pain. Antibiotics are prescribed for obvious bacterial infection.
Enveloping agents (Almagel A, Gastroceptin) are more suitable for patients with a chronic course of the disease.
Antacids are a group of drugs that can neutralize stomach acid. They use combinations of magnesium, aluminum, calcium, silicon salts (Maalox, Phosphalugel, Gastracid, Altacid, Palmagel, Topalcan, Gaviscon, Rutacid, Gastal).
The effect does not occur immediately, but lasts a long time
Proton pump blockers act directly on the glands of the mucous membrane that produce hydrochloric acid (Omez, Omeprazole, Rabeprazole). H2-histamine receptor blockers act by reducing tissue sensitivity to histamine (Ranitidine, Famotidine). They have an anti-inflammatory effect.
If the disease is associated with Helicobacter infection, a course of treatment with antibiotics (Amoxicillin and Clarithromycin) in combination with Denol and Trichopolum is used. Often patients need sedatives and normalization of sleep.
Physiotherapeutic methods are used to enhance healing:
- electrophoresis;
- applications of paraffin and ozokerite;
- magnetotherapy.
People's Councils
Among the popular recommendations for the use of herbal medicine, the most advice is on the use of herbal infusions and teas with mint leaves and chamomile flowers. Careful use of St. John's wort is required. Its undesirable carcinogenic properties have been discovered.
You can use natural honey from beekeeping products (add a little to porridge, tea, decoction). Propolis tincture is diluted with milk or warm water. It has a healing effect on inflammation of the stomach and has a negative effect on Helicobacter.
The course of treatment with propolis is no more than a month, it must be taken one hour before meals
Diet for gastritis with high acidity
For the treatment of gastritis, diet becomes an important aspect of successful recovery. The patient should consume only warm food in small and frequent portions to prevent the development of high stomach acidity. It is recommended to avoid alcoholic beverages, spicy, salty foods, sour fruits, rich fatty broths and fatty meats.
If the corresponding signs of the disease appear, it is recommended to include porridge cooked in water, boiled rice and mashed potatoes in the diet. When inflammation decreases, other products can be added. Meals are provided balanced and enriched with vitamins. Products should be consumed in crushed, creamy, liquid, or puree form.
Sour foods, spices, spicy snacks, and especially black coffee are not allowed to be consumed.
Complex dietary treatment for stomach disease reveals a sufficient amount of energy value, proteins, fats and carbohydrates, the ratio of which is 1:1:4. The diet should not include foods that activate gastric secretion. These include:
- Broths from meat, fish, mushrooms;
- Fatty meat products;
- Any freshly baked and rye pastries that provoke the formation of hydrochloric acid;
- Salted, pickled, pickled vegetables;
- High fat dairy products;
- Sweet sodas that increase acidity concentration levels;
- Dried fruits, chocolate, ice cream;
- Salted and fatty fish;
- Mayonnaise, ketchup. Ginger is a product that increases the function of hydrochloric acid production;
- Legumes, corn grits, millet, barley porridge;
- Fried eggs and hard-boiled eggs.
Prognosis of cure and preventive measures
If treatment is started on time and carried out in full accordance with the scheme and proper courses, the prognosis is quite favorable. If the patient refuses to give up bad habits, alcohol consumption, or follow a diet, one should expect the disease to progress to gastric and duodenal ulcers.
For the purpose of prevention it is necessary:
- monitor the regularity of nutrition, do not allow any diets without the consent of a doctor;
- Reduce coffee consumption to two cups per day;
- do not drink sparkling water;
- diversify your food with fruits and vegetables, give up fast food;
- observe personal hygiene requirements;
- take medications only if truly necessary.
Your doctor will tell you how to properly treat hyperacid gastritis at your appointment. This species is not considered as dangerous as the hypoacid species. But in the absence of therapy, peptic ulcer disease with all subsequent problems becomes a complication. Therefore, you should take full advantage of the chance of cure.
