Giardia is a single-celled parasite that colonizes the small intestine and alters the functions of the digestive system. In addition to an acute lack of nutrients, people with giardiasis experience general intoxication of the body. The prevalence of this disease is very high - every 7th person in the world has had it. The infection is especially often diagnosed in children, since Giardia is transmitted from person to person quite often through contact. Unfortunately, it is children who are most at risk of being infected, but there are other ways of transmitting the infection.
Why is it important to avoid Giardia infection?
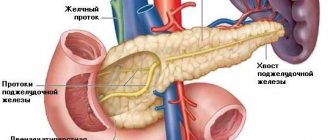
Despite its almost microscopic size and relatively primitive structure, Giardia can cause significant damage to the human body. After infection, they multiply very actively and their colonies can very densely populate the small intestine. It is known that the breakdown of food components and their partial absorption occurs in it.
Unlike the large intestine, the small intestine absorbs the substances and compounds most necessary for life. In addition, this section of the digestive tract, albeit indirectly, is involved in the formation of immunity and hormonal levels.
After infection with Giardia, large-scale changes occur in intestinal functions:
- The secretory function decreases, due to which complex substances are broken down into simpler ones. Because of this, the human body is deprived of most of the compounds necessary for its functioning.
- The barrier-protective functions are weakened, due to which the aggressive compounds contained in the chyme do not injure the mucous, submucosal and muscular layers of the intestine. Because of this, intestinal disorders and inflammatory processes may occur.
- Motor-evacuation functions slow down, due to which the timely removal of already processed food from the small intestine occurs. Since peristalsis is inhibited, chyme can “ferment,” causing intestinal upset, and in some cases, intoxication of the body.
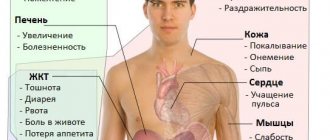
Such phenomena are especially dangerous for children, whose bodies cannot yet actively resist infection. They may experience delayed physical and mental development. Due to the lack of certain elements, irreversible changes occur in children. Adult patients may also experience significant discomfort, and it may be associated not only with digestive disorders. Giardia can cause hormonal disorders, inflammatory and dystrophic processes in individual organs.
Since giardiasis is transmitted quite easily, and the pathogen remains alive for a long time, it is necessary to soberly assess the possible risks of infection. But to do this, you need to know the main methods of transmission of the parasite.
Features of Giardia
Giardiasis is caused by single-celled parasites, which, as previously thought, select humans as a carrier. These representatives of the flagellate family are distinguished by their ability to feed on warm-blooded animals, mainly humans, in whose intestines they live. Recently it was found that not only people, but also some animals become infected with Giardia. The disease is especially often diagnosed in dogs and cats, as well as in some wild animals.
The peculiarity of Giardia is that this type of parasite can exist in two forms:
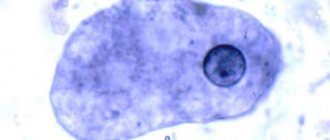
- Cysts are living organisms enclosed in a dense, impenetrable membrane. This form allows the infectious agent to survive in unfavorable conditions. Only prolonged heating can destroy it. Giardia can exist in a cyst state for up to 2.5 months if they are kept in a humid, warm environment. When released into water, especially tap water, the microorganism in the form of a cyst remains viable for 3 or more months. Cysts found in feces have the shortest lifespan. It does not exceed 3 weeks.
- Giardia itself is a living organism without a protective shell. For their survival and development, constant temperature and humidity are required, which can only be provided by a host - a person or another warm-blooded creature. In this case, Giardia is located in a place where there is a nutrient medium, that is, in the small intestine.
Cysts are considered dangerous for humans in terms of infection. Depending on where these types of pathogens are located, experts identify several routes of infection with giardiasis.
Despite its almost primitive form of existence, the single-celled parasite is very dangerous, since Giardia can be transmitted in ways that most people are unaware of.
Specifics of treatment
The course of treatment consists of 3 phases:
- Following a strict diet. Some foods have a beneficial effect on the existence of parasites in the body. You should follow a balanced diet, the main products of which will have a detrimental and destructive effect on the development of the disease. You need to exclude the following foods: chocolate, candy, flour, milk-based products, sweet-tasting fruits, foods high in starch.
- Taking anti-parasite medications. Medicines directly affect the vital activity of Giardia, removing them from the body.
- Taking multivitamins. Since anti-parasite medications have a number of serious side effects, you should keep your body in good shape. A course of taking multivitamins will help you cope with this.
Self-medication for giardiasis can also lead to unpleasant consequences. After all, only a specialist can identify the type of parasite through laboratory testing. It is impossible to make this diagnosis at home.
Complications with giardiasis
The disease that appears in children is much more dangerous to health than in adults. After all, the child’s internal organs are not strong, their destruction occurs faster
It is important to undergo effective treatment on time and to be observed by a doctor throughout the entire period of the disease. Giardiasis can lead to the following consequences:
- inflammation of the small and large intestines, as well as other organs in which Giardia is present;
- digestive system disorders;
- dry skin, rashes;
- renal failure;
- liver diseases.
