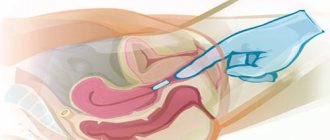
Inflammatory processes often occur in the female genital organs. They are dangerous because they can harm the entire body as a whole. As a result, the normal state of the appendages and uterus is disrupted. Very often, an ectopic pregnancy is provoked or it does not occur at all.
It is possible to prevent dangerous consequences only through early diagnosis and modern treatment. It is the symptoms of inflammation of the ovaries and appendages that will be discussed in this article.
Location
Judging by its appearance, the ovary is comparable to a peach pit, the length of which does not exceed 4 centimeters and 2.5 centimeters in width.
In this case, the thickness of the paired organ is 1-1.5 cm.
The outer layer is well protected by the tunica albuginea.
It has appropriate properties, so pathogens do not penetrate inside the ovary.
Thanks to this membrane, inflammatory processes develop less frequently than in the fallopian tubes and the uterus itself.
The next layer is the cortex. Several follicles of unequal maturity are constantly present on its surface. These capsules look like bubbles filled with liquid, and a full-fledged egg should grow in them. When this process is completed, ovulation occurs. As a result, the follicle wall is destroyed, and the egg is ready to meet sperm for the purpose of fertilization. If conception does not occur, it dies, and if not, it begins to move through the tubes to gain a foothold in the uterus.
As for the ovaries themselves, they are responsible for the formation of key female hormones - progesterone and estrogen. Thanks to these substances, reproductive function is carried out.
Inflammation is often called an ovarian cold. In fact, if the body is overcooled, it is much easier for pathogenic microorganisms to enter the genitourinary system.
Reference! In the presence of a focus of infection, inflammation of the ovaries develops. In most cases, the source of infection is the omentum or fallopian tube.
What does inflammation mean in women?
Infectious processes are caused by various pathogenic microorganisms. Infection occurs due to unprotected sexual contact with a sick partner, and also extremely rarely through the use of other people's personal items. But often it can be triggered by certain factors that push towards the development of inflammatory processes. These include a decrease in the body’s defenses, as well as changes in the normal microflora of the vagina.
Female genital organs
Other important factors that provoke the development of inflammatory pathologies are trauma to the mucous membrane due to harsh sexual intercourse, the birth process, abortion, surgery, etc. As a result of a decrease in the body's defenses, pathogenic microorganisms rapidly become more active and penetrate further along the ascending path.
Among other factors influencing the occurrence of the inflammatory process are:
- Prolonged and uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs
- Hypothermia
- Stressful situations
- Endocrine disorders and poor nutrition
Inflammatory diseases in gynecology include the following:
- Candidiasis or thrush
- Cervical erosion
- Endometritis
- Condylomas acuminata
- Vaginitis
- Vulvitis
- Furunculosis of the vulva
- Adnexitis, etc.
In order to seek help from a doctor in time, it is important to know the symptoms of inflammatory processes. We will learn more about this below in the article.
General signs
The symptoms themselves that a woman has a cold on her ovaries are quite varied, but the principles are non-specific, since they can be confused with other diseases. Under the influence of the disease, the structure of the organ itself changes.
Pain in the lower abdomen
Such sensations indicate the presence of acute inflammation of both the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Discomfort occurs in the right or left side because the organ increases in size due to swelling and the action of biologically active organisms.
Important! The painful sensation is primarily of a pulling and aching nature. The intensity increases if the visceral peritoneum is involved.
As for the duration of pain, it varies depending on the type of inflammation and treatment, if any. Sometimes discomfort can last up to four weeks.
Inflammation of the vagina
- I. moderate or abundant mucous discharge, gray (for viral), yellow or green (for purulent), white with crumbly inclusions (for fungal) inflammation
- II. itching, burning, discomfort, less often pain in the vaginal area
- III. pain during sexual activity
Inflammation of the vagina during sexually transmitted infections
The inflammatory process in the vagina, with thrush, appears as a result of damage to the genital organ by fungi of the genus Candida.
This fungus is opportunistic.
An increase in the number of this fungus leads to inflammation.
It should be understood that the inflammatory process can occur in acute and chronic forms.
Attention! Treatment of inflammation caused by candidiasis should begin immediately.
If the problem is ignored, the disease becomes chronic.
With candidiasis of the vagina, the following symptoms are observed in women:
- Painful urination
- Aching pain in the lower abdomen
- Weakness
- Specific curdled discharge
Upon examination, the doctor may see an inflamed cervix and vagina.
Damage to the female genital organ by Treponema is accompanied by inflammation and foamy discharge.
The discharge is usually yellowish in color, sometimes with a green tint.
In this case, itching, burning during urination and discomfort in the urinary tract are noted.
