Treatment regimen
The pathology in question requires complex treatment, since it affects other systems and organs. The treatment regimen for chronic pancreatitis is as follows:
- Maintaining a strict diet during exacerbation of pathology.
- Elimination of pain symptoms due to inflammation of the gland.
- Restoring the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Replenishment of enzyme levels.
- Fighting the inflammatory process.
- Restoration of tissues of the affected organ.
- Following the rules of prevention.
Treatment of the chronic form of the pathology includes taking antibacterial drugs when an infection is detected in the body. The average course of antibiotics is 1 week.
Treatment
As a rule, the disease does not last more than a week and does not pose a particular threat to health.
Drugs that relieve inflammation in the pancreas
Initially, you should: get rid of pain, restore the amount of fluid in the body, reduce the load on the gland, while slowing down the process. During the first visit to the doctor, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, which significantly reduce inflammatory symptoms. Many people prefer paracetamol, but it is better not to take it if there is liver pathology, and in general the drug has a hepatoxic effect.
If the drugs do not help, then it is necessary that the patient is prescribed narcotic analgesics (tramadol, Creon), antispasmodics and proton pump inhibitors (rabeprazole, lansoprazole). Physiological solutions are also used intravenously - 0.8% sodium and 5% glucose. If hypovolemia is present, then colloidal solutions are prescribed; in case of bleeding, a transfusion is given or an erythrocyte substance is administered.
To unload the pancreas, they use a diet in which you cannot eat anything fatty and generally prohibit eating for a couple of days; you should forget about alcohol and smoking.
There are almost always exacerbations of pancreatitis, so here the patient is required to reduce the risk of recurrence. To do this, you need to eat right, forget about alcohol and smoking, and separate meals. When there is pathology of other organs, you should quickly seek help.
https://youtu.be/by7UNc4PKr8
Review of effective antispasmodics
Pain in chronic pancreatitis develops for several reasons:
- due to swelling of the digestive gland and its stretching;
- due to spasms of the sphincter of Oddi;
- with involuntary contraction of the tissues of the gallbladder and its ducts;
- due to the reaction of the autonomic system to the release of adrenaline into the blood.
With chronic pancreatitis, pain spreads to the entire abdominal cavity. Antispasmodics can soften the symptomatic picture of the disease:
- Drotaverine;
- Papaverine;
- Aprofen;
- Mebeverine;
- Atropine.
Most often, to relieve spasms during pancreatitis, doctors prescribe No-shpa or Papaverine.
Antispasmodics are available only in tablet form or capsules, so they are not used for emergency care. When treating chronic gastritis, medications can be taken for a long time - up to 24 weeks.
Complications
Conservative or surgical treatment of the disease must be timely and correctly selected. If you ignore the pronounced symptoms of exacerbation of pancreatitis or self-medicate for a long time, you can provoke serious health complications, sometimes incompatible with the patient’s life (for some patients they can result in death). Potential pathologies are presented in the following comprehensive list:
- internal bleeding;
- icteric cholestasis;
- thrombosis of the splenic veins;
- formation of pseudocysts;
- hypovolemic shock;
- infectious lesions of the body (abscesses);
- distress syndrome;
- renal failure;
- encephalopathy;
- pancreas cancer.
complication of acute pancreatitis
If exacerbations of chronic pancreatitis are not treated promptly or completely, there is a high risk of developing a number of life-threatening complications:
- Development of pseudocysts with possible compression of neighboring organs.
- Obstructive jaundice, which, if left untreated, provokes the development of liver cirrhosis.
- Pancreatic necrosis
- Ductal adenocarcinoma.
All of the above complications are treated surgically, after which long-term administration of antibiotics is required, especially for pancreatic necrosis.
The main sign of the development of complications is the inability to somehow relieve symptoms. No matter what you use to relieve the pain syndrome during an exacerbation, it is not possible to completely stop it, even with the use of narcotic analgesics. This situation requires increased alertness of the doctor and additional examinations.
If you do not carry out competent and complete treatment of chronic pancreatitis in a timely manner, then the following complications will begin to actively progress against its background:
- pancreatic ascites;
- diabetes mellitus of pancreatogenic type;
- abscess;
- formation of phlegmon in the retroperitoneal space;
- inflammatory process in the excretory ducts;
- chronic duodenal obstruction;
- B12 deficiency anemia;
- portal hypertension;
- gastrointestinal bleeding may occur due to rupture of the pseudocyst;
- formation of malignant tumors.
https://youtu.be/5eFcGVwLo58
Enzymatic preparations
The choice of enzymatic preparations should take into account the characteristics of the course of the disease.
