Constipation what is it? This is a disorder of the intestines, manifested by incomplete emptying, difficulty or delay in bowel movements for more than 48 hours. According to modern research, constipation (constipation) occurs several times more often in older people than in young people. At the same time, women are considered to be most prone to intestinal dysfunction. According to scientists, about 20% of the world's population suffers from the disease.
Prevalence of constipation
Constipation is very common among people who have indigestion. The tendency to constipation often leads to the formation of very serious proctological diseases. Thus, this problem is characterized by a high degree of social significance. Due to its prevalence and characteristic deterioration in the quality of life of patients, chronic constipation is classified as an independent syndrome. Today, the problem of constipation is very often studied by gastroenterologists and proctologists, as well as many other specialists.
Constipation often affects young children and elderly people over 60 years of age. If there is a constant feeling of difficulty in defecation and if relief is impossible (even with strong straining), it will be necessary to use stimulants that will help release fecal contents from the rectum. Also stimulating actions will be pressing on the perineum or on the walls of the anus.
Due to the constant feeling of insufficient emptying of the rectum, prolapse of the perineum syndrome develops. Chronic constipation occurs when the frequency of bowel movements occurs less than three times a week. Defecation is difficult and requires considerable effort. In this case, the consistency of the resulting stool is quite dense, lumpy, and characterized by a feeling of incomplete release of the rectum.
Special cases of the disease
If the supply of nerves to the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, then a person develops conditions like Hirschsprung's disease. Multiple sclerosis and spinal cord problems are also possible. All this leads to chronic constipation.
Very often people face a similar problem due to long-term use of antibiotics. As a rule, violations occur if the course lasted about a month. Because of this, the overall activity of the intestines is weakened, dysbiosis begins, the organs absorb more water than necessary, and as a result, feces are retained.
Constipation occurs as complications after surgical interventions. For example, this is possible during gall bladder surgery. Due to its removal, intestinal tone decreases, peristalsis worsens and obstruction appears.
Other operations on the gastrointestinal tract can also be dangerous. Almost any action with an open intestine is considered relatively risky, since as a result, inflammatory processes begin, adhesions appear, and peritonitis often develops.
Judging by the fact that you are now reading these lines, victory in the fight against diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is not yet on your side...
Have you already thought about surgery? This is understandable, because the stomach is a very important organ, and its proper functioning is the key to health and well-being. Frequent abdominal pain, heartburn, bloating, belching, nausea, bowel dysfunction... All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand.
Nausea. Belching. Digestive disorder, such as diarrhea or constipation. Heartburn.
In advanced cases, gastric perforation occurs at the site of the ulcer, which leads to internal bleeding. In case of this complication, which is manifested by severe pain, a drop in blood pressure, and pale skin, emergency surgery is performed immediately.
Gastritis and constipation
Constipation and fever may indicate an exacerbation of gastritis. During the period of remission, that is, when the inflammatory process subsides, there are usually few or no manifestations of the disease. Relapse of the disease can be caused by errors in nutrition, and in this case, constipation is one of the most common manifestations of the disease.
Intestinal function is completely restored after the inflammatory process is eliminated. That is, in order to get rid of constipation due to gastritis, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease. Compliance with the prescribed diet prevents exacerbation of inflammation of the gastric mucosa, which in turn prevents the occurrence of difficult bowel movements.
Acute gastritis often develops as a result of food poisoning. The pain appears sharply, then nausea and vomiting begins, and there may be diarrhea. After poisoning, constipation most often develops after dyspeptic disorders. And difficult bowel movements can be caused by taking a number of medications used to combat intoxication.
Sharply increasing pain, at first it is mainly localized in the lower abdomen. In the future, the stomach may hurt in all its parts. Nausea. Vomiting and constipation. When vomiting, brownish feces with an extremely unpleasant odor are released. Abdominal bloating, and in some patients it is asymmetrical. Severe weakness, tachycardia. Lack of appetite. Weakness and dizziness.
With acutely developing intestinal obstruction, all symptoms quickly increase. Constipation and nausea can sometimes be the only manifestation of chronic intestinal obstruction.
If the patient does not undergo surgery in time, perforation of the intestinal walls will occur, feces will be released into the abdominal cavity, and severe peritonitis will occur. In this case, there is no guarantee that the patient will recover.
Helminthiasis
Stomach ache. They mainly occur after eating. Flatulence. General weakness. Frequent headaches. Decreased appetite. Periodic nausea. Constipation.
Helminth infections often cause allergic diseases - asthma, rhinitis, skin rashes and itching.
Constipation or diarrhea. Excessive gases produced. A sudden sensation of immediate bowel movement. Discharge of mucus from the rectum. Feeling of incomplete bowel movement.
