Causes
So far, doctors cannot name the exact cause that causes torsion.
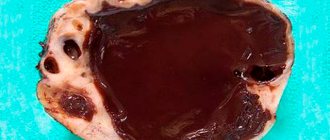
The cyst forms within one month.
In the future, it can either disappear or continue to develop, it depends on changes in hormonal levels.
Against the background of hormonal imbalance, the cyst grows and moves, causing the patient to feel pain. Sometimes it even gets twisted. The reasons for this process are as follows:
- Excessive physical activity. This includes not only regularly lifting weights in the form of grocery bags, but also working out in the gym. In both cases, the body can give its own reaction;
- Making sudden movements. Sometimes the neoplasm is located very poorly, so sudden jumps, running, jerking forward and even carelessly getting out of bed after a night's sleep can lead to the most dire consequences;
- The presence of a weak press in the peritoneum. Doctors often say that a woman should have muscles in the abdominal area. If we are talking about young patients, then the press will help you get into shape as quickly as possible after childbirth, and during the birth of the baby it will allow it to come out without any problems. In the case of those who have given birth, the muscles will help the abdominal organs function normally;
- Constantly full bladder. You cannot endure it for a long time if you feel the urge to go to the toilet. This is fraught, among other things, with torsion of the cyst;
- A sharp decrease in usual weight. In this case, the organs begin to gradually shift because excess fat is absorbed;
- Enlargement of the uterus during pregnancy. There is pressure on other organs;
- Increased pressure in the abdominal cavity due to sudden movements, physical activity or fear;
- Intestinal pathologies. These include constipation and flatulence, increased peristalsis;
- Long stem cyst. This reason is one of the most common. It is the long leg that leads to the pathological condition. Here even a slight change in body position can be a provocateur.
Attention! Doctors note that torsion can occur with medium-sized cysts, since small tumors resolve on their own.
Twist forms
It is necessary to dwell separately on the forms of torsion, since the symptoms that appear and the prescription of further treatment depend on this.
There are two main ones:
- full. The cyst twists 360 degrees. Then the woman will feel severe, almost unbearable pain. Sometimes discomfort forces the patient to sit up abruptly, since the legs cease to serve as support;
- incomplete. The twist occurs approximately 180 degrees or even less. Then the symptoms will appear gradually or not make themselves felt at all.
It is believed that the most dangerous is the full form. However, doctors are convinced that incomplete torsion is much more serious, since against the background of weakened symptoms, women do not pay attention to the problem, but refer to temporary fatigue.
Reasons for the development of the disease
In fact, the causes of ovarian apoplexy can be different. But in most cases, the gap appears against the background of diseases accompanied by dystrophic or sclerotic changes in the ovarian tissue.
- Often apoplexy is the result of progression of polycystic disease. In most cases, such a disease begins against the background of hormonal disorders in a woman’s body. Small cysts are formed in the ovarian tissues, prone to growth - gradually the pressure inside the organ increases, which can result in the rupture of its tissues. In addition, this disease increases the risk of malignant cell degeneration.
- Varicose veins of the ovaries are another cause. Expansion of the lumen of blood vessels and a decrease in their functionality leads to accumulation of blood. There is always a risk of rupture of the vascular walls inside the ovary. This pathology is associated with increased fragility of the venous walls, hereditary predisposition, as well as improper use of hormonal contraceptives.
- Apoplexy may result from oophoritis. Against the background of this disease, inflammation of the ovarian tissue is observed, which is often complicated by severe swelling, formation and accumulation of purulent masses, which, in fact, can lead to rupture. Oophoritis most often develops against the background of infectious lesions (in particular, against the background of the activity of sexually transmitted microorganisms).
- The list of causes also includes sclerosis of the ovarian stroma. The pathology is accompanied by the proliferation of connective tissues, which gradually replace the functional, glandular structures of the organ.
- Hyalinosis is a form of protein dystrophy, which is accompanied by the accumulation of plasma proteins and lipids in the ovarian capsule, as well as on the walls of blood vessels.