Diagnostics
The examination plan for suspected gastritis is based on the following laboratory and instrumental studies:
- General blood analysis. Leukocytosis and an increase in ESR will indicate the presence of an active inflammatory process of a bacterial nature, lymphocytosis and leukopenia of a viral nature.
- Blood chemistry. A decrease in total protein and its fractions is a sign of exhaustion of the body due to lack of incoming food. The appearance of CRP indicates an autoimmune pathology. The presence of high levels of ALT, AST and other enzymes will allow one to suspect secondary pathologies: hepatitis, pancreatitis, etc.
- Stool analysis. Normally, it contains no undigested dietary fiber, the appearance of which occurs when digestion processes are disrupted.
- Gastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) is a visual assessment of the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus of the stomach and duodenum. Using this method, you can not only evaluate the course of gastritis, but also identify many complications: erosion, ulcers. During the procedure, a biopsy is usually taken, followed by histological examination and determination of the morphological variant of gastritis.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. The degree of change in neighboring organs is assessed.
- Intragastric pH-metry. An increase in the acidity of gastric contents will confirm the diagnosis.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane detected during FGDS
Additionally, many more studies may be prescribed (many hours of pH monitoring, scintigraphy, measurement of gastric motor function, CT, MRI, gastric manometry, etc.), but they are not mandatory.
It is important to identify signs of “alarm” that exclude the diagnosis and indicate the presence of a more serious and life-threatening pathology:
- pronounced leukocytosis;
- anemia;
- presence of blood in stool or urine;
- cachexia.
Diet
Nutrition for gastritis with high acidity is the basis for a favorable treatment outcome and the key to preventing relapses of the disease. He needs to pay special attention to:
- exclude spicy, fatty, fried, sour, salty foods from the menu;
- refusal of carbonated drinks, strong teas, coffee;
- the frequency of meals ranges from 4 to 5-6 times a day;
- food portions are small;
- the predominance in the diet of boiled meat, steamed dishes, vegetables with low starch and fiber content;
- the carbohydrate part of the dietary menu is filled with complex carbohydrates - pasta from durum wheat, cereals;
- The temperature of the dishes is average, exclude cold and too hot ones.
A gastroenterologist develops a diet taking into account individual characteristics.
What kind of disease is gastritis?
Most often, gastritis of the stomach with high acidity is diagnosed using FGDS, but this is not a common diagnosis that defines a specific pathology or disease, but a general concept that consists of a number of interrelated inflammatory and pathological processes in the human gastrointestinal system.
How the disease manifests itself clinically depends on the location of the lesion, its course, and the causes of its appearance.
The mechanism of damage determines three types of gastritis.
Type A is considered the rarest. It manifests itself as an autoimmune inflammation with local pathologies in its composition.
Stomach acidity with a level above normal appears due to damage to the bottom of the stomach and the cells of the intestinal walls.
Besides:
- the absorption of B vitamins is impaired, resulting in autoimmune disorders;
- anemia develops.
For a long time the disease practically does not show itself.
Disorders in the nervous system may be observed, as well as the first signs of anemia: a reddened, slightly smooth tongue, dizziness due to anemia, poor coordination of movements.
General symptoms also appear: nausea, unpleasant belching, constipation, abdominal pain after eating.
Type B is the most common, diagnosed in 50% of cases.
When inflammation happens:
- Antral, inflammation at the entrance of the stomach walls - a superficial type of lesion, after a few years it passes into the deep passages, forming ulcers, this happens in the presence of infectious agents;
- Exogenous hyperacid gastritis. Formation takes place under the influence of external listed reasons;
- Helicobacter pylori causes the atrophic subtype; with deep inflammation, the cells become cancerous.
Gastritis with high acidity, symptoms resemble a stomach ulcer.
The complaints mainly concern:
- pain in the epigastrium at night or on an empty stomach;
- belching and sour taste, heartburn;
- dizziness, nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea and constipation.
Type C is associated with the penetration of toxic or allergic substances into the mucous membrane: drugs, nicotine, alcohol.
A lesion forms at the bottom of the gastric walls.
It is accompanied by reverse (reflux) reflux coming from the duodenum.
