In medical terminology, pain in the sacrum is called sacrodynia or sacralgia. And if with sacralgia the symptoms are associated directly with anomalies in the development of the spine and various pathologies, then with sacrodynia they mean radiating pain to this part. It is possible to determine why the sacrum hurts before menstruation and alleviate the symptoms only by identifying the source of the disease.
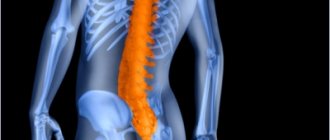
Location of the sacrum in the body
Most patients who complain of pain in the sacrum mean discomfort of varying degrees of intensity in the lower back. Moreover, these are mainly complaints about problems with the lower back or coccyx, since it is with this spinal region that patients often confuse the sacrum.
From an anatomical point of view, the sacrum is a wedge-shaped bone located at the bottom of the back. These are five vertebrae fused together, designed to pass through the spinal canal. The upper part is connected to the last lumbar vertebra, the lower part of the sacrum is connected to the coccyx.
On the side there are two joints that connect the sacrum to the pelvis. The convex, curved part is attached to the pelvis, thanks to which the internal organs are maintained in their normal position, namely the bladder, rectum, ovaries, appendages and uterus.
Therefore, the causes of pain in the sacrum and lower abdomen, as a rule, are explained by the nearby internal organs, as well as by the significant load on the vertebral skeleton itself.
Diagnosis of pain in the coccyx
What examination should be performed for pain in the coccyx area?
To effectively treat pain in the tailbone, it is necessary to correctly diagnose and identify the cause of the discomfort. A patient with similar symptoms will need to visit doctors of several specialties and undergo a comprehensive examination.
The following specialists can help remove pain in the tailbone, depending on the cause: surgeon, neurologist, gynecologist, proctologist, chiropractor, osteopath. The patient will have to tell the doctors in detail about the location of the pain, its nature, and clarify whether there have been injuries or operations in the pelvis in the past.
The most effective methods for diagnosing pain in the tailbone are:
Palpation
To determine the exact source of pain in the tailbone, the first step is to palpate the problem area. When examining with your hands, pressure on the tailbone can cause the appearance or intensification of painful sensations. Pain may also be triggered by touching the area 5 cm around the tail bone.
An informative method is palpation of the coccyx area through the rectum. This will assess the mobility of the vertebrae and exclude tumors in the rectum and vagina. If necessary, rectoscopy, sphincterometry, and balloonography are also prescribed.
External palpation to exclude cysts and other formations in the coccyx area is carried out by a surgeon. For an internal examination for anal fissures, hemorrhoids, and formations in the rectum, you should visit a proctologist. A gynecologist examines a woman for inflammatory diseases in the pelvis and to exclude tumor formations.
Radiography
Among the instrumental methods for studying pain in the coccyx area, radiography is considered the most informative. Using x-rays of the sacrococcygeal region, you can identify injuries that led to pain, displacement of the vertebrae, and determine the presence of hernias.
For a more accurate result, you must follow a diet and do a cleansing enema before the procedure. But due to the structural features of the coccyx of a particular person, which are not related to the occurrence of pain in it, sometimes the result of an x-ray examination does not give any results.
Magnetic resonance and computed tomography, ultrasound
The main task when performing magnetic resonance and computed tomography of the lumbosacral region is to exclude spinal pathology in the coccyx area. These studies will also help determine the presence of inflammation and swelling of the tissues surrounding the tailbone, tumors and diseases of the genital organs, organs of the urinary system and abdominal cavity, which can lead to pain in the tailbone.
In terms of diagnostic significance, ultrasound, MRI and CT are inferior to X-ray examination. If metastases are suspected, doctors additionally prescribe bone scintigraphy - this is a procedure for introducing radioactive isotopes into the human body for further recording of their radiation.
But it also happens that even after carrying out all the necessary studies and excluding possible neurological, proctological, urological and gynecological diseases, it is not possible to identify the cause of pain in the tailbone. Then the patient is diagnosed with anococcygeus pain syndrome.
Causes of pain
Determine the indirect and direct causes of the development of pain in the sacrum. If clinical symptoms are directly related to diseases of the spine, then sacralgia is considered. Moreover, the nature of the discomfort in such situations is more piercing, in contrast to pain in other parts of the spine.
This condition may appear during:
- osteochondrosis;
- spinal injuries;
- lubalization - deformation of the first vertebra of the sacrum;
- radiculitis.