The main components of this group of medications are protease and lipase. The active components are extracted from the pancreas of pigs, since this animal is closest to humans in terms of biological characteristics. In chronic pancreatitis, the necessary enzymes are destroyed by hydrochloric acid, which is part of the gastric juice, so all enzyme preparations are placed in a special capsule with an acid-resistant shell. All manufactured medications are divided into two categories: with one shell and two.
Drugs of the second group are more effective due to the special release of active components. The active ingredients are placed in special microspheres, which in turn are located in a capsule. The drug gradually dissolves in the intestines and, due to microspheres, is evenly distributed over the walls of the organ. This group includes Pancitrate, Creon.
Pancreatin and Mezim are produced with one shell. They are often prescribed for acute pancreatitis. The drugs can reduce the activity of the digestive organ and reduce inflammation of its tissues.
Some types of enzyme preparations are contraindicated for the disease in question, for example, Festal, Digestal. Medicines contain elements of bile, which accelerate the secretion of the pancreas and thereby intensify attacks of pain.
Features of treatment
Manifestations of pancreatitis in the acute stage may resemble other pathologies. Therefore, before starting treatment, it is advisable to undergo diagnostics. It will help exclude acute appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, internal bleeding, peritonitis, and cancerous tumors. For this purpose, ultrasound of the pancreas and blood tests are prescribed. Sometimes it is also necessary to do an MRI or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
But even when you first contact a doctor before the examination, he will advise the patient what to do to reduce pain and improve digestion. Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis is most often treated at home. Only if a tumor or blockage of the ducts is suspected, the patient needs to go to the hospital.
Treatment of exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis at the initial stage should obey three basic principles: hunger, cold and rest. This approach should continue for several days until the inflammation subsides. The absence of food is necessary to facilitate the work of the pancreas. After all, even a small amount of food stimulates the production of pancreatic enzymes, which increase inflammation. And during hunger, the pancreas has the opportunity to recover.
Cold compresses help relieve an attack quickly, as they relieve swelling and inflammation. And rest is very important for the patient because physical activity causes increased pain.
Compliance with the basic principles of treatment of acute pancreatitis will help to quickly stop the attack
The main goal of treating pancreatitis during an exacerbation is to relieve pain and inflammation. The principle of “cold, hunger and peace” copes well with this. But additionally, drug treatment is mandatory. At the initial stage, these are mainly antispasmodics. Then, when the patient begins to eat little by little, other drugs are needed: enzymes, prokinetics, metabolic agents, multivitamins. It is very important to follow a strict diet for 1-2 weeks. Gentle nutrition will help relieve the pancreas and speed up its recovery.
Exacerbation of pancreatitis must be treated under the supervision of a doctor. Indeed, in addition to relieving pain and inflammation, it is necessary to restore the normal functioning of the pancreas. This often requires compensating for endocrine insufficiency and normalizing secretory function. In addition, it is necessary to normalize the functioning of other organs of the digestive tract that have suffered due to impaired digestion.
First aid
The prospects for quickly stopping an attack without complications depend on how well the patient is provided with first aid. Often you have to do this yourself, waiting for the doctor to arrive.
Therefore, all patients with chronic pancreatitis should know what to do when an attack begins:
- First of all, you must immediately stop eating. This will help stop the production of enzymes and relieve the pancreas. You are only allowed to drink plain water.
- Cold should be applied to the area of the pancreas. The best thing is not ice, but a heating pad with cold water. This will help relieve swelling and inflammation a little and dull the pain.
- To reduce blood flow to the gland, bed rest must be observed. The patient should take a comfortable position and try not to move.
- It is allowed to take only antispasmodics for the first 3 days to relieve pain. These are No-Shpa, Drotaverine, Spazmalgon.
In the first days after the onset of an attack, you should not eat anything, you need to limit physical activity and avoid stress. It is also not recommended to take any more medications unless prescribed by a doctor. It is especially harmful to drink enzyme products at this stage.
In addition, it is recommended to consult a doctor and undergo an examination, even if the patient is sure that he has an exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis. This is necessary in order to exclude tumors, necrosis of gland tissue or blockage of the ducts. In this case, the attack must be treated in a hospital setting, where doctors, if necessary, will provide emergency care to the patient: provide parenteral nutrition, stop intoxication, or perform surgery.
You can stop a simple attack at home, but it is still recommended to undergo an examination
Drug treatment
One of the main methods of treating pancreatitis in any form is drug therapy. But medications should be prescribed by a doctor depending on the severity of the patient's condition.
- Antispasmodics and painkillers are most often used. They can be taken from the very first day of the attack. This could be Papaverine, No-Shpa, Analgin.
- Sometimes cytostatics, for example, Cyclophosphamide, are prescribed to stop the inflammatory process. NSAIDs are not used, as they severely damage the digestive tract.
