2
Hallux valgus is a disease of the musculoskeletal system that causes changes in the alignment of the bones. Under the influence of a number of certain factors, a bump appears on the foot, which causes serious discomfort to a person. Most often, the pathology occurs in women who like to wear narrow high-heeled shoes.
In men, the disease can occur exclusively after injury or due to a genetic predisposition. If treatment for hallux valgus is not started in a timely manner, a person may experience serious complications. In this case, surgical intervention is indicated.
Factors influencing the development of hallux valgus in a child
Hallux valgus in children can be a congenital anomaly or an acquired pathology. In all cases, this is an incorrect position of the feet in relation to each other. The changes lead to the fact that the main load when walking falls on the inner surface of the foot. The presence of symptoms in children under 3 years of age indicates intrauterine changes. The diagnosis is made by an orthopedist after a thorough examination.
Factors that trigger the development of pathology include:
- lack of nutrition;
- improper diet;
- lack of vitamins and minerals in the body (calcium and/or vitamin D deficiency), leading to fragility and softness of bone tissue;
- early rise of the child to his feet;
- incorrectly selected shoes;
- frequent acute respiratory infections;
- ankle injuries;
- prolonged immobility of the lower limb due to being in a cast.
If a child begins to walk early (before 1 year of age) or his parents force him to do so, in many cases the foot becomes deformed. At an early age, the formation of the ligamentous apparatus occurs, which is often not ready for stress.
Causes of the formation of hallux valgus
Congenital anomalies in the development of the musculoskeletal system in children are deformations that develop in utero and appear after birth. The degree of curvature in the case of congenital hallux valgus is very pronounced. This is due to various malformations of individual elements of the musculoskeletal system, anomalies in the fetus of genes or chromosomes. There is a violation of the location of the bones of the foot and their shape in utero. Deformation of the feet appears already in the first months after the baby is born.
An example of a genetic disorder is Edwards syndrome, an abnormality of a certain chromosome that causes a severe degree of valgus curvature of the foot of a newborn - rocker foot.
Other causes of congenital hallux valgus in a child include a number of pathologies that are diagnosed from the first weeks of life:
- in 80% of cases - connective tissue dysplasia with congenital hip dislocation;
- myodystrophy;
- cerebral palsy;
- polio and other infections of the central nervous system;
- neuropathy – pathology of peripheral nerves.
The acquired form of valgus is the result of the influence of one or several factors after the birth of the child. Initially, the main reason is a weak ligamentous apparatus of the foot, which causes a violation of its correct position. This condition is diagnosed in the first days after the birth of the child. The development of pathology can be influenced by:
- prematurity or low birth weight;
- overweight child;
- endocrine pathology (diabetes, hypothyroidism);
- metabolic disorders (osteoporosis, disorders of fat and carbohydrate metabolism).
Surgery for hammertoe deformity
As is known, in the later stages of Hallux Valgus it is combined with hammertoe deformity of the II-V fingers. It looks unattractive and negatively affects the functions of the foot. To correct it, a number of surgical interventions are used.
These include:
- Closed redressing.
The essence of the technique is to forcibly correct the defect non-surgically. Unfortunately, redressal has little effect, and relapses often occur after it. - Tenotomy or tendon transposition.
Operations are performed on the ligaments of the foot. Their skillful intersection or movement allows you to correct hammertoe deformity. - Bone resection.
During surgery, doctors excise the base of the middle or head of the main phalanx. This allows you to get rid of excess bone mass and eliminate deformation. - Weil or Wilson osteotomies.
They resemble Scarf and Chevron operations, but are performed on the II-V metatarsal bones. Surgeons cut them open and then fix the bone fragments with titanium screws.
Osteotomy is most effective in treating hammertoe deformity. This is what is performed in the most severe and advanced cases.
Visible signs of pathology
Nagging pain in the legs at the end of the day is the most common complaint of a child with planovalgus foot deformity. Objectively, the pathology is manifested by the following general signs:
- unsteady gait, shuffling, waddling when walking from side to side;
- the formation of calluses or corns on the sole;
- constantly spread fingers;
- Difficulty when trying to place your heels together.
There are three types of valgus:
- Transverse - expansion of the forefoot with pronounced tension in the muscles and tendons that are responsible for the extension movements of the toes. This causes nagging pain in the child.
