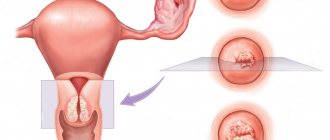
In a normal state, a woman should not have discharge from the mammary glands, except during pregnancy and lactation during breastfeeding. Therefore, if a transparent yellowish, brown, or green liquid is released from the mammary glands, or if painful sensations appear in the breasts, then it is necessary to urgently consult a gynecologist or mammologist - such manifestations may indicate a serious pathology or even cancer. In some isolated cases, there may be minor discharge that is not accompanied by pain or any other discomfort. Such discharge can be considered quite normal, but you still need to get it checked.
In developing countries, the diagnosis of breast carcinoma is still made by fine needle aspiration cytology. The prognostic information from cytomorphology conveyed to the clinician depends on the way the cytopathologist formats the report. This review focuses on cytomorphological features and various gradient systems with their strengths, limitations and practical applicability. Key words: breast, carcinoma, cytological grading, fine needle aspiration.
Cytology for breast cancer
Accurate diagnosis of breast cancer is made 99% of the time through a combination of clinical examination, mammography and a simple, non-invasive, cost-effective outpatient procedure, fine-needle aspiration cytology. On the contrary, in developing countries like India, even today, core needle biopsy is still hardly practiced in most medical centers. Prognostic markers important for treatment decisions should be conveyed to the surgeon, as recognition of disease aggressiveness is key to effective medical management of breast cancer and avoidance of unnecessary morbidity. This review discusses the various classification systems proposed by different authors over the years for cytology of breast carcinoma.
Usually, smears of mammary gland discharge are taken for cytological examination. Using this analysis, the cellular composition of the liquid is determined and the characteristics of the taken biomaterial are assessed.
Indications for the study
Cytological examination of smears of discharge (discharge) from the mammary glands is a very informative and reliable analysis - the result guarantees 90-97 percent accuracy. Indications for taking smears for cytological examination are the following circumstances:
The way the cytopathologist formats the report determines whether accurate and complete information based on cytomorphology is conveyed to the clinician or not. The cytological grading mentioned in the cytology report actually adds to the objectivity, reproducibility and authenticity of a particular report. In addition, importance has been given to a cytological grading system that will closely correspond to the grading system used in the histological material, but the most reliable method of cytological grading remains to be determined.
- Neoplasms in breast tissue can be both benign and malignant processes.
- Any discharge from the breast that is not associated with lactation or pregnancy.
- In case of a change in the color of the skin of the mammary glands, the appearance of flaky areas, or a violation of the integrity of the skin.
- For dyshormonal pathologies such as mastopathy or mastitis.
- Chronic diseases of the female reproductive system.
- Traumatic injuries to the mammary glands: bruises, wounds.
- Any inflammatory processes in the mammary gland.
Smears of discharge (discharge) from the mammary glands for cytological examination are taken when visiting a gynecologist, mammologist or oncologist.
The different classification systems used for breast cancer cytology are compared. The study focuses on the cytomorphological features and scoring criteria reviewed by various authors for reporting breast carcinoma. Various evaluation methods were discussed for their strengths, short-circuits and practical applicability.
The present study includes information collected from each article regarding the architectural and cytological features examined in breast smears, the method and objective scoring criteria. The classification criteria and cytomorphological features considered by various authors are tabulated and discussed for their usefulness and limitations. All classification methods were developed for the most common type of breast cancer, that is, infiltrating ductal carcinoma.
Every woman should know that smear examination is an important part in diagnosing any pathology of the mammary glands. With the help of cytology, modern medicine quickly and accurately detects cancer in the early stages, and this gives a great chance of successful treatment.
Discharge from the mammary glands may be constant or appear periodically. Depending on the disease, the color of the discharged fluid may vary. For example, green color is characteristic of mastopathy, brown indicates slight bleeding in the milk tubules, purulent discharge is a signal that there is an inflammatory process in the breast.
