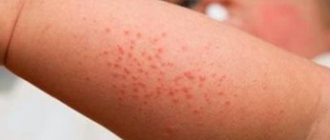
Atopic dermatitis (neurodermatitis) is a chronic skin disease accompanied by periods of relapses and remissions. Characterized by intense skin itching and rash. It occurs in infancy and can accompany a person throughout his life.
Atopy is an increased sensitivity of the body to external and internal stimuli. When exposed to them, the body responds with inadequate reactions, manifested in the form of external signs.
Causes of the disease
Neurodermatitis is not a contagious disease. Often its root cause is a genetic predisposition to allergies. The human body can react with illness to any irritant - from the fur of a pet to your favorite cosmetic product.
Experts believe that common causes of neurodermatitis are:
- neuropsychiatric health disorders;
- medications;
- climatic factors;
- work in hazardous conditions and other irritating factors;
- poor nutrition, general toxic pollution of the body;
- prolonged psycho-emotional, mental and physical overload, depression;
- profound disturbances in the functioning of the immune, central and peripheral nervous systems, vegetative-vascular syndrome;
- sources of chronic infection, foci of inflammation in the body and bacterial accumulations on the skin;
- gastrointestinal diseases associated with disorders of fermentation processes, disruptions in the endocrine system, ENT diseases;
- genetic determination of the tendency to various allergic reactions, which is proven by the high intensity of diseases of close relatives and identical twins;
- endogenous factors - a polluted state of the surrounding external (street) and internal (indoor) environment, which can cause skin hyperreactivity.
Despite the variety of factors that provoke the development of neurodermatitis, dermatologists believe that the disease triggers an allergic mechanism. At the first meeting with an allergen, the body produces antibodies to a new compound, but the second time the antibodies combine with the body and are carried through the bloodstream to all tissues and organs and destroy the membranes of their cells.
During the process of degranulation, active substances are released, among which is histamine. This substance causes redness and thickening of the skin, an increase in local temperature and a feeling of itching or burning. In case of secondary infection, body temperature rises.
Scientists explain damage to the nervous system as the cause of neurodermatitis by dysfunction of peripheral nerve fibers. Therefore, the patient begins to experience severe itching, and rashes appear on the body. The desire to scratch the skin leads to injury, increased intensity of itching and swelling of the tissue.
Causes of neurodermatitis
Lichen simplex chronicus Vidal
Its etiology is not fully understood. Most often it occurs in adults. The main pathogenetic factor is an increase in skin sensitivity to various irritants. It is assumed that this occurs due to the proliferation of nerve endings and the predisposition of the epidermis to irritation as a response to mechanical injury.
The main role in the development of limited neurodermatitis is played by metabolic disorders in the body, functional disorders and diseases of the digestive organs, especially the biliary system and pancreas, resulting in the development of chronic autointoxication and the formation of autoantigens. Often limited neurodermatitis is the final stage of the development of other dermatoses.
It is also assumed that the cause of the development of pathology may be the influence of environmental factors, various dysfunctions of the central and autonomic nervous system, endocrine disorders, stress and excessive emotional and psychological stress. In some cases, the participation of allergic factors in the mechanisms of development of pathology cannot be excluded.
Atopic dermatitis
Its share among all dermatoses is about 4%, and allergic dermatoses - about 30%. The multifactorial nature of the disease consists of the interaction of various hereditary characteristics and many environmental factors. In the pathogenesis of the disease, the main hereditary links are:
- features of the morphological and functional state of the skin;
- a constitutional anomaly, which consists in the genetically programmed readiness of the body for excessive production of class “E” immunoglobulins and the release of biologically active substances as a response to exposure to allergens.
A predisposition can exist for an indefinitely long time without any clinical manifestations, therefore this form of dermatitis, even if the clinic develops only, for example, by the age of 20–30, is called atopic.
So, for example, if the child’s parents are healthy, then the risk of developing the disease does not exceed 10%; if one of the parents is sick, the risk of the disease is already approximately 56%; both parents – 75%. In the case of illness in one child, the risk of illness for the second is about 22%, and in monozygotic twins it is up to 85%.
External factors take part in the implementation of genetic information in the phenotype of a sick person. They are a provoking factor in the onset of the pathological condition, causing its chronic course and the occurrence of relapses. At the same time, pathogenetic factors and their various combinations when exposed to the external environment of varying intensity can be inherited separately.
The nature of susceptibility to external factors largely depends on age. In children in early infancy and childhood, the main influence on susceptibility is exerted by dysfunctions of digestion and absorption caused by insufficient maturity of individual parts of the digestive system (lactase deficiency), allergies to certain foods, malnutrition of the child, disorders of metabolic processes and functions of the liver and biliary tract , excess foods (citrus fruits, honey, smoked meats, strawberries and wild strawberries, chocolate, etc.) containing large amounts of histamine liberators - substances that promote the release of histamine in the body by mast cells, etc.
In older ages, allergens in the air (pollen, animal hair, house dust and mites, fish food), lack of a rational regimen, stress and psycho-emotional fatigue, depressive states leading to disorders of autonomic function become increasingly important in the development of diffuse neurodermatitis. nervous system, hormonal dysfunction or changes in hormonal levels in the body, etc. An example of the latter is neurodermatitis in adolescence or neurodermatitis during pregnancy, both atopic and limited.
