Colpitis - what kind of disease?
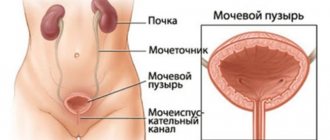
Colpitis is inflammation of the vaginal mucosa. The second name is vaginitis. Every third woman on the planet suffers from this disease. The disease affects people of absolutely any age and even children.
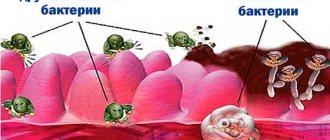
Colpitis in women can be caused by opportunistic microorganisms: staphylococci, streptococci, Proteus, E. coli, Trichomonas, chlamydia, Candida fungi and others that enter the body through sexual contact or through the rectum.
Vaginitis poses a health threat. It can cause inflammation in the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovary. The disease occurs in several forms.
https://youtu.be/2tislZJakpg
Risk factors for the development of atrophic colpitis
Even more interesting:
Tongue with HIV infection photo
Yarina or Dimia
Because estrogen levels begin to decline during menopause, most people tend to think that menopause itself causes this condition. However, decreased estrogen can also occur in other cases.
All factors that can lead to decreased estrogen levels in women are potential risk factors for developing atrophic colitis and may include:
Vaginitis: forms and types
Conventionally, the disease is divided into the following types:
- Bacterial colpitis. It can be specific and non-specific. The first type is caused by opportunistic bacteria that appear under certain conditions, and the second is when intestinal infections enter the vaginal mucosa.
- Non-infectious colpitis is the body’s reaction to antibiotics. It could also be an allergy to underwear, ointments, creams, pads.
Vaginal colpitis develops:
- In acute form. It is characterized by copious discharge, which has an unpleasant odor and is accompanied by painful sensations.
- In the subacute form, there are no pronounced symptoms.
- In chronic form. This is an untreated acute form. Rarely causes discomfort. Can cause ascending diseases of the uterus and appendages.
Classification and code according to ICD-10
The ICD-10 classification indicates that code No. 76.0 includes acute and chronic colpitis that occurs during the postmenopausal period.
The disease can take on a specific nature, the causative agent of which can be tuberculosis, syphilis, or hepatitis C.
The next form of colpitis is nonspecific, caused by a fungus of the genus Candida, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus epidermidis.
A non-infectious type of vaginitis occurs when the vaginal mucosa is irritated by latex, tampons, intimate hygiene products, or during sexual intercourse without moisturizing.
Why do you think hemoglobin is increased in women? Is it necessary and how to reduce it? We'll tell you! You can learn about the treatment of chronic chlamydia in women from this material.
What medications should I take for cystitis in women? Read about this in this publication.
Causes of the disease
Colpitis appears in women due to a number of different reasons:
- Sexually transmitted diseases.
- Any infection that reduces the body's protective functions.
- Mechanical damage - abortion, childbirth.
- Hormonal disbalance.
- Antibiotic therapy.
- Allergy to ointments, creams, pads, underwear.
- Lack of personal hygiene.
- Bad habits.
Colpitis occurs most often among women of childbearing age, the causes of which lie in opportunistic flora. The causative agents of the disease are transmitted sexually. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully approach the choice of a partner. Or at least use a condom.
How to recognize the disease?
Timely diagnosis and treatment of vaginitis will save a woman from many problems in the future, including its consequences such as infertility.
Colpitis in women, symptoms:
- Mucus discharge that has an unpleasant odor. Sometimes the discharge takes on a cheesy appearance and resembles thrush.
- Itching, burning in the perineal area.
- The external genitalia have a slightly swollen, reddish appearance.
- Urination becomes painful.
- There is pain in the lower abdomen.
The disease may not always be accompanied by such symptoms. Subacute and chronic forms occur unnoticed and are detected only with a thorough gynecological examination. Therefore, visiting a gynecologist is a mandatory procedure that must be performed at least once a year.
Clinical manifestations
As mentioned above, the symptoms of genitourinary menopausal syndrome are more persistent the more time a woman has been in menopause.
The clinical picture of vaginal atrophy is characterized by a continuously relapsing course.