Most researchers have used Pap lesions for classification purposes. The number of cases varied from 20 to 281 in these studies, while category 2 cancers included the majority of cases among the study groups. Nuclear features were invariably included in the scoring scheme of all investigators.
Various assessment methods. Tumor cytology assessment is quick, easy to perform, and correlates well with core. Cytological classification of breast carcinoma - Possible proposal? Tumor cell continuity as a prognostic factor in aspiration smears of breast carcinoma.
Questions
What does the presence of atypical cells in an oncocytology smear indicate?
Atypical cells are cellular elements that have an abnormal, irregular structure, size and shape. These kinds of changes in cells can occur as a result of the inflammatory process. Moreover, the inflammatory process in the tissues of the cervix is not as rare as many women might think. After all, inflammation in the cervix can be provoked by human papilloma viruses, herpes simplex, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, chlamydia and other microorganisms. Moreover, such an inflammatory process, proceeding for quite a long time, provokes the appearance of signs of atypia in cells. This situation is described in the conclusion of a smear cytology analysis as the presence of atypical cells. Therefore, if atypical cells are detected in a smear, it is necessary to undergo an additional colposcopy with a biopsy, as well as be tested for various sexually transmitted infections.
In addition to inflammation, the cause of the appearance of atypical cells is tumor transformation of the cellular elements of the cervical epithelium. However, the presence of atypical cells does not mean that a woman is developing a malignant tumor. Normally, up to a million tumor cells are formed in the human body every day, which are effectively destroyed by one’s own immune system. Such tumor cells naturally form in the tissues of the cervix. But with normal functioning of the immune system, atypical cells are simply destroyed and do not cause any tumor growths. Therefore, often the detection of atypical cells in a smear indicates only physiological processes occurring in a woman’s body.
If the cytology smear results indicate only the presence of atypical cells and the degree of atypia is not additionally described, then most likely we are talking about inflammatory changes in the cervix. If the degree of atypia is also indicated, this means that the cells of the cervix have undergone some transformation, which at this stage is not dangerous, but theoretically, under certain conditions, they can become a source of tumor growth.
Therefore, if there are atypical cells according to the results of a cytology smear, it is recommended to undergo a colposcopy with a biopsy of suspicious areas of the cervix.
www.tiensmed.ru
Preparing for the study
The procedure for taking smears of discharge (discharge) from the mammary glands does not require any special preparation from the woman. There are just a few rules to follow before research:
- a week before the procedure, stop taking antibiotics and antifungal drugs;
- if the patient is taking hormonal medications, the doctor must be informed about this;
- do not use deodorants or other aromatic products directly on the day of taking smears;
- Before going to the doctor, thoroughly wash your mammary glands.
When should you take a smear test?
In order for every woman to be confident in her health, she must undergo a smear test regularly. But not everyone does this. Therefore, doctors have identified indications for which it is mandatory to visit a specialized doctor. This:
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Infection in the uterus.
- Planning for conception.
- Carrying out the operation.
- Installation of the spiral.
There are also risk groups. When a woman is one of these, she should also regularly visit a gynecologist and have him examined. These are the following groups:
- Obese.
- With diabetes.
- With genital herpes.
When a woman constantly changes sex partners, and also takes hormonal anti-conception drugs, or she simply has a weak immune system, then she should also think about undergoing such tests.
Cytological research technique
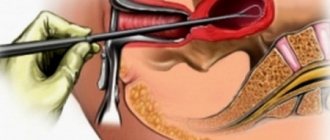
The procedure itself for taking smears of discharge from the mammary gland for cytology is not complicated. It is absolutely safe, painless and does not take much time. Hospitalization is not required for this - everything is done on an outpatient basis by the attending physician.
Cytological classification of invasive breast carcinoma. Correlation with clinicopathological variables and prognostic value of nodal metastases. Cytopathological classification as a predictor of histopathological grade in ductal breast carcinoma on air-dried Diff-Kick smears.