It often manifests itself as a complication after surgery to remove part of the stomach.
It does not manifest itself for a long time, a slight bloating is felt, as well as loose stools.
In more advanced forms, there are the following symptoms: heaviness in the epigastric region, pain on an empty stomach or at night, heartburn, nausea, dizziness, hunger pain.
Medicines - antacids
Antacids are drugs that reduce the acidity of gastric juice for a short time (6-7 hours). These drugs are divided into two groups: absorbable and non-absorbable. The first ones very quickly penetrate the walls of the stomach and begin to act, but after their influence ends, an even larger amount of hydrochloric acid is produced in the organ.
The second group of antacids reduce acidity in the stomach well, but can cause side effects such as arrhythmia, kidney failure, and urolithiasis. Some antacid medications may contain painkillers. Antacids are not used for systemic treatment, since their long-term use can cause the development of severe gastric pathologies. With their help, it will be possible to relieve symptoms for a short period of time, but will not cure gastritis. Such drugs include Phosphalugel, Gasterin, Altacid, Almagel, etc.
In order to reduce pain during attacks of gastritis, No-spa or Drotaverine hydrochloride is usually prescribed.
Important information: Diet for weight loss and how to gain weight with gastritis
Features of nutrition with low acidity
Gastritis with low acidity is characterized by poor quality, difficult digestion of food. The symptoms of this form of the disease are the following: heaviness after eating, pain, unpleasant taste in the mouth, nausea, dyspepsia.
A diet for gastritis with low acidity allows you to consume:
- steamed cutlets from lean meats;
- omelette;
- the tea is not strong;
- biscuits and crackers;
- porridge with milk and water;
- vermicelli, noodles;
- vegetable soup;
- boiled turkey, rabbit, veal and chicken;
- milk, cottage cheese, cheese and sour cream.
The diet for atrophic gastritis with low acidity prohibits:
- garlic;
- sorrel;
- turnip;
- smoked meats;
- rich broth, borscht;
- alcoholic drinks;
- hard fruits;
- confectionery;
- black bread.
For an inflammatory process with low acidity, traditional medicine can be used. Medicinal tea brewed from mint, chamomile, chicory and lingonberry effectively eliminates symptoms. The mixture in a volume of 1 tablespoon is poured into 250 ml of boiling water.
If the acidity level is low, the following recipe will help: take one part each of potato, cabbage and carrot juice, add ten parts water. Take 200 milliliters on an empty stomach daily.
A diet for gastritis with low acidity involves a balanced menu for every day. You can use the following example for one day:
- 30 minutes before breakfast, drink chicory decoction;
- breakfast - zucchini casserole, warm tea and crackers;
- lunch – jelly, biscuits;
- lunch – a serving of vegetable soup;
- afternoon snack – ½ cup of fresh cottage cheese;
- dinner – steamed meatballs, noodles;
- An hour before bedtime, you can drink 250 ml of lemon balm decoction.
For gastritis with low acidity, the diet continues for at least three weeks. After the onset of remission, it is recommended to stimulate the production of hydrochloric acid. Once a day you should eat a piece of herring or a pickled cucumber. Before meals you need to drink water with lemon juice. After two months, the menu can be expanded.
Treatment with folk remedies
This includes decoctions, infusions of medicinal herbs, vegetable juices with the properties of reducing acidity, soothing pain, and neutralizing acid. It is possible to use these remedies only after consulting a doctor, and in no case should they replace traditional treatment.
In complex therapy, a decoction of flax seeds and jelly from this seed are widely used. The product has a pronounced antacid effect, normalizes digestion, and helps cope with the symptoms of heartburn and nausea.
Juice from raw potatoes contains a lot of starch, which has a coating effect. The recipe for preparing it is quite simple: grind the peeled tubers, squeeze out the juice through cheesecloth and take 100 ml three times a day, half an hour before meals.
Lifestyle correction involves giving up disordered, chaotic eating. It is necessary to develop an acceptable nutrition schedule. A prerequisite for recovery is the cessation of drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking. You also need to devote time to sports activities, which you can start with exercise therapy.