So, atrophic vaginitis can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- Feeling of dryness, persistent, severe itching, burning in the genital area;
- Painful sensations during intimacy (dyspareunia), often accompanied by minor capillary bleeding.
The painful sensations themselves, as a rule, are associated not only with vaginal dryness, which is natural for this period of a woman’s life, but also with thinning of the mucous membrane, as a result of which the nerve endings are “exposed”, providing hyperesthesia (increased sensitivity).
Bloody discharge also occurs due to the thinning of the vaginal epithelium and the exposure of most of the small blood vessels, which are often injured during any intervention, be it sexual intercourse or examination in the mirrors at a doctor’s appointment.
- Leucorrhoea, pathological vaginal discharge. This symptom depends on the severity of the inflammatory reaction and the type of causative agent of vaginitis.
Discharges can be:
- 1Scanty/moderate/abundant;
- 2Watery/mucous/mucopurulent/purulent.
Symptoms of atrophic vaginitis with estrogen deficiency may be accompanied by a decrease in libido, as well as urinary disorders (dysuria, frequent urination, night trips to the toilet, urinary incontinence, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder).
We can say that the main clinical manifestations of atrophic colpitis are not very different from other types of vaginitis, but it is very important to correctly diagnose the atrophic nature of the process, since further treatment tactics depend on this. Let's move on to diagnostics.
Trichomonas colpitis in women
The disease is caused by an opportunistic bacterium, Trichomonas, which enters healthy microflora only through sexual contact. The incubation period is one to two weeks, after which the first symptoms appear: mucous (foamy or curd-like) discharge, accompanied by itching and burning, as well as pain in the lower abdomen.
Both partners should be tested for the presence of Trichomonas. Since the disease is very often not accompanied by characteristic signs, it is advisable to carry out bacteriological culture of the vaginal microflora.
Treatment is prescribed for both women and men. It includes antimicrobial agents and topical agents (creams, suppositories, gels). Don't forget about immunostimulating drugs.
After a course of treatment, re-diagnosis is required.
Treatment of the disease
Pathology should never be ignored, so treatment of the disease is a key point for every patient. It is very important not only to receive prescriptions from a doctor, but to strictly comply with all his requirements, without hoping that pathological changes can magically disappear. Competent treatment of colpitis and compliance with all the doctor’s requirements is the key to successful and quick relief from atrophic colpitis.
The basis of treatment for the disease is the prescription of hormone replacement therapy. After hormone levels increase, the vaginal mucosa will begin to renew itself in the same way as it did before menopause.
Hormonal drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets or suppositories. It is necessary to take the drugs for a fairly long period of time - from a year to three years, but the first positive changes become noticeable after three months. It is impossible to interrupt treatment of the disease, since this will lead not only to a relapse of the disease, but also to the possible addition of a secondary infection.
Most often, for atrophic colpitis, suppositories Estriol and Ovestin . The main active ingredient of these drugs is the estrogen component, which effectively eliminates vaginal itching, genital dryness, soreness and frequent urge to urinate.
Gynoflor E has a good effect . With the help of lactobacilli acidophilus, the vaginal microflora is normalized, the blood supply to the vaginal epithelium is improved, the formation of new cells is stimulated, and normal vaginal acidity is maintained due to the development of lactic acid bacteria in the woman’s vagina.
Among other equally effective drugs, Elvagin , Orthoginest , Estrocard , Estrovagin , Ovipol Clio .
To reinforce local treatment, systemic drugs are also prescribed - Climodien, Cliogest, Divina, Pauzogest. The drugs are prescribed for early signs of atrophic colpitis, but after the complete end of menstruation, and Kliogest can be used as a preventive measure for pathology. Doctors also recommend continuing to take standard medications that are indicated for menopause - Activel, Cliofit, Eviana, Klimadinon, Menopace and others.
Contraindications
In some cases, women are not prescribed hormonal drugs. Hormone replacement therapy should not be used in patients who suffer from breast cancer, endometrial cancer, bleeding, or vascular thromboembolism. It is not recommended for those who have liver problems or pathologies of the cardiovascular system (myocardial infarction, angina).