With trichomoniasis, inflammation may appear after 5-20 days.
Inflammation with bacterial vaginosis can be caused by infections such as:
- 1.Gonococcus
- 2.Chlamydia
- 3. Ureaplasma
- 4.Mycoplasma
These bacteria contribute to inflammation.
How to understand that a woman suffers from vaginosis?
It's pretty simple.
Vaginosis is usually accompanied by a very unpleasant and foul-smelling discharge.
They can be white, gray or greenish in color.
May manifest as a burning sensation in the vagina.
Diagnosis of vaginal inflammation
When the first signs of vaginal inflammation appear, be sure to visit a specialist.
In order to prescribe the correct treatment, the cause of the disease must be determined.
In this case, laboratory diagnostics are prescribed.
At the first stage of the study, the doctor conducts a visual examination.
Collects anamnesis of the disease, studies the symptomatic picture.
After this, an examination is carried out in a gynecological chair using a special gynecological speculum.
During a visual examination, hyperemic vaginal mucosa will be visible.
This is the main inflammatory sign.
During the examination, the doctor takes a material (smear) and prescribes a series of laboratory tests.
Diagnostics includes:
- Smear microscopy
- Bacterial seeding of material
- PCR analysis
When examining a smear under a microscope, they find out which flora predominates in the vagina.
Bacteriological culture is carried out to identify pathogenic microbes.
In addition, an antibiogram is performed to determine the sensitivity of the microorganism to a particular antibacterial agent.
In the future, this will help prescribe effective treatment.
If necessary, the doctor may refer you for cytological studies.
To identify complications of vaginal inflammation, an ultrasound is additionally performed.
After the doctor receives the test results, he will prescribe a course of treatment.
The type of drug depends on the flora that was isolated during the research.
Upon completion of the course of therapy, control studies are carried out to check the effectiveness of treatment.
If the control results are negative, then we can say that the woman is healthy.
Vaginal inflammation: treatment
If you do not pay attention to the problem in time, you can get a number of serious complications.
How to treat vaginal inflammation? - you ask.
The first step is to understand the reason for the appearance of such a symptom.
To do this, the doctor conducts an examination and prescribes laboratory tests.
Tests and therapy must be prescribed to the sexual partner.
After the diagnosis has been confirmed, antimicrobial drugs are prescribed.
When prescribing a drug, the doctor relies on the type of pathogen and the form of the disease that this microorganism caused.
The treatment regimen includes antibiotics.
They can be either in tablets or in the form of suppositories that are inserted into the vagina.
In order to eliminate bacteria and symptoms of vaginal inflammation, use:
- Metronidazole
- Clindamycin
- Hexicon
If inflammation of the vagina appears during pregnancy, local treatment is preferably used.
The final choice of drug depends on the type of pathogen.
For fungal inflammation of the vagina, the doctor prescribes antifungal drugs.
In tablets it can be Fluconazole or Nystatin.
In ointments and suppositories can be used for local use:
- 1.Pimafucin
- 2. Candide
- 3. Clotrimazole
The course of treatment includes drugs that relieve inflammation and itching.
To strengthen the functioning of the immune system, the treatment regimen is supplemented with immunomodulators.
Treatment with drugs aimed at destroying bacteria lasts approximately two weeks.
If the control laboratory test results in a positive result, the course of treatment is repeated.
To restore vaginal flora after antibiotic therapy, probiotics containing lactobacilli are used.
Folk remedies will help speed up the healing process.
Remember! Self-treatment leads to a number of complications and a chronic course of the disease.
If there is inflammation of the vagina, treatment should only be prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment
This or that treatment tactic for a woman who has a cold in her appendages should be based on the form of the disease and the type of infection that provoked it.
When it comes to the acute form, the woman is placed in a hospital for constant stay in bed under the supervision of medical workers.
Cold compresses are placed on her lower abdomen. In addition, it is customary to use antipyretic, analgesic and antibacterial agents. Also, based on the individual clinical picture, antibiotics are prescribed.
The subacute form of inflammation involves quartz irradiation of the affected area. If we are talking about the chronic type, then medications, medicinal baths and elements of physiotherapy are used:
- electrophoresis;
- treatment with leeches;
- gynecological massage;
- IR, laser therapy;
- magnetotherapy.
Reference! If the causative agent of the pathology is a sexually transmitted infection, then both partners must undergo treatment.
Are vaginal infections classified as sexually transmitted diseases?
Patient question
Is a vaginal infection a sexually transmitted disease and can a woman spread it to her partner?
Doctor's answer
Among the three most common vaginal infections (bacterial vulvovaginitis, trichomoniasis and thrush), only trichomoniasis has recently been classified as a sexually transmitted disease, and even then conditionally.