But as a rule, the cause of significant discomfort is sacroiliitis or an inflammatory process in the iliosacral region.
In rare cases, the causes are diseases that are associated with the following ailments:
- metastases in the vertebral region during various neoplasms on internal organs;
- syphilitic or tuberculosis diseases.
However, there may be cases when discomfort in the sacrum is not associated with pathologies in the spine.
In these situations, painful symptoms are defined as sacrodynia, which may indicate the presence of:
- diseases in the digestive tract;
- pathologies of the iliac and pelvic veins;
- disturbances in metabolic processes;
- tumor neoplasms;
- the presence of urological pathological processes.
In addition, if women have pain in their tailbone and lower abdomen while sitting, this may be due to gynecological diseases. The tailbone often hurts during menstruation and in late pregnancy.
In the male half, the causes of discomfort can be explained by prostate adenoma and prostatitis.
Quite often, the pain syndrome is psychogenic in nature, that is, it appears due to severe stress, as well as significant mental and emotional stress.
Cyclic changes in the uterus
How it hurts: Medium dull pain, periodic, disappearing after menstruation. Where does it hurt: Lower back, lower abdomen Additional symptoms
- irritability, headache;
- nausea;
- increased heart rate,
- chills;
- sleep disorders
- heavy periods.
Related article: What treatment options are there for kyphosis in adults?
Causes of occurrence Caused by hormonal disorders in the body, the predominance of prostaglandins over progesterone. With increased levels of estrogen in women after 28-30 years of age, heavy periods are observed. Due to excessive activity of the thyroid gland, pulse irregularities may additionally occur.
Symptoms disappear after the onset of menstruation and the appearance of discharge.
Who treats
- gynecologist
- endocrinologist
How to treat They use drugs that relieve spasms - No Shpa, Spazgan.
To level the hormonal balance during the period between menstruation, perform therapeutic exercises.
Relationship between symptoms and diseases
Painful sensations in the sacrum, or more precisely, their character, can suggest what pathology this feeling is associated with. The main symptoms and nature of concomitant diseases or injuries look like this:
- Osteochondrosis. As a rule, aching or dull pain begins to bother you, and it can also spread to the lower extremities. You feel stiffness directly in your back. Discomfort increases with body bending, unsuccessful movements, and increased load on the spine. It decreases if the patient takes a comfortable position.
- Damage and injury. Feelings of discomfort are caused by muscle spasms. In order to reduce it, the patient tries to take an unnatural position.
- Intervertebral hernia. The pain begins to radiate to the tailbone, groin and lower limbs. Unpleasant sensations are stronger in the morning and may decrease in the evening. Oh, they become less pronounced after “pacing”.
- Old coccyx injury. It is difficult for the patient to bend over and change body position. The pain can be paroxysmal and acute, or monotonous and dull.
- Pelvic displacement to the right. There is pain on the right side of the body. The functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted. The patient is rapidly losing weight and has frequent diarrhea. Women develop gynecological pathologies.
- Pelvic displacement to the left. Soreness is noted on the left side of the body. Immunity deteriorates, disturbances in the functioning of the heart and breathing are noted. Patients quickly gain weight and experience frequent constipation.
- Spondylolisthesis. Develops after a direct injury or jump. The pain is aching in nature.
- Pathologies of the sacral joints. The pain is one-sided. There are convulsions in the lower extremities, and the gait changes. The patient begins to limp.
- Thrombophlebitis of the iliac and pelvic vessels. The pain radiates to the sacrum or lower back.
- Disorders of spinal development. Appears unexpectedly. The main factor in this condition can be significant loads, falling on your feet, a sharp turn, or an unsuccessful bending of the body.
- Adenoma and prostatitis. Pain in prostate pathology can be either one-sided or felt in the center.
- Enlargement of the sigmoid colon. Stitching and bursting pain both in the lower abdomen and in the back area. Both diarrhea and constipation may occur.
- Infectious diseases. Regular minor pain, which does not go away even after a night's rest, increases significantly with movement.
- Metastases in the sacrum due to neoplasms. Soreness in the sacrum appears in the later stages and is aching and constant. Discomfort increases at night and does not subside after rest.
- Uterine cancer. Soreness in the sacrum is noted in the middle or is unilateral.
- Disorders of metabolic processes. Back pain becomes worse with significant physical activity.