- Longitudinal - manifested by a change in gait, shape of the foot (severe pain appears when it is palpated), fatigue from being on your feet for a long time due to discomfort and pain.
- Combined.
Flat feet
The problem may be congenital or acquired. In the second case, the causes of flat feet are: rickets, trauma, regular overload of the affected area, or so on. With this pathology, there is a drooping of the transverse and/or longitudinal arch of the foot, which is normally supported by muscles, bones and ligaments. There are three degrees of the disease: the first is almost asymptomatic (discomfort occurs only after long walking), in the third, posture and gait are disturbed, and movement is accompanied by constant pain.
What and how to treat?
Correction of hallux valgus in children involves restoring the normal position of the joints, muscles and ligaments of the legs. The goal of treatment is to be able to walk without pain or discomfort. Therapy must be comprehensive. To treat hallux valgus in a child, the following are used:
- conservative;
- operational;
- an alternative method (osteopathy - allows you to cure almost any pathology, except genetically determined).
Conservative includes:
- medicinal;
- kinesio taping;
- orthotics;
- physiotherapy.
Medicines
Medications for X-shaped curvature of the lower extremities are used to relieve inflammation and relieve pain in the joints. Taking NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) or GCS (glucocorticosteroids) is prescribed for symptomatic purposes. They act for a short time and are dangerous for the child’s body due to side effects.
The tablet is not always suitable for a small child, so intra-articular administration of drugs (Diprospan) is used.
New techniques
A modern method of treating hallux valgus is kinesio taping, an innovative method for the treatment and prevention of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. It is based on a non-drug effect on muscles using a special tape - kinesio tape. The name of the method was formed from two words: “kinesio” means movement, “tape” - the actual tape. It consists of applying special tapes made of elastic material with an adhesive base that does not cause allergies. The taping method was developed several years ago by Japanese doctor Kenzo Kase for the treatment of sports injuries. Later it became widespread. Kinesio taping for hallux valgus in children has been widely used recently. This is due to the safety of the technique: when using it, there is no restriction of movement, discomfort, and allergies do not occur.
Fabric from which the tape is made:
- has a fibrous structure;
- allows air to pass through well;
- does not retain sweat;
- does not lead to pain or discomfort;
- does not hinder movements;
- not afraid of water - you can swim without removing the tape.
Proper taping (sticking tape) accelerates the recovery of joints, ligaments and muscles without the use of drugs, and can stop the progression of pathological changes. This safe method helps:
- pain relief;
- preventing further progression of the disease;
- complete recovery.
Kinesio taping rules:
- The tape is applied only to clean, dry skin;
- for longer use of kinesio tape, it is necessary to round its edges;
- After gluing, the tape is rubbed, activating it.
Kinesio tape is applied for 3-5 days, after this period its properties are gradually lost. After bathing, blot with a soft towel; rubbing is not recommended. When peeling off the edges of the tape, you must carefully cut them off. The patch is removed after wetting it with a special solution.
Effect of massage
When the arch of the foot flattens, the muscle tissue changes, which leads to poor circulation, and subsequently to the development of irreversible processes. Therefore, massage is an indispensable part of treatment. This is one of the physiotherapeutic methods of influence. No special skills are required to perform it, so you can do it at home. The course consists of 10 sessions, if necessary it is recommended to repeat it every 3-4 months. The total time of one session is 20-30 minutes. You should start with a general massage - the child is lying on his stomach with his arms extended along the body and his head turned to the side. Movement and pressure of the hands should cause pain.
Name of surgical techniques
In the initial stages of the disease, doctors try to perform minimally invasive operations. After them, the patient recovers quickly and returns to his normal lifestyle within 3-4 weeks. With advanced hallux valgus deformity, the need for more complex surgical interventions arises.
Let's see which of them are most often used in modern orthopedics.
Operation McBride
The most popular among all surgical interventions on the soft tissues of the foot. Its essence is to move the tendon m. adductor halluces on the head of the first metatarsal bone. This allows you to bring the metatarsal bones closer together and restore the normal muscle-tendon balance of the foot.
McBride.
Unfortunately, the abductor pollicis muscle is unable to withstand constant stress. This is why the relapse rate after McBride surgery is quite high. If a person does not eliminate the effect of provoking factors, he will soon develop Hallux Valgus again. Wearing orthopedic shoes, avoiding heels and heavy physical work helps to avoid this.
