Instructions for use
Metronidazole is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial and antiprotozoal agent. It is available in the form of tablets, solution for infusion, vaginal gel and suppositories. All dosage forms are used for the treatment of gynecological diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to metronidazole.
Indications
Vaginal gel and suppositories are prescribed to patients suffering from:
- urogenital trichomoniasis (disease of the genitourinary system caused by Trichomonas vaginalis);
- nonspecific vaginitis of various origins if clinical manifestations of the disease are observed and the causative agent of the infection is identified.
Tablets and solution for intravenous administration are prescribed for the following diseases:
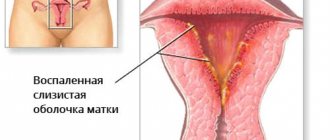
- endometritis (inflammation of the endometrium - the inner mucous layer of the uterus);
- endomyometritis (not only the endometrium, but also the muscular layer of the uterus is involved in the pathological process);
- adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages);
- abscess of the oviducts and ovaries;
- vaginal vault infection;
- trichomoniasis, including urethritis and vaginitis;
- vaginitis of bacterial etiology.
Metronidazole is used not only to treat these diseases, but also to prevent them after surgical interventions on the pelvic organs.
Directions for use and doses
Metronidazole in suppositories for trichomonas vaginitis is prescribed 1 suppository once a day. Course 10 days.
If nonspecific vaginitis is observed, then 1 suppository is prescribed 2 times a day, the course is 1 week. Metronidazole tablets may be prescribed at the same time.
The gel is administered intravaginally using an applicator. Single dosage 5 g (1 full applicator) 2 times a day, for 5 days.
Tablets for trichomoniasis are prescribed in parallel with vaginal suppositories according to the following schemes:
- 250 mg morning and evening for 10 days;
- 500 mg 2 times a day, course from 5 to 8 days;
- 2 g once.
Both sexual partners should undergo treatment.
Features of the treatment of trichomoniasis in men and women.
For gynecological diseases, the dosage is selected individually depending on the severity of the infection; the maximum daily dosage can be 1.5-2 g.
For the purpose of prevention, the drug is prescribed orally in a daily dosage of 0.75-1.5 g, which should be taken in 3 doses 3-4 days before surgical treatment, or 1 g once within 24 hours after surgery.
In case of severe kidney pathologies, when CC is less than 10 ml per minute, the daily dosage should be reduced by 2 times.
Metronidazole in the form of an intravenous solution is prescribed when it is impossible to take it in tablets.
The drug is prescribed in an initial dosage of 0.5-1 g intravenously over half an hour, after which the medication is administered at 0.5 g every 8 hours at a rate of 5 ml per minute. If the drug is well tolerated, then after 2-3 infusions it is administered as a stream.
The duration of therapy is 7 days, if necessary it can be extended. The maximum daily dosage is 4 g (for renal and liver failure, no more than 1 g, divided into 2 doses).
In order to prevent complications after surgical treatment, it is administered dropwise into a vein in a dosage of 0.5-1 g on the eve of the operation, on the day of the operation and the next day after it - in a daily dosage of 1.5 g (500 mg every 8 hours) . After 24-48 hours, metronidazole tablets are prescribed.
Contraindications
Metronidazole in all dosage forms is not prescribed if the following pathologies are observed:
- hypersensitivity to the composition of the drug;
- intolerance to nitroimidazole derivatives;
- blood pathologies, including a history of leukopenia;
- organic lesions of the nervous system;
- liver diseases (for use in large doses).
A contraindication for the use of vaginal gel is impaired coordination of movement.
The drug is prescribed with caution
Prescription of medication during pregnancy and lactation
The active substance penetrates the placenta.
Metronidazole in all dosage forms is contraindicated in the first trimester.
Starting from the second trimester, you can use all dosage forms as prescribed by your doctor.
Metronidazole is incompatible with breastfeeding, so it is worth transferring the baby to artificial feeding during treatment.
Overdose
With intravaginal administration, an overdose is unlikely.
When taking metronidazole orally and intravenously, the following may be observed:
- nausea;
- epilepsy attacks;
- vomit;
- violation of movement coordination;
- polyneuropathy.
There is no specific antidote; therapy is aimed at eliminating signs of overdose.
Side effects
With all routes of administration, the following adverse reactions may occur:
- loose stools, stomatitis, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, inflammation of the tongue and pancreas, intestinal colic, dryness and metallic taste in the mouth, constipation;
- movement coordination disorder, vertigo, convulsions, impaired consciousness, asthenia, depression, sleep problems, headaches, hallucinations, polyneuropathy;
- inflammation of the bladder, staining of urine in a brown-red color, incontinence, an increase in its volume, impaired urination;
- thickening of the T wave on the electrocardiogram;
- decrease in leukocytes and neutrophils;
- an allergic reaction, which can manifest itself in the form of hives, rash, redness of the skin, fever, joint pain, nasal congestion;
- thrush.
Thrombophlebitis may develop with intravenous administration.
When administered vaginally, local reactions may occur:
- vulvitis, which can manifest itself as itching, burning pain, redness of the vaginal mucosa;
- burning or irritation of the penis in a sexual partner.
Compound
Tablets contain 0.25 g or 0.5 g of metronidazole.
As excipients they contain:
- starch;
- methylcellulose;
- lactose;
- octadecanoic acid.
The solution for infusion contains 5 g of metronidazole. It contains water for injection and disodium salt as excipients.
Each suppository contains 0.5 g of metronidazole. The auxiliary components include boric acid and solid fat.