Disease prevention
The most important way of prevention is maintaining basic hygiene and getting rid of bad habits, namely:
- wash your hands after using the toilet and before eating;
- do not eat unwashed foods;
- do not drink raw water;
- do not bite nails, pens, pencils;
- change underwear daily;
- Do wet cleaning with disinfectants once a week.
If such rules are familiar to a person, then his body is not afraid of any parasites.
The main routes of infection with Giardia
More than 80% of patients diagnosed with giardiasis do not know how the infection can be transmitted - such disappointing statistics were announced by the WHO back in 2010. Over the years, the numbers have changed little, which suggests why Giardia is still one of the most common parasites in humans. It is this ignorance that allows the disease to affect millions of people every day.
To avoid infection with this single-celled microorganism, it is enough to know where Giardia cysts may be located. Most often they are found:
- in ordinary tap water;
- on the surface of fruits and vegetables;
- on the hands of a person with giardiasis;
- on objects used by Giardia carriers;
- on pet fur.
If you take a closer look at the list above, it becomes clear that transmission of infection in most cases occurs due to non-compliance with hygiene standards.
Giardia infection through water
The greatest chance of becoming infected with Giardia is to drink water contaminated with cysts of the parasite. This method of infection accounts for about 60% of all cases. In most cases, cysts enter water supply networks due to insufficient water purification, as well as during accidents in water supply and sewerage networks.
Infection through water can occur:
- when drinking unfiltered tap water;
- when using water from open reservoirs for drinking, and sometimes when accidentally swallowing it while swimming;
- in case of accidental ingestion of water in a swimming pool that is not properly cleaned.
To avoid contracting giardia through water, standard precautions must be followed. Firstly, you shouldn't drink it raw straight from the tap. Boiling for a few minutes can destroy pathogens. Secondly, it is necessary to competently approach the choice of places for swimming.
It can be difficult to determine the quality of water offhand, so if in doubt, it is better to conduct an independent analysis or use boiling or additional filters for drinking water. You should also avoid visiting questionable pools and beaches.
Giardia infection through food and hands
In approximately 20% of cases, Giardia is transmitted, as they say, from hand to hand. In most cases, food is involved in this process. Cysts can get on them with water during watering or from the hands of an infected person during cleaning or preparing dishes that do not require long-term heat treatment.
Despite the fact that food can become infected from water, the percentage of this probability is too small. In most cases, human infection occurs due to dirty hands, which may contain viable cysts.
The likelihood of infection in this way can be reduced only by careful preparation for processing and consuming products:
- It is necessary to wash your hands before and after contact with vegetables and fruits. It is advisable not to use a common towel for drying. Disposable paper will be more rational and safer in terms of infection with any infections.
- It is advisable to rinse products with thick skin with boiling water. This will not kill all the parasites on their surface, but it will reduce their number by about half.
- If you need to dry food after washing, do not wipe it with cloth towels or napkins. The same rule applies here as for hands - using disposable paper towels is much safer.
If products are sold not in specialized stores, but on street stalls or roadside tents, the risk that they may be infectious increases significantly.
Giardia infection from animals
Pets, as well as people, are at risk of contracting giardiasis. By the way, they suffer from this infection much more often than their owners, but they are not always diagnosed and treated. This is how a furry family member becomes a carrier of a dangerous disease.
Most often, Giardia from animals is passed on to children and those who train them. In this case, the cysts located on the pet’s fur cling to the skin of the hands and can immediately enter the digestive tract. Again, the problem of infection is again due to lack of hygiene.
To prevent infection, it is enough to periodically examine your pets for parasites and treat them. It is also advisable to prevent animals from coming into too close contact with small children.
Particular attention should be paid to walking dogs. Animal feces should not fall on objects that may come into contact with humans. The same applies to cats - their trays should be placed in places inaccessible to children. It is also worth limiting pets’ free access to human food.
Knowing about the ways in which you can become infected with giardiasis, people gain the opportunity to prevent the spread of infection. In most cases, you can ensure the safety of yourself and your family members only by observing hygiene standards, because it is not for nothing that this disease is classified as a disease of dirty hands.
More information about giardiasis in the video:
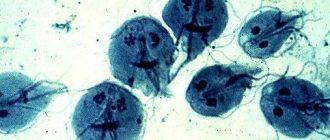
Giardiasis is a common parasitic infection caused by the protozoan microorganisms Giardia. Giardia is not an intestinal parasite in the usual common sense; it is not a helminth. Yes, their principle of parasitism is similar: both exist at the expense of humans. The difference is only in the “scale of personality.” Giardia are tiny parasites, the entire essence of which fits into one cell, which, in turn, is a single integral organism. Giardia is not particularly concerned about the “housing issue”: it lives well not only in humans, but also in many other mammals.
