Description of the disease
The problem involves rapid progression of hemorrhage into the organ. As a result, fluid flows outside the appendage. In this case, women feel a sharp pain localized in the abdomen. If a very large vessel is affected, then the outflow of blood into the peritoneum is recorded. Only the right or left ovary may burst, and not two at the same time, but the causes of apoplexy are the same.
Reference! This diagnosis is mainly found in patients aged 20-35 years. Most often, the ovary on the right suffers; this situation is associated with its more voluminous blood transfer.
How is an ovarian rupture diagnosed?
The first diagnosis given to patients immediately after hospitalization is “acute abdomen.” In order to establish the causes of the disease, examinations are carried out by several doctors at once (gynecologist, urologist, surgeon). However, if this is ovarian apoplexy, then you cannot hesitate; as a result of increased bleeding, the condition rapidly worsens, even to the point of threatening the patient’s life.
In order to diagnose rupture of ovarian tissue, a gynecologist performs an examination, measures hemoglobin levels, performs a puncture of the vaginal vault, performs laparoscopy and ultrasound. Typical signs of ovarian apoplexy are sharp abdominal pain (especially in the middle and at the end of the cycle), bloating, and painful sensations on the side of the affected ovary, which manifest themselves on palpation. A general blood test shows a clear drop in hemoglobin and leukocytosis.
At the same time, a blood test for hCG is taken to rule out ectopic pregnancy. Additionally, a vaginal examination is performed to determine the source of the pathology. During it, pain in the posterior and lateral vaginal vaults, pulsation of blood vessels, and prolapse of the posterior vault (with profuse hemorrhage) are detected.
When moving to the sides of the uterine cervix, acute pain appears. The size of the uterus remains the same, sometimes slightly enlarged, but the density remains the same. The affected appendage reaches the size of a chicken egg, is elastic and practically motionless. Often bloody substances are released from the genital tract.
Puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix will show serosanguineous fluid or pure blood. An ultrasound will reveal the presence of fluid in the abdomen and the presence of bleeding in the tissue of the diseased ovary. The diagnosis is completed by laparoscopy, which serves to eliminate bleeding.
Causes
This pathology in itself is considered very dangerous.
In the total number of acute diseases in gynecology, it is 17%. In 2.5% of women, the cause is abdominal bleeding , and this poses a threat to their life, and therefore they are promptly hospitalized.
The blood leaving the vessel passes the dangerous stage of hematoma and is directed into the peritoneum. Every woman needs to know about the causes of this pathology, these include:
- the appearance of thrombocytopenia;
- excessive load on blood vessels;
- long-term use of anticoagulants prescribed by a physician;
- hormonal imbalance;
- progressive von Willerbrand disease;
- inflammatory process occurring in the pelvic organs;
- formation of adhesions;
- cyst;
- follicle rupture;
- incorrect position of the uterus.
There are also certain situations that can cause bleeding. In particular, it is better to avoid injuries, physical strain, rough sex or intense movements during sexual intercourse, and mistakes while riding.
Important! Bleeding can develop if a girl is rudely examined on a chair by a non-professional gynecologist or if inept douching is performed.
Specialized diagnostics
Ovarian rupture has symptoms very similar to other equally serious pathologies of the pelvic organs. A diagnostic test is carried out to confirm or refute that the “acute abdomen” is caused by a ruptured ovary.
To do this, the doctor studies the background of the disease to understand whether there is a connection with the phases of the menstrual cycle. The presence of blood in the space behind the uterus is determined.
A laboratory test of blood is carried out to determine coagulability and hemoglobin content. This will allow us to determine what type of apoplexy is present in this particular case. If an increased concentration of leukocytes is observed in the blood, this indicates an existing inflammatory process.
The patient undergoes an ultrasound. This is necessary in order to study the structure of the corpus luteum and determine whether there is hemorrhage in it.
Diagnostic laparoscopy is done as follows: an endoscope is inserted through a puncture in the peritoneum and a thorough examination is performed. Thanks to which the exact cause of bleeding is determined and what type of apoplexy is present in a particular case. Laparoscopy can also eliminate pathology.
General symptoms
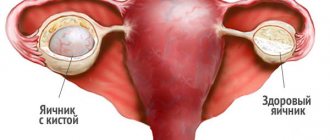
The source of blood outflow during apoplexy is the corpus luteum or a formed cyst.
The process of formation of these elements begins after the follicle ruptures and the egg is released.
If the patient is healthy, then the corpus luteum is assigned a temporary hormonal function: progesterone is synthesized, which is necessary for the onset and maintenance of the initial stages of a high-quality pregnancy. If fertilization does not occur, the VT is destroyed.
External factors can often have a negative impact on it. In particular, the accumulated fluid begins to put pressure on the inner wall of the cystic membrane, as a result, the vessels located in it are damaged. As a result, hemorrhage occurs.
Important! The two main symptoms that can help identify a ruptured ovary are heavy bleeding and pain.
Now let's move on to other signs that an ovary has burst. These include:
- lower abdominal pain. The woman also experiences discomfort in the lumbar region. The pain often radiates not only to the stomach, but to the legs and rectum. When palpating the ovary during an examination on a chair, the pain syndrome intensifies. The nature of the pain itself is cramping, sharp or pulling. Unpleasant sensations increase during movement. A dull pain occurs several days before the rupture.
- Increased heart rate and decreased blood pressure. When a patient loses copious amounts of blood, her heart rate increases and her blood pressure drops sharply. In this case, paleness of the skin is observed. This condition accompanies the anemic form of the disease. Here, the patient’s health condition depends on the amount of blood lost. Sometimes frequent fainting cannot be ruled out.
- Weakness. Impotence develops due to the fact that tissues need additional oxygen. When blood flow is strong, the functioning of nerve cells in the brain slows down. As a result, the girl begins to fall into an apathetic state. Oxygen starvation of myocytes provokes the onset of muscle weakness. The state of health worsens in direct proportion to the amount of blood lost.
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle. Against the background of progressive pathology, irregularities in menstruation are recorded. In this case, bleeding is observed between menstruation. Sometimes the ovary ruptures during menstruation, and this factor only complicates the diagnosis of the disease. The cycle remains regular in very rare cases.
- Frequent urination. This phenomenon is observed due to pressure on the walls of the bladder. The number of urges per day exceeds 10 times. Sometimes frequent trips to the toilet are provoked by prolonged use of specialized medications.
