The pancreas is one of the most important organs of the gastrointestinal tract in the human body. Its weight barely reaches 200 grams. The gland is located retroperitoneally, behind the stomach, as evidenced by the name itself, approximately at the level of the first two lumbar vertebrae. The maximum mass of the organ is observed between the ages of 30 and 40 years, and then it begins to gradually decrease in size.
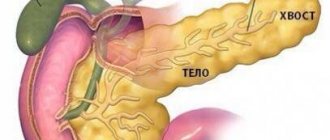
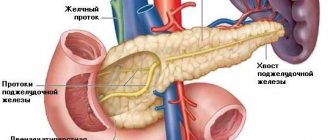
The anatomy in this case is quite simple. The human pancreas consists of three parts - the head, body and tail. The head is slightly thickened, then there is a small section of uniform length and thickness - this is the body. The gland ends with a slight narrowing, which is the tail. The tail touches the left kidney and its vessels (artery, vein), the body touches the aorta and vein, which collects blood from the spleen, and the head touches the renal artery and various vessels of the abdominal cavity.
The functions of the pancreas are very diverse. It is an organ of mixed secretion. What does it mean? The endocrine function is to produce hormones, which include:
- Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood glucose levels. It lowers sugar. If it is insufficient or completely absent, a well-known disease called diabetes mellitus develops, and then patients are forced to remain on insulin injections for life.
- Glucagon - this hormone is also involved in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism, but its effect is opposite to insulin. It increases blood glucose levels. Diseases associated with impaired secretion are much less common.
- Somatostatin is a hormone that inhibits the production and action of somatotropin (growth hormone).
- Pancreatic polypeptide is a substance that is directly involved in the digestive process, helping to fully absorb food.
Main pancreatic duct
The main channel is named Wirsung, in honor of the German scientist who discovered it for science. The main duct originates from the tail part of the organ and stretches to the duodenum 12. The flow of fluid is regulated by the sphincter, which is located at the end of the duct. Its size varies along its entire length - at first it has a diameter of two millimeters, towards the middle it reaches three, and at the edge it is already more than four. In appearance, the canal resembles an arc, which follows the structure of the pancreas.
The duct has small channels along its entire length that flow into it. Their number is individual for each person, and, depending on this, their distance changes. There are two types of ducts - main and loose, with the first type there can be about 35 canals, and with the second type there are more than 60. With the main form, the distance between the ducts varies by about 1.5 cm, but with the second type it is significantly reduced. The length of the main stream can reach 20 centimeters.
Anatomy
This is an oblong organ, about 20 cm long. It occupies part of the retroperitoneal space, the lumbar spine is located behind, and the stomach is in front. Structural parts:
- Head. Close contact with the horseshoe-shaped depression formed by the bends of the duodenum allows the pancreatic ducts to open into this section of the intestine and provide the digestion process with the necessary enzymes.
- Body. It has three sides and resembles a prism. At the border with the head there is a notch for the mesenteric vessels.
- Tail. Directed to the spleen.
The duct of Wirsung runs along the axis of the organ. The organ is located in a connective tissue capsule. The anterior surface of the gland is covered with peritoneum.
Additional ducts in the pancreas area
The pancreatic duct is an accessory duct located in the central part of the pancreas. In most patients, this element is attached to the Wirsung duct. However, in 35% of people it was found that the additional duct is disconnected from the main one and is located above the duodenal nipple. Thus, it forms the Santorini nipple. With such an anomaly, the pancreatic flow independently performs the function of supplying gastric fluid. Pancreatic juice flows through the canal and enters the intestine thanks to the Helly valve, which regulates its flow. Therefore, pancreatic fluid does not enter the gastrointestinal tract.
We also recommend viewing: Spots on the skin due to diseases of the pancreas: causes and treatment methods
In most people, the head of the pancreas has a system of separate ducts. There are only three forms:
- General – originates from the body of the pancreas.