- The cause may be various diseases accompanied by blood thinning. The same picture is observed against the background of long-term use of anticoagulants.
- Sometimes apoplexy develops against the background of neuroendocrine disorders, which are accompanied by fundamental hormonal imbalances.
In addition, doctors identify some risk factors that, if there are prerequisites, can provoke ovarian rupture. Their list includes:
- obesity (excess fatty tissue in the peritoneum often compresses blood vessels, disrupting normal blood circulation in the ovaries);
- horse riding, heavy lifting, intense/excessive physical activity;
- abdominal injuries;
- aggressive sexual acts;
- some gynecological procedures.
It is worth noting that sometimes ovarian rupture occurs at rest or even during sleep.
General symptoms
As noted earlier, the symptoms of torsion of the pedicle of the formation can be either acute and pronounced, or appear gradually in a woman.
The main ones include:
- pain in the lower abdomen where the cyst is located. Discomfort appears suddenly, in separate attacks. Localization - upper abdomen. Sometimes the pain radiates to the limbs.
- Nausea and frequent vomiting. It all depends on the degree of pain. Vomiting occurs during the most acute attack.
- General weakness. The woman begins to feel unwell, she wants to lie down, she complains about the inability to walk even a short distance.
- Problems going to the toilet. This refers to gas and constipation.
- The pulse quickens. The patient begins to break out in a cold sweat.
- Rapid breathing. Cells require increased amounts of oxygen, exhibiting a response to severe pain.
- Pallor of the skin.
- An increase in body temperature is a sign of the development of an inflammatory process.
- Tight abdomen, which makes itself felt on palpation.
- Frequent urination. Typically, torsion of the pedicle occurs near the bladder.
- Dry mouth occurs. As a result, a person becomes thirsty.
- Bleeding developing against the background of tissue damage.
Important! If torsion occurs, the patient always takes an unnatural position for her in order to more easily endure the pain. The most beneficial is considered to be pulling bent legs towards the stomach.
When it comes to incomplete torsion, the intensity of the above symptoms decreases. It happens that the cyst itself deforms slowly. Then you should expect a gradual increase in pain, the result of which is a sharp attack.
Treatment
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate; you must fully adhere to the doctor’s recommendations. It is he who, after making a diagnosis, determines therapy. Often it is necessary to perform surgery to untangle the stalk and completely remove the tumor.
It is important to contact a gynecologist as soon as possible, since the further outcome of treatment depends on this. This is especially true for women of childbearing age who are yet to become pregnant.
When a patient goes to the hospital late, there is a huge risk of ovarian pathology. Sometimes they cannot be preserved, so the ability to procreate is lost. After torsion, infections spread even more intensely.
Depending on the patient’s condition, treatment may be as follows:
- when the cyst is small and not malignant, it is simply unraveled. This should lead to normal blood flow. If everything went well here, then the neoplasm will be removed without any fear for neighboring organs;
- when the cyst is unraveled, but blood circulation is not restored on its own, the ovaries have to be removed to prevent the massive spread of infection. Whether it will be possible to save at least one of them depends on how many cysts there are;
- If it is determined that the tumor is classified as malignant, then all ovaries will be removed. The same fate awaits the nearby lymph nodes.
Most often, doctors resort to laparoscopy. This method serves not only diagnostic, but also therapeutic. The consequences of the operation are minimal, and the prognosis is positive.
After surgery, doctors switch to conservative treatment methods. Its main purpose is to reduce pain. For this purpose, various anti-inflammatory and painkillers are prescribed.
The following activities are also recommended:
- bed rest after surgery;
- a diet containing a huge amount of nutrients;
- complete restriction of physical activity.
Hormonal medications are part of the treatment. The operation eliminates the formation itself, but not its cause. The active substance and dosage will be different in each case. When appointments are made, age, the presence of concomitant ailments, and the general condition of the reproductive system are taken into account.
https://youtu.be/hjK9Pb3YZdw
Recovery after treatment and surgery
Adhesions may form in the abdominal cavity due to inflammatory processes after surgery. Scars lead to repeated ovarian apoplexy. To prevent this, doctors prescribe rehabilitation treatment to the patient.