Important! Severe pain is completely unusual for the anemic form of the disease, but it can be present in a completely unexpressed form. Then it is predominantly radiating in nature.
Sometimes symptoms of the disease include blue nails and lips, shortness of breath, chills, frequent vomiting, fainting and false urge to defecate.
Complications of the disease
If an ovary bursts, the consequences can be very serious. Rupture of large vessels causes large blood loss, which, in turn, causes a significant drop in blood pressure (hemorrhagic shock). It is impossible to treat apoplexy at home. If a woman does not go to a medical facility in time and does not receive the necessary help, this can be fatal.
Therefore, if a sharp cramping pain occurs in the lower abdomen, especially when it occurs in the middle between menstruation, a woman should definitely go to bed and call an ambulance.
The most common complications after ovarian apoplexy are adhesions in the appendage, recurrent rupture. Some women do not become pregnant after suffering from the disease. The likelihood of such complications is much higher after conservative treatment. The patient's reproductive health can be restored if the treatment was carried out laparoscopically. Laparoscopy is a gentle surgical operation that is performed through small holes in the abdominal wall.
Treatment methods
In mild forms of apoplexy, conservative practice is used, but in most cases there are obvious signs of bleeding. These methods usually include:
- maintaining strict peace;
- use of antispasmodics;
- taking vitamins;
- application of cold to the abdomen;
- use of suppositories with belladonna;
- administration of hemostatic agents.
Reference! When the dangerous period passes, electrophoresis is prescribed, but if signs of increased bleeding appear, immediate surgical intervention is indicated.
As for the surgical method, we will talk about laparoscopy. The only contraindication to its implementation is hemorrhagic shock. The operation is then carried out as carefully as possible so that the internal tissues are preserved as best as possible.
The operation may consist of the following manipulations:
- coagulation of places where tissue rupture occurred;
- resection;
- seam cover;
- oophorectomy;
- andesectomy.
An important point in treatment is washing the peritoneum and removing clots to prevent the formation of adhesions.
Ovarian rupture: treatment
Treatment tactics for ovarian ruptures depend on the degree of blood loss and the intensity of bleeding. With mild severity, many doctors choose conservative tactics for managing patients - strict bed rest, cold on the stomach and complete rest with monitoring of hemoglobin, hematocrit level and general condition are recommended.
Standard treatment methods will be effective only if apoplexy has not reached the average stage of severity and does not have pronounced signs of bleeding. In this case, bed rest, suppositories with belladonna, cold compresses on the abdomen, antispasmodics, vitamins and hemostatic agents are prescribed. When the exacerbation is over, Bernard currents, diathermy, and electrophoresis with calcium chloride are needed.
If there are necessary indications, laparoscopy is performed, but under the following conditions:
- physical and ultrasound examinations confirmed that there is more than 150 ml of blood in the abdominal cavity, hemodynamic parameters are stable, and the general condition of the patient’s body is stable;
- conservative treatment methods are ineffective for 1-3 days, intra-abdominal bleeding still makes itself felt (ultrasound confirmation is required);
- Acute surgical and gynecological pathologies were diagnosed.
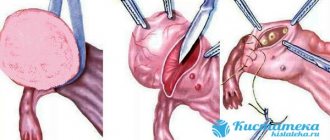
Surgical operations for ovarian apoplexy should be carried out in a gentle manner, with an attempt to preserve the tissue of the affected organ: the area of the rupture is coagulated, the cyst is opened (puncture is possible), the contents are removed using an aquapurator-suction, and the ovary is resected. If the damage is too great and there is no way to save the organ, it is completely removed. An equally important step is washing the abdominal cavity and removing blood clots, which is also the prevention of infertility and adhesions.
Laparotomy is also possible if:
- hemorrhagic shock occurred: the patient’s condition was serious, hemodynamics were impaired as a result of intra-abdominal bleeding;
- if laparoscopy is hampered by adhesions and increasing hemorrhage from the affected ovarian vessels.
Surgical intervention is performed through a suprapubic Pfannenstiel incision or an inferomedial approach. In general, the scale of the intervention does not exceed laparoscopy, however, during laparotomy, blood transfusion from the abdominal cavity is possible. If the bleeding intensifies, then urgent surgery is necessary.
Recently, surgical operations are usually performed to treat ovarian apoplexy. Conservative treatment methods are prescribed only to those patients whose pathology is still in a mild form, except in cases where the woman plans to become pregnant (then surgery is performed). The most commonly used types of operations are laparoscopy and transsection (if endoscopic intervention is not possible). In the presence of severe hemorrhagic shock, operations are contraindicated.
As for the rehabilitation period, here the course is taken to prevent the formation of adhesions, restore reproductive functions and bring hormonal processes back to normal. After this, a careful selection of contraceptives is made, the patient undergoes a course of physiotherapy (laser therapy, zinc electrophoresis, electrical stimulation of the fallopian tubes, magnetic therapy and ultrasound therapy).
For a pathology such as ovarian rupture, treatment involves providing emergency medical care. Severe blood loss can be fatal. Conservative therapy is carried out exclusively in mild cases when there are no signs of internal bleeding. As symptoms increase and the volume of lost blood increases, surgical intervention is required. The algorithm of medical actions is directly related to the manifestations, severity of symptoms, and the extent of damage to the uterine tissue.
Conservative treatment of ovarian apoplexy is possible with a slight degree of damage to the gland. This method of therapy is used if the volume of blood lost by the patient does not exceed 150 ml. In this case they use:
- ice on the lower abdomen;
- hemostatic drugs (Etamzilat);
- antispasmodics – Papaverine hydrochloride, No-Shpa;
- vitamins – thiamine, pyridoxium, cyanocobalamin.
At the recovery stage, after the acute period has been eliminated, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed for a speedy recovery:
- electrophoresis with calcium chloride;
- Microwave therapy;
- Bernard currents;
- diathermy.
Conservative treatment is carried out exclusively in a hospital, under constant medical supervision. With the development of a repeated attack of pain, deterioration of the condition, instability of hemodynamic parameters, an increase in the volume of blood accumulated in the peritoneal cavity, ovarian apoplexy requires surgical intervention. It is performed using laparoscopy, which speeds up the recovery period.