Fact! In case of pronounced deformities, the McBride operation is supplemented with SCARF osteotomy of the first metatarsal bone.
SERI
Refers to minimally invasive operations. During surgery, patients undergo a transverse osteotomy through a 1 cm long skin incision. After this, the distal bone fragment is shifted in the lateral direction and fixed using a special wire.
SERI.
CHEVRON
During the operation, the surgeon performs a V-shaped osteotomy
. He saws the first metatarsal bone in the area of the head, and connects the bone fragments using special titanium screws. Since the fixation is very strong, the patient does not need plaster immobilization in the postoperative period.
CHEVRON.
Note that Chevron osteotomy is effective only for minor deformities of the first toe. Nowadays, it is used less and less in orthopedics. Instead, most doctors perform a Scarf osteotomy.
SCARF
The Scarf Z-shaped osteotomy is the gold standard for the treatment of hallux valgus. It allows you to set the head of the metatarsal bone at the desired angle. During surgery, doctors also remove deformation of the joint capsule and change the direction of some tendons.
SCARF.
When Scarf surgery is not enough, surgeons perform a proximal wedge osteotomy or arthrodesis.
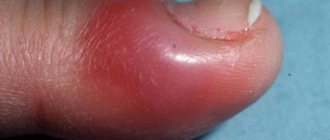
Important! In most patients with hallux valgus, doctors detect callus (exostosis). The growth is localized on the medial surface of the head of the first metatarsal bone. As a rule, it is removed during all operations, including minimally invasive ones.
Do not confuse cutting down a bone spur with an osteotomy. These are two completely different manipulations. The goal of the first is to remove a cosmetic defect, the second is to restore the normal functional state of the foot. Remember that callus removal (Schede procedure) will not cure you of Hallux Valgus.
Possible consequences of hallux valgus in children
Valgus feet lead to changes in the entire musculoskeletal system. This is due to the unevenly distributed load. Occurs:
- shortening or deformation of the legs;
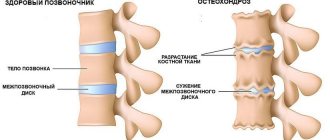
- osteochondrosis;
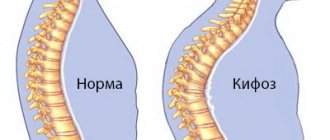
- scoliosis of different parts of the spine.
The hip, knee, heel joints, bones of the hip joint and ankle change - arthrosis develops.
The child has:
- gait deteriorates;
- Physical activity (running, active games) becomes impossible due to pain and inflammation in the joints.
Symptoms
During movement, the load on the foot is unevenly distributed.
In infants and older children, valgus curvature of the legs looks like an X-shaped deformity, in which the child’s knees are connected, and the ankles diverge in different directions, simultaneously turning inward. The heel and toes are retracted to the outside, because of this, a change in gait is observed - when walking, the entire load is concentrated on the middle part of the foot. The muscle that moves the toes becomes deformed, causing the big toe to bend.
Over time, the ankle ligaments weaken, and a 3-year-old baby will walk unsteadily, clumsy, and shuffle his feet. Swelling of the feet in children is often observed; the baby refuses to walk for a long time, because the legs quickly get tired and begin to hurt. If foot valgus is not treated, the spine and joints of the lower extremities begin to suffer, flat feet, osteochondrosis, arthrosis, and deformation of the pelvic bones develop.
Dr. Komarovsky about hallux valgus and flat feet
The famous children's doctor and author of books on children's health, Dr. Evgeny Komarovsky, believes that to prevent valgus, early standing of a child is unacceptable. Average statistical medical standards indicate an approximate age for the onset of walking to be 9-15 months; in his opinion, the child cannot be rushed. This leads not only to disruption of the anatomy of the foot, but also to spinal disease.
From birth, every baby has flat feet - this is a feature of babies. The arch of the foot is formed gradually as the legs grow and receive loads. The formation process is completed by the age of 12. Dr. Komarovsky believes that the problem can and should be corrected before this age.