However, doctors believe that the development of bacterial vulvovaginitis is almost always closely related to sex, since most women acquire pathogenic microflora through contact with a sexual partner.
How are these conditions different? The fact is that the bacteria that cause inflammation in women of the lower part of the urogenital tract are most often harmless for men and do not lead to the development of an inflammatory process in them in the genitourinary organs.
But the causative agents of sexually transmitted diseases affect both partners equally.
How to treat ovarian inflammation?
Acute inflammation of the ovaries is treated in a hospital setting with bed rest. Cold is applied to the lower abdomen. The main direction of therapy is the use of antibiotics. In addition, medications are prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation, as well as physiotherapy.
The most commonly used antibiotics are:
- penicillins – amoxicillin, ampicillin;
- aminoglycosides – gentamicin, netilmicin;
- cephalosporins – cefazolin, ceftazidime;
- Metronidazole.
The average course of treatment is 7-10 days. The drugs are prescribed intramuscularly or orally. The dosage is selected individually.
To reduce the severity of pain and accelerate the relief of the inflammatory process in acute oophoritis, the following are used:
- Non-steroidal drugs to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. The main drugs are diclofenac, indomethacin. They can be prescribed in the form of tablets or suppositories. The second option has fewer side effects.
- Immunostimulating drugs. Preparations containing recombinant interferon are used, as well as herbal remedies that increase the body's resistance.
- Vaginal suppositories. They may include phytocomponents (propolis, oak bark, walnut extracts) or local antiseptics (natamycin, chlorhexidine, povidone-iodine).
After the symptoms subside, physiotherapeutic treatment is practiced:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- phonophoresis with magnesium and calcium;
- ultrasound with hydrocortisone ointment;
- radon baths and so on.
If a purulent abscess forms, surgery is performed. During the intervention, it is opened and local antibiotics are administered.
Gynecological fees
Patient question
Will herbal medicine help? Tell me, what herbal remedy can I buy at the pharmacy for vaginal inflammation?
Doctor's answer
Pharmacies sell special gynecological collections of medicinal herbs that have antiseptic properties, selected according to their composition in certain proportions. It includes yarrow, chamomile, St. John's wort, sage, and sometimes nettle is added. You can buy such preparations and use them for vaginal douching according to the recipe indicated on the package. But herbal medicine cannot always relieve the inflammatory process.
In this case, you need to find out what is causing the inflammation. If this is a banal colpitis and there are no pathogenic (infectious) microorganisms, then it makes sense to use herbal decoctions. Although it is necessary to warn: you should not get carried away with douching, because this washes out the normal flora of the vagina.
Forms of adnexitis
Inflammatory damage to the ovaries and fallopian tubes has 3 forms of development - acute, subacute and chronic. They differ in the severity of symptoms and require different amounts of therapeutic intervention. The period of transition from the acute form to the chronic phase can take up to several months.
Acute
Inflammation of the appendages occurs with pronounced clinical manifestations. The predominant symptoms are pain and hyperthermia, accompanied by chills. Additional symptoms:
- Unpleasant sensations during urination - burning, feeling of complete emptying of the bladder
- Irritation of the peritoneum - an attempt to touch the stomach causes reflex tension
- Copious vaginal discharge. The secretion has an unpleasant odor, purulent nature, and a thick consistency.
The woman is indicated for emergency hospitalization in the gynecological department of the hospital. Comparative diagnostics are carried out with manifestations of appendicitis, acute intestinal obstruction, and ectopic pregnancy. If you do not pay attention to the treatment of the pathology or do not complete the therapeutic course completely, the symptoms of inflammation weaken and it takes a chronic course.
Subacute
This form of damage to the appendages occurs in the form of less intense symptoms than with acute adnexitis. Manifestations of the disease are aches in the sacral region and lower abdomen, periodic episodes of increased body temperature, and vaginal discharge. A late visit to a gynecologist is due to the fact that the symptoms of the pathology are weakly expressed. In 90% of cases, the patient explains her condition by nutritional errors, hypothermia, incorrect body position during sleep, or fatigue. The goal of the therapeutic approach is to prevent the disease from becoming protracted.
Chronic
Occurs in cases where acute adnexitis is not cured. The disease proceeds unnoticed by the patient. Exacerbation of the condition occurs more often than once every six months. Manifestations of the disease:
- A pulling sensation in the sacral region, which decreases slightly when changing body position.
- Pain of a pressing type during intimacy.
- Discomfort while sitting.
- A small amount of secretion from the genital tract.
- Neurological disorders - lack of sleep, physical weakness, irritability.
Often, a woman finds out about the presence of chronic adnexitis only when attempts to become pregnant remain unsuccessful. The pathology, which has taken a protracted course, leads to the formation of adhesions, which prevents fertilization and causes the development of secondary infertility.