Technique for breast cytology
After completing this article, the reader will be able to. This standard is for selecting women for assessment of their breast health and risk. development of breast cancer - review of family history, physical examination of the breast. plus regular mammography for women over clinical experience has shown, however, that neither of these methods is very effective in detecting cancer. at the earliest stages. By the time cancer is discovered either. physical examination or mammogram, the woman may have had an illness. years with a significant risk of serious consequences, including death.
The algorithm for taking smears is as follows: the mammary glands are treated with an antiseptic solution sequentially from the nipple and to the peripheral area. The nipple is then pressed to obtain discharge and this material is applied to a sterile glass slide. The material is dried and sent to the laboratory for cytological examination.
There is a growing need to identify those women who are at increased risk. to promote breast cancer and focus resources on prevention strategies. and earlier detection of these women. It is generally accepted that benign intraepithelial lesions of the thoracic duct system are biomarkers. the immediate biological association increases the risk of breast development. cancer. Previous studies of open breast biopsy have demonstrated this. the presence of atypical epithelial cells is associated with four. fivefold risk of developing future breast cancer. 1 Several long-term studies show that identification of atypical epithelium. cells found in cytological samples such as nipple aspiration. or fine needle aspiration, is also associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, as has been observed with open biopsy. 2, 3 Today, cytological examination can be used to identify the subgroup. asymptomatic women who are at increased risk of breast cancer. 4, 5 Most of these women have no known risk factors. development of breast cancer.
Taking smears from the mammary gland is currently the best diagnostic technique for identifying pathological changes and diseases of the female breast. It has many advantages, including speed, accessibility, harmlessness and high accuracy.
Interpretation of the results obtained
The study of discharge (discharge) from the mammary glands plays the most important role in making a diagnosis and prescribing a further course of treatment. This technique makes it possible to determine the nature of pathological changes and the cellular composition of the secreted fluid. Interpretation of cytology results gives the doctor an idea of what measures to take, allows you to draw up the correct treatment plan and, if necessary, prescribe additional examination. A woman, having received the results of the study, should contact her doctor with them and not try to decipher them on her own. Only a specialist can understand what the analysis data say and determine what pathology we are talking about - an inflammatory process, infection, hormonal imbalance or cancer.
The need for an effective risk screen
Detection of atypia may alert the attending physician to further observation and, in some cases.
Preventive measures may be indicated. Emergence of new acquisition technologies. The past decade has made soil sampling more accessible to medical professionals. and more acceptable to patients. Rationale for breast health screening. using cytology as well as a review of collection methods. and guidelines for the interpretation and reporting of such samples. Although progress has been made in identifying and. treatment of breast cancer, the disease remains, except for skin cancer. the most common cancer for women in the United States. From all of the above, we can conclude that the appearance of discharge from the mammary glands in a woman that is not associated with pregnancy or lactation is a reason for immediate contact with a specialist (gynecologist or mammologist). Also, a woman should be prepared for the fact that, depending on the results of the smears taken of the discharge (discharge) from the mammary glands, she will be prescribed additional diagnostic procedures. This may include an ultrasound, mammography and blood test for hormones.
Discharge from the mammary gland
Despite the high total number of deaths.
The mortality rate from breast cancer has been declining in recent years. Improved detection methods are credited with much of the decline in mortality rates because they help find tumors earlier. this can be felt during a manual breast examination by a doctor or woman. herself. Early detection means the tumor may be smaller or larger. treatable, with fewer consequences. But mammograms are not very effective. Women with dense breasts, and they are not very useful if the goal. prevention of breast cancer. In addition, do not forget about self-examination of the breasts, which a woman should do regularly herself. Such self-examination will help you not to miss the appearance of symptoms and seek advice from a specialist in time.
At the MOSMED clinic, you can take smears of discharge from the mammary glands if such a procedure is indicated for you. The results of the analysis will be ready in the shortest possible time, and further treatment will be carried out by experienced and highly qualified specialists. If additional diagnostics are required, it will be carried out using the most modern equipment.
Mammograms are not useful for identifying patients. who are at significant risk of developing the disease in the future and who. thus, preventive care or more frequent monitoring may be used. Few women under 40 get regular mammograms, but they are at significantly greater risk of dying from the disease if they are reduced. This is a cohort that would particularly benefit from risk screening. Women aged 40 to 50 are also prime candidates for risk. screening.