- The lower one makes up the common channel of the head due to its connection with the upper form.
- The upper one begins in the accessory duct, but sometimes connects with the lower form, and then does not have an independent outlet into the duodenum.
Diagnostics
Existing diagnostic methods make it possible to detect minimal pathologies of the ducts. Ultrasound is the most commonly used. With this study, the main duct is clearly observed, it is possible to assess its size and detect narrowing or expansion.
Sometimes some area of the ducts is not visualized or the procedure is difficult (for example, with excess body weight); in such cases, endoscopic ultrasound is used, which is a combination of ultrasound and endoscopy and allows the sensor to be brought directly to the object of study.
The most informative technique is endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).
During the procedure, the doctor, under the control of an endoscope, fills the canals with an x-ray contrast agent, after which he observes the ducts using an x-ray unit. The disadvantage of this method is its invasiveness.
Laboratory tests are also important: a biochemical blood test, determining the concentration of pancreatic digestive enzymes (their deviation from the norm towards a decrease indicates the presence of a problem).
Structural anomalies
More often, an anomaly in the structure of the pancreas is associated with a genetic defect. There was a malfunction during the formation of the organ. In the case where the main duct has two branches, a person has congenital stenosis. Then problems arise in the output channels. In most cases, they narrow, which provokes the development of various pathologies of the digestive system. The most common disease of the pancreas is pancreatitis. It can occur in a chronic form, that is, it forms an inflammatory process in the pancreas. It may also be accompanied by neoplasms in the head of the organ. The formations quite often develop into malignant tumors, and the patient is diagnosed with oncology. If the patient does not start treatment on time, surgical intervention will not be possible. The surgeon needs to remove part of the organ so that nothing threatens the person’s life.
Important. If there are disturbances in the ducts, changes in the water balance may occur, which leads to cystic fibrosis. The biliary tract is directly connected to the duct system in the pancreas. With any pathology with them, a person has problems with digestion and the pancreas.
In addition, the main duct can not only narrow, but also expand. This is a consequence of other disorders. For example, this occurs in the presence of cyst formation or pancreatitis. The main and accessory pancreatic ducts enlarge due to swelling of the soft tissues around the organ. Symptoms appear depending on the diseases themselves. A change in the size of the duct can only be treated with complex therapy, that is, the disease itself must be eliminated. With proper and qualified treatment, the ducts will restore their normal size and function correctly. The most important thing is to pay attention to the emerging signs of digestive disorders in time. Since it is much easier to cure the initial form of the disease. Indeed, in severe cases it will take more time, and it is also possible that the doctor will prescribe surgery. And the removal of part of the organs leads to the fact that the internal systems will no longer function normally, as in a healthy body. You will need to follow a certain diet. To identify violations, it is necessary to undergo a complete examination of internal organs every six months.
We also recommend viewing: Pain in the pancreas, corresponding signs, algorithm of actions
Folk remedies
The use of traditional medicine makes it possible to maintain the results of a therapeutic course, prevent the occurrence of pathological conditions associated with disruption of the bile ducts, and strengthen the biliary system.
St. John's wort decoction
The healing drink has an anti-inflammatory effect. You need to take 1 tbsp. l. St. John's wort, pour 200 ml of boiling water and put on low heat for 15 minutes. After time, the composition must be filtered. You need to drink ¼ cup of the decoction a few minutes before meals 3 times a day.
1 tbsp. l. dry herbs are poured with a glass of boiling water, left for an hour, then filtered. Take ¼ cup 30 minutes before meals 3 times a day.
1 tbsp. l. mint, pour 200 ml of boiling water and leave in a closed container for half an hour. Should be taken 3 times a day in small sips.
Lemon juice
Every day, every 2 hours, it is recommended to take two tablespoons of freshly squeezed lemon juice.
Hercules flakes
You need to infuse Hercules flakes in hot water, cool and take half an hour before meals - morning and evening.