In this case, therapy is replaced by other drugs that do not contain hormonal components. These can be douches and baths with decoctions and infusions of herbs, vaginal suppositories with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
Atrophic colpitis, unfortunately, is a familiar phrase for many women who have entered menopause. However, such changes in the body should not be taken with a negative connotation. The natural aging process cannot be delayed, but degenerative changes can be slowed down. This will not only prolong a woman’s healthy period, but will also help her endure the changes that occur to her body during menopause as easily as possible.
Interesting and educational video on this topic:
https://youtu.be/O8GILyACXBo
About
Traditional and non-traditional treatment of colpitis
Regardless of what form of colpitis was diagnosed, the treatment of the disease looks the same and consists of the use of antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal agents. It is also advisable to follow a light diet, excluding salty, spicy and sweet foods. Alcohol consumption is prohibited.
Folk remedies will help cure colpitis with great success. Of course, they are prescribed in combination with basic medications.
You can eliminate itching and burning with:
- Sea buckthorn oil, which is used to lubricate the vaginal mucosa.
- Douching with herbal decoctions (chamomile, rose hips, rosemary, sage, oak bark). Douching is carried out with warm, never hot, water.
- Tampons soaked in a solution of propolis and honey. Grind a small piece of propolis and melt it in a steam bath. When it cools down, add a little honey. Soak tampons in this liquid and place them in the vagina for two hours, twice a day.
If we talk about how to treat colpitis in women, we should mention herbal infusions that are taken orally:
- Pour boiling water over valerian, lemon balm and nettle at a ratio of 1:1:1, leave for one night, then drink a quarter of a glass before meals.
- Pour 20 grams of thigh with 300 ml of boiling water, boil for 10 - 15 minutes and leave. Drink the decoction every two to three hours. You can add honey.
- Pour one tablespoon of St. John's wort and millennium with water and bring to a boil. Drink 1 spoon before meals.
Colpitis in women is a rather insidious disease. Ignoring treatment can cause negative consequences. Therefore, you should always be on alert and immediately consult a doctor at the slightest symptoms.
Diagnosis of pathology
The first thing to do when unpleasant symptoms appear is to visit a doctor. To make a diagnosis, the patient will be prescribed and undergone the following procedures:
- standard gynecological examination;
- colposcopy (examination of the vagina using a video camera with an image displayed on a monitor screen);
- measuring the acidity level in the vagina;
- smear for infections;
- cytological smear (Pap test for cellular changes that provoke cancer);
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs.
Usually the picture becomes clearer during a gynecological examination, when the doctor sees a thinned, smoothed, as if stretched, surface of the vagina. It can diagnose areas of erosion, hyperemia, minor hemorrhages and purulent foci. Most often, the vaginal mucosa is swollen, has a serous coating and can bleed even with a slight touch. The chronic stage of the disease does not produce such clear symptoms, but they are all slightly present.
After receiving the results of laboratory tests and conducting additional studies, there is no doubt about the diagnosis. The doctor begins to formulate a treatment strategy for the disease.
Colpitis in men
Colpitis is a female disease, so it cannot develop in men with all its symptoms. However, representatives of the stronger sex are carriers of the pathogens of this disease. Most often, Trichomonas, chlamydia, ureaplasma and other pathogenic bacteria live in the urethra of men. They cause colpitis in women.
Symptoms of the disease may be absent or appear to a minor extent:
- Redness on the genitals, swelling.
- Painful urination.
- Itching.
- Curdled discharge.
Therefore, if colpitis is detected in women, treatment, as well as the diagnosis itself, is prescribed to both partners. The best way to identify pathogenic bacteria is bacterial culture of the microflora.
Vaginitis during pregnancy
Vaginitis is a side effect of infections such as chlamydia, trichomoniasis, ureoplasmosis, candidiasis, etc. Pathogenic bacteria displace healthy flora, causing inflammation of the mucous membranes. If the inflammation is not treated in time, it can spread to the uterus and appendages, which is especially dangerous during pregnancy.