- Parametritis. Nagging pain in the sacrum in women is long-lasting.
- Endometriosis. The pain is cyclical and intensifies during menstruation.
- Pain during pregnancy. It is caused by a change in the vertebral curvature, the occipital location of the fetus and its significant weight. There is aching pain that subsides when lying on your side.
- Pain during menstruation. Paroxysmal and low-intensity pain that radiates to the groin and lower extremities.
- Deviations that are caused by the location of the uterus. Soreness
- Increases in the lower back after standing for a long time.
Stressful situations need to be considered separately. Diagnosis of this pathology does not identify any abnormalities, but the patient experiences significant suffering. In this case, the pain can have different intensity and character.
Methods for treating pain in the tailbone
Painful sensations in the tailbone cause a person a lot of discomfort. Often, pain causes a noticeable limitation in a person’s mobility and prevents him from performing usual activities, thereby reducing the quality of life. In most cases, pain in the tailbone area can be managed without surgery. To do this, it is necessary to correctly determine the cause of discomfort.
Depending on the patient’s medical history, concomitant diseases and complaints, a comprehensive examination is carried out by different specialists. Treatment is usually conservative. The patient needs rest; in case of severe pain, pain relief, methods aimed at restoring blood circulation in the coccyx area and, of course, treatment of concomitant diseases (inflammatory processes in the genital organs, dysbacteriosis, hemorrhoids, osteochondrosis, etc.).
For inflammatory diseases, antibiotics and immunomodulators are prescribed; fractures and dislocations of the coccyx require routine observation, sometimes reduction or surgical intervention. Tumors undergo surgical removal and, in the case of a malignant course, undergo chemotherapy.
For true coccydynia, the standard set of measures aimed at relieving symptoms includes:
- taking medications
- massage and manual therapy
— physiotherapy and exercise therapy
- folk remedies
All these measures help improve blood circulation in the coccyx area, relieve muscle spasms, and relieve pain. The patient has the opportunity to fully or partially restore the range of motion of the coccyx.
First aid at home for tailbone pain
Just like the causes of its appearance, pain in the tailbone requires a variety of treatments. If you have pain in the tailbone area, and you can’t get to a doctor in the near future, you can take independent measures to alleviate your condition. You should start with a painkiller. Particularly popular in this regard are suppositories and microenemas, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
A compress with valerian tincture or an iodine mesh will help relieve pain and relieve inflammation. If you have severe pain, try to sit less, do simple exercises for your spine, and ask a loved one to give you a massage in the tailbone area. Do not allow proctological problems to worsen. Get more rest. Now let's take a closer look at all the methods aimed at relieving pain in the tailbone area.
Anesthesia
For moderate pain in the tailbone, the doctor usually prescribes the patient over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, ibuprofen, nimesulide, ketoprofen, diclofenac. All of these drugs have a similar effect, and their main side effect is the risk of gastric ulcers. Therefore, it is recommended to use them for no more than 3-5 days without exceeding the specified dosage.
If the patient's pain is severe, he may be prescribed novocaine blockades in the coccyx area, when the medicine is injected directly around the painful area. Similarly, hydrocortisone, lidocaine, Kenalog and other drugs are used for this procedure. Blockades will help relieve spasm of the tissues surrounding the tailbone and sometimes lead to complete recovery.
Laxatives
Going to the toilet with pain in the tailbone is quite painful, since straining the abdominal muscles leads to increased pain. Fear of defecation provokes psychological constipation. As a result, the patient is forced to use laxatives to facilitate the process. It is better to use herbal preparations and suppositories.
Physiotherapy
Any physical impact for pain in the tailbone is prescribed only after the inflammatory process has been ruled out. Among the methods of physiotherapeutic treatment for painful sensations in the coccyx area, the following are used: ultrasound treatment, rectal darsonvalization, UHF, laser therapy, ozokerite, diadynamic currents, therapeutic mud, electrotherapy, paraffin baths.
Physiotherapy is especially useful for patients suffering from chronic pain in the coccyx area, in whom spasms of the muscles around the coccyx become an obstacle to recovery. In this case, massage is additionally indicated.
Massage, manual therapy, acupuncture
Pain in the tailbone can be significantly relieved by massage of the pelvic floor muscles (when they are spasming) and digital massage of the rectal muscles. Manual therapy, which is carried out by a competent and experienced specialist, helps improve blood circulation in the coccyx area, eliminate congestion in the pelvis and lower back, relieve spasms and restore the motor activity of the coccyx and return the patient to the joy of a full life.