The recovery process after surgery includes physiotherapy methods:
- conducting laser therapy;
- electrophoresis with various drugs that affect the restoration of organ tissue structure;
- ultrasound treatment methods;
- use of microwave therapy.
The gynecologist will definitely recommend that the girl, after treating a ruptured ovary, use hormonal contraceptives until the functions of the organ are fully restored. This should last at least six months after surgery.
Review: Valentina (27 years old) told how she dealt with the consequences after her ovary burst: “I had apoplexy of the right ovary. After examination, doctors diagnosed blood in the abdomen and an ectopic pregnancy. I was operated on. But after that, against the background of weakened immunity, various sores and functional cysts began to bother me. Now my health is gradually returning to normal. I would like to give some advice to women who are faced with this pathology. Firstly, try to move immediately after surgery to avoid adhesions. Under no circumstances should you lie low and do a little exercise. Secondly, try to rest and minimize stress in the first month after surgery. Also take measures to support the immune system. Third, ask your gynecologist to prescribe an effective course of physical therapy.”
Possible complications
In case of torsion of an ovarian cyst and prolonged failure to see a doctor, certain complications cannot be excluded.
These include:
- rupture of the tumor, and this is fraught with the spread of bacteria and infections to other tissues and organs;
- heavy bleeding;
- Necrosis of tissues, including those surrounding the fallopian tubes and ovaries;
- The beginning of the adhesive process, which will remind you of itself from time to time with pain in the form of contractions;
- Ectopic pregnancy. Most often, in patients with torsion, the fertilized egg does not implant in the uterus;
- Constant nagging and aching pain;
- Infertility;
- Damage to one or two ovaries.
To prevent all of the above, you need to pay attention to the first symptoms and immediately go to the doctor with a description of the situation.
What is ovarian cyst torsion?
The phrase ovarian torsion refers to a pathological change in the position of the tumor and/or appendage. There is an inflection and inversion of the anatomical ovarian formations.
Torsion of ovarian cyst symptoms in women:
When the pedicle of an ovarian tumor is torsed, the most pronounced symptom is pain. A pulling, aching, periodic pain is observed when the ovarian structures are not completely bent. It intensifies with physical activity, jumping, and running.
The pain can be so severe that it simulates perforation of internal organs. Pain varies from dull aching to sharp stabbing pain. The woman takes a forced position on her side with her lower limbs bent at the knee joints and brought to her stomach.
Intense pain is characteristic of complete ovarian torsion in women. The pain is one-sided, the abdominal muscles are tense, there is no intestinal motility and no gas discharge.
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Dysuria;
- Pale skin, cold, sticky sweat appears;
- Increase in heart rate and decrease in blood pressure;
- Hyperthermia;
- Bleeding;
- Syncope.
Signs of torsion of an ovarian cyst are not always obvious and can be diagnosed; the clinical picture can be so blurred that a lengthy and thorough examination is required.
Forms of manifestation
In gynecological practice, torsion can involve the anatomical and surgical pedicle:
The anatomical pedicle refers to the connection of the cystic formation with the appendage through the infundibulopelvic (suspensory) ligament, vessels (arterial, venous, lymphatic), nerves, and mesentery.
How to find out that the pedicle of an ovarian cyst has become twisted
Category: Cysts 10/16/2015 1,711
An ovarian cyst is a benign tumor that in some cases disappears on its own. Because of this, you should not think that this is a harmless disease. Complications may arise at any time if a cyst is present.
Dangerous consequences of cysts:
- disruption of organ function due to compression by a large cyst;
- torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst;
- peritonitis;
- infertility;
- malignancy.
Note! If you have been diagnosed with an ovarian cyst and have been prescribed treatment, do not delay it.