This method of therapy is the main one for apoplexy. During the operation, doctors examine the affected area, remove blood from the abdominal cavity, and suture the ovary. With extensive damage to the gland, the question of its removal arises. When ovarian rupture develops, surgery is mandatory under the following conditions:
- more than 150 ml of blood has accumulated in the abdominal cavity, which is subject to ultrasound;
- conservative therapy did not bring the expected result within 2-3 days;
- there is a need for differential diagnosis of acute gynecological and surgical pathology.
Description of the disease
The problem involves rapid progression of hemorrhage into the organ. As a result, fluid flows outside the appendage. In this case, women feel a sharp pain localized in the abdomen. If a very large vessel is affected, then the outflow of blood into the peritoneum is recorded. Only the right or left ovary may burst, and not two at the same time, but the causes of apoplexy are the same.
Reference! This diagnosis is mainly found in patients aged 20-35 years. Most often, the ovary on the right suffers; this situation is associated with its more voluminous blood transfer.
How does a follicle rupture in the ovary?
In a healthy woman, a ruptured follicle in the ovary does not cause any special symptoms. This procedure occurs every menstrual cycle and, if desired, a representative of the fair sex can become pregnant at any time.
Follicle maturation occurs in both ovaries. There are cases when one dominant vesicle appears in the ovaries at the same time. This is not a cause for concern; most likely the woman will have twins. Ovulation proceeds without failure, and the egg is released from the ruptured sac.
The situation is worse when a persistent follicle appears. The point is this: a small follicle grows and develops as it should. It reaches the required size and is ready to burst, releasing a mature egg. But a failure occurs and there is no rupture. This forms a cyst on the ovary, which can increase over time. The first symptom of a cyst is a disruption of the menstrual cycle.
If the diagnosis showed a persistent follicle in any of the ovaries, ovulation will not occur. There can be many reasons for the occurrence of the disease, from increased levels of male hormones to the inflammatory process in the appendages and ovaries. If treatment is not done in time, a woman risks becoming infertile.
Treatment for an unruptured blister begins with hormonal therapy. From the fifth to the ninth day of the menstrual cycle, medications that suppress the male hormone are taken. Next, the doctor prescribes intramuscular use of hormones, which lasts no more than a week.
With the normal functioning of a woman’s genital organs, the follicle ruptures and releases a mature egg. In a healthy woman, ovulation occurs every monthly cycle and guarantees a positive result of conception. If there is a failure in the formation and rupture of the follicle, the egg cannot meet the sperm and pregnancy will not occur. A follicle that has not burst forms a cyst, which, if not treated in a timely manner, can lead to a lot of complications, including infertility. The presence of a cyst can be detected by ultrasound. The appearance of a tumor on the ovaries is accompanied by symptoms in the form of pain during menstruation and disruption of the menstrual cycle.
A sudden disruption of the integrity of the ovarian tissue and subsequent bleeding is called ovarian rupture or. Hemorrhage may reach the abdominal cavity. The age at which cases of apoplexy are likely is from 14 to 45 years, with the period from 20 to 35 years being the most dangerous. Recurrence of a once-occurring ovarian rupture occurs in almost 70% of cases.
Apoplexy most often occurs in the second half of the menstrual cycle due to the fact that during the period of ovulation and the onset of menstruation, the vessels are more susceptible to permeability and blood filling. The artery of the right ovary arises from the aorta. This is an additional risk of sudden rupture.
Causes of ovarian rupture
- Rupture can occur due to the growth of blood vessels in the corpus luteum of the ovary during ovulation.
- The danger is posed by inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity, uterus, ovaries or fallopian tubes, and the presence of cysts.
- Changes in blood vessels in the pelvic area (fibrosis, varicose veins, etc.). With these disorders, normal blood circulation is not possible.
- Adhesive disease.
- Trauma to the abdominal area, including due to very violent sexual intercourse.
- Excessive physical activity and heavy lifting.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Hypothermia.
First aid for ovarian rupture
If an ovarian rupture occurs, you must take a horizontal position and, until the doctors arrive, do not take painkillers or use cold or hot compresses. The first signs of apoplexy are sharp pain radiating to the leg, lumbar region, genitals or anus, weakness, dizziness, pallor, decreased blood pressure, rapid pulse, and sometimes cardiovascular failure.
If an ovarian rupture occurs, surgery is performed immediately. If there is hemorrhage in the abdominal cavity, it is eliminated by puncture through the posterior wall of the vagina. Further treatment of ovarian rupture is performed using laparoscopy.
The urgency of urgent treatment is explained by severe consequences - large blood losses, the possibility of developing adhesions, infertility, and peritonitis.
After the surgical intervention and removal of all existing blood clots from the abdominal cavity, mandatory rehabilitation is carried out aimed at restoring the reproductive function of the body in order to preserve the opportunity for patients to have children in the future.
Ovarian rupture is a dangerous complication, because with apoplexy of the left or right ovary, massive bleeding occurs. The patient needs urgent medical attention. In this article we will tell you what to do if you have pain in the ovaries, as a suspected complication, and what to do if an ovary bursts.
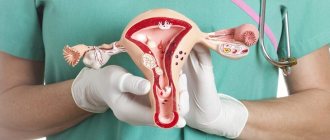
Ovarian apoplexy is a pathology that is characterized by a sharp rupture of ovarian tissue and is accompanied by intra-abdominal hemorrhage in the ovarian tissue and acute pain. To diagnose this disease, a general examination is performed, a puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix, laparoscopy and ultrasound examination of the pelvic area are performed. It is most often treated by emergency surgery of two types: radical or with preservation of organs. If you detect it in time and provide timely assistance (in the absence of adhesions and peritonitis), then there will be no threat to life and reproductive function.
Heart attack, rupture, hematoma - all these are variant names for ovarian apoplexy. This disease is found in 1-3% of the total female population aged 20 to 35 years with gynecological pathologies. The most common is apoplexy of the right ovary, which is a consequence of the fact that it is supplied with more abundant blood due to the ovarian artery arising from the aorta. The right ovary is larger in size, weight, and has a more developed lymphatic system. The left ovary is supplied with blood by the left ovarian artery, which arises from the renal artery.
In 0.5-2.5% of women, bleeding into the abdominal cavity occurs as a result of ovarian apoplexy. The hemorrhages themselves are of several types: from the ovary or from the stroma, from follicular cysts or from cysts of the corpus luteum, as well as from mature follicles during ovulation and with ovarian dysfunction.
General symptoms
The source of blood outflow during apoplexy is the corpus luteum or a formed cyst.