- Antisecretory agents are also needed that block the production of enzymes and prevent further damage to the gland tissue. These can be enzyme blockers, for example, Contrical, Trasylol or Somatostatin, or proton pump inhibitors - Omeprazole.
- When inflammation spreads to other organs, infection or purulent process occurs, antibiotics are necessary. Most often, Kanamycin or Monomycin are prescribed.
- After the inflammation is relieved, the patient needs to establish metabolic processes and replenish the lack of nutrients. For this purpose, multivitamins and metabolic agents are used.
- To facilitate the work of the pancreas during the period when the exacerbation subsides, when the patient begins to diversify his diet, enzyme preparations are needed. In mild cases, it may be Pancreatin or Cholenzym; in severe cases, Creon, Panzinorm or Ermital are prescribed.
- In difficult cases, with serious intoxication or changes in blood composition, colloidal solutions, amino acids and electrolytes are prescribed.
Nutrition
Treatment of pancreatitis is not complete without changes in the patient’s diet. In the first three days after the onset of the attack, you need to completely stop eating. Then you can start eating little by little. But during an exacerbation, you can only eat certain foods. These are berry jelly, pureed mucous porridge and vegetable soups, dried fruit compotes. As the inflammation subsides, steam omelettes, boiled lean meat, and steam cutlets are gradually introduced. All food should be well chopped. You need to eat in small portions, 5-6 times a day. This diet must be followed for at least a month.
But even after the attack stops, a patient with pancreatitis needs a diet. Be sure to exclude alcoholic and carbonated drinks, coffee, white bread, fried and fatty foods from the diet. The patient should not eat spicy or pickled foods, canned food, smoked foods, white bread and fresh pastries. You need to limit the consumption of salt, sweets, fresh vegetables and fruits. Only with such nutrition can exacerbations be prevented.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed in extreme cases. An indication for antibiotic therapy may be infection of the gallbladder or peripancreatitis against the background of the underlying pathology. For this purpose, patients are prescribed:
- Amoxicillin;
- Augmentin;
- Levomycetin;
- Cefoperazone;
- Cefixime.
If inflammation of the bile ducts is diagnosed during the disease, then patients are recommended to take Amoxicillin. Before using this drug, you must undergo a number of diagnostic measures:
- bacterial examination of bile, gastric and intestinal juice;
- bacterial seeding of biological material for flora;
- determination of the sensitivity of the pathogen to various groups of antibacterial agents.
Thanks to the tests, the doctor is able to select the most effective drug that will not provoke an imbalance in microbiocenotic processes and will have a minimal list of side effects. For non-infectious chronic pancreatitis, antibiotic therapy is not prescribed. In this situation, taking medications will do more harm than good.
Means for regulating secretory function
For chronic pancreatitis, medications are prescribed that block the production of histamine in pancreatic cells. Thanks to this therapeutic property, the synthesis of hydrochloric acid in the stomach is reduced, which softens the manifestation of clinical signs of the disease.
The category of drugs that regulate secretory function includes H2 blockers and inhibitors. The first group of drugs includes the following medications:
- Ranitidine;
- Cimetidine;
- Famotidine.
Despite their effectiveness, drugs in this group are gradually being replaced by more modern medications - proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). The action of PPI is aimed at reducing the production of hydrochloric acid in the digestive organ. The category of drugs under consideration includes:
- Rabeprazole;
- Omeprazole;
- Pantoprazole.
PPIs have side effects that include bloating, nausea, and headaches. A long course of drug treatment negatively affects the condition of bone structures, increasing the risk of fracture.
Prevention with folk remedies
Alternative medicine also offers some recipes that can prevent the development of pancreatitis. The most effective traditional medicine is considered to be a decoction made from bay leaves. It eliminates inflammatory processes in the gland and reduces the risk of their formation in the future. In addition to it, you can drink a decoction of blueberry leaves.
Decoctions prepared from various herbs are also effective. You can also drink juice from vegetables (for example, carrots or potatoes). Cranberry has also proven itself well. As you can see, folk remedies are quite diverse, and here you can choose the most suitable one for yourself.
Drugs for exacerbation of pathology
Acute pancreatitis can cause abnormal changes in the tissues of the pancreas. Pathology in the acute stage requires emergency medical care, as the condition often causes death.
Patients are often interested in what is the best way to relieve pain symptoms. It is important to remember that in case of acute pancreatitis, taking painkillers on your own is prohibited. Medicines will not have a noticeable therapeutic effect, but will distort the clinical picture of the pathology. Before the ambulance arrives, you are allowed to take a No-shpa tablet.
Depending on the severity of the disease, treatment can take place in a hospital or at home. In the latter case, the patient must strictly follow all the specialist’s recommendations. The main method of combating chronic pancreatitis in the acute stage is to adhere to the drinking regime and diet, and take prescribed medications.