So, the causes and risk factors are:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Presence since birth of enzymopathies, disorders of the stomach and intestines.
- Functional disorders of the central nervous and endocrine systems, gastrointestinal tract, liver and biliary system, dysbacteriosis.
- Poor nutrition, smoking, alcohol abuse during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Premature transfer of a child to artificial feeding and lack of proper nutrition.
- Foci of chronic infection in the body and states of immunodeficiency, manifested by a decrease in the blood of immunoglobulins “M” and “A”, Tn1 and Th2 lymphocytes and their imbalance, an increase in immunoglobulins “G” and “E” and eosinophils.
- The presence of allergic reactions, including in close relatives.
- The use of antibacterial drugs and antibiotics, improper vaccination during pregnancy, breastfeeding and early childhood.
- Climatic, environmental and social unfavorable factors, incorrect and age-inappropriate use of cosmetics for skin care.
Thus, the development and chronic course of atopic dermatitis are caused by a genetic predisposition in combination with functional disorders of the central nervous system, psychoemotional, gastrointestinal, neurovascular, metabolic and neurohumoral disorders, an allergic state of the body, poor nutrition, various intoxications and unfavorable environmental conditions.
Classification
Neurodermatitis is a disease that has several types, which determine the extent of the pathological process in the patient’s skin.
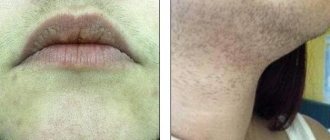
- Diffuse neurodermatitis. This form is characterized by the appearance of multiple lesions. As a rule, they are localized on the upper and lower extremities (in the popliteal cavities and elbow bends), as well as on the torso. However, diffuse neurodermatitis often affects the neck, genitals, anus and face. In this case, the lesions are merging lichenified and infiltrated skin areas. In some places, in addition to lichenification, flat shiny nodules appear. Sometimes patients experience short-term weeping after scratching. As a result, the lesions can become infected, complicated by lymphadenitis or pyoderma. Patients suffering from diffuse neurodermatitis are characterized by swelling and hyperemia of the skin, often covered with small scales.
- Limited neurodermatitis. This type of neurodermatitis is characterized by the appearance on the surface of the skin of plaques covered with nodular neoplasms on the neck, in the knee and elbow bends, in the perineum, and on the genitals. With this type of disease, a symmetrical arrangement of plaques is often noted. As a rule, they appear simultaneously on both elbows, knees, and feet.
- Decalvating affects hairy areas of the body, causing gradual hair loss.
- Linear neurodermatitis. This is a pathology in which the lesions are localized mainly on the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs and have the shape of stripes, sometimes with a warty or flaky surface.
- Follicular: formed on the scalp of the body in the form of rashes that look like pointed papules.
- Psoriasiform neurodermatitis. In this case, the lesions are red lumps covered with small silvery-white scales. Most often they are localized on the head and neck.
- Hypertrophic: expressed in swelling in the area of the lymph nodes, most often the inguinal ones.
Each type of neurodermatitis brings significant discomfort to a person, so treatment is required without delay.
Types of atopic dermatitis and their symptoms
The disease has an undulating course with exacerbations and relapses in the winter. In summer, partial or complete attenuation of the processes and the onset of remission are observed.
There are several forms of clinical manifestations.
Infantile – occurs between the ages of 1 month and two years. In this phase, focal skin lesions are observed with localization of the rash on the face, in the area of the elbows, knees, and buttocks.
The following signs are noted:
- enlarged lymph nodes,
- peeling and severe itching of the skin,
- the appearance of bubbles filled with liquid contents,
- the addition of fungal and bacterial infections,
- restless behavior
- sleep disturbance,
- fusion of affected areas.
Scratching the affected area provokes the appearance of crusts, wounds, cracking with the formation of weeping lesions.
A combination of certain factors can lead to a long course of the disease and transition to another age-related form. But it happens that the child grows up and the disease goes away irrevocably.
Children's - manifests itself in children from 2 to 13 years old. During this period, focal rashes predominate on the neck, bends of the arms and legs, in the hollows under the knees, and on the outside of the hands.
Clinical symptoms:
- redness and swelling of the skin,
- the appearance of an erythematous-squamous rash,
- thickening of the skin
- pigmentation disorder
- the appearance of a clearer pattern.
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, pigmentation of the skin around the eyes increases, and additional folds appear on the lower eyelid.
Adult – over 13 years old. In adolescence, both the complete disappearance of signs of the disease and its exacerbation with spread to large areas of the skin (face, neck, hands, feet, décolleté, shoulders) are possible.
Symptoms of manifestations:
- lichenification of the skin (fusion of skin scales and the formation of scabs),
- hyperemia,
- thickening of the epidermis,
- addition of a secondary infection.
Symptoms of neurodermatitis
The main symptoms of neurodermatitis in adults and children are characterized by rash, itching, neurotic disorders, redness, and peeling. Moreover, the area of distribution of the disease can be varied depending on its specific variety.