The process of formation of these elements begins after the follicle ruptures and the egg is released.
If the patient is healthy, then the corpus luteum is assigned a temporary hormonal function: progesterone is synthesized, which is necessary for the onset and maintenance of the initial stages of a high-quality pregnancy. If fertilization does not occur, the VT is destroyed.
External factors can often have a negative impact on it. In particular, the accumulated fluid begins to put pressure on the inner wall of the cystic membrane, as a result, the vessels located in it are damaged. As a result, hemorrhage occurs.
Important! The two main symptoms that can help identify a ruptured ovary are heavy bleeding and pain.
Now let's move on to other signs that an ovary has burst. These include:
- lower abdominal pain. The woman also experiences discomfort in the lumbar region. The pain often radiates not only to the stomach, but to the legs and rectum. When palpating the ovary during an examination on a chair, the pain syndrome intensifies. The nature of the pain itself is cramping, sharp or pulling. Unpleasant sensations increase during movement. A dull pain occurs several days before the rupture.
- Increased heart rate and decreased blood pressure. When a patient loses copious amounts of blood, her heart rate increases and her blood pressure drops sharply. In this case, paleness of the skin is observed. This condition accompanies the anemic form of the disease. Here, the patient’s health condition depends on the amount of blood lost. Sometimes frequent fainting cannot be ruled out.
- Weakness. Impotence develops due to the fact that tissues need additional oxygen. When blood flow is strong, the functioning of nerve cells in the brain slows down. As a result, the girl begins to fall into an apathetic state. Oxygen starvation of myocytes provokes the onset of muscle weakness. The state of health worsens in direct proportion to the amount of blood lost.
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle. Against the background of progressive pathology, irregularities in menstruation are recorded. In this case, bleeding is observed between menstruation. Sometimes the ovary ruptures during menstruation, and this factor only complicates the diagnosis of the disease. The cycle remains regular in very rare cases.
- Frequent urination. This phenomenon is observed due to pressure on the walls of the bladder. The number of urges per day exceeds 10 times. Sometimes frequent trips to the toilet are provoked by prolonged use of specialized medications.
Important! Severe pain is completely unusual for the anemic form of the disease, but it can be present in a completely unexpressed form. Then it is predominantly radiating in nature.
Sometimes symptoms of the disease include blue nails and lips, shortness of breath, chills, frequent vomiting, fainting and false urge to defecate.
Etiology
The causes and consequences of ovarian rupture will be discussed below.
In these organs, in a sexually mature woman, follicles grow in which eggs mature. The beginning of a new menstrual cycle gives rise to the growth of the dominant follicle, reaching about 20 mm in size by the middle of the cycle. During the normal course of this cycle, the follicular membrane ruptures with the release of the egg, which means the beginning of the ovulation process. At the site of the ruptured follicle, a corpus luteum is formed, in which hormones are produced that prepare the female body for pregnancy.
In the case of sclerotic and dystrophic dynamics in the ovarian tissues, which develop during various inflammatory processes and stimulation of ovulation with the help of drugs, disturbances occur in its process and the formation of the corpus luteum.
This leads to:
- blood vessels contract poorly at the site of rupture;
- a hematoma forms in the corpus luteum;
- intra-abdominal blood flow increases.
The following may also be causes of ovarian rupture:
- inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- hormonal disorders, including those caused by the abolition of contraceptives;
- formation of cysts on the corpus luteum or ovary - large cysts and tumors with a diameter of more than 50 mm most often rupture;
- bleeding disorders due to various reasons;
- excessive stress on the arteries during the onset of the menstrual cycle;
- frequent douching;
- pathologies inside blood vessels;
- formation of adhesive disease on the reproductive organs;
- strong physical activity;
- improper douching;
- excess body weight, which provokes compression of blood vessels;
- visiting a sauna or bath;
- violent coitus;
- horseback riding;
- abdominal trauma;
- bend of the uterus;
- retroflexion;
- compression of the ovary by a tumor of a nearby organ;
- sclerocystosis;
- varicose veins of the ovarian veins;
- rough examination by a gynecologist;
- taking anticoagulants for a long time.
The greatest number of cases of pathology is observed in women aged 25-30 years.
Treatment methods
In mild forms of apoplexy, conservative practice is used, but in most cases there are obvious signs of bleeding. These methods usually include:
- maintaining strict peace;
- use of antispasmodics;
- taking vitamins;
- application of cold to the abdomen;
- use of suppositories with belladonna;
- administration of hemostatic agents.
Reference! When the dangerous period passes, electrophoresis is prescribed, but if signs of increased bleeding appear, immediate surgical intervention is indicated.
As for the surgical method, we will talk about laparoscopy. The only contraindication to its implementation is hemorrhagic shock. The operation is then carried out as carefully as possible so that the internal tissues are preserved as best as possible.
The operation may consist of the following manipulations:
- coagulation of places where tissue rupture occurred;
- resection;
- seam cover;
- oophorectomy;
- andesectomy.
An important point in treatment is washing the peritoneum and removing clots to prevent the formation of adhesions.
Conservative treatment
In order to prevent the negative consequences of ovarian rupture in a woman, the causes of this disease must be eliminated in time. Treatment can be carried out according to the principle of conservative therapy or surgical intervention.
The first method can be used in case of minor blood loss (up to 150 ml) for women who have passed the childbearing period or are not planning a pregnancy in the future.
In this case, the following measures and medications are prescribed:
- "Fenuls", "Tardiferon" and other iron-containing products;
- “No-spa”, “Drotaverin”, “Baralgin” and other antispasmodics and analgesics for pain relief;
- hemostatic agents to reduce pain: vitamins B1, B6, B12, C, Vikasol, Etamzilat;
- a rubber heating pad with ice down the abdomen to provoke vasospasm, which will reduce pain by stopping bleeding;
- the use of belladonna candles;
- resorption therapy is used to prevent adhesions, anti-inflammatory drugs, enzyme preparations, and vitreous are used;
- strict bed rest.
Treatment for ovarian rupture continues after symptoms have subsided. The patient is prescribed electrophoresis with calcium chloride, treatment with Bernard currents, and diathermy.
Conservative treatment in many cases leads to infertility; 50% of women who have undergone such therapy experience relapses. This is explained by the fact that blood and clots, which are removed from the abdominal cavity during surgery, remain in it, contributing to the formation of adhesions in the pelvis.