Cost of foot surgery
The cost of surgical treatment depends on the degree of deformity, the type and complexity of the operation, the level of the medical institution and the qualifications of the specialists working there. Removal of exostosis in Moscow costs from 40,000 to 50,000 rubles. Prices for reconstructive operations start at 70,000 rubles. Please note that the price does not include preoperative examination, specialist consultations, consumables and rehabilitation.
If you want to have surgery abroad, pay attention to the Czech Republic. Treatment there will cost you in euros including rehabilitation. In Germany and Israel, the same operation will cost much more.
Prevention of the occurrence and development of the disease
Prevention is aimed at strengthening the articular and muscular-ligamentous apparatus in children. Basic rules for preventing the disease:
- Compliance with the regime and daily routine: balanced nutrition, hardening, therapeutic exercises, massage, good sleep.
- Elimination of heavy loads on the legs before 9-12 months - you can stand the baby for a very short time, always supporting him.
- Early specific and nonspecific prevention of the development of rickets. During pregnancy, you need to go out into the sun more often (vitamin D promotes the absorption of calcium and phosphorus in the bones and is produced in the skin under the influence of ultraviolet rays).
- Attending medical examinations: the sooner foot pathology is detected, the easier it will be to cure it.
- The use of massage, physical therapy, and orthopedic devices can eliminate defects in the development of joints in the early stages.
Choice of treatment tactics
The choice of surgical intervention method is entirely determined by a qualified attending physician. He will send you for an extensive diagnostic examination, which will determine the most appropriate and safe treatment tactics. It is necessary to determine whether the periosteum is involved in the inflammatory process, whether there is a cyst, arthritis and other complications. When determining the method of exposure, it is also important to determine the degree of deformation. To prepare for surgery, a person is sent to physical therapy, massage or physiotherapeutic procedures.
It is also recommended that a person wear special orthopedic insoles before surgery. With their help, it is possible to reduce the load on the joints, which has a positive effect on well-being. Keep in mind that the sooner you contact your doctor, the faster the pathology can be diagnosed. In the initial stages, it is much easier and faster to get rid of it, and the risk of dangerous negative consequences is significantly reduced.
Many people think that surgical treatment of bunions is a dangerous procedure that should be avoided as long as possible. In fact, the earlier the surgery is performed, the higher the likelihood of a full recovery.
Remember that the operation is performed under full anesthesia - you will not feel any discomfort. On average, the recovery period lasts several weeks. After this time, you can return to a normal lifestyle.
Medical and physical training complex
Special physical exercises are prescribed by an orthopedic doctor or rheumatologist, selecting the type of physical exercise for each patient individually. Active exercises for flatfoot in children help strengthen the ankle and plantar joints and form the arch. For adults, prolonged exercise helps:
- increase blood circulation;
- relieve inflammation;
- reduce pain.
The physical therapy complex will be especially effective for the second and third degrees of pathology. You need to play sports continuously throughout the course of treatment, and sometimes gymnastics continue even after the end of therapy. You can perform the exercises at home, with the means at hand, or by purchasing special orthopedic gymnastics supplies in the store: massage mats, spiked balls, plastic sticks. Examples of exercises:
- walking along a narrow path (an inverted bench), in a herringbone pattern, on a triangular board, on a rope;
- rolling a ball with spikes;
- passing the rubber hedgehog to each other.
Gymnastic exercises can be performed with or without music, in a relaxing, cozy environment. For planovalgus deformity of the legs, classes are carried out daily, each exercise is repeated 3-4 times. What will help your child:
- Walking in a narrow lane. You can draw it yourself or make it from thick fabric. You cannot go beyond the boundaries of the line.
- Walking on a mat with a grooved surface.
- Pulling the toe towards you and turning it inward. The exercise must be performed while sitting on a hard chair.
- Walking around the room on the inside of the sole.
- Grabbing small objects from the floor with your toes - special sticks, pencils, balls. To make the exercise more difficult, you can hold objects with your fingers for a few seconds.
- Squatting in place without lifting your legs off the floor. If your baby is doing the exercise, support him with your back to prevent him from falling.
- Rising to full height from a “sitting cross-legged” position. You need to sit so that your legs are bent at the knees and your soles are crosswise.
- Alternate or simultaneous lifting on your toes, followed by rolling onto your full leg.