Methods of treating the disease
After diagnosing gastritis with high acidity, the doctor prescribes treatment regimens. Therapy consists of a complex of methods, such as:
- mode;
- therapeutic diet;
- use of medications.
It is necessary to follow recommendations to exclude junk food, tobacco products and alcoholic beverages. Treatment will not be beneficial if the underlying factors causing the disease are ignored. When starting therapy, the patient should avoid stress and heavy physical activity.
Drug therapy
The main goal in treating gastritis with high acidity with medications is to reduce the concentration of secretory secretions. Depending on the complexity of the pathology, the attending physician may prescribe antacids “Phospholugel”, “Almagel”, “Piren”, “Astrin” or “Platifilin”.
Enzyme-containing medications help restore the digestive process in case of high acidity. From this medication group, Digestal, Panzinorm or Mezim are prescribed.
If the cause of hyperacid gastritis is the Helicobacter bacterium, then Pilorid, Omeprazole, Amoxicillin or Tindazole are prescribed. Depending on the form of the disease, different medications are prescribed. So, for chronic gastritis with increased secretion, Sulpiride, Mezim, Pangenorm or Neosmectin are prescribed.
To eliminate duodeno-gastric reflux with high acidity, use Ursodex, Ursosan, Motilium or Ganaton. In addition, they take sedatives such as Valerian extract or Alimemazine. To reduce the secretory secretion of gastric juice, it is recommended to take Rennie, Fomotidine or Trichopolum.
After drug treatment, doctors advise visiting a sanatorium. Attention should be paid to institutions where prevention is aimed at gastrointestinal diseases.
Therapeutic diet
The main goal of a therapeutic diet is to eliminate inflammation of the gastric mucosa. The patient must be strict with his diet. Hyperacid gastritis can develop into complications that will be difficult to cure.
When dieting, you need to eat often and in small portions (up to 5 times a day). The patient will need to monitor the temperature of the food. Ideal when the dish is neither hot nor cold. The diet should consist of vitamins and fiber.
During an exacerbation of gastritis with increased secretion, they eat porridge with water, rice and mashed potatoes.
Products are taken in crushed form. Vegetables are ground and pureed. If you need to consume liquid, then eat puree soups. Dietary meat is pre-twisted in a meat grinder. The patient should avoid drinking coffee on an empty stomach. You cannot eat bread and other baked goods, corn grits, millet porridge and barley grits.
You should avoid borscht, cabbage soup, okroshka and rich broths made from meat, fish and mushrooms during recovery. The patient is advised not to buy sausages, sausages and canned food. It is worth paying attention to fresh white cabbage. But it should not be used if there is increased gastric secretion.
Fruits must be selected that are ripe and do not have a sour taste. In order not to irritate the intestines, you need to forget about fatty fermented milk products for a while.
For gaperacid gastritis, you can eat buckwheat, semolina, rice and oatmeal. Vermicelli is recommended for pasta products. Puree soups are prepared with potato or carrot broth. It is recommended to make vegetable first courses. You can add previously boiled dietary meats. Season the broth with butter or cream. Only wheat bread is recommended. As for flour products, you can eat buns with jam once a week.
If you have increased stomach acidity, you can take river fish. It is considered low-fat. Among the permitted vegetables, boiled carrots, potatoes, cauliflower and beets are consumed.
Traditional methods
The use of folk remedies to combat hyperacid gastritis is made after a diagnosis has been made by a doctor. Some plants can aggravate health conditions. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a specialist.
Herbal medicine is effective in eliminating pain in the stomach and solar plexus. Decoctions and infusions for gastritis are made from St. John's wort, heather and buckthorn bark. From each component, take an equal pinch of the plant and crush it. There should be 2 tbsp of raw materials. l. Then the crushed components are poured with 100 ml of hot boiling water. The mixture is infused for a quarter of an hour. The decoction should be consumed 30 minutes before meals. The infusion is taken 4 times a day.