Penetrating into the uterus, the infection affects the placenta, making it more vulnerable. The result is premature birth, miscarriages in the early stages and miscarriage in later stages. Sometimes the infection that develops along with vaginitis penetrates the placenta to the fetus. In this case, the child (if it is a girl) may become infected and various developmental pathologies may occur.
Treating the disease during pregnancy is quite difficult. Strong drugs are prohibited, and weak ones do not always give results. Therefore, traditional medicine methods will be effective.
Do not forget about proper and balanced nutrition, a complex of multivitamins and stimulation of the immune system. You should also lead a healthy lifestyle and avoid stressful situations.
Vaginitis in pregnant women can be identified by general symptoms - itching, discharge with an odor, pain in the lower abdomen. Of course, such signs can indicate many different diseases that gynecology deals with. Colpitis, however, is the most common. Therefore, any abnormal discharge should always alert a woman.
Age-related colpitis
Optionally, inflammation of the vagina can be caused by pathogenic microorganisms. Often the cause of the disease is hormonal imbalance, reduced immunity, or a course of antibiotics.
Women over forty are at risk. Due to the restructuring of the body and menopause, the vaginal flora also becomes vulnerable.
The main symptom of age-related colpitis is purulent discharge that has an unpleasant odor. Heaviness and pain in the lower abdomen may also be observed.
Treatment of the disease is carried out with a course of antibiotics and immunostimulating drugs. Vitamins and medications are required to correct hormonal levels.
Vaginitis in children
Colpitis is an insidious disease that even children are susceptible to. Most often, the reasons for the appearance are the following:
- Lack of personal hygiene or improper washing of the child, in which intestinal bacteria enter the vaginal mucosa.
- Allergy to detergents, creams, linen.
- Long-term use of antibiotics and other strong medications.
- In rare cases, vaginitis can be caused by worms.
- Foreign objects in the vagina.
The disease is often accompanied by inflammation of the external genitalia. In this case, a pediatric gynecologist can diagnose vulvovaginitis. The disease, in the absence of timely treatment, leads to infertility. At risk are girls who often suffer from sore throat, ARVI, cough, diseases of the genitourinary system, and dysbacteriosis. In a word, children with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms of colpitis in children:
- Redness and itching of the genitals.
- Discharge.
- Pain in the genital area.
- Painful urination.
In addition to medications, treatment of the disease necessarily includes immunostimulating agents, as well as topical antiseptics.
Why does this disease occur?
The main reason that provokes atrophic colpitis is the reduced production of female sex hormones. They are the decisive factors influencing the condition of the vaginal epithelium. Estrogens most actively maintain stability in the vagina, because they determine the acidity of the vaginal environment, which is the norm for women. In such an environment, only beneficial bacteria live in the vagina, and the growth of other microorganisms that can upset the balance is not provoked. Estrogens also ensure stable blood circulation in the epithelial layer.
Age-related changes and the onset of menopause are the main markers that the vaginal environment will undergo certain changes. But if at first, even after the end of menstruation, the level of hormones can still provide the minimum norms for vaginal acidity, then already in postmenopause women begin to experience all the “delights” of a deficiency of female sex hormones.
Lack of estrogen leads to thinning of the vaginal epithelium and narrowing of its lumen. And microbes, previously restrained by the acidic environment, receive favorable conditions for development. Most often, microbes provoke the chronic course of the disease, and with mild symptoms, a woman may not be aware of the presence of pathology.
Another important reason is the influence of external factors. In some cases, atrophic colpitis is caused by taking hormonal drugs for a long time. And the course of the disease is aggravated by stress factors: hypothermia, previous genital infections, previous radiation therapy, removal of the ovaries, weakened immunity. Risk factors include excess weight, thyroid disease and diabetes.
Prevention of colpitis
It is better to prevent any disease in a timely manner than to treat it. In addition to the fact that diseases can recur, causing complications, they also have a significant impact on finances.
The best prevention of infections of the reproductive system is a regular sexual partner and personal hygiene. You also need:
- Regularly undergo examination by a gynecologist and other specialists.
- For casual sex, use a condom.
- Use only proven intimate cosmetics, as well as high-quality natural lingerie.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, take vitamins and maintain immunity.
- Do not self-medicate and consult a doctor promptly.