Acupuncture is also quite often prescribed as an auxiliary method of relieving pain in the tailbone. Of course, in this matter it is very important to find a competent doctor. The correct choice of biologically active points during acupuncture will help completely relieve you of pain.
Physiotherapy
It is not only possible, but also necessary for people with pain in the tailbone to engage in physical activity. True, still with some restrictions. You need to avoid straining your abdominal muscles, running, any sudden movements, jerking and jumping. To achieve a good effect, it is recommended to slowly perform a set of special exercises twice a day.
Gymnastics for pain in the tailbone should include the following exercises:
1. Lying on your back on a hard surface, bend your knees and spread them apart. Place the palms of your hands on the inner sides of your knee joints. Bring your knees together, stopping yourself with your hands. Repeat 8-10 times.
2. In the same starting position, hold the ball between your knees. Place your hands, palms down, on your stomach. Squeeze the ball with your knees for 5 seconds, preventing your stomach from protruding with your hands. Repeat 5-7 times, taking a break to rest.
3. Starting position – lying on your back. Squeeze the ball between your straightened feet. Using force, squeeze the ball with your feet for 5 seconds. Repeat 5-7 times.
4. Lying on your back, spread your legs, bent at the knees, to the sides, lifting your pelvis for a few seconds, while straining your buttocks. Repeat up to 7 times.
Special pillows
In many pharmacies and orthopedic salons you can purchase a special pillow in the shape of a donut or wedge, with which you can relieve the load on the tailbone area. The essence of these pillows is the absence of contact of the tailbone with a hard surface. Pillows will also help prevent relapses of the disease.
Folk remedies for pain in the tailbone
For pain in the coccyx area, the following folk remedies are used:
1. Compress with valerian tincture
Moisten a small piece of any cotton cloth with tincture of valerian and apply it to the sore spot. Cover the top with a plastic bag and put a warm layer (for example, a scarf). Secure the resulting compress with an adhesive plaster and leave it overnight.
2. Fir oil
Rub fir oil into the tailbone area several times a day. This helps reduce pain and relieve inflammation.
3. Iodine
A couple of times a week at night, lubricate the preheated area of the tailbone with iodine tincture and then wrap yourself up. The procedure can be repeated for 1-2 months.
4. Blue clay
A blue clay compress will help relieve pain in the tailbone. To do this, add a teaspoon of apple cider vinegar to 500 g of clay and mix thoroughly. Apply a layer of the resulting mixture to the sore spot, cover with a plastic bag, place a warm scarf or handkerchief on top and leave overnight.
5. Magnet
The ring magnet must be moved clockwise in a circular motion in the lumbar region for 15-25 minutes several times a day.
How to relieve tailbone pain during pregnancy
Unfortunately, doctors cannot provide practically any help when pregnant women experience pain in the tailbone. After all, pregnant women are prohibited from taking all anti-inflammatory and painkillers, X-rays and MRIs are contraindicated, so often pregnant women can only endure the pain and try to relieve it themselves by placing a soft pillow under the tailbone.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
Taking into account the fact that pain in the sacrum can be caused by many different pathologies, diagnosis begins with studying clinical symptoms and collecting anamnesis. The patient’s accompanying complaints and symptoms can help the specialist determine subsequent diagnostic tactics.
But tests and external symptoms alone are not enough to distinguish sacrodynia from sacralgia.
During the presence of pain in the sacrum, as a rule, the following is prescribed:
- CT or MRI;
- radiography.
In addition, an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvis is performed. The patient must provide urine and blood for examination.
After a preliminary examination, the specialist establishes an accurate diagnosis or sends the patient for additional differential diagnosis. During times of intense pain in women in the sacrum, ultrasound of the genital organs, including the uterus and ovarian appendages, is certainly used.
Coccyx fracture
A fracture is diagnosed somewhat less frequently than a bruise and is a serious disease. The pain develops acutely and, depending on the location of the fracture, can persist for a long time or disappear several days after the injury. In such a situation, the victim may not seek medical help in a timely manner, and because of this, the disease will only progress, resulting in a serious complication that may even cause disability. It hurts in the tailbone area then constantly.