Folk myths
There are a lot of misconceptions about how infection occurs. Here are the main ones:
- You can often hear that the parasite can be transmitted from person to person during a kiss. This is a baseless statement, since saliva is an aggressive environment for Giardia. The parasites die in it.
- While relaxing on the sea coast, you can become infected with giardiasis if water gets into your mouth. This is another fiction, since these parasites do not live in sea water.
- It is a common belief that some children became infected with Giardia by petting a backyard cat or dog. Indeed, stray animals are often infected with Giardia. But the type of parasites that live in cats and dogs is different from the microorganism that prefers to live in humans. Therefore, animal Giardia does not pose a danger to humans through direct contact.
So how can you become infected with Giardia?
Giardia: in complex words about the simplest
Giardia enters the human stomach along with water and food in the form of an inactive cyst that is resistant to external influences, where, under the influence of gastric juice, the protective shell of the cyst dissolves and the parasite transforms into an active form (trophozoite). Migrating lower along the gastrointestinal tract (into the duodenum and small intestine), lamblia finds its final “shelter”, clings to the villi of the mucous membrane, where further growth and reproduction of the microorganism occurs. Having undergone several cycles of divisions, lamblia forms a cyst, which, along with feces, is released into the environment, closing the cycle.
Giardiasis infection
A person can become infected with giardiasis if cysts enter his gastrointestinal tract with food, water, or contaminated household items. They transit through the stomach and enter the duodenum, under the action of the enzymes of which Giardia emerges from the cysts and multiplies. Moreover, the intensity of this process is influenced by the following factors: lack of bile, abundance of carbohydrate foods, and the presence of dysbacteriosis. In the large intestine, Giardia becomes covered with a membrane and is excreted along with feces. This happens after 1.5-2 weeks.
There are periods of time lasting several days when they are not present in the stool (this is reflected in the diagnosis of giardiasis, which will be discussed below). There are several million cysts in just 1 g of feces.
There are many ways to become infected with giardiasis, but there are only a few ways to be cured.
Some of the cysts from the feces can get on the hands and, if a person does not wash his hands after visiting the toilet, he will contaminate all objects that he touches with them. A person can infect himself again if he neglects the rules of personal hygiene, especially if he is a child. The cysts of these parasites are quite stable in the environment; they can survive on objects for up to three months, and in feces for up to three weeks. If a certain amount of them (10 or more) gets on the hands of a healthy person and then in the mouth, he will become infected with giardiasis. Thus, giardiasis is transmitted by the fecal-oral route.
If drinking water is not sufficiently disinfected, a person can also become infected by drinking it directly or by washing vegetables and fruits with it.
Symptoms of giardiasis
The clinical picture of giardiasis is largely determined by the location of the infection - the small intestine. This is where the gastrointestinal symptoms of the disease arise, which begin to appear 1-3 weeks after infection with the parasite:
- frequent bowel movements that are liquid in consistency, characterized by a pungent odor and the absence of any impurities (mucus, streaks of blood), which happens, for example, with dysentery;
- pain in the abdomen, mostly in the upper part. The nature of the pain varies in the range from unexpressed aching to acute cramping;
- increased gas formation. This is explained by a violation of the quantitative and qualitative composition of the intestinal microflora, which entails a disruption of digestive processes.
These symptoms are the first signals of giardiasis. In the future, two scenarios for the course of the disease are possible: either after 2-3 weeks these symptoms disappear (the condition for this is strong immunity against the background of a low degree of pathogenicity of Giardia), or the disease becomes chronic.
In addition to gastrointestinal symptoms, giardiasis has other manifestations, which are explained by a violation of the processes of absorption of nutrients necessary for the normal functioning of the body:
- symptoms of general malaise (weakness, fatigue, drowsiness, decreased performance, headaches, deterioration of memory and attention);
- anemia. The absorption of cyanocobalamin (B12) and folic acid (B9), which play an important role in the formation of blood cells, is impaired;
- weight loss;
- a decrease in immunity and the associated risk of developing other infectious diseases;
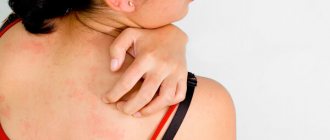
- allergic manifestations (conjunctivitis, rhinitis, rash, itching).
How contagious is Giardia?
The main routes of human infection are water, food, and household items. Water contamination occurs when it is consumed raw. This mainly concerns liquid that is supplied through a water pipe. If Giardia manages to contaminate water, human infection will be widespread. This is what happens in undeveloped countries. In such an area, 95% of the population is infectious. Giardiasis manifests itself in different forms.