With irritable bowel syndrome, it is rare, but there is nausea and vomiting, and loss of appetite. The syndrome occurs against a background of stress, disturbances in intestinal motor function, and often the pathology first debuts after an intestinal infection. A teenager can suffer from IBS, since the development of the nervous system occurs during puberty.
Causes of chronic constipation
The causes of constipation can be defined as those that depend on the lifestyle and dietary preferences of the patient. Constipation can occur in those people who often restrain the urge to defecate, which subsequently inhibits the reflex activity of the gastrointestinal tract. Constant constipation can result from prolonged bed rest, frequent travel and moving, and hard work. Frequent use of laxatives due to an unreasonable expectation of early stool, a diet that does not contain the required amount of plant fiber, lack of sufficient daily fluid - all this contributes to the development of chronic constipation.
Constipation is considered one of the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome. With this pathological condition, intestinal motility changes, which is why unstable stools may occur, that is, this problem is further complicated by the release of scanty stools of a hard consistency (sometimes mucus is released). It happens that such constipation alternates with diarrhea. Stress contributes to the deterioration of the intestines.
Constipation is often the result of severe conditions that require emergency surgery. For example, mechanical intestinal obstruction often contributes to the development of coprostasis. Regarding the degree of narrowed lumen, obstruction is divided into complete and partial. The cause of obstruction of the intestinal lumen may be:
- tumor process;
- scar change;
- formed adhesions;
- volvulus;
- emerging diverticula of the large intestine;
- even helminthic infestations.
Coprostasis is characterized by a prolonged absence of bowel movements, a feeling of fullness in the intestines and bursting pain in the abdominal area. It happens that the liquid contents bypass the hard fecal plug and come out as diarrhea.
Symptoms and complications
The signs of fecal retention are quite extensive. They vary depending on the disease causing constipation. In different cases, constipation is either one of several symptoms of the disease, or the only complaint of the patient.
The feces acquire a very dense or even hard consistency. The act of emptying itself takes place with great effort. With chronic constipation, the frequency of bowel movements varies from once every 3 days or less. In some cases, constipation gives way to diarrhea.
The most common symptoms are:
- bloating,
- flatulence,
- heaviness and pain in the abdominal area.
The process of defecation brings relief to the patient. Also, patients with a chronic form of the disease note the presence of odor from the oral cavity, loss or decrease in appetite, deterioration in performance and sleep.
With the protracted nature of the disease, there is a risk of various complications. These include deformation of the intestinal walls, the development of inflammatory processes, as well as the development of hemorrhoids, paraproctitis or anal fissures. One of the most dangerous complications is intestinal obstruction, the treatment of which requires immediate surgical intervention. This condition provokes a decrease in blood supply to the intestinal vessels and their further death.
Psychological and neurological reasons
Another cause of constipation is also a psychological fear of defecation, which develops due to diseases of the rectum and is accompanied by a characteristic pain syndrome.
Regarding neurological disorders, including depression and stress, various types of nervous shocks, they also lead to the formation of chronic disorders at the time of bowel movement.
It should be said that many medications can cause a side effect in the form of inhibition of intestinal motility, which contributes to frequent constipation. Chronic constipation is also caused by pathologies of the innervation of the intestinal wall (Hirschsprung's disease, spinal cord injuries and multiple sclerosis).
Are there any characteristic signs?
Constipation due to food poisoning is characterized not only by the very fact of lack of desire to visit the toilet, but also by a number of specific manifestations that are not directly related to the act of defecation. But it is precisely these symptoms that make it possible to distinguish the condition of constipation, in which the body requires help, from non-pathological stool retention that occurs for natural reasons.
Intestinal dysfunction is accompanied by the following accompanying symptoms:
- Abdominal pain is usually nagging or dull, with a clear localization.
- Bloating in the abdominal cavity, hardness of the abdomen on palpation.
- Uncontrollable flatulence.
- Increased body temperature, within 37 degrees; with a long absence of bowel movements, severe fever develops, up to 39 degrees.
- Skin rashes, usually acne on the face and neck, caused, like an increase in temperature, by intoxication of an already weakened body due to the accumulation of waste in the intestines.
- Headaches, usually dull, aching, localized in the back of the head.
However, the most important sign that disorders requiring treatment have developed is the desire to visit the toilet, which does not lead to results. That is, a person wants to go big, but he can’t.
If such signs are observed by the end of the week after poisoning, measures should be taken without delay. Constipation is extremely dangerous because it becomes a harbinger of a more serious pathology - intestinal obstruction.