The main symptoms that appear with a fracture of the coccyx are particularly severe pain, swelling, redness in the affected area , as well as difficulty walking. In many ways, the symptoms of a fracture are similar to a bruise, and therefore an x-ray is mandatory to diagnose it.
Possible treatments
The treatment strategy for pain in the sacral spine will depend directly on the type of pathology that provoked this condition. However, there are also general methods of therapy that can significantly alleviate the patient’s condition.
This is, first of all, pain relief. For which analgesics can be used, however, non-steroidal drugs have the best therapeutic results.
In case of very significant pain, blockades are performed using anesthetic injections into active painful areas, in some cases simultaneously with corticosteroids.
Therapeutic and preventive physical education
You can start doing physical therapy or some other training only during recovery. If the sacrum hurts very much, then it is advisable to treat it in other ways. The spine needs relaxation and peace.
The first exercises must be done without jerking, very smoothly and slowly. Be sure to start training with stretching, performing the exercise no more than 15 times in the morning:
- Lying position on your back. Pull your knees towards your chest, trying not to lift your pelvis from the floor.
- Without changing your position, stretch one leg along the floor and press the other towards your chest. Then change legs.
- Lie on your back, place your hands under your sacrum, and bring your legs together. Slowly raise your legs, taking the “birch” position. Hold this position for 20 seconds. Then carefully lower your legs. Repeat no more than 15 times.
- Get on all fours. Slowly bend your back in an arc, while you need to lower your head to your chest. Then you need to bend over, raising your head up.
This complex can be performed every day in the morning or before bed, when the acute pain has passed.
Manual treatment and massage
Massage is a good treatment option for lower back pain. It reduces the intensity of pain, and also improves lymph flow, blood circulation, and relieves swelling. In certain situations, it is advisable to seek help from a chiropractor; if the internal organs in the pelvis are displaced, the doctor will be able to help restore their normal location.
Attention! During pain caused by the presence of intervertebral hernias in the sacrum, massage is strictly prohibited.
Fixation with a corset
Limiting motor function makes it possible to reduce pain in the sacral region. For this reason, patients are recommended to use semi-rigid orthoses that immobilize movement in the 3rd and 4th vertebrae.
The corset is used until the pain is completely relieved; during relapses, its use is resumed. To get a positive result, you need to choose the correct corset size.
Treatment
After establishing an accurate diagnosis, the necessary treatment is prescribed. The treatment regimen depends on the existing symptoms and is most often carried out conservatively. Pain in the tailbone caused by the approach of menstruation can be significantly reduced or completely eliminated with the help of a small set of exercises.
They take very little time to complete. The woman should lie on the floor on her back and place her hands, palms down, under her buttocks. In this case, you need to slowly raise your legs and then lower them just as smoothly. During menstruation, when the tailbone hurts, ten repetitions of the exercise are usually enough to eliminate the discomfort. An effective remedy for pain may be massage.
If the pain is very severe and creates significant discomfort, the doctor may recommend painkillers and antispasmodics to the woman. Such drugs help relieve symptoms, but do not eliminate the cause of the pain.
Basic preventive measures
There are no special preventive measures, especially primary ones, for these painful symptoms. The development of these clinical symptoms is due to various diseases.
Therefore, in order to prevent the appearance of sacrolgia and sarcodynia, it is necessary:
- train the muscle corset that supports the spine;
- maintain a correct lifestyle;
- use a corset when it is necessary to carry out heavy physical work;
- avoid excessive loads.
Timely diagnosis of diseases of internal organs will allow timely identification of serious pathologies. If you experience frequent pain and increased discomfort, you should consult a doctor to avoid later encountering an advanced tumor or osteochondrosis. Great attention must be paid during pregnancy: pain can indicate both natural divergence of bones and inflammatory processes in the pelvis.
Causes of pain before menstruation
Menstruation is the beginning of a new cycle for a woman . This change in physiological state is quite painful for the female body. Why do some women experience pain in the sacrum during menstruation?
Ask your question to a neurologist for free
Irina Martynova. Graduated from Voronezh State Medical University named after. N.N. Burdenko. Clinical resident and neurologist of the Moscow Polyclinic. Ask a question>>
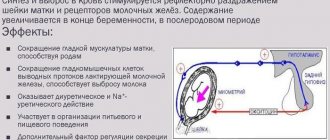
The female reproductive cycle and the onset of menstruation are regulated by hormones - estrogen and progesterone. At the hormonal level, the process looks like this:
- the beginning of the menstrual cycle - estrogen in the blood, the woman is active, productive, pain is minimized;
- the corpus luteum forms in the ovaries and blood begins to release progesterone;
- conception has not occurred - the corpus luteum dies, a minimal concentration of female hormones is observed in the blood, the body is preparing for the transition to a new phase of the cycle.