Giardia is contagious to a person who does not follow basic hygiene rules. And also for a child who puts fingers, toys, other objects in his mouth, or eats unwashed fruits and berries. In addition, the risk of developing giardiasis depends on the frequency of contact with an infectious person. A nanny who takes care of a sick small child every day runs the risk of getting sick herself. An infectious child in a house with giardiasis infects everything around him. Giardia will gradually be transmitted to all family members. A sick kitchen worker in a public establishment can infect all visitors through food. The scale of infection is estimated to cover vast territories. An adult becomes infected with giardiasis along with a child. Parasites are able to function in a chronic form without causing significant symptoms of the disease. In 1 gram of feces of a child there are about 250 thousand cysts, in an adult - up to 12 ml. On the territory of our country, Giardia can be transmitted through contact and household contact. However, infection through the entry of wastewater into the drinking water pipeline cannot be ruled out. Viable parasites are found even in waters with high chlorine content.
Diagnosis of giardiasis
It would seem that it could be easier: take stool and examine it for the presence of Giardia cysts. If only everything were so simple... Let's start with the fact that cysts do not begin to be released immediately. This means that there will be no traces of parasites in the stool for at least 3 weeks. And even in chronic giardiasis, the release of cysts from the intestines is subject to the biological cycles of the parasite and does not occur constantly, but periodically. Therefore, you cannot determine anything with a single stool analysis: it is necessary to carry out a series of microscopic analyzes over the course of a month at seven-day intervals.
Based on the number of mentions in medical periodicals, the so-called enterotest using a nylon thread has recently gained particular popularity. The patient swallows an enteric gelatin capsule containing this thread. After a few hours, the thread comes out along with the feces, after which the biosample obtained with its help is subjected to microscopic or cultural examination.
From the point of view of diagnostic value, a biopsy (examination of a fragment of tissue of the duodenum or small intestine), which allows not only to make an accurate diagnosis, but also to determine the stage of the pathological process (the degree of change in the tissue structure of the intestine), seems to be a more effective method. The main (and decisive) disadvantage of biopsy is the high cost and labor-intensive nature of the method.
Another diagnostic method used for giardiasis is immunological. In response to the invasion of foreign agents, the human body begins to produce immunoglobulin antibodies. It is by these antibodies that one can determine the “hero of the occasion.”
Who can avoid getting infected with giardiasis?
Fortunately, not everyone who gets cysts into their body becomes infected.
There are factors that prevent the development of invasion:
- if an insufficient number of cysts enters the body to reproduce and form a colony;
- due to innate or acquired immunity, giardiasis does not occur;
- self-recovery - with an asymptomatic form of the disease, a person does not focus on some unpleasant manifestations, attributing everything to fatigue or bad weather, as a result, the immune system defeats giardiasis;
- with the systematic consumption of foods with a sharp, bitter taste, such food is “killer” for parasites.
Treatment of giardiasis
Includes medication, hygiene and dietary components. At the first stage of treatment, the task is to physically remove parasites from the intestines and eliminate enterotoxicosis. This is achieved by correcting the diet (introducing such natural sorbents as porridge, bran, baked apples, dried fruits, vegetable oil, warm sauerkraut brine in the morning on an empty stomach), cleansing the intestines with enterosorbents (SUMS, polyphepan). Then comes drug therapy itself.
The following medications are used to treat giardiasis (in accordance with the instructions for use):
And in conclusion, a few words about the prevention of giardiasis . This disease can be safely included in the category of “unwashed hands” diseases. This is where the main preventive measures follow: eat only thoroughly washed vegetables and fruits, drink only filtered or boiled water, do not swim in “stinky rivers”, teach your child not to put all objects in his reach into his mouth.
Video on the topic: “Giardiasis”
Giardiasis is a protozoal disease caused by lamblia (Lamblia intestinalis), which is characterized by inflammation of the wall of the small intestine and disruption of the processes of digestion and absorption.
Prevention
It is believed that giardiasis is a disease of dirty hands, and this statement is not unfounded. Therefore, the number one rule for preventing parasites is careful adherence to hygiene. Always wash your hands when you come home, use your own toothbrush, towel, and bed linen. If you have children, teach them to follow these rules from early childhood and monitor the process. There is always an increased risk of worms among pet owners, so every six months, if you have pets, you need to undergo a preventive course of treatment.
Also try to eliminate as much as possible the possibility of infection with giardiasis in other ways: do not eat raw meat or fish - when preparing them, subject them to thorough heat treatment. Wash fruits, vegetables and herbs under warm water before eating. Do not drink raw water, do not swim in suspicious bodies of water, and boil homemade milk. Follow these simple rules and be healthy!
Giardia is a single-celled parasite that chooses an organ such as the small intestine as its place of existence. Giardiasis is caused by parasites called cysts. Giardiasis cannot be defined as a serious disease, but infection with Giardia partially destroys the body, preventing it from functioning fully.
All about Giardia
Giardia was first discovered by Kharkov University professor D.F. Giardia in 1859 in the feces of children suffering from diarrhea. The pathogen Lamblia intestinalis is named after him. However, in foreign literature, another name for the pathogen is often used - Giardia lamblia, and the disease is called giardiasis.
