Characteristics of the pathology
A retention cyst belongs to the group of female pathologies, and its formation is observed in the ovaries. The disease can be diagnosed as a retention tumor of the left ovary or as a thickening of the right paired organ.
In women, the glands in the body produce a special secretion that can move through special ducts. When they narrow or become blocked, a large amount of fluid accumulates, which subsequently provokes the appearance of a cystic formation.
Ovarian retention cyst is a common disease of the female reproductive system, but at the same time the most harmless. Mostly the neoplasm is diagnosed in patients of childbearing age, but it can appear during menopause and during the neonatal period.
https://youtu.be/NDBExm0S25I
Pathology and pregnancy
The most important question that worries women is whether it is possible to get pregnant if you have an ovarian retention cyst? The neoplasm does not grow into the ovarian tissue and, in the earliest stages of its growth, does not disrupt the normal maturation of other eggs.
The danger comes from large neoplasms that compress the ovarian cortex for a long time. They disrupt blood flow, cell nutrition and subsequent maturation suffer, which gradually leads to infertility.
It is difficult to predict how a cyst will behave during pregnancy. In some cases, it undergoes reverse development under the influence of hormonal changes in the body. However, its further growth is possible with the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. The pregnant uterus puts pressure on the cyst, which sometimes leads to its rupture - this situation requires emergency surgical intervention.
Classification
Experts identify the following types of this disease in women:
- luteum cyst is localized at the site of the corpus luteum. Mostly, such a tumor does not grow and does not turn into cancer.
- A follicular cyst is formed from a follicle in a situation where it does not rupture and ovulation does not occur. This type of cystic formation is not characterized by the process of malignancy and the risk of developing cancer is minimal.
- A paraovarian cyst appears from the mesentery of the fallopian tube. For a long time, it does not cause the development of pronounced symptoms, but when it increases to a large size, it begins to put pressure on the ovary.
- Endometrioid cystic formation in medical practice is considered as one of the types of endometriosis. The presence of such a neoplasm provokes disruptions in hormonal homeostasis
- dermoid cyst appears and develops during embryogenesis. Inside it may be the rudiments of the internal organs of the embryo.
- A mucinous cyst is a neoplasm in which mucus accumulates. When it ruptures, simultaneously with the contents, mucinous cells enter the peritoneal cavity, which becomes the reason for the generalization of the process.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Differences between cytology and colposcopy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
All types of retention cysts have a common feature - the capsule has a thin transparent wall. In addition, the likelihood of each type of tumor developing into cancer is minimal.
Medical practice shows that most often follicular and corpus luteum cysts disappear on their own after three menstrual cycles.
Ovarian retention cyst
Do you know that:
Over the course of a lifetime, the average person produces no less than two large pools of saliva.
The rarest disease is Kuru disease. Only members of the For tribe in New Guinea suffer from it. The patient dies of laughter. The disease is believed to be caused by eating human brains.
Many drugs were initially marketed as medicines. Heroin, for example, was originally brought to market as a cure for children's coughs. And cocaine was recommended by doctors as an anesthesia and as a means of increasing endurance.
According to many scientists, vitamin complexes are practically useless for humans.
In 5% of patients, the antidepressant Clomipramine causes orgasm.
Research shows that women who drink several glasses of beer or wine per week have an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
An educated person is less susceptible to brain diseases. Intellectual activity promotes the formation of additional tissue that compensates for the disease.
74-year-old Australian resident James Harrison has donated blood about 1,000 times. He has a rare blood type whose antibodies help newborns with severe anemia survive. Thus, the Australian saved about two million children.
According to WHO research, talking on a mobile phone for half an hour every day increases the likelihood of developing a brain tumor by 40%.
The human stomach copes well with foreign objects without medical intervention. It is known that gastric juice can even dissolve coins.
People who eat breakfast regularly are much less likely to be obese.
The cough medicine “Terpinkod” is one of the top sellers, not at all because of its medicinal properties.
The liver is the heaviest organ in our body. Its average weight is 1.5 kg.
According to statistics, on Mondays the risk of back injuries increases by 25%, and the risk of a heart attack by 33%. Be careful.