To eliminate pain and reduce acidity in gastritis of the stomach, calamus, knotweed, St. John's wort, mint, yarrow and plantain plants are used. Each component is taken in equal parts. The amount of collection should fit into 2 tbsp. l. It is poured with hot boiling water, and the mixture is infused for 30 minutes. If necessary, before taking, the decoction can be diluted in equal proportions. You need to take the infusion before meals, 500 ml 3 times a day.
To reduce the acidity of gastric secretions, grated burdock root is used. For cooking you will need 2 tbsp. l of raw materials, which is poured with 100 ml of hot boiling water. The liquid is poured into a thermos and left for 2 hours. It is recommended to drink 500 ml of the infusion every morning on an empty stomach. The decoction is first diluted with water.
Potatoes are recommended in a therapeutic diet with high acidity, and the juice from the vegetable has beneficial properties. There are no problems in preparing it. The peeled root vegetable is ground in a blender or juicer. It is recommended to add oatmeal to the diet along with the drink. This is done to consolidate the recovery process.
To treat gastritis with high acidity, oatmeal porridge is used. The liquid helps eliminate the disease in a short period of time. The course of therapy is no more than 1 week. To prepare the decoction you will need wholemeal oatmeal poured with boiling water. The dish is cooked for an hour over low heat. Then cool for 30 minutes.
Add pharmaceutical dill and 2 tbsp to the decoction. l chopped walnuts. To add sweetness, add 4 teaspoons of honey and a pinch of salt. The resulting porridge is divided into 3 servings. It is consumed before meals 3 times a day.
A popular medicine among people is bee bread. It is recommended to take it in its pure form, 1 tsp 3 times a day. The course of treatment is up to 3 months.
When using bee bread, the temperature of the liquid must be taken into account. It depends on the degree of acidity of the stomach.
Causes
It is customary to identify several main areas in which causal factors operate. These are external and internal stimuli and their combination. As mentioned above, young patients and children suffer.
This situation arises due to the influence of external causes. Let's name the most significant of them:
- nature of nutrition;
- diet;
- bad habits;
- occupational hazards;
- environmental and medicinal effects.
Young people and children, especially teenagers, are prone to frequent consumption of harmful foods. The reality today is that normal foods in the diet are often replaced with snacks on the go. Moreover, it is customary to snack on widely advertised so-called “fast food” products, various chips, crackers, and nuts, which are sold in retail chains. The manufacturing technology of these food products involves the addition of strong flavoring and chemical additives. They are addictive in humans, that is, the desire to eat them arises again and again, which leads to constant irritation of the stomach and increased acid secretion.
Diet plays an important role in the occurrence of digestive pathologies. Irregular meals, most of which occur in the evening or at night, snacking on hot, spicy foods or drinks lead to the erratic production of acid, which corrodes the walls of the stomach.
Smoking and alcohol are the enemies of a healthy mucous membrane. Hot cigarette smoke entering the digestive tract contains harmful chemical impurities that cause secretory activity. At the same time, smoking suppresses the feeling of hunger, which leads to a lack of appetite, food does not enter the irritated stomach, and the acid acts on its walls for a long time. Alcoholic drinks themselves are harmful to the body; they also cause increased appetite, which results in a person overeating, which stimulates the production of gastric juice.
Occupational factors can be of a chemical or psychological nature. Vapors of acids, alkalis, and other chemical compounds affect the body of workers during the production process. If personal protective equipment is neglected or absent, the harmful consequences of such influence may occur.
Emotional stress regularly causes an increase in the secretory activity of not only the epithelium of the stomach, but other organs, which cannot pass without leaving a trace. The same applies to environmental factors: constant living in unfavorable conditions with increased levels of harmful chemicals in the air, water, and products causes erosive gastritis. Some medications have side effects and cause stomach irritation when taken orally.
Internal causes of inflammatory changes in the gastric mucosa include:
- hormonal disorders;
- infectious diseases;
- hereditary predisposition.