During exacerbation of pathology, drugs are prescribed to suppress the production of enzymes by the pancreas. These substances destroy the tissues of the digestive organ. The following groups of drugs are used to treat pathology in adults:
- preparations for detoxification measures;
- antispasmodics;
- antacids;
- antimicrobial agents;
- sedative medications;
- anticholinergics.
Which of the drugs from each group will be prescribed in a particular case is determined by the gastroenterologist, taking into account the characteristics of the disease.
In the remission stage of pancreatitis, drug treatment is supplemented with physiotherapy - electro- and phonophoresis with anesthetic drugs, magnetotherapy, mud therapy.
Symptoms of exacerbation of pancreatitis
The symptoms of chronic pancreatitis are not due to characteristic signs. The disease can occur without causing discomfort or pain to a person. The disease has periods of remission and exacerbation. The period of exacerbation is complex, severe, accompanied by severe pain, so it is recommended that treatment be carried out in a hospital setting.
In rare cases, exacerbation occurs in a mild form. Then treatment of chronic pancreatitis can be carried out at home using recommended drug therapy. If chronic pancreatitis worsens, you should not try to relieve pain on your own. This is extremely dangerous and can be fatal.
People suffering from this disease know that it is necessary to regularly follow a diet, eliminate alcohol, and try to avoid stressful situations. These are precisely the main factors that provoke an exacerbation. Even minor symptoms should be a reason for immediate qualified help. It can be:
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- vomiting or retching;
- heartburn;
- unpleasant belching;
- dry mouth;
- lack of appetite;
- sudden weight loss;
- yellowness of the sclera and skin.
The pain syndrome appears in a severe form of exacerbation. It may appear approximately a week after the listed symptoms. But we cannot say that such symptoms are typical for everyone. Signs of the disease vary from person to person. If one patient suffers from endless vomiting and nausea, which cannot be alleviated by anything, then another does not experience such a severe course. Almost everyone experiences loose stools with a characteristic shine. Diabetics have a sharp increase in appetite.
Diet for chronic pancreatitis
For chronic pancreatitis, certain nutritional rules are followed to prolong the period of remission. Among the permitted drinks for pathology, mineral water (Essentuki No. 17, Narzan, Arkhyz), lightly brewed tea without added sugar should be noted. In the absence of clinical manifestations of pancreatitis for a long time, the menu is supplemented with rosehip decoction and jelly.
Food is taken warm and ground. Preference is given to vegetable purees, cereals and jellies. Dishes taken for chronic pancreatitis should not be too hot, spicy or sour. The following are completely excluded from the menu:
- bananas;
- mushrooms;
- beans;
- eggs;
- sweets;
- flour products.
The preferred method of cooking is boiling or stewing. Products are taken in small portions, but often (5-6 times a day).
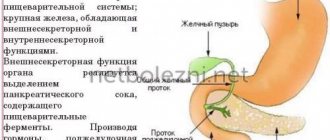
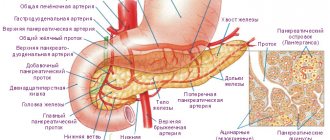
Chronic pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas that cannot be completely eliminated. In order for pathological problems to appear as rarely as possible, it is necessary to take medications and follow nutritional rules. Otherwise, it will not be possible to avoid exacerbation of the pathology. This condition leads to irreversible pathological changes in the gland tissue and affects the patient’s quality of life.
How dangerous is the disease?
Chronic pancreatitis is accompanied by disturbances in the production of trypsin and lipase, enzymes necessary for proper digestion. Long-term circulatory disorders lead to the proliferation of connective tissue and sclerosis of pancreatic cells. With such a pathological condition of the gland, pathogenic microflora can easily penetrate inside and cause an exacerbation of the disease.
The cause of exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis may be biliary dyskinesia
Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis often begins due to intestinal dysbiosis or is caused by biliary dyskinesia. Exacerbation of the chronic form can occur due to:
- inflammatory stenosis;
- Vater's nipple tumors;
- insufficiency of the sphincter of Oddi;
- alcohol abuse;
- suffered stress;
- eating disorders;
- changes in the rhythm of life.
The inflammatory process can affect part of the digestive organ or cover the entire pancreas. A chronic disease can last a long time and cause complete destruction of the gland without proper treatment.
The patient is at risk of developing complications such as:
- abscess;
- cyst;
- calcification of gland tissue;
- diabetes;
- thrombosis of the splenic vein;
- cicatricial inflammatory stenosis;
- obstructive jaundice.
Long-term pancreatitis with frequent exacerbations causes the development of pancreatic cancer. This disease leads to the rapid spread of metastases to all internal secretion organs, and the person dies from cancer.