Rupture of an ovarian cyst (apoplexy): how to recognize and what are the consequences?
Apoplexy, or rupture of an ovarian cyst, is a pathological condition in which hemorrhage occurs in its tissue, disruption of integrity, destruction of the cyst capsule with the release of the contents of the latter and blood into the pelvic cavity.
The disease develops mainly in teenage girls and women of reproductive age. Among acute surgical pathologies it accounts for almost 11%, and among acute gynecological diseases - 10-27%, occupying third place. The number of exacerbations of this complication occurs in 40-69% of women.
What is ovarian apoplexy
Synonyms of the term are the concepts of rupture, hematoma, infarction, and violation of integrity. The pathology occurs in fertile women and is associated with the characteristics of their body, which prepares for pregnancy every month.
Theoretically, every girl once a month has the risk of ending up under the “surgeon’s knife” due to rupture of ovarian tissue. ICD-10 code for ovarian apoplexy N.83 and pathology refers to non-inflammatory processes of the female reproductive system.
Physiology
In the ovaries, follicles grow, inside which the egg matures. With the onset of menstruation, it increases to 18-20 mm, after which its shell “bursts,” releasing a full-fledged female reproductive cell and a small amount of fluid. Instead of a burst follicle, an active corpus luteum is formed, which produces progesterone. The latter is responsible for preparing for pregnancy and if it occurs during the first 12 weeks. This is how monthly ovarian cycles normally proceed.
Due to certain factors, disruptions occur in the process of ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum. At the site of ovarian rupture, the integrity of the blood vessels is disrupted, which leads to intra-abdominal bleeding. At the same time, due to the fragility of the vessels, a hematoma forms in the already formed corpus luteum. Increasing bleeding can be dangerous not only for a woman’s health, but also for her life.
More often, a rupture of the right appendage is detected. This is explained by the fact that it is more intensively supplied with blood from the right ovarian artery, which is directly connected to the aorta, while the left one departs from the renal artery and the blood flow to the left appendages is less. Also, the right ovary is larger in size and weight, and its lymphatic system is more developed. This adds complexity to the diagnosis of pathology: apoplexy is mistaken for acute appendicitis.
Having considered the causes of ovarian rupture in women, we note that the disease has several varieties. So, depending on the clinical manifestations, the following forms of pathology such as ovarian rupture are distinguished:
- painful – accompanied by pain, nausea and vomiting, increased body temperature;
- anemic - resembles in its manifestations a ruptured tube that occurs during an ectopic pregnancy; the main symptom is bleeding.
In addition, there is a classification of ovarian apoplexy according to the amount of blood loss. It is directly used in drawing up an algorithm of medical care. Doctors highlight:
- mild degree - the volume of blood released from the genital organs does not exceed 100-150 ml;
- average – blood loss in the range of 150-500 ml;
- severe - the volume of lost blood exceeds 0.5 liters.
Apoplexy of the right ovary, a painful form, is characterized by severe, piercing pain, which is accompanied by nausea. The picture of an acute abdomen—tension of the abdominal muscles, decreased blood pressure, pale skin, stabbing pain—causes a diagnostic error. Surgeons often mistake the disorder for appendicitis. The absence of external bleeding does not allow a woman to independently identify the disorder and consult a doctor.
Due to the characteristics of the blood supply and dense blood network, apoplexy of the right ovary is more common. The hemorrhagic (anemic) form is accompanied by severe bleeding from the genitals. Often it is internal - blood pours into the abdominal cavity. Characteristic symptoms develop:
- weakness;
- pale skin;
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- dry mouth mucous membranes;
- vomit;
- increased frequency of urination;
- frequent urge to defecate.
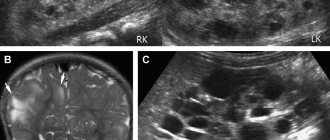
Using ultrasound of the pelvic organs, such changes cannot be visualized. The doctor detects only an accumulation of blood in the retrouterine space. This is how ovarian apoplexy is detected directly on ultrasound. For differential diagnosis, examination of the woman in a chair is required. In addition, to determine a violation, use:
- establishing hemoglobin level;
- puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix;
- laparoscopy.
Characteristic signs of the disorder are acute, unbearable pain in the middle or second half of the menstrual cycle. Menstruation after ovarian apoplexy may be displaced or absent. Direct pain often becomes an indication for a comprehensive examination of the reproductive system. Early diagnosis and timely emergency care eliminate the risk of complications and shorten the duration of the recovery period.
Causes of apoplexy and its consequences
A rupture can occur in the presence of an ovarian cyst of any origin. Most often this happens when ovulation is disrupted, which results in the formation of the corpus luteum with the formation of a cyst of a non-ovulating follicle (the so-called functional cyst). In 90-95% of women with apoplexy, the latter occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle or in its second phase. Of these, during ovulation in approximately 17%, in the second phase of the cycle - in 82%.
The consequences of rupture of an ovarian cyst are mainly the development of adhesions in the pelvic cavity with the subsequent formation of tubo-peritoneal infertility, especially with a conservative treatment method. As a result of the adhesive process, the pregnancy rate after a ruptured ovarian cyst is only about 26%.
The occurrence of pathology during pregnancy
Due to hormonal changes in the body during this period, this phenomenon is rare. But when it occurs, gentle therapy is usually carried out. Sometimes operations are also performed that should not cause damage to the fetus. Treatment is most dangerous in the first trimester of pregnancy, as it can lead to spontaneous abortion.
To increase the chance of pregnancy after surgery, hormonal therapy may be prescribed. A fertilized egg can be artificially implanted into the uterine cavity. In this case, damage to the ovary or even its absence will not affect the further course of pregnancy.
Clinical manifestations
The main symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst are:
- Sharp, sudden pain associated with hemorrhage into the ovarian tissue, with stretching and rupture of its tunica albuginea, with irritation of the peritoneum by spilled blood, as well as with ischemia (impaired blood supply) in the area of blood supply to the corresponding ovarian artery. Ischemia occurs due to compensatory spasm of the artery. Pain appears in the lower abdomen, less often in the area below the navel. It can radiate to the groin area, inner thigh, lumbar region and anus. Gradually, the pain becomes less intense and spreads to other parts of the abdomen. In some cases, an attack of acute pain the day before is preceded by unexpressed and intermittent dull pain, discomfort in the lower abdomen, and soreness in the groin area. These symptoms are associated with excessive blood filling and swelling of the ovary, as well as minor hemorrhages in its tissue.