Degrees
The extent to which deformation of the feet in children can develop and be expressed can be seen by dividing them into degrees of deviation from the norm in degrees:
- light – 10-150°;
- average – 160-300°;
- heavy – more than 300°.
In addition to this indicator, the following types can be distinguished:
- static – poor posture;
- structural – congenital pathology in which the talus bone is located in a vertical position;
- paralytic - a complication after diseases such as encephalitis and polio;
- rachitic – corresponds to the name and is a consequence of rickets, and can also develop along with the disease;
- traumatic – observed after fractures and ligament ruptures.
Correction of moderate severity is very difficult, and severe correction is not always possible due to serious curvatures. Therefore, you should visit an orthopedist or surgeon on time to prevent problems and even disability in the future.
Forecasts
The formation of the foot occurs before the age of 12, so by this time it is possible to correct it, getting rid of problems. The sooner the disease is noticed and treatment begins, massage and other procedures are carried out, the greater the likelihood that the defect can be eliminated and troubles avoided.
With late detection and the beginning of correction, the risks of complications are much greater, and prognoses in moderate or severe condition are not always comforting and often end in surgical intervention.
What is hallux valgus
Children's legs are formed from birth and gradually reach the correct proportions over time. However, very often you can notice that during this period the leg may be bent, and the gait may be awkward and deviate from the required anatomical indicator.
Planovalgus pathology is a disease that interferes with walking, causing discomfort, heaviness and even pain. The structure of the foot is designed to provide excellent functionality regardless of movement. For this purpose, the bones are firmly connected, and the device itself has mobility and good resistance to stress, acting as a shock absorber, becoming more active during walking, running or jumping. Therefore, distortion of the shape of the foot or its individual components directly affects the entire structure, causing a lot of trouble for an adult and especially for children.
As a result, the lower limbs weaken, lose strength, muscle tone and support, resulting in deformation. Congenital, it occurs quite rarely and is immediately detected in the maternity hospital. Most often, the problem develops as an acquired one, and is better manifested after the start of walking and is considered a very common disease, especially when the arch drops, which leads to displacement of the metatarsal bone and tibia.
That is why it is important for all parents to monitor the development of their children, visit an orthopedist and surgeon in a timely manner, and wear proven and high-quality products from. The catalog on the website presents a good range of products of the highest quality at very reasonable prices for everyone.
How is the disease diagnosed?
To diagnose hallux valgus, the patient is examined, talked to, and an additional examination is prescribed.
During the survey, they find out in detail what is bothering the patient. After all, pain in the thumb area can occur not only with this pathology. They clarify exactly when pain occurs, whether there have been foot injuries, whether there is a genetic predisposition, or other diseases.
Hallux valgus, orthopedic insoles for foot care
During the examination, special emphasis is placed on the person’s gait, and the placement of the first finger relative to the neighboring ones is determined. The entire foot and skin surface are examined. The motor capabilities of the sore finger are determined.
Additionally, an x-ray examination is prescribed. Its results allow you to see existing pathologies on the foot and determine the stage of curvature. An ultrasound may also be needed to check the blood flow system in the foot. If surgery is necessary, urine and blood tests will be required.
Causes
Symptoms increase when using uncomfortable, narrow shoes. The situation is aggravated by excess body weight or concomitant metabolic pathologies.• Lying on your back, applaud with your legs raised, spin the “bicycle.”
The most common causes of deformation are:
- injuries;
- connective tissue diseases;
- hereditary predisposition;
- prolonged exposure to low temperatures;
- congenital malformations of the osteoarticular apparatus.
Even a slight deformation of the foot area can cause the development of diseases such as arthrosis and osteochondrosis. In addition, people with deformities experience changes in posture, even scoliosis.
Symptoms
Hallux valgus deformity of the lower foot (see photo) is diagnosed in children by the first year of life. During this period, they begin to actively stand on their feet and try to walk. Parents need to monitor how the baby stands on the foot; if there is a suspicious collapse of the arch, as well as greater emphasis on the inside, you should immediately contact a specialist.
In this case, you will need the help of a pediatric orthopedist. He will determine the possible cause of this curvature, establish the stage and prescribe the necessary measures for treatment and correction of the deformity.