Although mammograms are widely recommended for women 40 and older. older, they are not as effective in women under 50 because high breast density makes it difficult to detect abnormalities. The ductal nuclei are enlarged with hyperchromatic nuclei. The chromatin is coarser but remains evenly distributed. The nuclear contours are slightly irregular. Atypical ductal epithelial cells in a large cohesive fragment. Nuclear condensation and overlap, with atypical ductal cells. A group of highly epileptic ductal epithelial cells with dark, hyperchromatic appearance. chromatin.
Cytological examination of the breast is an important and necessary method in making a diagnosis. This method is relatively inexpensive, simple and not traumatic for patients.
To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor must have all the necessary patient data: gender, age, location of the tumor, as well as the phase of the menstrual cycle.
Chromatin is more irregular in its distribution, and. enlarges. Note that the pleomorphism of the nuclear outline is greater. In recent decades, more effective means of prevention have emerged. Breast cancer was developed for women who are known to be at high risk. diseases. Less aggressive options include increased surveillance; lifestyle changes regarding diet and exercise; and the use of advanced imaging techniques. In some cases, more aggressive agents such as chemoprophylaxis may be used.
Why and how rebirth occurs
Although it has long been proven that cells with altered DNA are formed in the human body all the time, and we are not talking about single cells, but about millions, their transformation into tumor cells does not always occur. The process of aging and cell destruction (apoptosis) is laid down in DNA from the very beginning. This process occurs at the genetic level and is responsible for such cells being removed from the body by self-destruction.
If the human body is not all right in terms of health, this means that the repair system is failing. The risk of atypical cells degenerating into cancerous cells is called “oncogenesis.”
Although such atypical cells have signs of a tumor (analysis can show this), they are not cancer yet. Their complete transformation into oncogenic ones will occur slowly and gradually. The stage of degeneration, when minimal signs of cellular mutation (atypia) begin to appear, is a precancerous condition.
Cytology objects
Objects of breast cytology are:
- Cyst contents.
- Discharge directly from the nipples.
- Scrapings from lymph nodes.
- Breast tumors.
- Lymph node punctures.
- Scrapings from areas of the nipple or breast skin that have undergone ulcerative and eroded processes.
This research method is carried out by an ultrasound specialist or attending physician. If the object is nipple discharge, it is removed by applying pressure on or around the nipple area. The tissue of the entire mammary gland is also affected. When conducting diagnostics, the first and also the last drops of discharge are taken for analysis.
National Surgical Adjunct Breast and Bowel. The project showed that administration of tamoxifen reduced the risk of invasive and non-invasive breast cancer. almost 50% in all age groups. In a subgroup of patients with ductal atropy. prophylactic tamoxifen reduces the incidence of breast cancer by 86%. 7 There are also established algorithms to guide the situation with women. with an increased risk of breast cancer. 8.
Despite the presence of these preventive measures. approaches, traditional methods for assessing the risk of breast cancer are not very large. useful for identifying patients who may benefit from them. Between 50% and 70% of women who develop breast cancer have no identifiable risk factors. except age, using modern standard risk assessment tools. Statistical risk assessment methods - for example, the Gale model, which uses a woman. personal and family medical history to assess risk - more useful. epidemiological tool than for identifying personal risk. 9 For example, the Gale model is known to underestimate risk in some patients. population and often overestimate the risk in others. 10 Because these traditional methods have proven inadequate, they continue. interest in developing readily available biomarkers that can identify. risk of breast cancer with an acceptable degree of individual prognosis. accuracy.
If the punctate is a liquid, sodium citrate is added to it, otherwise it may curdle. The test object is then placed in a centrifuge, and smears are made from the resulting sediment. Next, the result is deciphered.
Principles of Cytology:
- Analysis of the composition of cells in normal conditions and pathological changes in breast cancer.
- Analysis of a group rather than a single cell. The background of the drug is important.
- A cytological examination always ends with the formulation of a conclusion.