When lovers kiss, each of them loses 6.4 calories per minute, but at the same time they exchange almost 300 types of different bacteria.
Causes
The main reason for the formation of an ovarian retention cyst is considered to be a change in the hormonal levels of the female body. Normally, a woman produces both estrogens and progesterone in equal quantities, prevailing in a certain phase of the menstrual cycle.
In order for the follicular membrane to rupture, the concentration of estrogen must be quite high, and progesterone, on the contrary, low. With hormonal imbalance, the natural processes in the body are disrupted, and in subsequent cycles further growth of the follicle occurs.
The following factors can provoke hormonal imbalance in the body:
- psycho-emotional stress;
- various infections suffered by the woman;
- increased physical activity on the female body;
- a sharp decrease or, conversely, increase in weight;
- traumatic brain injuries of varying complexity;
- pathology in a chronic form.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Echosigns of adenomyosis
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
Retention cystic formation may be a consequence of the penetration of modified epithelial cells into the ovary. They are able to break away from the mucous membrane of the reproductive organ and penetrate into any organ of the female body along with the bloodstream.
When menstruation arrives, the cells begin to bleed. When cells enter the ovaries, the blood released from them will gradually accumulate and lead to the formation of a cyst. Often the cause of this disease is abortion and early puberty.
Possible symptoms of retention neoplasms
The ovaries not only produce female sex hormones (estrogens), but also participate in the maturation of eggs. To do this, up to twenty small vesicles called follicles are formed inside the organ every month. As they mature, they increase in volume and their wall becomes thicker. At the same time, estrogen production increases, reaching a peak when the mature follicle approaches the edge of the ovary and ruptures. Then the egg in it is released into the abdominal cavity and then enters the fallopian tube, ovulation occurs.
Retention cysts occur when the process of maturation of the female reproductive cell is disrupted for one reason or another, but the follicle remains intact. Normally, each time a small amount of fluid accumulates in it, which contributes to the rupture of the vesicle and the release of the egg. If the follicle does not rupture, but the contents continue to accumulate, a cyst gradually forms.
A similar development mechanism is typical for other types of retention cavities.
Symptoms
In most cases, a retention cyst develops without the appearance of a pronounced clinical picture and is discovered during examination by a doctor. If the tumor reaches an impressive size, you may experience pain in the lower abdomen, depending on the location of the cyst.
Most often, pain intensifies during physical exercise or during sexual intercourse. During menstruation, a woman may experience spotting, and there is a change in the level of hormones in the body.
The pain syndrome becomes more acute when a benign formation ruptures. The contents of the capsule are released into the abdominal cavity, which causes discomfort and a rise in temperature in the woman.
Main types
A retention cyst is always benign and functional, and therefore never creates metastases in the body. The clinical picture, as well as the choice of strategy and treatment methods, completely depend on the location of the cyst in the patient’s body. It is customary to distinguish the following main types of retention cysts.
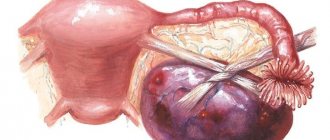
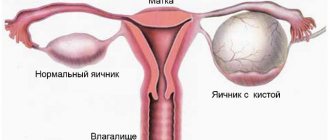
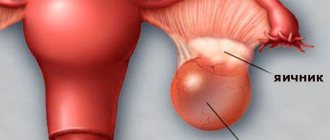
Ovarian retention cyst
The tumor in this case develops as a result of disruption of the normal functioning of the gonads, as well as disruptions of the menstrual cycle. An ovarian retention cyst is a neoplasm containing fluid or blood. The cyst consists of follicular cells, and its walls consist of thin plastic tissue that can stretch and grow. Depending on the location, a cyst of the right ovary or the left may develop. It is believed that the tumor on the left is more severe. Depending on the tissues from which it was formed, several types of ovarian retention cysts are distinguished:
- Follicular neoplasm. It develops from a pathogenic follicle during the period of ovulation, and inside there is fluid interspersed with blood;
- Corpus luteum cyst. It arises from an already ovulated follicle that has not received further development. The contents of the tumor are serous fluid with blood elements;
- Endometrioid. Formed due to pathological proliferation of endometrial cells outside the uterus. It develops especially strongly during menstruation. Inside contains a characteristic dark liquid;
- Dermoid. Appears as a result of disorders of embryonic development and consists of embryonic tissues, as well as partially formed formations;
- Mucinous. Its distinctive feature is that it is multi-chambered, so this type of cyst is the largest in size. Inside there is mucus interspersed with blood cells.