With neurodermatitis, the function of the adrenal glands is significantly reduced, so the skin may darken noticeably. A person loses weight, which negatively affects the general condition of the body. Blood pressure decreases, fatigue, apathy and weakness increase, gastric juice secretion and blood glucose levels decrease. Neurodermatitis sometimes leads to lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes), which impairs the functioning of many organs.
It should be noted that the symptoms of neurodermatitis are most pronounced in the winter and in the evening, and in the summer, on the contrary, noticeable improvements are felt. Neurodermatitis on the hands brings the greatest discomfort, since moisture and frequent mechanical stress only worsen the disease.
Kinds
Depending on the area occupied by the foci of neurodermatitis on the skin and the characteristic signs, the pathology occurs in the following possible forms:
- limited - manifested by localization on individual, small fragments of skin - focal neurodermatitis;
- disseminated - characterized by the fusion of several areas with limited neurodermatitis;
- diffuse - spreads in the form of diffuse lesions, without clear separation of boundaries (face, neck, upper limbs, knee joints).
Since the nature of skin changes is not clear, doctors divide the disease into types:
- Psoriasiform – mainly the spread of neurodermatitis on the face and scalp is observed. The symptoms are partially similar to psoriasis and are accompanied by areas of peeling.
- White – manifested by areas of depigmentation.
- Decalvating - doctors record lesions of the scalp. The clinical picture of neurodermatitis on the head is manifested by alopecia.
- Hypertrophic – affects the groin area. The disease can manifest itself at any age and make itself felt throughout life (tumor changes on the skin).
- Linear - diagnosed by characteristic skin manifestations with clear linear neurodermatitis in the form of stripes.
- Follicular – determined by the formation of papules, with characteristic pathological sharp ends in areas of hair growth.
Adequate treatment of neurodermatitis is possible only after an accurate diagnosis and determination of the cause of pathological changes. Only the attending physician can prescribe treatment regimens.
Today, diseases are usually explained by psychosomatics; neurodermatitis and its development also have its own reasons for its appearance. You can be skeptical about science, but there is some correlation between skin manifestations and a lack of maternal love, the need for protection from external negative factors, or the development of complex partnerships.
How to diagnose correctly?
Diagnosis of neurodermatitis is carried out by a dermatologist at the first visit. To do this, the patient’s complaints and examination of his body are enough. To confirm the diagnosis, the patient may be prescribed laboratory and biochemical tests: his blood is checked for the number of leukocytes and eosinophils.
Most patients exhibit eosinophilia and leukocytosis, and immunological studies show an increased amount of IgE immunoglobulins. When secondary diseases occur, treatment of neurodermatitis and its symptoms can be adjusted in accordance with the overall clinical picture.
Diagnostic measures
Neurodermatitis or atopic dermatitis is often differentiated from psoriasis, various types of dermatitis, scabies, eczema, and lichen.
Therefore, to identify the disease, it is necessary to contact a dermatologist or allergist and carry out the necessary diagnostics:
- visual inspection of the skin,
- general blood analysis,
- skin tests,
- provocative tests (to identify and eliminate the allergen). The results of the examination will help determine the necessary ways to eliminate the disease.
How to treat neurodermatitis?
Often neurodermatitis is treated in a very truncated manner and attention is paid only to skin manifestations. For relief of which local treatment is directed. However, it is worth considering the process as a whole and paying attention to all stages of treatment.
- Diet. Therapy begins, especially in the case of children, with dietary measures. It is ideal when it is possible to identify the main allergens that provoke the process and eliminate them from food. In adults, therapy also begins with the introduction of a diet with limited alcohol and spices. They try to breastfeed children or switch them to cow protein hydrolysates.
- General mode. Normalization of the general regime should include a full night's sleep (and for children, daytime sleep), sufficient time in the fresh air and rational mental and physical stress, excluding overwork and overexcitation of the nervous system. Treatment of neurodermatitis in adults with total lesions, localization on the palms, secondary purulent complications can be carried out on an outpatient basis with the issuance of a certificate of incapacity for work.
- Treatment of dysbiosis. During periods of exacerbation, it is also recommended to correct dysbiosis and start taking a course of enterosorbents (Enterosgel, Polyepana). It is not advisable to use sorbents on an ongoing basis, since they lead to the removal from the intestines of not only allergens, but also vitamins, which are quite difficult to replace due to dietary restrictions and intolerance to synthetic analogues.
- Sedatives. If necessary, patients are prescribed courses of sedatives or drug therapy for more severe neurological or mental problems.
General recommendations for neurodermatitis that can be performed at home:
1) The most important thing is to stop constantly scratching your skin. No treatment will be effective if the patient continues to scratch the lesions. For this:
- cut your nails short
- at night during an exacerbation, wear cotton gloves on your hands or sleep in cotton pajamas. This will reduce involuntary scratching during sleep.
2) It is very important to avoid contact with allergens that cause aggravation. For this:
- hypoallergenic diet required
- New clothes should be pre-washed.
- You should use soap-based laundry detergents
- clothes should be rinsed thoroughly
- Wet clean the house daily
3) Reduce dry skin. For this:
- Use creamy soaps and detergents with a moisturizing effect.