- Moderate bleeding from the genital tract, quickly stopping as the pain subsides.
- General weakness, shortness of breath, dampness and pallor of the skin, pallor of the conjunctiva of the eyelids, dizziness, and sometimes short-term loss of consciousness.
- An increase in heart rate, a short-term increase in blood pressure (during an attack of pain), followed by a decrease as blood loss into the abdominal cavity increases.
- Nausea, single vomiting, associated with irritation of the peritoneum by gushing blood.
- Increased body temperature, sometimes accompanied by chills.
- In some cases, hemorrhagic shock may develop (with significant blood loss).
If an ovarian cyst bursts, the clinical manifestations may be dominated by pain or bleeding symptoms. Depending on this, the disease is conventionally divided into painful, hemorrhagic (anemic) or mixed forms.
However, when making a diagnosis, the main importance is given to the severity of the condition, which is associated with the amount of blood loss that is immediate or gradual over a short time:
- Mild degree, in which the loss of blood into the abdominal cavity is no more than 150.0 ml.
- Average degree - with bleeding of 150.0-500.0 ml.
- Severe - blood loss exceeds 500.0 ml.
The more pronounced the bleeding, the more clinical manifestations and complaints the patient has. The amount of blood loss is determined by the severity of symptoms (indicators of blood pressure dynamics, pulse rate, pallor and moisture of the skin), blood tests for hemoglobin content, hematocrit indicators, ultrasound data, as well as the amount of blood in the pelvic cavity during diagnostic laparoscopy (if necessary ). The degree of severity determines the choice of treatment tactics.
Research methods
Most often, pathology is examined, paying attention to the patient’s complaints of acute abdominal pain. Also, during the course of research, it becomes clear that pain occurs in the area of the damaged ovary. A general blood test demonstrates the fact that hemoglobin has decreased. After puncture of the posterior fornix, the fact of bleeding is revealed. As a rule, an ultrasound is also performed. Laparoscopy is performed both for diagnosis and for direct correction.
View gallery
Treatment
A ruptured cyst is usually a 1 cm long tissue defect that is covered by a blood clot, causing minor bleeding to quickly stop. This process occurs with a painful form of apoplexy.
In case of satisfactory general condition, stable hemodynamic parameters, absence of liquid contents and clots during echographic examination, that is, in the absence of pronounced signs of intra-abdominal bleeding, conservative treatment is possible. It consists of bed rest, the administration of cold to the lower abdomen, antispasmodic and analgesic drugs orally or in the form of vaginal suppositories, and hemostatic agents.
Surgery for rupture of an ovarian cyst is performed in the event of a repeated attack of pain, a deterioration in the general condition, or obvious intra-abdominal bleeding that causes the patient to have a moderate or severe degree of severity.
Surgical treatment is usually carried out using the laparoscopic method, which allows for preliminary differential diagnosis with appendicitis, perforation of the colon diverticulum, disturbed ectopic pregnancy, torsion of the cyst pedicle, acute inflammatory process of the appendages, etc.
If it is not possible to carry out surgical intervention using the laparoscopic method (abdominal adhesions, intense bleeding and the patient’s serious condition), it is performed via laparotomy (an incision through the anterior abdominal wall parallel to the symphysis pubis).
The essence of the operation is to stop bleeding by electrocoagulating small bleeding vessels or applying a suture in the area of the rupture. If necessary, enucleation of the cyst, resection of the ovary (if the formation is large) or oophorectomy (removal of the ovary) is performed.
Even conservative treatment should be carried out only in a gynecological hospital. A woman’s timely seeking of medical help allows her to save not only her life, but also her reproductive function.
Diagnostics
The disease is determined at the stage of a gynecological examination. The vaginal mucosa becomes pale in color. When pressing, pain is observed in the uterus and in the ovary area.
The most reliable way is ultrasound. Diagnostics shows the presence of fluid and the formation of blood clots.
Apoplexy can also be detected by a clinical blood test. If ruptured, it will show decreased hemoglobin. However, the result is sometimes increased because the blood thickens. For some, the number of white blood cells increases.
Most common reasons
First, it’s worth understanding what a tear or rupture of an ovary is before talking about the reasons.
There are a large number of diseases and various problems associated with the female genitourinary system, so it is simply impossible to know about all diseases without a highly specialized medical education.
Ovarian apoplexy (the name of the disease) is a sudden hemorrhage in the ovary, which is caused by rupture of blood vessels. In this case, blood enters not only the ovary itself, but also into the abdominal cavity, which can cause inflammation of neighboring organs. Let's move on to the reasons why the ovary burst.
- Menstrual cycle. Oddly enough, the cause of the rupture can be normal menstruation. This happens for the reason that the movement of blood in the organs accelerates, and the permeability of blood vessels also increases. That is, any healthy woman or girl can experience a rupture simply because during menstruation, blood moves too quickly through the blood vessels.
- Internal factors. Internal factors, in addition to menstruation, include any diseases that are somehow related to the ovaries. These include the following: polycystic disease, varicose veins of the ovary, inflammation of the appendages, sclerosis, hyalinosis, fibrosis and other diseases.
Causes of ovarian rupture
This is a spontaneous process that is associated with a disruption of the physiological process of the menstrual cycle. Apoplexy is caused by complex pathogenesis and changes in the blood supply to the pelvic organs. More than 90% of cases of gland rupture occur in the middle of the cycle and in its second phase. During ovulation and before the onset of menstruation, the blood supply to the ovarian vessels increases and their permeability increases. This creates the conditions for apoplexy.
Factors contributing to the development of pathology may be:
- inflammation of the genital organs,
- pathologies of ovarian vessels (fibrosis, sclerosis, varicose veins),
- decreased blood clotting,
- adhesions in the pelvic organs,
- hormonal disorders,
- pituitary dysfunction,
- abdominal trauma,
- treatment with anticoagulants,
- stressful situations,
- excessive physical activity, very rough sex.
The impact of these factors leads to the development of sclerotic and dystrophic processes in the ovary. Once ruptured, the vessels are unable to contract, causing prolonged bleeding.
Symptoms indicating a rupture
Ovarian apoplexy manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- Severe sharp pain.
- Weakness that does not go away after drinking invigorating drinks.
- Headache and dizziness.
- Nausea
- Vomit.