Hormonal imbalance can be congenital or acquired under the influence of drug therapy, injuries to the internal secretion organs, their diseases, etc. As for infectious diseases, it is necessary to mention Helicobacter pylori - a microorganism that can live and multiply in the acidic environment of the stomach, simultaneously causing irritation of the mucous membrane and hypersecretion of acid. Gastritis can be a consequence of intestinal salmonellosis, amoebiasis, enterocolitis, yersiniosis.
Hereditary factors play a significant role in the occurrence of irritation of the gastric mucosa. First of all, this is the way of nutrition and life, defects in secretory activity or enzyme deficiency.
The main causes and mechanism of increased acidity
Gastritis occurs due to malnutrition, infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, and alcohol abuse. Often the cause is uncontrolled use of medications and hormonal drugs used to treat somatic diseases. The inflammatory process and hormonal disorders can change the secretion of hydrochloric acid.
Normally, hydrochloric acid is produced by the parietal cells of the fundic glands. Their number differs in different departments. Most of the glands are in the fundus and body of the stomach. Therefore, it is here that the acidity of gastric juice is highest and normally amounts to 0.4–0.6%.
The acidity level is displayed on a pH scale from 0 to 14.0, where pH 7.00 is a neutral environment. As the number of hydrogen ions included in acids increases, the pH decreases. In the fundus of the stomach it is 1.5–2.5, and in the antrum it is 4.6–7.4. This is due to the fact that there are fewer parietal cells. In addition, gastric juice becomes diluted as food moves towards the duodenum, which reduces the concentration of acid.
Increased acidity can be caused by the bacteria Helicobacter pylori. They are capable of parasitizing in the antral mucosa of the stomach. During its life, Helicobacter pylori produces alkali, which protects them from the aggressive effects of hydrochloric acid.
At the same time, alkalization of the antrum, through feedback, signals the need for additional acid production. This also increases salivation. It turns out to be a vicious circle. Therefore, without adequate treatment, antibiotic therapy, it is impossible to reduce the level of hydrochloric acid production.
Excess acid reduces the resistance of mucosal cells, facilitating their damage under the influence of various factors. Therefore, with increased acidity, the following are more often observed: the transition of gastritis to erosive, the formation of ulcers, malignancy (degeneration) of mucosal cells. Specific symptoms help to identify this disorder and prescribe adequate treatment aimed at reducing HCl production and protecting the stomach walls.
Treatment of hyperacid gastritis with medications
Therapeutic measures are determined by the etiology of the disease, stage, degree of damage to the functional and secretory activity of the stomach, and morphological changes in the mucous membrane.
With gastritis, such functions of the stomach as motor, secretory, and excretory are disrupted. In hyperacid gastritis, the main destructive factor acting on the gastric mucosa is gastric juice.
Therapy goals:
- Elimination of inflammatory processes in the gastric mucosa.
- Normalization of secretory function: in case of increased secretion, drugs that reduce the aggressiveness of hydrochloric acid: antacids Almagel, Maalox, Vitair.
- Histamine receptor blockers – Ranitidine, Cimetidine.
- Creating conditions for regeneration of the gastric mucosa: restoration of motor function of the stomach, protection of the mucous membrane.
- Pain relief - antispasmodics.
- Prevention of ulcer formation - antibiotics that destroy the pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Which doctor should I contact?
Treatment of pathologies of the digestive tract is carried out by general practitioners-therapists and specialist doctors - gastroenterologists.
Antibacterial drugs for gastritis
Helicobacter pylori is the only type of bacterium that can exist in the acidic contents of the stomach. Often it is this that causes gastritis in a person. To combat this infection, different combinations of antibacterial drugs are used, for example Clarithromycin (other trade names of this medicine are Klacid, Clamed, Fromilid, etc.), Metronidazole (Bacimex, Klion, Metrogyl, Metronidal), Amoxicillin (Amoxil, Danemox, Flemoxin Solutab, Amoxillate), Tetracycline, Levofloxacin. You are not allowed to take such drugs on your own. The treatment regimen and combination of medications is determined by the doctor individually, based on the clinical picture of the disease.
Important information: What can stool look like with gastritis?