Classification
- Full torsion involves rotating the cyst 360 degrees. Due to compression of the tumor vessels, severe ischemia begins, and then tumor necrosis due to the cessation of blood supply. Symptoms in this form are typical of an acute surgical disease.
- Incomplete twisting causes the tumor to receive less blood, but it still does. This option manifests itself as blurry, unclear symptoms. Patients complain periodically and may not seek medical help for a long time.
- Acute torsion causes cessation of arterial and venous blood flow. Tumor cells begin to die, infection sets in, and peritonitis may occur.
- With gradual twisting, blood first stops flowing through the venous vessels. Blood from the cyst does not drain well, accumulates and causes an increase in the size of the ovary. There may be heavy bleeding from the cyst.
Ovarian cysts
Codes:
- N83 - non-inflammatory lesions of the ovary, fallopian tube and broad ligament of the uterus;
- 5 - torsion of the pedicle of the ovarian cyst ICD 10 (1990).
How to find out that the cyst stalk has become twisted
The cyst usually does not manifest itself in any way, but if torsion of the pedicle of the ovarian cyst occurs, the symptoms are pronounced. This condition requires emergency surgery.
Symptoms:
- Severe sharp pain in the lower abdomen. It can be periodic or constant, localized on the side where the ovarian cyst has formed. The pain radiates to the thigh, lower limb, lower back, back, perineum, vagina and anus.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Sharp weakness and cold sticky sweat.
- Sometimes gas and stool stop passing, and the stomach becomes bloated and tense.
- Heart rate 90 beats per minute or more.
- Breathing is rapid, more than 20 respiratory movements per minute.
- Body temperature rises to 39°C, chills are possible.
- Reduced blood pressure.
- The patient's skin and visible mucous membranes become pale.
twisted (twisted) ovarian cyst
Important! If the symptoms described above appear, do not hesitate to call an ambulance.
Diagnosis
The doctor collects complaints and a history of symptoms. Twisting of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst is usually promoted by physical activity, dancing, weight lifting, pregnancy, childbirth, weight loss, and tumor enlargement.
When examining the abdomen, tension in the abdominal muscles and painful pressure will be noted. A vaginal examination will reveal a formation on the affected side in the area of the uterine appendages. The tumor has an elastic consistency and is sharply painful when pressed and displaced.
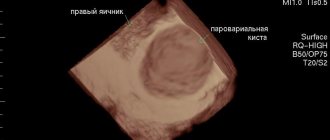
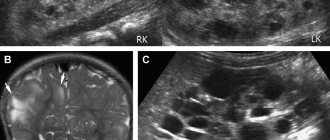
In blood tests, the patient will have an increase in the content of leukocytes and an acceleration of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). An accurate diagnosis can be established by ultrasound of the pelvic organs with a transvaginal sensor. This study confirms the presence of a cyst and inflammatory fluid in the pelvis.
Treatment
If torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst is detected, emergency care consists of immediate hospitalization and surgical intervention.
torsion of ovarian cysts treatment
An endoscope is inserted into the abdominal cavity through the hole and the condition of the ovary and tumor is assessed. Instruments are inserted through other pinholes and the cyst stalk is untwisted. If blood circulation in the ovary is restored, the cyst is removed. If the vessels do not function, then the ovary is removed.
If complications arise (peritonitis, tissue necrosis), the operation is performed with an expanded incision (laparotomy). The non-viable ovary and fallopian tube are removed, and the excised material is sent for histological examination. It is studied in the laboratory to detect cancer cells.
The woman’s further quality of life after twisting the pedicle of an ovarian cyst depends on the timeliness and technique of the operation. This is a very serious condition, so if you have an ovarian cyst, regularly visit your gynecologist and have an ultrasound scan. If conservative treatment does not help, then elective surgery is preferable.
vseomatke.ru
Methods for diagnosing ovarian pedicle torsion
Diagnosis of torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumor includes several stages and mandatory studies in order to establish the location and size of the ovarian tumor.