Classification of constipation
The classification of constipation is based on the etiological factor and the mechanism of their development. According to this classification, the following types are distinguished:
- nutritional (those associated with certain diets);
- psychogenic (associated, first of all, with the psycho-emotional state of a person);
- neurogenic (they are caused by disorders of neuro-reflex activity);
- toxic (in case of mercury or lead poisoning);
- types of constipation caused by anorectal diseases (in the case of anal fissure, hemorrhoids or paraproctitis);
- This classification should also include proctogenic types of constipation (those associated with disorders of the pelvic day diaphragm muscles);
- constipation associated with various kinds of mechanical obstacles (due to tumors, scar-like changes, strictures or polyps, as well as abnormalities of the digestive tract);
- Iatrogenic constipation is another type of pathology that occurs as a result of taking medications.
Danger of the disease for adults and children
Intoxication with prolonged constipation threatens human health.
If feces remain in the intestines for a long time in adults and children, there is a risk of developing the following pathologies:
- overdistension of the rectum and colon;
- decreased sensitivity of the nerve endings of the intestines, which causes the cessation of urges and the accumulation of feces;
- compaction of feces - causes injury and bleeding from the anus;
- obstipation – formation of fecal stones. It is impossible to extract them on your own. This will have to be done in a hospital setting;
- inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract;
- the appearance of rashes, including purulent ones;
- rectal cancer;
- the child has a slowdown in development, fear of defecation.
Impaired bowel movements have a negative impact on the emotional state. The patient becomes nervous and irritable.
Symptoms of chronic constipation
Constipation is often accompanied by numerous symptoms, it all depends on the underlying diseases that cause them. But sometimes constipation is the only characteristic complaint of the patient.
You should be aware that the individual rhythm of bowel movements often differs from person to person. The process of defecation during constipation is characterized by the presence of special tension, which requires significant effort. Typically, feces have a dense consistency, dry, and their shape can be balls or beans. Very rarely, constipative diarrhea is observed, which is characterized by loose stools (often with mucus) with a prolonged absence of regular bowel movements and a feeling of fullness in the intestines. Liquid stool with the presence of characteristic mucus can also be the result of existing constipation due to irritated intestinal wall.
In children
Children are highly dependent on receiving a sufficient amount of calories daily; with constipation and fecal intoxication, the ability of the intestinal epithelium to absorb proteins and fats is greatly impaired. When toxins enter the nervous system, they greatly depress the child, he cannot eat food normally, and constantly cries and screams. High body temperatures are possible; thermoregulation centers are not fully formed. The liver is unable to inactivate most metabolites from the intestines.
The first step in treating intoxication includes eliminating constipation
Second stage of diagnosis
The next, second stage of the diagnostic measures being carried out is colonoscopy, that is, an endoscopic examination of the large intestine, as well as taking biopsy samples from the mucous membranes, cytological and histological examination of the material.
After this, the doctor usually prescribes methods for studying the functional state of the gastrointestinal tract in relation to the previously made diagnosis. Such studies include taking bacteriological samples, studying to identify hidden blood, coprogram, methods of manometry of the intestinal walls (this includes anorectometry and sphincterometry), as well as various laboratory tests to determine functional type disorders (primarily those disorders that are associated with secretory organs and the digestive tract).
The appointment of various diagnostic techniques takes place only after determining the relevant complaints, characteristic features of the intestine and possible assumptions about concurrent diseases. The latter also applies to the choice of treatment method.
Diagnosis
To diagnose constipation and the influence of toxins that are released into the blood, laboratory and instrumental examination methods are used.
Laboratory methods include:
- General blood analysis;
- General urine analysis;
- ALT and AST of the liver;
- Liver thymol test.
Instrumental methods:
- Sigmoidoscopy;
- X-ray of the abdominal organs;
- Colonoscopy;
- Ultrasound examination of the abdomen.
Before starting a diagnosis, the doctor must collect anamnesis, find out about the duration of the disease and the treatment that was undertaken at the pre-hospital stage.
https://youtu.be/QaVA7bYqXaw
Intestinal obstruction
However, the most difficult and dangerous consequence of prolonged constipation is persistent obstruction in the intestinal area, which requires immediate intervention by a surgeon. Such obstruction leads to developing ischemia of the intestinal walls and the development of necrotization is possible.
Sometimes constipation indicates that a tumor process is occurring in the human body. Constipation is also a sign of a malignant disease. Those constipations that are associated with a lack of fiber in the human diet affect the formation of carcinogens in the intestinal cavity.
Elderly patients who suffer from various mental disorders usually develop fecal impaction due to lack of regular trips to the toilet.
Symptoms
The presence of constipation in a person is indicated by the absence of stool for two days. At first, intoxication does not yet develop. A person is worried about bloating and flatulence. Constipation that lasts more than three days begins to manifest as loss of appetite, abdominal pain and fatigue. The last sign indicates the beginning of the development of intoxication.