- water procedures should be short-term (5-10 minutes), in warm (not hot) water.
- After washing or swimming in the pool, apply body cream or milk to your body.
- Loose clothing made of pure cotton should be worn.
- It is advisable to abandon woolen clothes and woolen blankets, replacing them with clothes and blankets made of other materials.
Treatment tactics for neurodermatitis are aimed at eliminating the disorders that provoked the development of the pathological process, as well as at preventing relapses and prolonging remissions.
Hormonal ointments for the treatment of neurodermatitis
Dexamethasone and other corticosteroid derivatives work well in cases of strong immune reactions to allergens. Hormonal ointment for neurodermatitis is indicated for patients if the disease is severe. In such situations, drugs of this type help prevent infection and skin detachment. A doctor should prescribe hormonal medications in the form of ointments after taking a blood test.
List of the most commonly prescribed hormonal ointments for neurodermatitis:
Elokom
New generation ointment. Its use is indicated for patients starting from 2 years of age. The course of daily use is quarterly, but for children, the duration of therapy should not exceed 28 days.
Fluorocort
An ointment containing triamcinolone. The product has a positive effect on foci of inflammation and eliminates allergic manifestations. When used according to the instructions for a month, itching is eliminated and scratch marks heal.
Trimistin
The ointment includes miramistin and triamcinolone. Thus, the drug has antiseptic properties, eliminates itching, and relieves allergic symptoms.
Hydrocortisone ointment
An ointment with a low hormone content, therefore, good results are achieved when applied at the onset of the disease. Can be used for a long time without the risk of causing harm to the body.
Advantan
Highly effective ointment. It is prescribed to infants starting from 4 months. The course of therapy for children is no more than 30 days, for adults - a quarter.
Prednisolone
An ointment with universal properties. The structure of the product contains a hormone of synthetic origin with an effect aimed at eliminating allergic manifestations and relieving the inflammatory process. Important! The use of the ointment is indicated for no more than 14 days.
Drug treatment
The antiallergic niche of therapy involves the use of antihistamines, in most cases 2 and 3 generations of drugs, which have a less inhibitory effect on the central nervous system and at the same time stabilize mast cells and at the same time block the effect of histamine, but first generation drugs are still actively used. They have a relatively quick effect and cause drowsiness, which is actually not bad in the presence of itchy dermatosis.
- First generation: Fenistil in tablets or drops (Demitenden), Tavegil (Clemastin), in tablets or injections Pipolfen (Promethazine), Fenkarol (Hifenadine), Suprastin (Chlorpyramin).
- The second generation drug, Ketotifen (Zaditen), is preferable when a skin process is combined with bronchial obstruction.
- Third generation drugs: Astelong, Astemizole, Akrivastine, Acelastine, Allergodil, Gistalong, Histim, Claritin, Clarisens, Loratadine, Levocabastine, Semprex, Telfast, Terfenadil, Teridine, Cytherizine, Ebastine.
Glucocorticoids are used in severe cases of a common process during periods of exacerbation or the presence of allergic complications in the form of acute allergic reactions (urticaria, Quincke's edema).
- Natural: cortisone, hydrocortisone.
- Semi-synthetic corticosteroids: dexamethasone, triamcinolone, prednisolone.
Treatment with ointments with glucocorticoids is carried out once a day. Apply a thin layer, do not rub in. When taken as a course, they do not cause systemic side effects (Cushing's syndrome, adrenal insufficiency, skin atrophy and diabetes mellitus). When taken for years, the body's own release of adrenal hormones gradually decreases and systemic side effects develop.
- Weak strength drugs: non-fluorinated: hydrocortisone ointment, methylprednisolone aceponate.
- Moderate strength. Non-fluorinated: Laticort, Lokoid. Fluoridated: “Afloderm”, “Ftorokort”, “Triacort”, “Esperson”, “Lokakarten”, “Lorinden”.
- Strong. Fluorinated: “Dermovate”, “Cutivate”, “Beloderm”, “Celestoderm”, “Sinalar”, “Flucinar”, “Sinaflar”. Unphotorated: “Elokom”, “Advantan”.
The main task of non-hormonal drugs is to dry the skin (Zinc ointment or paste, Ski-derm) and have a softening effect (Gistan). However, some drugs also have an anti-inflammatory effect (Apilak, drugs based on tar and ichthyol), and also reduce itching (Elidel, Glutamol). They also use healing ointments (Bipanten, Panthenol).
Autosera are made from the patient’s own blood, which is collected at the peak of an exacerbation of neurodermatitis. Thus, the patient receives antibodies against allergens.
Classification of neurodermatitis
According to the degree of prevalence of the disease, there are:
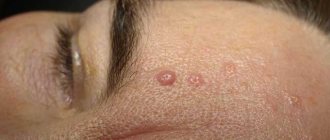
- Limited form - papular rashes form in certain areas and do not spread to other areas. It is characterized by intense itching (more pronounced at night), the appearance of pink or brownish spots covered with pityriasis scales when scratching. Increasing in size, they form foci with a clearly defined relief.
- Diffuse form - single papules appear, which merge to form large spots covering a significant surface of the skin. The skin thickens, becomes dry and hard. This is the most common form of the disease, found in children, often combined with bronchial asthma, hay fever, and urticaria.