- examination of the patient:
- collection of anamnesis of illness and life.
Based on primary data, laboratory and instrumental examinations are prescribed.
Gynecological examination
Vaginal examination may be difficult due to intense pain.
The patient is placed on a gynecological chair.
When palpating the suprapubic zone on the right or left side, a tight-elastic formation is detected; when pressing and trying to move it, painful attacks occur. During the examination of the abdomen, positive peritoneal symptoms of varying severity are noted.
Laboratory research
There are no specific indicators for torsion of a benign tumor. In the blood test, you can notice slight leukocytosis and an acceleration of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The leukocyte formula shifts to the left. Changes in the general urine test are observed with concomitant urogenital pathology: leukocyturia, cylindruria, protein in the urine, bacteria.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound plays an important role in diagnosing ovarian torsion. An ultrasound sensor can be used to examine and differentiate the cyst. The shape, size, location and structure of the pedunculated cyst are determined. When a benign cavity tumor is twisted, the contours are blurred, the capsule seems to consist of two layers, which signals its swelling.
Possible complications:
Refusal of medical care or failure to provide measures to improve the condition of ovarian torsion leads to complications in both girls and women. The result can be infertility, disability and even death.
Complications and risks for reproductive health:
- Necrosis of the leg, separation and temporary imaginary lull. The woman’s condition improves for 10–24 hours, and then worsens significantly;
- Development of peritonitis;
- The spread of inflammation to the reproductive organ and fallopian tubes, which serves as an indication for hysterectomy;
- Intra-abdominal hemorrhage, loss of blood is dangerous due to hemorrhagic shock;
- Adhesive process after an untimely operation;
- Ovarian apoplexy and removal of the appendage (oophorectomy).
Emergency care for torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst
Help with cyst torsion comes down to calling an ambulance and taking a comfortable position with your knees brought to your stomach (“fetal position”).
After hospitalization, the woman is urgently examined and a decision is made on surgical access; laparoscopy is preferable, however, in some cases laparotomy is performed.
Treatment
As a rule, conservative therapy is ineffective, therefore surgery is indicated; the execution time depends on the degree of neglect of the inflammatory process, on average it lasts from 40 minutes to 3 hours.
To excise a benign formation, the following techniques can be used:
- Cystectomy – cutting off the stem and cyst, preserving the possibility of further conception of a child;
- Wedge-shaped excision of the ovary - partial removal of the appendage when it is involved in the process;
- Oophorectomy – total removal of the appendage;
- Adnexectomy – elimination of the ovary and fallopian tube from the affected side.
In the postoperative period, the woman is prescribed antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and detoxification agents. If necessary, select an individual dose of hormonal drugs, immunomodulators and blood substitutes (fresh frozen plasma, washed red blood cells, cryoprecipitate, albumin).
Preventive actions
Primary prevention of torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumor is aimed at preventing the formation of tumors, inflammatory processes and sexually transmitted infections. Regular examination by a gynecologist is important - at least once a year.
Secondary prevention is aimed at preventing complications of a benign ovarian tumor, such as torsion of the pedicle, rupture of the capsule, etc. A woman should regularly undergo ultrasound to monitor the dynamics of cyst activity.
Women diagnosed with a cystic formation should remember about possible complications requiring emergency hospitalization. Timely treatment, normalized physical activity, non-aggressive types of coitus, a balanced diet and regular bowel movements can reduce the risk of complications.
Torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst is a fairly common complication that occurs as a result of bending or twisting of the tissue structures of the neoplasm. This condition is considered very dangerous and, in the absence of timely assistance, can lead to the death of the patient.
What does it come from?
To date, the exact reasons leading to the development of torsion of the cyst formation have not been established. It is believed that this pathology can be caused by hormonal disruptions, as well as topographic changes in the internal organs. In addition, there are a number of factors that contribute to the formation of torsion. These include:
- Inflammatory processes in the body.
- Weak abdominal muscles.
- Pregnancy.
- Physical overload.