Fecal poisoning can be accompanied by various symptoms. They depend on the type of intoxication. In its acute form, the following symptoms are noted:
- headaches, often occurring in the temples;
- drowsiness;
- constant nausea;
- vomit;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness and malaise.
Signs of intoxication of the body with constipation, which occurs in a chronic form, are less pronounced. But with prolonged fecal poisoning, a person experiences accompanying symptoms in the form of:
- constant aversion to food;
- bad breath and yellow coating on the tongue;
- frequent insomnia;
- nervousness;
- hair fragility and excessive hair loss;
- cloudy urine;
- skin rashes;
- swelling throughout the body;
- heartburn;
- systematic attacks of headaches;
- brittle nails;
- weight loss or gain.
Symptoms of intoxication with chronic constipation most affect the skin. In a sick person it becomes flaky. Rashes often appear on the temporal and frontal areas of the head. Long-term feces poisoning leads to constant exacerbations of chronic dermatitis.
In children, signs of intoxication of the body with constipation are more pronounced. The child is constantly irritated and whiny. He is worried about constant flatulence. Pustular rashes often appear on the skin.
A concomitant symptom of fecal intoxication in a teenager is acne. Children also experience anemia and weight loss, even leading to anorexia. A typical manifestation of fecal poisoning due to constipation in children is a constant feeling of pressure in the anus.
Treatment of chronic constipation
Treatment of chronic constipation is not limited to the use of laxatives. Self-medication is unacceptable, since prolonged constipation in adults is just a symptom of the disease or a sign of complications in the future.
Self-use of laxatives without any special recommendations and mechanisms of their action, as well as assessment of side effects, can lead to long-term problems with bowel movements as a result of a decrease in the motor function of the intestine itself.
It should be said that the dosage of the laxative can be increased over time. And after even more time, laxatives will cease to be effective at all.
Treatment of chronic constipation, in addition to symptomatic therapy, involves measures aimed at identifying and treating the pathological condition that caused the disease.
When understanding the mechanism of persistent constipation, the doctor will prescribe treatment for the patient, taking into account pathogenetic factors that contribute to the effective action of symptomatic drugs, without causing a vicious circle that only aggravates impaired intestinal motility.
First aid and therapy
Linex capsules for normalizing intestinal microflora
Conservative and surgical therapy is used to treat intoxication and the causes of the pathology. Drug therapy includes the following drugs:
- gentle remedies for constipation (Duphalac, buckthorn decoction);
- probiotics (Lactovit, Linex, Immunovit);
- antifoam agents (Espumizan);
- prokinetics to stimulate peristalsis (Motilium, Domperon);
- antispasmodics (Spazmalgon, No-shpa, Papaverine).
The following are prescribed as first aid in case of severe condition of the patient’s body:
- siphon enema;
- infusion therapy (droppers) with drugs to restore water-electrolyte balance and remove toxins (Ringer's solution, Reogluman, Trisol, etc.).
To treat mechanical constipation and some intestinal diseases, surgical intervention is used, the purpose of which may be the elimination of nodes, loops, adhesions and other mechanical obstacles, the formation of an anastomosis, the removal of a colostomy, the removal of a pathological section of the intestine, etc.
Diet for treating constipation
In the treatment of constipation, it is very important to follow a diet. Patients' diets should include foods rich in plant fiber (such foods include cereals and fruits), as well as plenty of fluids (usually it is recommended to drink 2 liters of water per day). If gas occurs during such a diet, doctors prescribe the drug Mucofalk. It is also necessary to exclude from the diet all those foods that aggravate constant constipation.
The patient should eat according to the regimen, that is, at least five times a day, eating small amounts of food. Long breaks between meals should not be allowed.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional medicine can be used in cases of occasional constipation. In case of chronic disease, traditional medicine can be used as additional therapy.
Before using any medications, you should consult a specialist.
- The fastest way to relieve constipation is the use of castor oil. The product is available for sale both in bottles and in gelatin capsules. For an adult, you need to drink a tablespoon of castor oil, no more than 2 times a day. Perfectly stimulates intestinal motility.
- A decoction of senna seeds has a strong laxative effect. Place 2 teaspoons of seeds in 3 cups of boiling water. Leave the resulting mixture in a warm place for 3 hours. Take 4 tablespoons every hour.
- A mixture of aloe, lemon and honey to improve peristalsis. Grind three aloe leaves and one lemon. Mix the resulting ingredients with liquid honey. Take the resulting mixture every morning on an empty stomach, 1 tablespoon with plenty of water.
- Herbal collection. Mix equal amounts of marshmallow root, dandelion root and rhubarb root. Pour 3 tablespoons of the resulting mixture into a liter of hot water and leave for a couple of hours in a warm place. Strain the infusion thoroughly and drink small portions throughout the day.