- Disseminated form - individual nodular rashes are distributed throughout the body. It is characterized by a long course and complications in the form of pyoderma (pustular formations caused by staphylococcal infection).
Physiotherapeutic treatment
A procedure such as phototherapy (using a quartz lamp, UV irradiation or selective phototherapy) has proven itself very well in the treatment of neurodermatitis. Selective phototherapy, which involves the use of UV rays with a wavelength of 315-320 nm, is indicated for patients suffering from neurodermatitis only during the period of remission of the disease. The duration of the course of treatment is 15-20 procedures.
Also, as a physiotherapeutic treatment for neurodermatitis, dermatologists recommend cryomassage (use of liquid nitrogen) and irradiation of lesions with a medical laser.
At the same time, sanatorium-resort treatment (on the coast of the Black and Dead Seas) has a very beneficial effect on the patient’s body.
Complications
Since even the older age group cannot withstand severe itching, the patient scratches the lesions, weakening the barrier functions of the skin, which opens the gates for infection. Before starting treatment for neurodermatitis in children, it is important to eliminate the symptoms that cause irritability and anxiety.
Common complications may include:
- Bacterial infection. Penetration of the pathogen Staphylococcus aureus into the focus leads to the appearance of erythema, exudation, and hardened crusts. The disease can develop into chronic neurodermatitis.
- Viral infection:
- Kaposi's eczema (herpetic);
- warts;
- eczema vaccinatum;
- molluscum contagiosum.
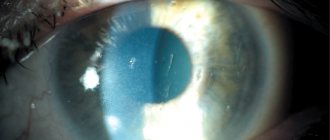
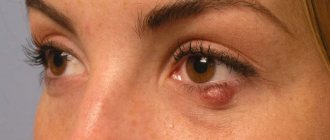
- In half of the patients, cataract is diagnosed as a complication.
Timely consultation with a doctor, avoiding self-medication and unconventional methods of getting rid of the disease, allows you to stop the disease in the initial stages and prevent the development of complications.
Folk remedies
Based on natural ingredients, you can prepare various home remedies to successfully combat skin ailments. This:
- Lotions, baths, rubdowns. For various treatments of inflamed areas of the skin and for lotions, herbal decoctions with an anti-inflammatory and soothing effect are ideal. Well proven: chamomile, string, oregano, nettle, pine needles, thyme, plantain, mint. You can make both one-component infusions and decoctions from a collection of herbs.
- Creams, ointments. Most often, to prepare an ointment, pork fat/lard is used as a fatty base; it must first be melted and purified sulfur added until a homogeneous mass is obtained. Before use, thoroughly clean the affected areas with baby soap.
- Another homemade ointment recipe that can be prepared from any bird fat, beeswax, and birch tar. Mix all components, place in a ceramic container and leave for 4 hours in a warm place or on a heated surface.
- Compresses. Blue clay, which can easily be purchased at a pharmacy or cosmetic store, has proven itself to be very positive in the treatment of illness. The clay should be mixed with sea salt in equal proportions, add water and apply this slurry in an even layer to the affected areas. Next, you need to wait until the mixture dries and carefully rinse with warm water.
Traditional methods of treatment
Treatment with medicinal herbs in some cases can significantly alleviate the patient's condition. But before you start using folk remedies, you should consult your doctor about the possibility of use.
Traditional medicine recipes:
- 2 tsp. dry dandelion leaves and roots pour 200 ml of water. Boil for 5 minutes, leave for 8 hours. Drink 100 ml hot before meals.
- Take an equal amount of burdock roots, elecampane and walnut leaves.
- 1 tbsp. l. Pour a glass of boiling water over the crushed mixture of herbs. Leave in a water bath for 10 minutes, strain and lubricate the affected areas of the skin.
- Grind fresh celery leaves, squeeze out the juice and lubricate purulent wounds 2-3 times a day.
- 1 tbsp. l. oak bark and 1 tbsp. l. steam calamus root with 300 ml of boiling water. Boil for 15 minutes and use as compresses for inflammation of the skin.
- Chamomile (contains essential oil) and in the form of baths has a healing effect on the skin. Use for skin rashes, abscesses, wounds. It is necessary to pour 250 g of the plant into 500 ml of water and boil for 15 minutes, then strain and use for bathing.
- In mild cases, herbal baths will help relieve skin rashes and itching. To prepare the decoction, take 3 tbsp. l. Brew herbs (chamomile, string, sage) with boiling water and leave for 30-40 minutes, then strain and add when taking a bath.
Nutrition rules
A diet for neurodermatitis in adults involves avoiding salt, hot and spicy foods, and foods containing large amounts of carbohydrates. In the acute period, foods with a high index of allergic activity are excluded from the diet:
- eggs,
- whole milk,
- seafood,
- chocolate,
- citrus
During the period of exacerbation, you should avoid eating fatty meats and fish, fast food, canned food, and products containing artificial colors and flavors.