A small tumor does not cause any harm to a woman’s health and may disappear on its own. Problems begin if it reaches 10 centimeters or more, when it begins to put pressure on nearby organs, causing severe pain. During menstruation, there is a risk of cystic tumor rupture, which can lead to peritonitis, an inflammatory process inside the abdominal cavity. During physical activity and during sex, there is a possibility of torsion of the leg or internal bleeding (usually a retention cyst of the left ovary). In such situations, urgent surgical intervention is required.
Retention cyst of the cervix
It occurs when the stratified epithelium of the vagina begins to pathologically cover the cylindrical epithelium inside the cervical canal. This problem is sometimes called a nabothian gland cyst. A neoplasm of the cervix most often develops against the background of diseases of the woman’s reproductive system (uterine erosion, cervicitis, sexually transmitted infections). Often, a cyst does not affect reproductive function, but can cause significant discomfort and cause infection of nearby organs and tissues.
When choosing treatment, the size of the tumor, its exact location and the presence of recurrent exacerbations of inflammation are taken into account. Thus, surgical treatment is impossible for inflammatory processes, however, with successful treatment of the primary cause of the tumor, for example, infection, the problem may disappear on its own.
Minor salivary gland cyst
The disease develops as a result of any pathological processes in the oral cavity or injury to the salivary gland; it is a tumor of the large and small salivary ducts. Most often it is located between the mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth and the upper part of the sublingual gland, so the neoplasm often takes the shape of an hourglass and has a dense septum of connective tissue between its parts. Depending on the location, three types of tumors are distinguished: sublingual, submandibular and direct tumor of the minor salivary gland.
https://youtu.be/UGKbyTXXUq4
Lower lip cyst
It is a round swelling that can reach 2 centimeters in diameter. As a rule, the neoplasm is dense to the touch, and when its membrane ruptures, a white-yellow infiltrate oozes. It occurs as a result of a thermal burn or accidental biting of the lip, and also often goes away on its own. However, if the disease has developed to a large size and causes discomfort while eating, surgical removal is recommended.
There is a possibility of rupture, due to which pathogenic bacteria can enter directly into the oral cavity, and then into the esophagus. Plus, the constant release of cyst infiltrate onto the mucous membrane leads to tissue destruction.
Pulmonary retention cyst
The problem arises due to the accumulation of bronchial secretions, most often due to respiratory failure, which often occurs with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bronchi and the lungs itself.
A tumor of this type almost always appears suddenly and in the initial stages is completely asymptomatic, so the problem is discovered only when the lung retention cyst has reached a large size. Depending on the location, a retention cyst of the right or left lung may be observed.
Tooth cyst
It occurs as a pathological reaction of the body to the entry of pathogenic bacteria into the oral cavity. In some cases, the disease may develop after improper treatment of caries or tooth extraction, in which case the tumor may be located in the gum. Treatment should include not only removal of the tumor, but also elimination of the inflammatory process that was the cause of the problem.
Diagnostics
All women should be examined by a gynecologist at least twice a year. This will allow you to timely identify a retention neoplasm and take the necessary measures. The danger of such a disease lies in the likelihood of death if the cyst ruptures.
A retention cyst usually does not cause the appearance of obvious signs, so it is most often discovered completely by accident. However, some women with this pathology may complain of nagging pain in the abdominal area, the severity of which is determined by the location of the formation.
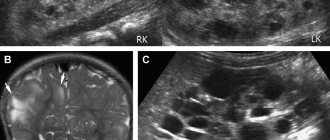
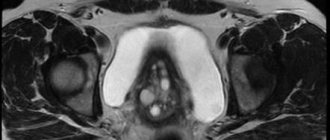
Ultrasound examination plays a decisive role in diagnosis, thanks to which it is possible to determine the location of the cyst. If a rupture of a retention neoplasm is suspected, a puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix is performed, which makes it possible to diagnose fluid in the peritoneal cavity.