Share the article on social media. networks:
Medications
It is also necessary to monitor regular bowel movements. It is better if the individual rhythm is restored naturally. There is no need to restrain the urge, this negatively affects peristalsis.
When taking medications that impede the transit of feces, they should be replaced with medications that cannot affect digestion. To stimulate the gastrointestinal tract, as well as to strengthen the tone of the intestinal muscles, it is recommended to lead an active lifestyle, walk in the fresh air, swim, do aerobics or fitness. A positive attitude towards life has a good effect on a person’s psycho-emotional state, preventing the occurrence of stress.
Laxatives are usually prescribed in rare cases where there is persistent constipation that cannot be corrected by diet or proper regimen. The drug that is best suited for a certain stage of constipation is usually prescribed.
If you prescribe a laxative, you should remember that its prolonged use can irritate the intestinal wall and increase peristalsis, which can lead to the development of a syndrome called “lazy bowel” syndrome. The latter means the inability to go to the toilet independently after stopping the drug.
Why does constipation occur after poisoning, what to do?
There are not many reasons for the appearance of disturbances in the functionality of the intestines. As a rule, defecation delays occur due to the following:
- Features of nutrition - the predominance in the diet of difficult-to-digest food that requires a long time to digest.
- Lack of fluid in the body - we must not forget that juices are not a drink from a nutritional point of view, and alcohol, like coffee, promotes the removal of fluids, “drying”.
- Lack of physical activity and activity - a “sedentary” lifestyle is especially dangerous; if a person spends most of the day in a sitting position, it provokes the formation of areas of poor patency inside the intestinal lumens.
- Regular use of laxatives, or long-term use of products or dietary supplements with a laxative effect.
- Use of certain medications.
- Specific diseases - hemorrhoids, tumors in the rectum, acquired physical anomalies or congenital anatomical disorders.
- Diseases of the digestive system and liver.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Helminthic diseases or dysbacteriosis.
- Climate change.
Inaccessibility of a toilet can also lead to constipation. If a person endures for a long time without being able to empty the intestines, then with systematic repetition, this leads to the development of disturbances in peristalsis.
Food poisoning somewhat narrows the range of causes. As a rule, after an intestinal disorder, the lack of desire to visit the toilet appears due to the following:
- Empty intestinal lumens - as a rule, with severe intoxication, people do not eat anything for up to three days, that is, there is simply nothing to go around with.
- Not completely complying with a therapeutic diet means eating heavy foods, for example, beef, which a weakened intestine is not able to cope with.
- The use of stool-hardening medications during the treatment of intestinal disorders.
- Physiological disturbances in the functionality of the intestines that appear as a result of poisoning - in this case, the condition of constipation is accompanied by severe abdominal pain and bloating of the peritoneum.
Of course, there may be other reasons for the development of intestinal dysfunction. For example, dehydration, which often overtakes a person with food poisoning, may well lead to constipation. Staying in bed for a long time can also cause bowel retention, especially in a child or an elderly person.
Disturbances in the balance of internal microflora and the composition of intestinal juices also cause delays in bowel movements. In adults, problems with going to the toilet often arise due to an extremely rapid transition from a gentle diet to regular food.
Constipation is classified as follows:
- spicy;
- chronic.
- In addition, pathologies in peristalsis are divided into the following types:
- primary - this type includes pathologies that have developed due to congenital or acquired anatomical abnormalities of the colon;
- secondary - this type of peristalsis disorders develops as a result of various injuries, mechanical effects, for example, due to prolonged sitting, or any diseases;
- idiopathic - with this type of disease, disturbances in peristalsis occur due to weakened intestinal motility, without the presence of any obvious prerequisites for this in the form of diseases, injuries or anomalies.
Constipation after poisoning can develop according to any of these types. Diarrhea accompanying intestinal disorders often injures the intestines, especially if their consistency consists not only of watery contents, but also of solid inclusions.
Often, disturbances in peristalsis that appear after an intestinal disorder occur in an alternating pattern - constipation and only diarrhea, and there is no normal stool. This development of the disease does not indicate problems with motor skills, but an imbalance in the flora, dysbacteriosis, the presence of helminthic infestation, or other similar pathogenesis. The cause of this course of peristalsis disorder can also be polyps in the rectum.
Acute constipation is a condition in which there is no bowel movement, despite the urge to do so, for more than 5 days. If a disturbance in peristalsis is caused by poisoning, then doctors talk about the occurrence of an acute type of intestinal disturbance after 6-7 days.
The chronic type of intestinal dysfunction is not a consequence of food poisoning. But this state of the body significantly increases the risk of developing constipation after treatment of intoxication.
There is another type of classification of this disease. Lack of stool may be:
- Alimentary – arising due to a lack of fluids inside the body or adherence to a strict diet, for example, this type of intestinal dysfunction develops during Lent.