- If there is a large loss of blood, fainting may occur.
As for the pain, it is localized exclusively in the lower abdomen, and can radiate to the umbilical area or to the lower back. The pain can be constant or in the form of attacks, be stabbing or like contractions.
Weakness after a rupture may be due to low blood pressure, so be sure to check your blood pressure to confirm the presence of a rupture.
Separately, it is worth mentioning that along with the above symptoms, which indicate that your ovary has burst, you may also experience dry mouth, chills, and frequent trips to the toilet.
Ovarian apoplexy - symptoms
Ovarian apoplexy is expressed mainly by pain and symptoms of internal hemorrhage. The pain is sharp and acute, localized in the lower abdomen, but can move to the navel, lower back, rectum, and perineum. The nature of the pain is also varied: constant or in the form of periodic attacks (lasting from 30 minutes to several hours), cramping or stabbing.
Increasing bleeding during ovarian apoplexy leads to the fact that the pulse quickens or weakens, the skin becomes pale, blood pressure decreases, there is general weakness, fainting, dizziness, dry mucous membranes, chills, frequent urination, nausea, the urge to empty the rectum. Often, after a delay in menstruation, the genital tract produces bloody discharge. If emergency measures are not taken, bleeding into the abdominal cavity may intensify and threaten the woman’s life.
At a mild stage, ovarian apoplexy manifests itself as brief painful attacks, nausea, while shock and peritoneal phenomena are absent. With moderate severity, the pain is pronounced, the body is weakened. Most often accompanied by vomiting, loss of consciousness, stage I shock and mild peritoneal phenomena.
Ovarian apoplexy requires correct and high-quality diagnosis, because its symptoms may resemble peritonitis, renal colic, pancreatitis, ectopic pregnancy, or torsion of an ovarian cyst.
When an ovarian rupture develops, the symptoms are so pronounced that it is difficult to miss the onset of the pathological process. Women notice sudden, sharp pain in the lower abdomen. It is a consequence of irritation of ovarian tissue receptors, the effect of spilled blood on the peritoneum. This leads to spasm of the muscle structures of the lower abdomen. The pain has a clear localization and occurs on the side of the damaged gland. Women note:
- severe weakness;
- dizziness;
- vomiting;
- nausea;
- loss of consciousness.
In the painful form of the pathology, there is no hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity. Blood is secreted into the tissue of the follicle, the corpus luteum. At the same time, the clinical picture of mild hemorrhagic and painful forms is similar. When examining a woman in a gynecological chair, the uterus is of normal size, the ovary is not very enlarged and painful. The vaginal vaults deepen and become free.
Signs of a ruptured ovary can simulate an ectopic pregnancy. Usually, apoplexy occurs suddenly, against the background of completely normal health, more often in the evening or at night.
When an ovary ruptures, sharp paroxysmal pain in the abdomen is characteristic, localized on the right, less often on the left. Occasionally, an attack may be preceded by tingling pain in the groin area on the right or left.
Pain may be:
- paroxysmal throughout the entire time,
- can begin with an attack in the side, moving to the lower back, perineum and then become blurred throughout the abdomen.
As blood accumulates in the abdominal cavity, symptoms of peritoneal irritation appear:
- pain when feeling the abdomen,
- slight bleeding from the vagina,
- tension in the abdominal wall closer to the affected area,
- pallor develops
- increased heart rate,
- decreased blood pressure, lightheadedness,
- tinnitus, nausea, dizziness.
- occasional increase in temperature.
It is necessary to distinguish ovarian rupture from appendicitis and ectopic pregnancy, but often the final verdict is made during the operation.
Consequences of a breakup
Depending on the severity of the disease, the consequences may be as follows:
- Hemorrhagic shock (a critical condition that occurs due to the loss of large volumes of blood; in this condition, all tissues of the body suffer from oxygen starvation, lack of nutrients, as well as the lack of removal of toxins and waste products).
- Peritonitis (inflammation of abdominal tissue).
- Adhesive disease (formation of film compounds in the abdominal cavity, the main task of which is to stop the flow of blood or pus to the organs).
- Fertility disorders (problems related to childbirth, reproductive system).
These are not the most serious consequences of ovarian rupture, since depending on the causes and severity of the disease, in the worst case, death is possible.
Forms
If a woman’s ovaries burst, the reasons will influence what type of disease will manifest itself. About 2.5% of all internal abdominal bleeding occurs due to ovarian apoplexy. There are three forms of this disease in total. Firstly, this is a painful form, which manifests itself in severe discomfort and the absence of signs of internal bleeding. Secondly, the form may be anemic. In this case, the symptoms of bleeding appear more clearly. And in the mixed variety both forms converge.
If an ovary bursts, there may be more symptoms, and modern doctors believe that this classification is incomplete. Someone argues that apoplexy cannot exist without bleeding. For this reason, in the modern classification, depending on the reason for the rupture of the ovary and the consequences, mild, moderate and severe forms are distinguished. The form depends on the scale of blood loss.
View gallery
Treatment and diagnosis
Since the disease is more than serious, the patient requires immediate treatment based on preliminary diagnosis and specialist opinions.
The doctor begins the diagnosis with a general examination, interviewing the patient, studying the medical history, and palpating the skin area. Based on a general examination, the doctor can draw the first conclusions, after which he will send you for an ultrasound scan.
Using an ultrasound, a specialist can only see the accumulation of fluid in the retrouterine space, which will indicate the presence of bleeding. Laparoscopy is performed to see the rupture.
Medication
Let's start with drug treatment of ovarian apoplexy. It’s worth saying right away that surgery can be done only if the hemorrhage is minor, which corresponds to a mild form of apoplexy.
Treatment includes strict rest with the absence of any physical activity, placing cold compresses in the ovarian area, using anal suppositories with belladonna, taking antispasmodics, as well as hemostatic drugs and various vitamin complexes.
Further treatment involves heating the inflamed tissues with currents and electrophoresis.
Surgery
The operation is performed if a moderate or severe form of the disease is diagnosed. During the operation, an incision is made in the abdominal cavity, through which blood and other fluid is removed using a special suction.
If the rupture is caused by a cyst, then it is promptly removed. If the gap is severe, which calls into question the further functioning of the organ, then the ovary is removed. In this case, only the ovary that is severely damaged must be removed, and not both organs.