- The birth process (difficult labor is especially dangerous in this case) and the postpartum period.
- Sudden change in body position.
- Increased blood pressure in a tumor neoplasm.
- Overfilling of the bladder cavity.
- Increased peristalsis in the small or large intestine.
- Active sports.
- Straining, physical work, heavy lifting.
- Changes in pressure in the intra-abdominal cavity.
- Constipation.
- Movement of a tumor into the abdominal cavity from the pelvic area.
- Flatulence.
- A sharp and significant increase (or, conversely, decrease) in the patient’s body weight.
- Asymmetry of the neoplasm.
- Age factor (young women under the age of thirty-five are most susceptible to this pathology).
Is it possible to treat at home?
Ovarian rupture is a pathology that cannot be cured on its own. Large blood loss can lead to death within a few hours. Therefore, at the first signs of this disease, you should immediately call an ambulance.
There is also the possibility of another dangerous complication, which is caused by hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity - peritonitis. Symptoms of ovarian rupture are similar to other dangerous pathologies that require immediate surgical intervention (appendicitis, intestinal perforation and ectopic pregnancy).
Important! The only thing that can be done in case of suspected apoplexy is to take a horizontal position.
You cannot self-medicate, do not try to relieve pain or apply ice to your stomach. It is prohibited to use folk remedies, as these “experiments” can affect the girl’s health or pose a threat to life.
Types of torsion
Torsion of the pedicle of a cystic formation in the ovaries is usually divided into two types: complete and incomplete. Let's look at them in more detail:
- Complete torsion of the tumor pedicle is torsion of the tumor by 360 degrees or more. This type of pathology is characterized by pronounced symptoms and a complete cessation of blood supply to the cyst.
- Incomplete torsion of the tumor pedicle is torsion of the tumor less than 360 degrees. This type of torsion is characterized by impaired blood circulation in the area of the cyst. This type of pathology is the most difficult to diagnose because it has mild symptoms.
In addition, depending on the speed of development, torsions are divided into acute and gradual forms. With gradual torsion, compression of the veins is observed, leading to overflow of the vessels and an increase in the size of the tumor. This condition is dangerous due to bleeding into the peritoneal cavity or hemorrhage into the ovarian tissue.
Acute torsion is invariably accompanied by impaired arterial circulation, which is fraught with necrosis of cystic tissues with accompanying infectious and septic complications, the most common of which is peritonitis.
Forms and types
Doctors note that among the main causes of hemorrhage in the abdominal cavity, up to 2.5% of cases are due to ovarian infarction.
There are three forms of this pathology, which are classified depending on which symptoms predominate:
- anemic or hemorrhagic form (the main symptom is increasing internal bleeding. The pain syndrome is not pronounced);
- painful form (pain sensations are pronounced, but there are no signs that there is intra-abdominal bleeding);
- mixed form (combines the characteristics of the first two forms. In this case, both small and large vessels, as well as tissues, are ruptured).
Signs of torsion
The symptoms of torsion of the pedicle of a cystic ovarian neoplasm largely depend on the form and type of pathology, as well as on the speed of its development. In general, the following symptoms are characteristic of this condition:
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower extremities, lower back and back.
- Nausea and bouts of vomiting.
- Pallor of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Constipation.
- Possible increase in body temperature.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Increased sweating.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Decreased muscle tone.
- Abdominal wall tension.
- A sharp decrease in blood pressure. Possible hypotensive crisis.
- Tachycardia.
- Vaginal discharge of a bloody nature.
- Possible fainting.
- Bloating.
- Feeling of dry mouth.
- General weakness.
In the case of incomplete torsion and a gradual form of development of the pathology, as well as in elderly patients or, on the contrary, too young, the symptoms are less pronounced. However, you should know that torsion of the pedicle of a cystic neoplasm is a dangerous condition, fraught with numerous negative consequences. Therefore, if you detect at least a few of the above signs, you should immediately seek medical help.