- Mechanical - appearing due to various damage to both the muscle walls and the mucous membrane.
- Dyskinetic – formed as a result of disruptions in the innervation of the intestine and other types of disturbances in its functionality.
Food poisoning can provoke every type of disturbance in peristalsis. Therefore, the choice of treatment should be approached taking into account your own feelings.
Constipation in old and senile age
Constipation in old age is much more common than in young people. This is explained by age, weakening of the abdominal muscles and pelvic floor, and frequent cases of impaired intestinal motility are also noticeable. Changes occur in the composition of intestinal microorganisms, and the production of digestive enzymes decreases.
Also common causes of constipation in old age are due to the use of various medications.
Constipation in old age can lead to complications. Fecal stones lead to intestinal obstruction, and due to intestinal stagnation, ulcers can form. This is why it is so important to pay attention in time, undergo examinations and treatment, so that constipation does not develop into intestinal complications.
What examination do you need to undergo?
In diagnosis, it is important to interview the patient, find out his eating habits, frequency of meals, motor mode, and the connection between stool retention and anxiety. With manifestations, it is necessary to contact a pediatrician for children, and a therapist for adults. You may need to consult a neurologist or gastroenterologist.
The minimum examination includes blood tests, urine tests, and a coprogram (will allow you to evaluate the elements of constipation of stool, the presence of intestinal bleeding, the degree of disturbance in the digestion of food). The irrigoscopy method is based on the administration of a contrast agent with an enema, followed by a series of x-rays. Shows the patency of the large intestine, the presence of tumor-like formations, and anomalies of the sigmoid colon.
Colonoscopy refers to endoscopic examinations. A thin tube with a camera at the end is inserted through the patient's rectum under general anesthesia. It allows you to examine the intestinal lumen, mucous membrane, and take material from suspicious areas for biopsy. To determine the full functioning of the sphincter apparatus, the doctor may prescribe sphincterometry and anorectometry.
These studies make it possible to determine the possibilities of contraction of the intestinal muscular apparatus.
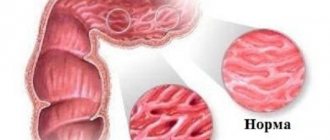
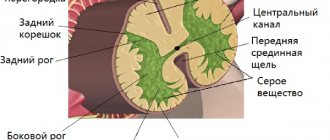
Comparative view of unfilled and contrasted intestine
Main types
Constipation can be primary, secondary and idiopathic. The former are associated with congenital intestinal defects, the latter develop as a result of diseases of internal organs, taking certain medications, poisoning, etc.
. Idiopathic constipation is caused by impaired intestinal motility of unknown etiology. Secondary constipation can be:
- endocrine in nature;
- toxic genesis (for example, due to chronic nicotine poisoning);
- reflex (due to compression by inflamed organs, in women - by the pregnant uterus);
- psychogenic (ranging from phobic disorder, fear of visiting the toilet at a party or at work and ending with overwork);
- hypodynamic (associated with a decrease in physical activity);
- nutritional (related to poor diet);
- proctogenic (associated with diseases of the rectum);
- medicinal;
- helminthic (caused by intestinal damage by parasites - worms);
- caused by disturbances in the content of electrolytes in the blood, often occur in patients with myocardial pathologies;
- neurogenic (caused by injuries to the lower back, herniated discs in the lumbosacral spine, tumors).
Nutritional constipation is a fairly common phenomenon, caused by errors in diet, or rather food preferences (the patient does not like foods high in fiber, prefers meat foods, coffee, chocolate). According to the flow, there are two types of constipation:
- spicy;
- chronic.
Failure to pass stool within 24 hours is considered acute constipation. Its causes may be mechanical damage (tumor growth), dynamic damage (inflammation of the abdominal organs), taking a number of medications, head injury, prolonged immobilization (for example, bed rest).
If the patient cannot defecate on his own (glycerin suppositories or finger manipulation are required), the stool is lumpy and dense, the intestines are not completely emptied, and stool occurs less frequently than once a week, such manifestations are considered chronic.
Etiology
There are many sources of stagnation of feces in the intestines, which is why they are usually divided into several large groups. The first category combines pathological conditions associated directly with this organ. These include:
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- dolichocolon - in this case, the colon is abnormally large, which slows down the transport of feces;
- dysbacteriosis and diverticulosis;
- megacolon;
- inflammatory, infectious or oncological lesions of this organ;
- the presence of additional loops in the sigmoid colon;
- prolapse of the colon - most often develops in females in the postpartum period;
- dolichosigma and transversoptosis;
- ileocecal valve insufficiency;
- disruption of the normal functioning of the sphincter of Oddi.