Melon seeds
You need to make flour from dried melon seeds. Pour 1 cup of flour with 1 cup of boiled milk. Leave for 1.5 hours, strain and drink half a glass on an empty stomach in the morning. The method is effective for dyskinesia.
Pancreas spleen canal
Many doctors call this channel the cardinal gray. This is because it affects the body's metabolism and also interacts with the liver and kidney systems. It is involved in the process of cleansing the body of toxic substances. Depending on gender, the spleen canal affects the functioning of other internal organs. In women, it is involved and affects the functionality of the uterus. During pregnancy, it is extremely important that the duct performs its functions normally, as it can affect the gestation of the fetus. In men, the duct is responsible for the quality and quantity of seminal fluid.
Important. The spleen canal has certain currents, thanks to which doctors are able to prevent unwanted pregnancy of the fair sex.
In addition, this duct performs other physiological functions in the body. Blood circulation in the vessels, the state of water balance depend on it, and it also participates in the breakdown of digestive elements, with the subsequent production of the necessary enzymes.
Treatment of the disease
To cure pancreatic stenosis, you should get rid of the root cause of the narrowing of its ducts. After diagnosing and establishing stenosis, the specialist will choose treatment tactics depending on the severity of the pathology. When treating gland stricture, a set of measures is used, which includes a special diet, drug therapy, and surgery - the most effective method.
Diet and lifestyle
Since most often stenosis is a consequence of pancreatitis, therapeutic nutrition for stenosis is prescribed according to that used to correct pancreatic inflammation.
The N5 therapeutic diet for the treatment of glandular diseases begins with several days of fasting. After this, food is taken in small portions (200-300 g) 6-8 times a day for a week. Food on this diet is consumed boiled or steamed, warm and chopped. Diet table N5 involves increasing the consumption of protein foods for 6-8 days, while reducing the consumption of fats and carbohydrates. Salt use is reduced to 5 g per day.
Nutrition for stenosis of the gland ducts excludes soups in broths, except chicken, fatty meat and fish, raw vegetables and fruits with coarse fiber (onions, spinach, radishes, radishes, white cabbage), canned food, seasonings, smoked meats, coffee, bread, flour and confectionery, carbonated drinks. Smoking and drinking alcohol are excluded.
Medication assistance
To eliminate the root cause of stenosis, a specialist may prescribe certain medications. For pancreatitis, especially its acute forms, drugs are used that weaken the production and activity of pancreatic digestive enzymes and detoxifiers. If necessary (if a bacterial infection spreads), antibiotics are prescribed.
- To improve digestion, which is upset due to stenosis, drugs such as Festal, Mezim can be used. They are drunk immediately after eating.
- For acute pain, analgesics are used (Baralgin, in more severe cases - Tramal).
- To relieve spasms, drink antispasmodics Papaverine and No-shpa.
- Since the enzymatic function of the gland is impaired during stenosis, chemotherapy is prescribed to restore it using drugs that replace enzymes. These are Digestal, Lycreaz, Creon, Pancreatin and others.
- To eliminate diarrhea and vomiting, antidiarrheal (Regidron, Tannacomp) and antiemetic (Cerucal, Metukal) agents can be used.
- To restore the functions of the gland, Pancretinol, Bifidumbacterin, Hilak-Forte are prescribed.
It must be remembered that with pancreatic stenosis, self-medication with medications is not acceptable, as it can only aggravate the problem.
Operation
Very often, laparoscopic surgery is used to treat ductal stenosis. Depending on the clinical situation, the following approaches may be used:
- recanalization of the narrowed section of the main duct using endoprosthetics through the skin;
- open reconstruction of the pancreatic duct and bile ducts;
- Less commonly, resection of the head of the gland is performed using bile duct plastic surgery.
Narrowing of the pancreatic duct is one of the disorders that develop against the background of pathologies of this gland. With timely and competent treatment of stenosis, the functions of the organ are restored along with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Source: podzhelud.ru
Norms for the size of the Wirsung duct of the pancreas
The type of main duct depends on the individual characteristics of the human body. More often it resembles an arc in shape, but there is also a knee-shaped type. Patients also have an S-shaped canal, which exactly follows the shape of the pancreas.