The emphasis in nutrition is on following a dairy-vegetable diet. It is healthy to eat fresh vegetables and fruits, salads with vegetable oil, and dairy products. It is recommended to drink more fluid (up to 2 liters per day). The diet includes boiled dietary meat, cereals, vegetable purees, and low-fat broths. It is better to replace sugar with xylitol or sorbitol. The preferred drinks are green tea, rosehip decoction, compotes, and mineral water.
Diet for neurodermatitis
Food is often responsible for exacerbating neurodermatitis. Which product caused the allergic reaction is determined in the laboratory. Based on the results of the study, a specific elimination diet is prescribed, in which foods harmful to his health are limited in the patient’s diet. The most allergenic dishes are fish and fish broths, fried meat and meat broths, chocolate, citrus fruits, sweet berries, honey, nuts, caviar, mushrooms, spicy, pickled, smoked foods, as well as food colorings. If the disease worsens, you need to completely abandon dangerous foods; in the future, in consultation with your doctor, they can be gradually added to the daily diet. In addition, short-term therapeutic fasting is possible under the supervision of a doctor. The basis of the diet of a patient with neurodermatitis should be vegetables, cereals, boiled meat, and dairy products. Also, the diet can be compiled based on the presence of concomitant diseases.
The most allergenic foods
The basis of the diet of a patient with neurodermatitis
Prevention
Prevention of neurodermatitis looks the same as prevention of any disease. Proper balanced nutrition, moderate physical activity, hardening and increasing immunity, avoiding stress. Dermatologists advise people prone to dermatological diseases to wear clothes made from natural materials that do not irritate the skin, so as not to provoke the development of the disease.
Also, during periods of remissions and exacerbations, you should not expose your skin to any irritants, for example, by doing peelings, scrubs, or using creams labeled “slimming” that contain substances that irritate the skin - pepper, cinnamon, menthol. And finally, it is important to protect sensitive skin from high and low temperatures.
Disease prevention
People with hypersensitive skin and a tendency to allergies should follow some recommendations:
- maintain the required temperature and humidity in the living room,
- follow a diet that excludes foods that cause allergies,
- carry out daily wet cleaning,
- remove all possible allergens,
- limit the use of household chemicals with high concentrations of harmful substances,
- use specialized care products for sensitive skin,
- use personal protective equipment when working with hazardous substances,
- wear close-fitting clothes made of cotton fabrics,
- monitor the integrity of the skin,
- avoid stressful situations,
- work to improve immunity.
The disease is not completely curable, but properly selected treatment can alleviate a person’s condition and lead to long-term remission without exacerbations.
Forecast
Since neurodermatitis does not threaten dangerous complications, the prognosis is the most favorable for life, although complete recovery does not occur in all cases. When the cause of neurodermatitis lies in deep allergic-genetic structures, it is impossible to exclude relapses, because therapeutic measures may not cover all manifestations of the disease.
Diffuse neurodermatitis with severe exacerbations can lead to long-term loss of performance. Limited neurodermatitis does not tend to become diffuse, which is why its prognosis is much more favorable.
Prevention and prognosis
The prognosis depends on the form of the disease. Limited neurodermatitis occurs more easily. The diffuse form forces the patient to concentrate on his condition, provoking psycho-emotional disorders. Symptoms of the disease significantly affect the patient’s quality of life and interfere with productive work. It is difficult to predict the outcome of treatment. There are many cases when there is a sharp improvement and spontaneous recovery of the patient.
Preventing the worsening of signs of pathology falls on the shoulders of the parents, since after the birth of the baby one should correctly approach the issues of nutrition and the prevention of neurodermatitis.
Prevention measures:
- do not give up breastfeeding;
- introduce complementary foods in accordance with the pediatrician’s recommendations;
- eliminate food allergens;
- strictly follow dietary recommendations;
- eliminate stress factors.
From an early age, parents should pay attention to strengthening the immune system, teaching them to follow a healthy diet, and developing a love of sports - this will help prevent the appearance of neurodermatitis in adults.
Symptoms
In order to make a timely diagnosis, you must be able to recognize the first signs of the disease. So, neurodermatitis can be identified by the following symptoms:
- severe itching, worsening at night;
- sensations cannot be controlled and the patient scratches the skin until weeping wounds form, which causes pain;
- after healing, the skin becomes rough;
- the tissues gradually become covered with rashes, pimples and spots.
The source of inflammation varies by zone. In the center, skin pigmentation is more pronounced and denser. The drawing is more clearly expressed. When papules form, they take on an unhealthy shine. These parts of the skin tend to be dry and flaky.
In addition to skin lesions, general symptoms may develop. Among them:
- general weakness;
- increased fatigue;
- decreased blood pressure;
- weight loss;
- decrease in blood sugar levels.
Some patients note malfunctions in the functioning of internal organs. Most often, with neurodermatitis, first aid may be required for the lymph nodes and adrenal glands.
Note! Constant itching can cause mental disorders.
In the presence of neurodermatitis, concomitant diseases often appear, especially bronchial asthma and contact dermatitis.
The course of neurodermatitis differs seasonally. The most striking manifestations of this chronic pathology are in the autumn-winter period.