Main criteria
The main criteria for this study are cells, nuclei and nucleoli.
Signs of disturbances in the nucleus in cancer:
- The size of the core is noticeably increased.
- The kernel is tuberous.
- Lack of an even contour.
- Polymorphism.
- Uneven chromatin pattern.
Signs of cell abnormalities in cancer:
- Increase in cell size.
- Changed form.
- Change in the proportions of the cell's cytoplasm and nucleus.
- Discrepancy between the parameters of cytoplasmic maturity and the parameters of nuclear maturity.
Signs of disturbances in the nucleolus:
- The size of the nucleus is significantly increased, or it has an irregular shape.
- Increased number of nucleoli compared to a healthy cell.
Criteria for a malignant disease are often detected, but there are cells in which this criterion is not present or is weakly expressed. In such cases, a cytologist studies changes in the nature of cellular relationships. The analysis of the result and the conclusion are made on the totality of all the signs.
Characteristics of cancer cells
A normal cell goes through a number of stages during its life - birth, maturation, life and subsequent death under the influence of a natural mechanism (apoptosis). The division follows a clearly established internal order. Cell development is subject to a precisely scheduled schedule, the change of which leads to unpleasant consequences.
Cancer cells are genomes with disrupted genetic development, formed from normal healthy tissues. Mutations occur under the influence of external factors or internal pathologies in the human body. Scientists have not fully figured out the exact reasons for such mutations. Research into the disease is still ongoing. Diseased cells do not respond to incoming signals from the brain, which is accompanied by external changes in the structure and appearance of the pathogen. Before degeneration into a malignant form, up to 60 different mutations occur inside the cell. During the mutation process, some die, the rest survives and begins to actively divide. This is how cancer pathogens are born.
Mutations lead to internal changes. The body does not respond to such forms, which provokes the formation of a tumor in a certain area of the body. Cells become immortal due to their immunity to internal signals requiring a change in life stage. The normal cycle is disrupted and causes dangerous diseases in humans. The rebirth takes place over several years. Sometimes a malignancy is discovered after a person has died, but this is rare. The first symptoms appear when there is a high concentration of diseased cells and a large size of the compaction.
Cancer particles form in the lymph nodes, on the skin, on the mucous membrane of internal organs, in brain tissue, and affect bone tissue and the circulatory and lymphatic systems. The female body undergoes changes in the mammary gland, uterus, appendages and ovaries. People who have an abundance of moles on their bodies are at risk.
Goals and objectives of cytology
The main goals when diagnosing the mammary gland using a cytological method are:
- Conclusion of specialists before the start of treatment.
- Fast diagnostics.
- Monitoring the degree of therapeutic effectiveness.
- Monitoring the course of the disease.
The diagnostic results using this method are compared with the results obtained in histology.
Diagnosis of breast cancer using cytology is considered one of the most accurate (90-96%). A small percentage of cases of such research are unsuccessful due to the unsuitability of the material for analysis.
What can testing show?
When the doctor takes a smear, the laboratory technician must examine it carefully. At the same time, he draws attention to the following points:
- Epithelium.
- Cell size.
- Cell location.
- The number of elements in a stroke.
- Changes in structure.
After testing, the doctor makes a conclusion and gives the result to the patient. Typically, it may take 1-2 days for the conclusion and examination of the results.
READ MORE: Cytology showed dysplasia and biopsy
The doctor can give the patient a conclusion with the following results:
- Negative. No pathologies were found and the patient is healthy.
- Inflammatory. Additional tests are ordered to determine the cause of the infection. After 2-3 weeks, the woman is sent for re-testing.
- Abnormal cells. This will require microbiological testing. The result can be drawn from the data received. Here, too, over time the woman will need to take additional tests.
- Oncology. Other methods are prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
Doctors also say that tissue testing results can only show what changes are happening in the body. Therefore, a diagnosis is made only based on such results.