As for the prognosis after the operation, it is positive. The woman will maintain her health, as well as her reproductive function, but only on condition that the operation was performed by professionals and the patient sought help on time.
Surgery for ruptures
For moderate and severe ruptures, an operation is performed with simultaneous infusion of blood replacement solutions and plasma. During the operation, they try to minimize the amount of intervention - resection of the ovary with damaged vessels is performed. If possible, laparoscopic surgery is performed without incisions, through punctures in the abdominal cavity.
If extensive intervention and removal of blood from the abdominal cavity is necessary, a lower-median laparotomy is performed with a thorough examination of the pelvic organs and abdominal cavity. When performing an operation, surgeons focus on the situation - if a rupture is formed on a healthy ovary, they coagulate the bleeding vessel and apply special sutures. If cysts are found on the ovary, the scope of the operation expands.
Treatment without surgery is possible only for mild forms of the disease, when there are no obvious signs of bleeding and culdocentesis does not give a positive result.
Emergency care in this case includes the following:
- peace;
- applying cold to the stomach;
- hemostatic drugs;
- antispasmodics;
- antibiotics to prevent infectious complications.
After the end of the acute period, physiotherapy is prescribed: electrophoresis using calcium chloride, diathermy, Bernard currents. If the pain intensifies or signs of intra-abdominal bleeding appear, surgery is performed.
In doubtful cases, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed, and the following facts are also in favor of surgical treatment:
- intense abdominal pain;
- detection of free fluid in the abdominal cavity by ultrasound;
- obtaining blood during culdocentesis.
Laparoscopy is the most preferred type of intervention. This is a minimally invasive operation with a short subsequent postoperative period and rehabilitation. After two or three punctures, manipulators are inserted into the anterior abdominal wall, with the help of which the injured area on the ovary is cauterized. The bleeding stops.
If the medical institution does not have laparoscopic equipment or a trained specialist, a conventional laparotomy is performed. The doctor's further actions are the same - suturing the ovary, removing blood from the abdominal cavity.
Recovery
Treatment of ovarian apoplexy ends with subsequent recovery of the body after surgery. All appointments are aimed at correcting hormonal levels, maintaining the reproductive system and generally strengthening the body.
It is necessary to eliminate physical activity for two to three weeks. During rehabilitation for a period of three to six months, the woman is prescribed hormonal therapy using combined oral contraceptives (Zhanine, Novinet, Regulon), taking into account the phenotype and concomitant diseases.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are useful: magnetic therapy, laser therapy, ultrasound, electrophoresis with zinc. Their main effect is aimed at preventing the formation of adhesions in the future.
Disease prevention
We figured out what ovarian apoplexy is, how serious this disease is, taking into account the consequences of lack of treatment. In conclusion, we will briefly talk about the prevention of the disease, and also talk about how to prevent re-rupture of the organ.
To prevent the development of the disease, diseases and illnesses associated with the reproductive system should be treated in a timely manner.
The cause of the rupture can be advanced diseases, such as: adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages), oophoritis (inflammation of the ovaries), cyst, as well as any diseases that are sexually transmitted.
Prevention of relapse is carried out during rehabilitation with the help of drug treatment, which is aimed at restoring the central nervous system, as well as brain function. Tranquilizers and diuretics are prescribed.
Such treatment is necessary in cases of severe and moderate disease to prevent relapse. Now you know why ovarian rupture is dangerous and what symptoms indicate a problem.
It is worth understanding that stopping internal bleeding is quite difficult, while a weakened body can be affected by any infection, so do not try to solve the problem at home with folk remedies, but contact a gynecologist as soon as possible.
Prevention
Timely treatment of gynecological diseases, treatment of vascular pathologies and preventive examinations by a gynecologist will help reduce the risk of ovarian apoplexy. Only a doctor will tell you exactly whether a woman’s ovary can burst, and when this can happen.
Regular visits to the gynecologist are an excellent prevention of apoplexy
In any case, a woman should avoid lifting heavy objects and ensure that sports training is not too intense.
If the first symptoms of pathology occur, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor. Only a qualified specialist will determine the causes and possible consequences of a burst ovary.
Can an ovarian cyst burst?
Often girls develop tumors on the ovaries, which can be eliminated with the help of medications. But the cyst can rupture.
There are types of neoplasms on the ovaries that can appear and resolve on their own within a few months, for example, follicular.
But sometimes it ruptures due to physiological changes. New growths of the corpus luteum may also rupture.
The rupture occurs due to the accumulation of serous fluid in the cavity of a benign formation, which sometimes turns into pus, it puts pressure on the walls, and one day they cannot stand it.
This happens most often from external factors, for example, due to sudden physical exertion. If an ovarian cyst bursts, urgent medical attention is needed.
When a girl knows that she has a cyst, she should be treated and also exclude active sports, sex life and heavy physical activity.
If the cyst has already been ruptured, then you need to adhere to the same methods of prevention, and return to the normal rhythm of life after the operation gradually, without overstraining the body.
An ovary burst: the mechanism of disease development
Hormonal levels are considered to be the fundamental factor in the emergence and development of this disease. One of the main reasons why ovarian rupture occurs is increased concentrations of pituitary gonadotropic hormones, as well as changes in the balance between them. Gonadotropic hormones include prolactin, LH and FSH. Any changes in their quantity and ratio lead to overflow of blood vessels (hyperemia) of the ovarian tissue.
The next most important factor is deviations in the functioning of the higher parts of the nervous system, which are noticeable with REG and EEG. This factor arises as a reaction to stress, poor ecology, excessive emotional activity, and living conditions. Thus, ovarian apoplexy involves not only problems with the reproductive system, but also many other diseases of the body as a whole, especially the nervous system.
What to do to prevent an ovary from bursting
In order to prevent ovarian apoplexy, it is necessary to cure all gynecological diseases (PCOS, STDs, oophoritis, adnexitis, etc.), eliminate factors that provoke this pathology, and regularly go for gynecological examinations. If there is a suspicion of this diagnosis, then it is necessary to immediately call a doctor, placing the patient in a supine position and ensuring rest until she arrives, after putting cold on the stomach.
Ovarian rupture or apoplexy is a pathological violation of the integrity of the ovary and its vessels, which causes bleeding into the abdominal cavity and abdominal pain. During ovulation, the ovary ruptures in the area of the follicle; this is a physiological phenomenon and is not accompanied by pain or bleeding. As a result of pathological changes in the body, apoplexy is formed.