Limited neurodermatitis
Limited neurodermatitis affects only local areas of the body and has clear boundaries, beyond which it does not spread. Development usually occurs in the presence of a hereditary and allergic factor; the prognosis in most cases is positive if there was a timely request for professional medical help.
a disseminated subtype is also distinguished , which is characterized by the presence of several areas affected by limited neurodermatitis, combined into a single focus.
Photo
For clarity, below is a photograph showing what limited neurodermatitis looks like, affecting various parts of the body:
Complications of neurodermatitis
Long-term use of hormonal ointments for the treatment of neurodermatitis entails the occurrence of recurrent bacterial, viral and fungal infections. Folliculitis, furunculosis, impetigo, hidradenitis are the most common manifestations of infection with Staphylococcus aureus or white Staphylococcus. If a fungus gets on the affected areas of the skin, then neurodermatitis is complicated by candidal cheilitis.
Often, warty tumors form in the area of the disease, which are mainly localized on the sole, back of the hands and in the inguinal folds.
The most severe complication is Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis, provoked by the herpes simplex virus. Eczema is characterized by the appearance of pustules and vesicles on areas of the skin affected by neurodermatitis. The rashes are abundant, round in shape, protrude above the surface of the skin and have a small depression in the center. The elements are protected from healthy skin by a roll of inflamed epidermis.
Clinical manifestations
Neurodermatitis is a chronic skin pathology that often recurs under the influence of provoking factors. The period of exacerbation is accompanied by severe itching, due to which patients begin to scratch the lesions at the level of reflexes. As a result, areas with injured skin begin to swell, the epidermis present on them becomes denser, after which oval-shaped papules appear on it. In most cases, relapses occur in the mid-season. After going into remission, many patients still have rashes on some areas of the skin, for example, around the lips.
Prevention of neurodermatitis
Those who have a clear genetic predisposition to this disease have the opportunity to avoid its occurrence if they strictly follow the recommendations for taking preventive measures. Thus, the most important factor is the avoidance of neuro-emotional stress . To do this, you should do meditation, yoga, or use other techniques. An important factor is limiting contact with allergens of various kinds. This also applies to foods that provoke allergic reactions . It is necessary to use only soft and hypoallergenic cosmetics in the process of body care, and protect the skin from frostbite and burns. It is also very important to promptly treat diathesis and childhood eczema .
Diagnostics
A dermatologist diagnoses neurodermatitis. As a rule, making a diagnosis is not difficult. It is important for the doctor to differentiate this pathology from scabies, lichen planus, chronic forms of eczema, and some fungal skin lesions.
The doctor listens to what complaints the patient has, asks him about the chronic diseases of his relatives, and issues a referral for a blood test for immunoglobulins. If the skin is covered with pustules, it is necessary to carry out a bacteriological culture of the smear.
What is neurodermatitis
The disease neurodermatitis is a chronic disease of the skin, the symptoms of which are similar to those of atopic dermatitis. It occurs due to negative changes in the endocrine and nervous system of an adult. Many scientists are inclined to believe that neurodermatitis may be hereditary, but this fact has not been confirmed. People with hormonal or nervous disorders are at risk. For the disease to worsen, you only need an irritating factor. Often this condition in adults is stress or increased load on the body's systems.
Therapeutic measures
Symptoms and treatment are determined by a dermatologist. Sometimes it can be difficult to differentiate neurodermatitis from atopic dermatitis and some other skin diseases, although the therapy will be largely similar.
Simple chronic lichen can be cured with an integrated approach. Classic therapy includes:
- taking antihistamines;
- physiotherapy to increase skin resistance to external infections;
- the use of drugs with a sedative effect, as well as drugs that regulate the functioning of the nervous system;
- the use of drugs for local treatment of the skin and stimulation of regenerative processes.
In severe cases of neurodermatitis, hormonal ointments are prescribed. The choice of drug is made based on the clinical picture and individual characteristics of the body. Hormone therapy using low concentration drugs is prescribed to young children.
Treatment of limited neurodermatitis involves mandatory detoxification of the body. For this purpose, enterosorbents and diuretics are prescribed. It is important to follow a hypoallergenic diet during treatment. Smoked foods, chocolate, strong meat broths, red fish, offal, honey, and exotic fruits are excluded from the diet. It is necessary to increase the consumption of fermented milk products, cereals, steamed and fresh vegetables.
If the nervous system is weak, tranquilizers and antipsychotics are prescribed: Levomepromazine, Trioxazine, Oxilidine. In the case of the development of depressive conditions against the background of neurodermatitis, tricyclic antidepressants are recommended.
Simple chronic lichen is successfully treated with ointments with naphthalan. This group includes drugs such as Naftaderm and naphthalan oil. They suppress inflammatory processes, promote skin regeneration, and reduce the risk of relapses. Preparations with zinc will also be useful for inflamed skin. Treatment of limited neurodermatitis using the drug "Desitin" is effective. It contains zinc oxide, which improves metabolic processes, creates a protective film on the surface of the skin, and inhibits the release of exudate by inflamed cells.
During treatment, it is advisable to limit water treatments, as they greatly dry out and weaken the skin. At the same time, dermatoprotective drugs, antiseptics, antipruritic and emollient ointments are prescribed.
Treatment of focal neurodermatitis
- Identifying the allergen and eliminating contact with it.