1 g of vaginal gel contains 0.01 g of active substance. As excipients it contains:
- glycerol;
- macrogol;
- hypromellosis;
- water;
- disodium edetate.
Pharmacology and pharmacokinetics
Metronidazole is a nitro-5-imidazole derivative. The metronidazole molecule contains a 5-nitro group, which is reduced by intracellular transport proteins of infectious agents. The reduced nitro group reacts with the DNA of bacteria and protozoa, which leads to their death.
Metronidazole is effective against the following bacteria and protozoa:
- trichomonas;
- bacteroids;
- lamblia;
- fusobacteria;
- eubacteria;
- clostridium;
- peptococci;
- dysenteric amoeba;
- peptostreptococci.
When administered into the vagina, almost 20% of metronidazole is absorbed into the blood. The half-life can be 8-10 hours.
When taken orally, up to 80% of the active substance is absorbed. Food intake does not affect the absorption of the drug.
The active substance is excreted from the body in the urine.
The half-life is the same as for vaginal administration. In case of kidney pathology, the active substance accumulates.
Once in the body, metronidazole undergoes metabolism.
When administered intravenously, the active substance has similar pharmacokinetics as when administered orally.
Conditions of storage and sale
All dosage forms of metronidazole are available with a prescription. They should be stored out of the reach of children.
Is it possible to take antibiotics for this disease?
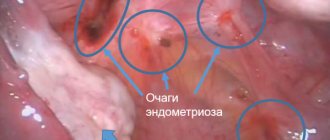
First, we need to remind you that endometriosis is a hormonally dependent disease in which increased cell division occurs in the upper layer of the uterus, which is called the endometrium. This process cannot be associated with the development of infection in the body, since its course is neither infectious nor inflammatory.
Antibiotics are drugs that quickly destroy pathogenic microflora, namely fungus, microbes and bacteria.
That is, in other words, why should a woman suffering from uterine endometriosis take this group of medications if she does not have microorganisms dangerous to health in her body? Doctors quite often prescribe antibiotics to patients with this pathology as a result of a severe decrease in immunity, which is further undermined due to the development of the disease. That is why the body of any woman is quite susceptible to the development of certain inflammatory diseases that will cause serious harm to the patient’s health. Therefore, during the course of endometriosis, the patient is prescribed one or more antibiotics, since it is quite easy for microorganisms to enter the genitals and cause this or that disease in the shortest possible time.
Endometriosis especially often leads to the development of the following diseases:
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- pyelonephritis.
When taking antibiotics, they quickly defeat many pathological processes occurring in the body, which are caused by pathogenic microflora.
As a result, the woman’s symptoms of inflammation and infection disappear very quickly. In addition, when these medications are taken correctly, the patient’s signs of endometriosis are reduced and its course is also alleviated.
This is due to the fact that this process quite significantly reduces the so-called tissue immunity, due to which the rapid growth of endometriosis cells is suppressed. That is why, with reduced immunity, such a pathology will develop quite quickly, which means it will cause a lot of harm to a woman’s health.
https://youtu.be/CsvU79otPPg
https://youtu.be/4KncHyDqGjM
Reviews
(Leave your feedback in the comments)
The gynecologist discovered that I had thrush and bacterial vaginitis. He prescribed metronidazole suppositories and tablets, as he explained to me, for better effect. 3 days after the start of treatment, the unpleasant odor disappeared, and after 5 days the discharge disappeared. After 10 days I was healthy. Olga
She was treated with metronidazole for vaginitis. I took 8 tablets at a time and forgot about the disease. You just need to be treated together with your partner. Maria
* — Average value among several sellers at the time of monitoring, is not a public offer
Symptoms and signs of colpitis
The risk group consists of the fair half of humanity aged 18 to 45 years. The most common form of colpitis is thrush. Itching and unpleasant discharge begin in the vaginal area. Vaginitis does not go away on its own. The disease must be carefully treated.
Symptoms of colpitis:
- characteristic discharge depending on the course of the pathological process: curd-like, watery, foamy, purulent;
- swelling and redness of the vulva;
- itching and burning in the intimate area, increasing as you walk;
- persistent sour odor;
- nervous system disorders: insomnia, irritability, anxiety;
- pelvic pain syndrome, especially during intimacy;
- increased body temperature (extremely rare);
- frequent urge to urinate;
- urinary incontinence.
The consequences of colpitis are not always the worst. In some cases, the symptoms go away and the woman calms down. But this means that the disease has gone deep inside. Over some period of time, signs of vaginitis will return. A timely check with a specialist will help avoid consequences.
Elimination of chronic diseases
The cause of bacterial colpitis can be chronic diseases, such as endocrine diseases.
Thus, the presence of diabetes mellitus in a woman plays an important role. The classification of vaginitis also includes allergic and atrophic (senile). The latter is more common in older women, after menopause.
Therefore, productive interaction between the patient, the obstetrician-gynecologist and another specialist who observes the woman, depending on the type of concomitant pathology (endocrinologist, allergist), is mandatory.
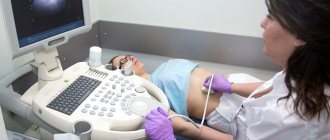
Diagnostics
To conduct an examination, you must make an appointment with a gynecologist. The doctor will clarify the complaints and conduct an initial examination. During the examination, characteristic signs are immediately detected, such as redness and swelling of the epithelium. Other changes, such as vaginal discharge, are detected. Material is collected for microscopy and serological tests. Identification of the causative agent is necessary for therapy.
If necessary, additional studies are carried out, such as PCR diagnostics.