In addition to the above organic causes of constipation, a wide range of ailments associated with other internal organs and systems can cause this condition. It follows from this that the second group of provocateurs is represented by:
- metabolic disorders;
- diabetes mellitus;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum or stomach;
- pancreatitis and cholecystitis;
- overweight;
- gastritis, regardless of etiology;
- hemorrhoids, which can be external and internal;
- colitis of both specific and nonspecific forms;
- tumors of a benign or malignant course, localized in the gastrointestinal tract. This also includes polyps and cystic neoplasms;
- pathologies of the endocrine system organs;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- pathological influence of parasites, worms and protozoa;
- mental disorders;
- polyneuropathy;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- portal hypertension;
- poisoning of the body with chemicals, medications or alcoholic beverages;
- severe dehydration.
Causes of constipation
As mentioned above, constipation develops in absolutely every person and elderly people are no exception. In addition to the above factors, the following can provoke the formation of such a problem in older people:
- the natural aging process of the human body, leading to changes in intestinal motility and a slowdown of all processes occurring in the digestive tract;
- disturbance of nervous regulation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- involutional deformations of the mucous membrane of this organ;
- the presence of a large number of chronic diseases.
It is noteworthy that such intestinal dysfunction is not uncommon among children, including infants, both breastfed and bottle-fed. In this category of patients, constipation is provoked by:
- enzyme deficiency;
- individual intolerance to a particular food product;
- rickets and myasthenia;
- adhesive disease and gastroduodenitis;
- Hirschsprung's disease and cerebral palsy;
- gigantism and paraproctitis;
- pheochromocytoma and febrile conditions;
- lactose deficiency;
- early introduction of complementary foods;
- errors in the diet of a nursing mother;
- poor nutrition that is not suitable for children by age;
- forced refusal of food;
- forced potty training.
As for gender, problems with defecation are most often observed among representatives of the weaker half of humanity. This is due to the presence of specific causes of constipation in women, including:
- hormonal imbalance caused by menopause;
- the period of bearing a child - during this time, the enlarged uterus compresses the internal organs and the intestines in particular, which interferes with the normal evacuation of feces;
- addiction to strict diets;
- the course of menstruation - constipation is considered a constant companion of PMS;
- weakening of the pelvic floor muscles after the birth of the child.
However, it is not always the case that constipation is provoked by reasons that have a pathological basis. The category of physiological predisposing factors, i.e. not related to the course of a particular illness, may include:
- long-term addiction to bad habits;
- prolonged refusal to eat, which entails subsequent overeating and problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- consumption of large amounts of fatty and spicy foods, preservatives and smoked foods, carbonated drinks and confectionery, as well as other “harmful” foods. It is for this reason that one of the main ways to get rid of constipation is diet;
- indiscriminate use of medications, in particular laxatives and antibacterial agents;
- ingestion of insufficient volumes of liquid;
- long-term influence of stressful situations;
- physical fatigue;
- physical inactivity.
It is noteworthy that in some situations it is impossible to find out the source of constipation.
What to do for prevention?
People who work at a computer all day and drivers of transport should especially take care of the prevention of chronic constipation. Lack of abdominal tension provokes “lazy” intestinal motility. It is necessary to take breaks with walking up the stairs, squats, and push-ups.
Danger awaits us during the holidays. Filling the intestines with delicious dishes becomes a heavy burden for several days. Therefore, nutritionists recommend preparing more light salads for the holiday table. Ashamed to seek help for constipation, some patients lead themselves to serious complications. It is necessary to help the body cope with physiological problems in time.
How to help yourself
If constipation has not entered the system and bothers you quite rarely, and is not accompanied by any accompanying symptoms, you can simply wait for the normalization of intestinal function and defecate at the first urge.
You will need to review your daily diet. First of all, sufficient fluid intake must be ensured. A wonderful remedy for sudden constipation can be plum juice or prunes. For prevention, it is useful to include various types of fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grain bread in your diet.
Moderate exercise not only helps strengthen the body as a whole, but also contributes to the smooth functioning of the intestines. Physical exercise can relieve stress, which often leads to constipation, and normalize the overall emotional state.
If the lack of bowel movements begins to seriously bother you, you can try laxatives. Which types of drugs to choose is an individual decision; you just need to take into account possible contraindications and side effects.
So, there are five main types of laxatives:
- irritant effects;
- osmotic;
- prebiotics;
- volumetric;
- oil
The most unsafe drugs are those belonging to the first group. These include both herbal preparations (buckthorn, senna leaves, castor oil) and synthetically produced products (Gutalax, Bisacodyl). This species quite strongly stimulates the activity of the intestines, causing it to work excessively. Therefore, their long-term use is extremely undesirable. Irritating drugs are contraindicated for infants, pregnant and nursing mothers.