Some types of Giardia parasitize the body not only of humans, but also of dogs, cats, large and small cattle, and rodents.
These protozoa exist in two forms - vegetative and in the form of cysts.
After cysts enter the human body with water or food, 2 motile trophozoites (vegetative form) are formed, which leave the cyst shell and attach to the surface of the epithelium of the small intestine. They reproduce by simple division.
Giardia lives in the small intestine, mainly in the duodenum. Due to intestinal contractions, some of the lamblia are torn off and carried into the lower intestines. Here they again turn into cysts.
When examined, cysts are found already in the initial part of the small intestine, but the largest number of them is concentrated in the cecum.
Unlike vegetative forms, cysts are resistant to the external environment. They live on household items for up to 2 weeks, and in water for up to 80 days.
Giardia cysts are often found in open water bodies near water intakes. Outbreaks of diseases associated with tap water occur in areas where the water is not well filtered and only disinfected with chlorine.
Chlorine-containing disinfectants have no effect on Giardia cysts.
The harmful effects of Giardia on the human body have been confirmed in a number of studies on volunteers.
Who are Giardia
Giardia
In nature, there are two types of Giardia: mobile and immobile. In fact, we are talking about a parasite that is actively functioning or, when negative conditions arise, turns into a cyst. This state helps to survive danger and continue to live when the threat is eliminated. The body of Giardia is very small, they are not visible to the naked eye. Parasites live in the small intestine. They destroy the mucous membrane and lead to the development of dysbacteriosis. Such an environment becomes comfortable for the development of pathogenic flora. A cyst forms when protozoa descend into the lower intestine. Together with the feces, the cyst leaves the body and, under favorable circumstances, enters the body of a new host.
The disease goes through the stages of infection development:
- Giardia in the form of cysts enters the intestines, under the influence of the internal environment, the integrity of the protective shell is disrupted, and a pair of Giardia leaves its “container”;
- cells parasitize, feed on useful substances, and multiply en masse;
- Some of the lamblia descend into the large intestine and take the form of cysts, leaving the body with feces.
How is Giardia transmitted?
The main source of infection is a person infected with Giardia. A secondary role is played by dogs, cats, cattle (especially calves), and rodents.
In the environment, Giardia cysts can remain viable for up to 120 days. Boiling, freezing below -13⁰C and ultraviolet irradiation lead to their death. The minimum infectious dose is 10-100 cysts. The period for the release of cysts by a sick person occurs on the 9-12th day after infection. The release of cysts occurs in periods, not constantly. An infected person is most dangerous after the diarrhea has subsided. At this time, he secretes the largest number of cysts (about 1.8 million per 1 g of feces).
Children under 9 years of age are most often infected with giardiasis, boys are 2-3 times more likely.
The mechanism of transmission of Giardia is fecal-oral. The main distribution routes are:
Infection through water
Giardia cysts remain alive in water at temperatures from 4⁰С to 20⁰С for 3 months. Sometimes outbreaks of the disease occur when drinking water from natural sources, wells, etc. Not all filters are able to purify water from cysts due to the sorbent pores being too large.
Contact and household path
This way of spreading Giardia is possible if there is a sick person in the close environment and non-compliance with hygiene rules.
Children in preschool institutions are especially often infected through toys, dirty hands, furniture surfaces and toilet items. In children who have the habit of holding their fingers in their mouths, biting their nails, pencils, pens, Giardia is detected much more often.
Food route
This path is less significant. Infection can occur through foods that are not cooked.
Flies can infect food. Live cysts can remain in their stomach for 30 hours to several days. In the intestines of cockroaches, cysts remain viable for up to 8 days.
How Giardia infects humans
There are only two ways of contracting giardiasis:
- fecal-oral;
- contact-household.
To the question whether Giardia is transmitted from person to person, the answer is affirmative - yes. The main reason is non-compliance with personal hygiene rules. How Giardia is transmitted from person to person. A simple everyday situation. One person has become infected with Giardia, but does not know about it yet. He went to the toilet, didn’t wash his hands, and then went to work. There, through a handshake, he transmitted Giardia cysts to his colleagues. Colleagues, forgetting to wash their hands before eating, swallowed parasites along with lunch. Another option for how giardiasis is transmitted from person to person is the use of household items (dishes, towels, bed linen) with the patient. People who bite their nails often become infected with Giardia. During the day, dirt, sebum, and foreign microorganisms accumulate under the nails, which do not disappear after simply washing your hands.
Development of the disease
Giardia cysts enter the mouth, then the esophagus. Stomach acid does not destroy them, and they enter the duodenum. There, from each cyst, 2 vegetative forms of the parasite are formed. Giardia is attached to the surface of the mucous membrane with a suction disk and absorbs digestive products. Thus, Giardia closes the absorption surface of the small intestine and intercepts the nutrients entering it.
Part of the food coma remains undigested and enters the large intestine in this form.
All this leads to the fact that carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals and trace elements do not enter the body. In addition, the synthesis of enzymes in the intestines is disrupted, which leads to intolerance to a number of foods.