In the body, the main duct is similar in its properties to a river into which small streams flow. Their shape and size largely depend on their number. The more channels included in the system, the wider it is. There is a certain standard at which minor deviations are acceptable:
- the head measures about 3.3 mm;
- the body varies in diameter from 2 to 3 mm;
- the tail can be from 1 to 1.7 mm.
Etymology [edit | edit code]
Named in honor of the German anatomist Johann Georg Wirsung (German: Johann Georg Wirsung, 1589-1643) who discovered it. [5]
The pancreatic ducts represent a whole system; large first-order ducts absorb a numerous network of smaller ones. All of them, uniting into one whole, ultimately connect to the main excretory duct. Thanks to this structure, it is possible to supply enzymes in the pancreatic juice produced by the acinus through the gland duct into the small intestine. The enzymes formed in it are delivered into the lumen of the duodenum (DC) through the main duct of Wirsung and the sphincter of Oddi.
Aberrant pancreatic duct
The presence of this duct in the body indicates its anomaly. It is rare, occurring in only 5% of the population. Appears due to disruption of rotation and migration. The duct originates from the head and reaches the valve, which regulates the flow of pancreatic fluid into the duodenum. People with such a defect live full lives, but digestive system disorders can still occur. When the aberrant duct is blocked, chronic pancreatitis relapses.
We also recommend viewing: The main causes and methods of eliminating pancreatic polyps
The normal functioning of the duct systems is important for the functioning of the entire organism. When their size is insignificant, they affect the functioning of the pancreas, kidneys and liver. Any disturbance in these organs causes an exacerbation of existing diseases, and in some cases the development of new diseases. For example, when enzymes are not produced correctly, the body develops the disorder pancreatic necrosis. With this disease, cell death occurs in the pancreas, which leads to death. To avoid such problems with the pancreas, follow the rules in nutrition. First of all, avoid spicy and fatty foods.
Important. They devote more time to physical activities. At the first discomfort, seek help from a doctor.
Function of internal (endocrine) secretion
The parenchyma of the organ forms pancreatic juice, which has an alkaline reaction in order to neutralize the acidic food bolus. The volume of juice per day is up to 2 liters. The basis of the juice is water, bicarbonates, potassium and sodium ions and enzymes.
Some enzymes are inactive because they are very aggressive. These enzymes include:
- trypsin, its inactive form is trypsinogen, which is activated by intestinal enterokinase;
- chymotrypsin, which is formed from chymotrypsinogen by activation with trypsin.
They are proteolytic enzymes, that is, they break down protein together with carboxypeptidase.
Active enzymes:
- amylase - breaks down carbohydrates (starch), also available in the oral cavity;
- lipase breaks down fats that are partially broken down into small droplets by bile;
- ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease act on RNA and DNA.
The structure of the pancreas implies the presence of individual islets of Langerhans, which occupy 1-2% of its parenchyma. A number of hormones are released:
- Beta cells synthesize insulin. It is the “key” for the entry of glucose into cells, stimulates fat synthesis, reduces its breakdown, and activates protein synthesis. Produced in response to hyperglycemia.
- Alpha cells are responsible for the production of glucagon. Ensures the release of glucose from the depot in the liver, which increases blood sugar. Synthesis activates a decrease in glucose levels, stress, and excessive exercise. Inhibits insulin production and hyperglycemia.
- Delta cells synthesize somatostatin, which has an inhibitory effect on the functioning of the gland.
- PP cells synthesize pancreatic polypeptide, which reduces the excretory function of the gland.
Pancreatic juice is secreted when:
- evacuation of the food bolus into the duodenum;
- production of cholecystokinin, secretin and acetylcholine;
- the work of the parasympathetic nervous system.