Pharmacology offers a fairly wide range of osmotic agents - sodium hydroxide, sodium and magnesium sulfate, Carlsbad salt. The mechanism of action of these drugs is the ability to retain fluid (water) in the intestines, which causes softening of the stool. An example of a common drug with such an effect is Forlax in powder form, which is often prescribed to children. Most often, osmotic laxatives are prescribed for food or drug poisoning. This type of drug in this group, such as polyethylene glycol, is prescribed even to pregnant and lactating women.
Prebiotics have an excellent laxative effect, stimulating the growth of beneficial microorganisms. Preparations based on lactulose are especially effective: Normaze, Duphalac, Prelax, etc. Sometimes taking these drugs can be accompanied by flatulence, which lasts for several days.
Taking medications from the bulk and oil groups should be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician, since their effects are quite specific.
However, we must remember that addiction to even the best of laxatives is extremely undesirable. Therefore, as soon as the action of the laxative has led to a positive effect, you need to address the cause of constipation: change your diet, normalize physical activity, and avoid stress.
If you have difficulty defecating for more than a week, even when using laxatives, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment of fecal poisoning
Treatment is aimed at eliminating current constipation, normalizing the body’s condition, and searching for the causes of defecation disorders.
Without identifying factors that contribute to the development of bowel problems, improvement will be short-lived.
Therapeutic measures:
- The use of laxatives - suppositories, tablets, drops.
- Adequate fluid intake - at least 2 liters per day.
- Discontinuation of medications that cause a decrease in intestinal motility.
- Enterosorbents – Enterosgel, activated carbon, Smecta.
- Antihistamines to relieve allergy symptoms.
A doctor will help you choose safe medications to relieve intoxication symptoms. Antibiotics are not used. Treatment is carried out at home.
The following shows measures to identify the cause of constipation. The examination plan includes:
- examination and analysis of the patient's medical history;
- blood and stool tests;
- blood for thyroid hormones;
- instrumental studies - endoscopy, x-ray;
- manometry – to study intestinal motility.
Treatment of constipation is impossible without normalizing nutrition. There is currently no specialized diet. It is enough to follow the principles of rational nutrition.
The diet should include foods rich in fiber - any vegetables, fruits, oat bran. Additionally, the use of products with a laxative effect is indicated. These are beets, prunes and plums in any form, dried apricots and apricots, fermented milk drinks, flax seed.
Effect of drugs on stool
Treatment with certain medications has a negative effect on the intestines. Constipation from thoughtlessly prescribed antibiotics is quite common. The reason is that antibacterial agents kill intestinal bacteria in addition to pathogens. The digestive tract is densely populated with a variety of microbes. New information is constantly emerging about the beneficial role of microscopic creatures. Among other things, bacteria produce chemicals that increase the contractility of the intestinal tube. A decrease in the number of microbial colonies on the colon mucosa automatically worsens excretory function. Therefore, constipation occurs after treatment. The body will gradually recover and grow a younger generation of bacteria. You can help by eating the favorite foods of microorganisms and introducing them from outside.
Foods that promote the growth of intestinal microflora (prebiotics)
- ubiquitously available vegetables such as onions, garlic, rarer asparagus, artichokes;
- legumes, especially dark beans, lentils;
- fermented milk drinks, chicory root.
There is no convincing evidence of the benefits of finished dosage forms containing live microorganisms. Capsules with bacteria will not cause any obvious harm. Pharmacies offer a huge variety of biological products with probiotics - lacto- and bifidobacteria. While taking a course of antibiotic therapy, you can buy a package of probiotics. However, you should definitely take advantage of natural support by saturating your body with beneficial bacteria from natural sources. The undisputed leaders are fermented milk and fermented products. Crispy pickled cabbage and exotic, spicy kimchi contain bacteria and dietary fiber that are essential for treating constipation.
Scientific name
Constipation is a disturbance in the process of defecation, which is manifested by the absence of stool for more than 2 days or incomplete bowel movements. There are 2 points of view on the problem of constipation: the World Health Organization classifies it as a disease (ICD-10 code K59.0), but the World Organization of Gastroenterologists believes that it is not a disease, but a symptom.
Bristol constipation scale
Many people are interested in knowing what constipation is called scientifically. To designate it, there are such medical terms as “constipation” and “obstipation”.
Physical education as a method of relieving constipation
As for exercises, there are also some that can help with constipation.
Exercise 1. Lie on your stomach, stretch your arms and legs. Alternately raise your right arm and left leg at once, without bending them, and then your left arm and right leg. Repeat the exercise 6-8 times.
Exercise 2. Lie on your stomach, lift only your body, while spreading your arms to the sides. Legs don't bend. Repeat the exercise 6-8 times.
Exercise 3. Standing on all fours, raise either your right or your left leg in a straight position.