Surgical intervention for apoplexy
Most often, apoplexy is treated surgically. In this case, laparoscopy is performed. This procedure has many advantages:
- To begin with, it is worth noting that this is the most gentle method, since the instruments are inserted inside through small punctures in the abdominal stack (no large scars are left on the skin);
- after this type of operation, the reproductive functions of the reproductive system are most often preserved;
- the rehabilitation period does not last long, there is no pain syndrome;
- the risk of tissue infection is minimal.
The technique largely depends on the form of apoplexy, the volume and rate of blood loss, as well as some other tissues.
- In most cases, the doctor simply carefully stitches the torn ovarian tissue back together.
- If necessary, coagulation of ruptures is carried out - a special bipolar coagulator is used for this purpose.
- Sometimes the affected ovarian tissue is excised and then sutured. At the same time, the formed adhesions can be removed.
- Complete removal of the ovary is carried out only if there is complete damage to its tissues or massive bleeding.
During the rehabilitation period, women are prescribed special medications. In addition, various physical therapy methods are used, including lidase and zinc electrophoresis, ultrasound therapy, magnetic therapy and electrical stimulation of the fallopian tubes. Such procedures help prevent the development of various complications, in particular adhesions.
Possible complications
The pedicle of the cyst is the main source of nutrition and blood supply to the neoplasm. When it is torsioned, compression of the blood vessels occurs, accompanied by significant disruption or even complete cessation of blood supply to the ovarian cyst. This process causes the development of inflammatory processes, necrosis of tissues and tumor structures. In some complex cases, torsion affects both the fallopian tubes and the so-called intestinal loops. In addition, this condition can lead to the following complications and consequences:
- Chronic pelvic pain.
- Necrosis of the fallopian tubes.
- Tumor bleeding.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Infertility.
- Formation of adhesions in the peritoneal cavity.
- Peritonitis.
- Fusion of the neoplasm with internal organs.
Distribution of pathologies by type
Ovarian apoplexy affects only women of reproductive age.
The process of rupture of the cyst and the organ itself is closely related to the production of eggs. If for any reason the functioning of the female reproductive system is disrupted, then there is a risk of a neoplasm. If these pathologies are not diagnosed in time, this threatens to rupture the cysts and ovary. In especially severe cases, apoplexy is complicated by intra-abdominal bleeding and peritonitis. The 10th revision classification of diseases identifies the following subtypes of apoplexy:
- No. 83.0. This designation codes for follicular cysts. Within this subtype, hemorrhagic follicular cysts and Graafian follicle cysts are distinguished.
- No. 83.1. This is what corpus luteum cysts are called. They are also called hemorrhagic neoplasms of the corpus luteum.
- No. 83.2. This subtype includes such neoplasms as retention and simple ovarian cysts. All unspecified neoplasms that resemble a cystic disorder are also included in this subtype.
All of the above subtypes form 1 large group, called non-inflammatory lesions of the ovary, fallopian tube and broad ligament of the uterus. Such pathologies can have serious negative consequences for a woman, so therapy must be started in a timely manner. At the first alarming symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst is carried out on the basis of a detailed study of symptoms, the general clinical picture, and the results of the anamnesis. A thorough gynecological examination using palpation and vaginal examination is required. They make it possible to identify the degree of tension in the abdominal muscles, possible inflammation in the layers of the peritoneum, characteristic of torsion.
To clarify the diagnosis and determine the form, type and stage of development of the pathology, the patient is prescribed the following procedures:
- Ultrasound examination to detect the presence of a tumor with a twisted base, the presence of an inflammatory process in the peritoneal cavity.
- Laparoscopy is a procedure that involves inserting a special endoscope equipped with a camera into the peritoneal cavity. This study allows not only to detect the presence of a neoplasm, but also to assess the condition of the internal organs and the degree of their involvement in the torsion process.
- General blood analysis.
- Radiography. It is carried out to exclude the presence of salpingitis, renal colic and acute appendicitis, which are similar in their symptoms to complete torsion in the acute form.