The main symptoms of hallux valgus in children that parents should pay attention to are:
- altered gait - walking is clumsy, the child places more emphasis on the inner parts of the foot. The sole of the shoe wears out more on this side;
- shuffling while walking;
- fast fatiguability;
- pain in the legs after walking - older children may complain of pain in the calf muscles after walking or active games. Little children will
- sit more or move on all fours;
- muscle cramps of the lower leg and thigh;
- moodiness - may occur due to pain or fatigue after walking.
Consequences
If the pathology is not recognized in time and its treatment is not started, the child may experience the following complications:
- rapid fatigue and chronic pain in the feet;
- osteoarthritis of the ankle, knee and hip joints due to improper distribution of load when walking;
- diseases of the spine – osteochondrosis, scoliosis, etc.;
- chronic back pain;
- flat feet;
- various postural disorders.
Severe pathology is one of the causes of disability in childhood. If the deformity is not very pronounced, and therapeutic measures are timely and adequate, then it seems possible to completely restore the normal functionality of the limb.
Diagnostics
If a child shows signs of abnormal foot formation, then most likely they will be noticed by a pediatrician who monitors the baby’s development. During an external examination, the doctor pays attention to the position of the toes and heels, the degree of flattening of the feet. To clarify the diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- X-ray stop. The x-ray is taken in 3 projections. The method allows you to detect asymmetrical placement of the feet.
- Plantography – obtaining foot prints. For small children, the usual procedure is carried out (the legs are smeared with special ink and the child is placed on a sheet of paper). More accurate results are obtained by computer plantography (scanning the feet at rest and under load).
- Podometry is the measurement of time intervals between the phases of foot movement when walking (support on the heel, the entire sole, on the toe). When children have foot deformities, there are characteristic changes in the rhythm of walking. Time measurements are carried out using a stopwatch or special instruments. The use of computer technology makes it possible to diagnose pathology at the very beginning of its development.
- Ultrasound. The method allows you to clarify the degree of curvature, the size of the feet, and detect the consequences of injuries.
Examination and treatment are performed by an orthopedist. Consultation with a surgeon and neurologist may be required.
Prevention
Orthopedists recommend preventing foot deformities, which includes:
- Wearing comfortable shoes that fit;
- Gentle physical activity;
- Contrast shower and foot baths;
- Walking barefoot, especially on uneven surfaces;
- Timely elimination of all diagnosed pathologies.
Foot deformities require complex treatment, the effectiveness of which depends on the stage of the disease. To exclude the development of severe complications, it is necessary to undergo regular examination by an orthopedist.
Forms
In this disease, the first phalanx of the foot is gradually deformed, going through several stages. Taking this into account, valgus is divided into degrees, which differ in the angle of inclination of the bone to the side. There are 4 degrees of hallux valgus.
- The initial stage, in which no discomfort is felt, the finger deviates by 15 degrees.
- The deviation of the finger is more than 20 degrees, signs of deformation are visually visible, and pain appears.
- Deflection angle over 30 degrees. Nearby fingers are also subject to curvature. Movements become limited.
- The phalanges rotate 50 degrees. Changes affect the entire foot, pain is constantly present.
Orthopedic bandage for the big toe bunion
With the first two degrees, intensive preventive measures will help. In subsequent stages, immediate treatment is required.
Possible complications
After reconstructive surgery, the same complications that are observed with any abdominal surgery may develop:
- Deep vein thrombosis;
- Tissue infection;
- Aseptic necrosis of the metatarsal head (an extremely rare consequence);
- Decreased motor function of the thumb;
- Nerve ligament damage;
- Allergic edema;
- Numbness of fingers;
- Pain in the ball of the foot
The listed complications occur rarely; in general, patients tolerate the operation well, both young and old.
The result of treatment of planovalgus foot
After complex treatment using a conservative or radical method, positive results are observed. The younger the patient’s age and the severity of symptoms, the faster the result of the work done is noticeable.
In young children, the pathology is completely cured. Older people with severe deformities may require a year to recover.
Corrective conservative measures to correct the arch help to level the position of the sole, due to the influence of clamps and correct, uniform loads when performing exercise therapy. Severe curvatures that interfere with movement will require surgery.
Surgery allows you to see positive results quite quickly. After joint reconstruction procedures, the foot takes on the correct shape. The healing period is quite long. The patient needs to avoid stepping on the operated leg for some time. At the next stage, a load is required, and classes on developing the foot begin.