Thanks to diagnostic laparoscopy, it is possible to visualize the formation on the monitor and determine the degree of damage to the tissue of the appendages of the genital organ. If malignancy of the cyst is suspected, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging may be prescribed.
Can it develop into cancer?
In some cases, after removal of the formation and histology, a tumor with signs of a cancerous process is diagnosed.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Do I need to remove an ovarian cyst if it doesn’t bother me?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
Dangerous signs are considered to be too large a cystic formation, rapid blood flow inside and the detection of fluid in the pelvis. In addition, cancer can be suspected if tumor markers are elevated and other signs of a pathological process are present.
Even a small cystic formation without signs of an active process inside can in some cases lead to the development of cancer. It is for this reason that a woman should regularly visit a gynecologist and follow all his recommendations.
Treatment
When the diagnosis of “retention cyst” is confirmed, taking into account its localization and growth dynamics, one or another treatment method is determined.
It is possible to cope with the pathology using non-invasive methods of therapy:
- elimination of pathology using hormonal stimulation;
- restoration of normal functioning the immune system;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
In addition, it is necessary to cure all inflammatory diseases occurring in the organs of the reproductive system. Most often, the tumor resolves without special therapy after 3 months. In a situation where this does not happen, and the cyst continues to increase in size, then surgical methods are resorted to.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Can there be a delay and a positive test for an ovarian cyst?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 4, 2020
The following types of therapy are used in medical practice:
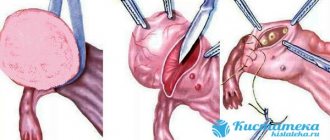
- Laparoscopy. Getting rid of an ovarian cyst is considered one of the most gentle methods. Removal of the formation is performed through several punctures made in the abdominal area.
- Laparotomy. This operation is considered more complex and allows you to remove both the tumor itself and the uterus and ovaries. Usually doctors try to preserve a woman’s reproductive organs, but, unfortunately, this is not always possible.
Surgical treatment for a retention cyst of the right ovary, as well as the left, is considered a last resort when all other methods have not brought the desired effect.
Treatment of the disease
If a small retention cyst is detected, treatment is not immediately prescribed. The doctor monitors the development of the pathology for three months, as the tumor may completely disappear. With an intensive increase in formation, hormonal therapy with combined estrogen-gestagen drugs is prescribed.
They normalize the hormonal balance, promoting tumor reversal. The remaining medications are selected individually based on the symptoms and characteristics of the patient’s body.
Treatment with medications generally lasts no more than two months; the effectiveness of treatment is assessed using ultrasound examination.
If conservative treatment does not bring results, the doctor recommends surgery to remove the cystic formation. Laparoscopy is most often performed - this is the most gentle and least traumatic method of tumor removal. After surgery, a woman must undergo a course of hormonal therapy.
Complications after cyst removal occur very rarely, so do not be afraid or postpone the operation.
Ovarian retention cyst is considered the most harmless neoplasm. It does not degenerate into a malignant tumor and often resolves without any treatment. But still, you should not start the disease; if you notice the first symptoms, immediately get examined by a gynecologist to exclude the development of complications.
Complications
One of the possible complications of the pathology is torsion of the cyst pedicle, in the thickness of which the vessels are located.
The flow of blood gradually stops and the consequence of this is tissue death and swelling. With this pathological condition, the woman is tormented by increasing pain in the abdomen, which forces her to take a certain body position.
Another complication of the pathology can be rupture of the wall of the neoplasm and hemorrhage into the cavity. With this pathological condition, fluid splashes from the follicle into the peritoneal cavity, which provokes severe irritation.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Can fibroids increase during menopause?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
Many nerve endings are localized in the peritoneal cavity, and any impact is accompanied by severe pain. Mostly unpleasant manifestations begin to bother you after physical exertion or violent sex.
The rupture of a cystic formation is accompanied by severe pain, attacks of nausea and even vomiting. In addition, there are manifestations of acute blood loss in the form of general weakness, tachycardia and dizziness.