Giardia causes mechanical damage to the intestinal mucosa over a large surface area. A large number of Giardia leads to irritation of the nerve endings of the intestinal wall.
Mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the small intestine causes activation of opportunistic microflora and leads to the development of severe forms of dysbacteriosis (dysbiosis). Metabolic products secreted by Giardia and dead Giardia are absorbed into the intestines and poison the body. This is manifested by various allergic reactions.
Insufficient consumption of protein foods, a predominantly carbohydrate diet, consumption of large amounts of sucrose, low acidity of gastric juice are factors predisposing to infection with giardiasis.
Is Giardia dangerous in children?
Giardia in children is caused by a parasitic infection. The parasites themselves are single-celled organisms that choose to reproduce in the liver and small intestine, interfering with the normal functioning of these organs. According to statistics, giardiasis is common to every third child and it is not always possible to protect the baby from these parasites.
What are the types of Giardia?
Cysts are the same Giardia, only modified. If Giardia penetrates the large intestine from the small intestine into an environment less favorable for it, they become oval-shaped cysts approximately 1 mm in size. Subsequently, when excreted from the body through fecal deposits, they enter the external environment and others are at risk of infection. Cysts can maintain excellent viability at 18 degrees, can survive in direct sunlight for about 7 days and even about 3 days in cold aquatic environments. Once in the human body and freed from the shell, Giardia again becomes vital.
The main sources of Giardia are contaminated water bodies, tap water, unwashed vegetables and fruits, and sandboxes unprotected from animals. In the vegetative form, the parasite takes on the appearance of a pear, half a millimeter in size, 4 pairs of flagella and a disk, with the help of which Giardia in a mobile form is firmly attached to the intestinal mucosa.
How does giardiasis manifest?
Symptoms are often similar to those of other diseases, but with careful monitoring, parents can still respond in time.
- Temperature. Usually does not rise above 37.5 degrees, but is noted for duration. If a child has a fever for 2 or more weeks in the evenings, you should pay attention to this and make an appointment with a doctor.
- Digestion. The regularity of stool and the processes of the digestive system are disrupted. Frustration or constipation may signal that a child has begun to become infected with Giardia. Of course, such symptoms can also indicate dysbiosis, so it is important to conduct an examination to exclude one of the causes.
- Teeth. If a child grinds his teeth while sleeping, this indicates a disruption of the central nervous system due to toxins entering the blood.
- Tone. Increased fatigue, low level of concentration, and superficial perception of information are also a signal for urgent consultation with a doctor.
- Pain. Aching and nagging pain in the abdomen, usually manifested in the right hypochondrium and in the navel area, is another symptom.
- Cough. The presence of a frequent and at the same time suffocating cough, enlarged lymph nodes - all of the above symptoms or several of them should prompt parents to consult a specialist.
Methods of infection with giardiasis
Through contact and household transmission, infection occurs from a sick person to a healthy person through dirty dishes, toys and other household items.
The risk of infection is also high in the process of biting nails and pencils.
Untreated tap water is also a source of Giardia infection.
If a child drinks water from the tap or takes a sip while bathing, this is already an alarming sign and a reason to watch him. The only exception is salty sea water.
Unwashed vegetables and fruits, meat that has not undergone heat treatment, significantly increase the chance of infection with Giardia.
Is the disease dangerous or not?
If Giardia is present in a child’s body, then the state of health worsens, and in general this does not go unnoticed for the state of health. Giardia cysts themselves, entering the body of children, are freed from their membranes and then they multiply, and very actively. But for successful reproduction, the presence of nutrients and nutrients in large quantities is also necessary.
Parasites simply take them from the human circulatory system. As a result, the child is deprived of a large amount of minerals and vitamins, which can provoke vitamin deficiency.
Giardia throughout its existence is capable of releasing a large amount of toxins into the human blood, which significantly contributes to the suppression of the immune system. The consequences are not long in coming: various allergic reactions, frequent acute respiratory infections, chronic bronchitis, utopian dermatitis. Treatment by a pulmonologist, allergist, or immunologist will be useless until examination and identification of Giardia.
Acute form of giardiasis
A large number of Giardia in a child’s body can provoke an overwhelming reaction in the child’s general condition. Appetite decreases significantly or the desire to eat disappears, nausea and vomiting occur. Body temperature in some cases reaches 39 degrees. Skin rashes and bloating occur. Giardiasis in acute form occurs more often in children under 3 years of age, since the immune system is not fully formed.
The disease acquires a chronic form due to late diagnosis. Abdominal pain periodically appears, the child loses weight, the skin becomes pale, the tongue turns yellow.
Serological diagnosis is effective during the first 3-4 weeks of a child’s infection. This test allows you to detect in the blood specific antibodies produced by the child’s body when infected with Giardia.
Scatological diagnostics allows you to detect cysts in a child’s stool, but this does not always give a 100% result.