- The uterus, during bleeding during menstruation, begins to contract, pushing out the inner, waste epithelial layer, for
- This causes the woman’s body to produce special substances – prostaglandins.
But the state of the uterus is also controlled by the autonomic nervous system and the central nervous system (hypothalamus).
The branches of the autonomic nervous system provide sensitivity to the cervix and connect to it the nerve plexus located in the sacrum. The second part of the nerves connects the muscles of the lower back and the body of the uterus through another nerve plexus (hypogastric). The hypothalamus, which regulates the activity of the central nervous system, responds negatively to nervous stress, fatigue, and the general painful state of the body.
During menstruation, two processes coincide - a high amount of prostaglandins in the blood against the background of a general depressed state of the body and a lack of female hormones causes excessive contraction of the uterine muscles and pain in the sacrum.
This condition can be called a hormonal feature of a woman; normally, in the absence of diseases of the internal organs, pain can be one-time, or repeated over long periods.
If lower back pain is constantly present, it is quite severe, causes discomfort, and reduces the quality of life - this is a reason to immediately see a doctor.
Inflammation of the coccyx
Inflammation of the coccyx occurs when an infection enters the area of the organ. This can happen with an open injury or with blood flow from a source of inflammation in the body. Less commonly, the infection penetrates into the tissues of the coccyx in diseases of nearby organs. Coccyx pathology appears in people of any age and gender equally . Additionally, a sedentary lifestyle, wearing very tight underwear or clothes, which impairs blood flow in the pelvic area, and previous injuries to the tailbone, increase the likelihood of the problem occurring. During pregnancy, there is also a higher risk of experiencing inflammation of the tailbone.
If it is violated, a dull aching pain occurs in the area of the coccyx, which noticeably intensifies when sitting and palpating the problem area. Also, if the inflammation progresses, redness of the skin above the tailbone and a local increase in temperature are observed. If therapeutic measures are not started at this stage, the pain becomes sharp and jerking, and general intoxication of the body develops. It leads to loss of performance and requires urgent medical attention.
Of particular danger is rapid purulent inflammation of the coccyx, which begins with acute intense pain . A person has pain in the anus and tailbone. With it, if you do not consult a doctor immediately, sepsis develops in a short time, causing the death of the patient. If the inflammation turns out to be chronic, then without treatment it eventually leads to the development of a cancerous tumor.
Treatment of inflammation is carried out in the initial stage with medication , and in advanced conditions or acute purulent process - surgically. What kind of therapy is required will be determined only by a doctor. When treating with medications, antibiotics are mandatory.
Osteochondrosis of the coccyx
Osteochondrosis of the coccyx is a spinal problem. If damaged, intervertebral discs and vertebral tissues are damaged. Like any type of osteochondrosis that affects the coccyx, it has its own striking manifestations and is easily diagnosed by a doctor. The disease must be treated urgently, and be sure to consult a doctor. On your own, you can only seriously worsen the patient’s condition. If the disorder is not treated, then as it progresses, the quality of life rapidly decreases.
The problem most often occurs due to injuries and lack of physical activity. Quite often, women who have had a natural birth with a large fetus face this problem. Pain in the tailbone appears almost immediately after the birth of the child and can be very intense.
The main symptoms of the disease are:
- pain that is constantly present or occurs in attacks (the back in the tailbone area hurts as with any form of chondrosis);
- increased pain during physical activity and sudden transition from a sitting to a standing or lying position;
- discomfort in the tailbone.
Exacerbations of the disease occur with varying intensity. Osteochondrosis of the coccyx can remind itself once every few years, or maybe several times a year. Treatment of the disease is aimed at relieving acute symptoms and prolonging periods of remission. The main provocateurs for the appearance of symptoms of osteochondrosis are strong physical exertion, hypothermia, severe stress and unsuccessful movements, which place unnatural pressure on the tailbone. The problem especially often manifests itself in winter during periods of heavy ice, when movements become very tense and constrained. Regular performance of physical therapy exercises at this time helps to avoid exacerbation of the pathology.