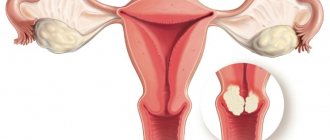
Forms of breast cancer
Approximately 70% of breast cancer cases are classified as invasive ductal. 10% of cases are cancer of the combined ductal-lobular structure. About 10% are rare forms: signet ring cell, secretory, lipid-secreting, colloid, squamous cell, Paget's cancer, apocrine.
Favorable prognoses are observed for tubular, juvenile, medullary, and adenoid cystic forms. The infiltrative lobular form of breast cancer reduces the favorable course of the disease. In lipid-secreting, infiltrative ductal, signet ring cell forms of the disease, researchers give a poor prognosis.
Intraoperative cytology
The intraoperative method is considered the basis of the cytological method. It reveals the pathology of the malignant process, as well as the spread of metastases to the liver and lymph nodes. The reliability of this method is about 98%.
Cytological examination of the mammary gland studies the pathomorphosis of treatment during photodynamic, as well as chemoradiotherapy. This method allows you to determine the nature and extent of the malignant process in the mammary gland even before surgery. The cytological method predicts the course of the disease and identifies factors that have a significant impact on determining the correct treatment regimens.
The reliability of this study is increased through the use of the liquid cytological method, as well as the introduction of special laboratories, the use of completely new microscopic systems that allow decoding and morphological analysis of the dynamics during the life of cells.
Why do atypical cervical cells appear?
- Mechanical damage to the uterus, trauma.
- Changes in the vaginal mucosa, which later spread to the uterine area.
- Processes of keratinization of the cervix and internal genital organs. In medical language, this disease is called leukoplaxia.
- Damage to the cervix during childbirth or during a procedure that requires cleaning the uterine cavity, including abortion.
- Injury to the uterus by means of contraception such as coils and caps, damage to it due to inept insertion of a tampon or the use of sex toys.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, hormonal imbalances and imbalances of hormones in a woman’s body.
- Infection of a woman with the papilloma virus, including in the intimate area.
- Having promiscuous sex with more than three sexual partners at the same time, or having sex with a partner who is not faithful to his partner.
- Losing your virginity too early in adolescence.
- Bad habits, and smoking especially affects the condition of the female genital organs.
- Weak immunity, due to which a woman is exposed to serious diseases.
- Incorrect treatment of previously occurring diseases of the genital organs.
- Infectious diseases that are sexually transmitted.
Differentiation of cytological diagnosis
Intraductal form of breast cancer.
Here, epithelial cells are grouped in the form of papillary complexes, as well as small solid and rosette-shaped ones. Most often, cells have one type, there is no disharmonic polymorphism. In the solid complex, the cells of the center are intensely stained in comparison with less stained cells located on the periphery, and in half a percent of cases there is a high degree of staining of the nucleus (“ink spots”).
Infiltrative moderately differentiated ductal form of breast cancer.
In this case, the changed cells are grouped. In 88% of the diagnostics performed, complexes were found that had papillary, as well as chain-like and solid forms. They have an association with a destructive or filamentous cell.
Moderately differentiated infiltrative lobular form.
The cytological picture represents a grouped half of the cell number into single rosette-shaped, as well as solid and chain-shaped complexes. Grouping a larger number of all cells (80%) gives the picture of fibroadenoma. The rosette complexes are epithelial cells that are cylindrical in shape, while the papillary and solid complexes are cuboidal in shape.
Paget's cancer.
A large mass of altered cells does not differ from poorly differentiated and moderately differentiated forms of cancer. The main feature is the existence of lighter and larger cells.
Cancer with a low degree of differentiation.
This form of the disease is characterized by a monomorphic picture. Here the cells have a round shape. The nuclei are characterized by uneven contours, and the chromatin has a clumpy structure. There are cases when the picture of this disease is similar to malignant lymphoma.
Cancer with squamous metaplasia.
In this form, the cells are polymorphic, scattered and have hyperchromatic nuclei and intense homogeneous cytoplasm.
Colloid cancer. With this type of cancer, the cells are clustered, arranged tightly and have mucus in the cytoplasm or outside the cells, looking like masses that are basophilic stained.