Duodenal examination is performed for children over 10 years of age and allows for effective examination of bile. Giardia cysts are always present there. In young patients this procedure is much more difficult to carry out.
How to treat Giardia in children?
Treatment of giardiasis does not go as quickly as we would like, it is important to stick to the regimen. Traditional medicine in the treatment of children under 10 years of age is undesirable and dangerous. As a rule, a small patient is prescribed antiparasitic drugs (metronidazole, Macmiror), the dosage interval of which is prescribed by a specialist who treats Giardia in children. Independent selection of dosage threatens intoxication and entails serious consequences, having the most negative impact on the functioning of the liver and kidneys.
After about 5-6 days after treatment for Giardia in children has begun, your child’s well-being may deteriorate significantly, which is normal. This happens because Giardia die and disintegrate in large quantities in the intestines. This condition is caused by the presence of toxic products released into the blood, which causes deterioration. The condition can be alleviated by taking antihistamines and laxatives (drugs). Clear improvements are observed on days 9-11 after the course of treatment begins. The skin becomes clear, coughing symptoms disappear, and the nodes (meaning lymph nodes) become significantly smaller. Diagnosis and treatment must be repeated to exclude recurrence of the disease.
x
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BJNGqKCo9aw
If there is Giardia in children, treatment with traditional methods can be used as an addition to the main medication, but not as an independent procedure. Those. Such a scheme is unacceptable to cure the disease. A sweet habitat is favorable for the reproduction of Giardia; an acidic environment causes rapid death. Therefore, fermented milk products can significantly increase the effectiveness of drugs prescribed by the doctor and significantly reduce the risk of complications.
Practical recommendations
Prevention of giardiasis in children reduces the risk of infection. The most important thing is cleanliness. Before eating food, it is important to carefully process it and observe hygiene standards. It is advisable to wash eggs, vegetables and fruits with soapy water and rinse with boiled water, since most often Giardia enters the baby’s body through these products. Personal hygiene habits, such as washing hands before eating and after using the toilet, will reduce the risk of infection. Bad habits of biting nails and other small objects also increase the risk of infection. Close contact with pets is undesirable for a child's body. Teach your child to wash their hands after playing with pets.
x
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3sRlF_LxfRY
It is advisable to cover children's sandboxes with film and do not allow animals to be in them. Doctors do not recommend swimming in open fresh water for children under 5 years of age. Sea salt water is not a contraindication; there is no Giardia in such water.
By following all the above recommendations, you can reduce the level of infection by 50-60%. Timely contact with a specialist will facilitate and speed up the process of treating giardiasis.
VseoParazitah.ru>
Symptoms of giardiasis
The symptoms of giardiasis are varied. Severe cases of the disease with fatal outcome are unknown.
According to the WHO classification, the following forms of giardiasis are distinguished:
- giardiasis carriage (latent form),
- Giardiasis (clinically expressed form).
In turn, clinically pronounced giardiasis is of the following types:
- intestinal form (duodenal dyskinesia, duodenitis, enteritis, enterocolitis),
- hepatobiliary form (biliary dyskinesia, cholecystitis),
- Giardiasis as a concomitant disease.
The incubation period is 1-3 weeks.
In the latent form, giardiasis occurs without noticeable manifestations. This form is observed in 74-77% of infected people. In this case, malabsorption in the intestines and decreased immunity occur. But there are no obvious symptoms.
Clinically expressed form of giardiasis
Giardiasis can be acute or chronic. The acute period lasts 5-7 days. In most cases, the acute period subsides and becomes chronic.
The acute period is characterized by the following symptoms:
- watery diarrhea (3-5 times a day, stools are foamy, foul-smelling, with a characteristic oily sheen),
- abdominal pain (in the stomach area, in the right hypochondrium), not associated with food,
- nausea,
- belching,
- heartburn,
- bitterness in the mouth,
- bloating,
- loss of appetite,
- skin itching,
- fast fatiguability,
- decreased vitality.
It is no coincidence that the discoverer of Giardia, D.F. Lambl, called it “a parasite of melancholy and sadness.”
Allergic manifestations are varied:
- pale skin,
- uneven coloring of the skin (multi-colored skin),
- marble white nose skin,
- dirty skin tone
- dark circles under the eyes,
- the tongue is covered with a white coating,
- bad breath.
With a long course of the disease, giardiasis manifests itself with symptoms similar to those of the following diseases:
- duodenal dyskinesia,
- duodenitis,
- enteritis,
- enterocolitis.
Symptoms of giardiasis
The clinic generally appears 4-10 days after Giardia has settled in the body. In some situations, the incubation period extends for three months. The onset of the disease can be both acute and gradual.
The main signs of giardiasis:
- diarrhea, often accompanied by a sharp, unpleasant odor;
- cramps in the abdominal area;
- high temperature (but not more than +38ºC);
- nausea and vomiting;
- flatulence;
- dyspepsia;
- fatigue;
- poor appetite;
- significant weight loss (up to approximately 4.5 kg).