- Prescribing a hypoallergenic diet. If the allergen is food, it is completely excluded from the diet. Otherwise, all difficult-to-digest and highly allergenic foods (mushrooms, honey, vegetable fats, smoked meats, canned food, etc.) are sharply limited.
- The use of antihistamines (suprastin, fenkarol, claritin).
- Glucocorticosteroids orally and locally in the form of ointments (prednisolone).
- Calming agents.
- Adsorbent preparations for removing toxins (Multisorb, Enterosgel).
- Vitamins.
- Ointments with antibiotics and steroids (Lorinden, Sinaflan, Trimistin), creams with vitamins, compresses with tanning agents (Delasquin, Dimexide).
- Physiotherapy (electrophoresis, phonophoresis on rash sites, UV irradiation, etc.).
For neurodermatitis, all therapeutic measures, starting with the identification of the antigen, should be carried out by professionals - dermatologists, allergists and related specialists. Only in this case can therapy become adequate and effective.
Treatment
The most effective treatment is complex treatment of the disease, which includes:
- Taking pharmacological drugs.
- Use of local treatment products.
- Undergoing physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Compliance with a special dietary complex.
- Compliance with precautions during the rehabilitation period.
A course of treatment can only be prescribed by a specialist who determines the appropriateness of certain measures in each case, taking into account its individual characteristics and the patient’s health condition.
Diet
Regardless of the specifics of the prescribed course, compliance with the dietary complex is a prerequisite.
In accordance with it, the following foods and drinks should be excluded from the diet:
- Whole cow's milk.
- Citrus fruits.
- Mushrooms.
- Strawberries, dark grapes, bananas, raspberries, peaches, apricots, persimmons, kiwi, sea buckthorn, pineapple.
- Carrots, beets, pumpkin.
- Any nuts.
- Alcohol products.
- Products containing preservatives, dyes and flavor stabilizers.
- Honey.
- Chicken eggs.
- Soy.
- Sea fish, any seafood.
- Chocolate and any confectionery and sweets.
- Meat by-products.
- Legumes.
- Spices, hot spices and seasonings.
- Cocoa, strong coffee.
- Strong tea.
- Semolina.
The basis of the diet can be the following products, the consumption of which is not subject to any restrictions:
- Various types of permitted cereals.
- Fermented milk products of natural origin.
- Meat with reduced fat content.
- Fresh greens, cabbage, light varieties of pumpkin and zucchini.
- Pears, light varieties of apples, red currants.
- Juice from green apples mixed with water in equal proportions.
- Butter.
- Sunflower and olive oil.
- Low-fat varieties of cheese to which no spices are added.
- Diet bread, unsweetened cookies, savory bread, crackers and dryers.
- Weak tea, preferably without added sugar.
Ointments
An important part of therapy is the use of various ointments; most often, experts prescribe the following drugs:
- "Bepanten" or any analogues of this ointment. It relieves the feeling of itching and accelerates the process of regeneration of damaged tissues and skin. Also used for dermatitis. Here you can see a photo of dermatitis on your hands.
- “Gistan” has a completely natural composition, which allows you to get rid of the feeling of itching and eliminate flaking of the skin.
- "Eplan" is an ointment that has a whole range of useful properties: an antiseptic effect to reduce the risk of infection, relieve inflammation, eliminate itching, accelerate the process of restoration of damaged areas.
- "Advantan" is a hormonal ointment; it is one of the most effective drugs in its class. It is usually prescribed in the most complex or advanced situations.
- Prednisolone is another hormonal ointment that eliminates allergic reactions and relieves itching.
Prednisolone is also used in the treatment of skin areas infected with streptococci. In another article you can read in detail what streptoderma is in children and adults.
Systemic drugs
Systemic drugs are no less important; in different cases, the following drugs can be prescribed for the treatment of neurodermatitis:
- “Festal”, “Mezim Forte” and other enzymatic agents are prescribed if there are problems with the digestive system that lead to the occurrence of neurodermatitis or are its consequence.
- Probiotics are prescribed for severe intestinal dysbiosis.
- Hepatoprotectors are intended to normalize the functioning of the liver; they are prescribed in the later stages of the disease or in the treatment of chronic neurodermatitis.
- Antihistamines are a mandatory part of therapy; one of the following drugs is usually prescribed: Chlopyramine, Astemizole or Ebastine.
- Ketotifen in tablet form is often prescribed to block histamine receptors.
- 10% calcium gluconate solution , used for intravenous administration.
- Vitamin complexes containing vitamin A, B and E.
Neurodermatitis in children
Dermatological disease - neurodermatitis - can be different. There are several types of this problem, and each of them requires individual therapy and prevention. For example, the diffuse form occurs in a purely chronic form and is diagnosed in 80% of all cases in children under 5-6 years of age. In babies who are breastfed, the chronic form of the disease is not the leading one. The more severe neurodermatitis in children, the greater the likelihood that the immune system is not working properly. Such neurodermatitis in children is treated comprehensively, where complete protection of the skin is important for local therapy, which will help relieve itching and eliminate dryness. Drugs with an antipruritic effect and those that relieve inflammation are used. It is important to prevent contact with factors that provoke the disease.