Without appropriate treatment, symptoms appear within a month or two with subsequent improvement.
In a certain number of patients, the pathology becomes permanent. Then the disease is accompanied by chronic diarrhea or regularly repeated episodes. The chronic form of the disease can drag on for two years. In children, the permanent form causes delays in growth, mental and mental development. People who undergo treatment in a timely manner rarely suffer from this disease for a long time.
Diagnostics
- The most informative method of laboratory research is the detection of vegetative forms of Giardia in the duodenal contents, which is collected during fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
- Fecal smears are examined to detect cysts.
- In the chronic form of the disease, cysts are released periodically, so to establish a diagnosis, it is recommended to examine stool 5-6 times over 2-4 weeks.
- Serological methods are optional. From the 12-14th day of the disease, it is possible to detect IgM to Giardia antigens using immunofluorescence analysis (ELISA). But this study must be confirmed by microscopic methods.
- There may be no changes in the general blood test.
- In a biochemical blood test, the content of gammaglobulins is sometimes increased or there is a tendency to decrease the content of albumin in the blood serum.
- A large amount of mucus, leukocytes and cells of the prismatic intestinal epithelium are found in the duodenal contents and feces.
- Microscopy of stool reveals steatorrhea (large amounts of fat in stool).
- Certain changes can be observed during ultrasound examination of the gallbladder, duodenum, and pancreas.
Drug treatment
Anti-giardiasis drugs have various side effects. Therefore, they should be taken only with a confirmed diagnosis and under the supervision of a doctor.
Treatment with medications is indicated only when a pathogen is detected and clinical manifestations are present.
A highly effective drug is albendazole - adults and children over 12 years old, 0.4 g orally per day; children 2-12 years old - 15 mg/kg body weight per day in one dose 1 hour before meals or 1.5 hours after meals. Course - 5-7 days.
Tinidazole is effective - for adults in a dose of 2 g orally once; children over 12 years old - 50-75 mg/kg body weight per day (no more than 2 g) once after meals. Course - 1 day.
The course of treatment with metronidazole is described in the article about this drug.
Is it possible to get infected from a cat?
Infection from animals is allowed. The parasite can be found on the cat's fur, so after contact with the animal it is best to wash your hands with soap.
Infestation can also occur when a person cleans a cat's litter box without following hygiene standards. In addition, a cat can get sick from a person.
Treatment of giardiasis is a rather lengthy and labor-intensive process. Therefore, it is better to avoid infection than to treat it. Compliance with hygiene rules significantly reduces the risk of invasion.
Giardia infection can occur at any time, and a person will not be aware of the invasion for a long time. If any symptoms appear, it is better to go to the hospital to make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy.
Diet for giardiasis
The diet is aimed at creating conditions that suppress the reproduction of Giardia. An excess of carbohydrates in food consumed by humans stimulates the growth of Giardia, while the predominance of proteins somewhat inhibits it.
It is necessary to introduce into the diet products that act as sorbents:
- porridge,
- baked apples,
- pears,
- lingonberries,
- cranberries,
- dried fruits,
- vegetables,
- vegetable oil.
You should limit your intake of carbohydrates, especially sweets.
To improve intestinal motility, puree is administered:
- beetroot,
- pumpkin,
- squash,
- carrot,
- from boiled dried fruits (prunes, dried apricots).
Recommended dairy products:
In addition, you should consume ripe tomatoes, berries and fruits.
Choleretic agents
The use of these drugs reduces congestion in the biliary tract and promotes faster elimination of inflammation.
Such means include:
- 5-10% magnesium sulfate solution,
- egg yolks,
- sorbitol,
- xylitol
Relaxation of the tone of the biliary tract is facilitated by:
- no-shpa,
- platifillin,
- belladonna leaf extract,
- barberry preparations,
- aminophylline.
Detoxification Products
To remove toxins from the body, use:
- lactofiltrum,
- neosmectin,
- smecta,
- enterosgel,
- reaban,
- Polysorb MP.
Remedies for dysbacteriosis
To eliminate dysbiosis and enzymatic disorders of the intestines and pancreas, prebiotics are used in combination with probiotics and enzymatic preparations (Creon, Festal, Enzistal, Mezim-Forte).
Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment for giardiasis is carried out 5-6 days after treatment; 2-3 times scatological analysis (stool analysis) is required with an interval of 1-2 days.
Traditional recipes for giardiasis
Traditional medicine offers several herbal infusions that have a detrimental effect on Giardia.
- St. John's wort: Brew 10 g of dry St. John's wort herb with 1 glass of boiling water and leave. Take 1 tablespoon 2-3 times a day.
- Common wormwood, Chernobyl: pour 1 teaspoon of the herb into 2 cups of boiling water (brew like tea) and drink a glass before meals 3 times a day.
Tansy infusions are also used. But it should be borne in mind that tansy is a poisonous plant and must be used with caution.