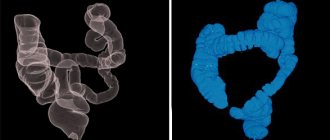
CT scan of the intestine is most often used as a diagnostic tool in the gastroenterological area. This method is non-invasive and is based on the use of x-rays. Allows you to obtain very clear and detailed images of internal organs. Often, computed tomography of the intestines is also called “virtual colonoscopy,” since the effectiveness of the procedure allows you to examine the intestines no less accurately than invasive methods.
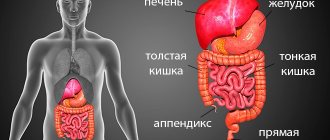
Computed tomography of the intestine
CT bowel
shows what is happening to the internal organ and allows not only to examine one section of it, but to study the condition of the large intestine along its entire length: from the cecum to the rectum. The three-dimensional image that is obtained makes it possible to carefully examine and determine the thickness, as well as the relief of the mucous membrane, and evaluate the entire structure of the walls. This method allows you to identify and study various processes associated with inflammation, tumors and erosive and ulcerative lesions.
The advantage of CT examination of the intestine is that the procedure is painless, unlike colonoscopy, it does not lead to complications, does not injure the mucous membrane and cannot lead to internal bleeding. Therefore, this method is considered as safe as possible for the patient, even in serious condition.
When is a bowel CT scan prescribed?
There are three main reasons for ordering a CT scan of the colon. This is a study of inflammation in diseases such as Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, the search for various neoplasms, and also to detect the source of intestinal bleeding. The method helps to detect polyps and metastases. It is also recommended that people over 40 years of age be examined every 5-8 years as a preventative measure.
Purposes of application
Computed tomography of the intestine is used in several aspects:
- as a screening method;
- if you suspect an acute abdomen requiring urgent surgery;
- comprehensive diagnosis of neoplasms;
- monitoring treatment results;
- For carrying out various therapeutic and diagnostic procedures.
Since this research method involves radiation exposure, the indications for its implementation must be clearly formulated.
To whom and when is it assigned?
Tomographs are capable of displaying a very clear layer-by-layer (up to 128 layers) image of tissue, which makes it possible to detect the smallest pathological process in tissue.
- CT scanning is recommended for people who, for one reason or another, cannot undergo a colonoscopy procedure.
- Computed tomography of the stomach and intestines is allowed for those patients who have a pacemaker or metal implants.
- CT scanning of the stomach and intestines is sometimes used in pediatrics and for diagnosing very elderly patients, since it only takes a few minutes.
- Under X-ray control, operations and punctures are performed, and chronic pain syndrome is treated.
- The study is prescribed as a comprehensive examination of various intestinal diseases.
- CT scan is prescribed for Crohn's disease.
- The oncology community recommends that men and women over 50 years of age have a cancer alert and have a CT scan of the intestine every 5 years. This is a painless way of early screening for colon cancer.
- For people with a family history of gastrointestinal cancer in close relatives, examination is indicated earlier. Cases of intestinal cancer are also common at the age of 35, so from the age of 35 you need to have your intestines checked every 3 years.
- This method is also indicated for those with a predisposition to intestinal diseases, frequent constipation, bleeding, and anemia.
Sometimes the patient refuses a CT scan for fear of X-ray radiation. However, the radiation load on the organ is small and dosed. Neighboring organs are not exposed to radiation. So this method is relatively safe.
What does it show
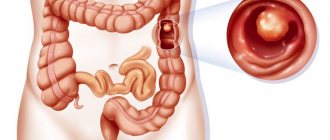
Pathologies that can be detected by CT diagnostics:
- inflammation of the small and large intestines;
- polyps;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- erosions and ulcers;
- risk of perforation.
What does a CT scan of the intestines show?
What does a CT scan of the intestine show? The only difference between this method and colonoscopy is that it is less accurate, since with a CT scan it is impossible to see the color of the mucous membrane or take a biopsy from pathological lesions. However, with the help of three-dimensional scanning, you can view the organ from all sides, which is the great advantage of CT. The technique allows you to study the relief of the intestinal mucosa, the thickness and structure of its walls. If diffuse thickening is detected, it is easy to diagnose lymphoma, leiomyoma and leiomyosarcoma. It is also possible to examine the small intestine to determine its patency.
Indications for research
Computed tomography is the final study that allows you to make an accurate diagnosis. It is indicated for a thorough study of the small and large intestines. Objects for study are:
- polyps;
- tumors;
- neoplasms;
- inflammatory foci;
- scarring.
Scanning allows you to determine the exact location of the pathological focus, the degree of its prevalence, the risk of perforation, and oncology. Thanks to effective images, the doctor receives information about the blood vessels, the degree of tumor growth through the intestinal wall, and polyps degenerating into a tumor, which allows timely treatment to begin.
Indications for a bowel scan are:
- ulcerative colitis;
- intestinal bleeding;
- anemia;
- stomach ache;
- intestinal abnormalities.
Tomography determines the presence of both single and multiple polyps
This study is widely used for the prevention of cancer in people over 50 years of age. In pediatrics, the procedure is recommended to be performed no earlier than 14 years of age. If there is an urgent need, then if indicated, diagnosis can be done at an earlier age. MRI is usually recommended for examining children.
CT scan of the intestines: preparation for the procedure
Preparation for a CT scan of the intestines is usually the same for everyone, but you should always consult with your doctor in advance and follow all his instructions to achieve the best results during the examination.
Purgation
Since the study is carried out on an empty stomach, doctors usually prescribe the procedure in the morning. Computed tomography of the intestine requires preparation, namely, cleansing measures should be carried out. It is necessary to get rid of accumulated gases in the intestines; for this you should take Espumisan, as well as an enterosorbent such as activated carbon. The doctor should also prescribe an osmotic laxative, which is taken the day before the examination. It is advised to completely cleanse the intestines with an enema, and drink half a liter of still water an hour before the CT scan.
Diet
Of course, it is necessary to completely cleanse the intestines of feces; to do this, you should switch to a special diet for 2-3 days, which excludes from the diet foods that contribute to the formation of gas. These are fermented milk products, legumes, raw vegetables and fruits, sweets, and fermented foods. You should also not eat foods that promote constipation to avoid constipation, but it is also not recommended to eat foods with a laxative effect to prevent flatulence. The day before a CT scan of the intestine, it is best to consume liquid food, water, and broth.
Contraindications
You cannot do a CT scan of the stomach and intestines without contrast in the following cases:
- during pregnancy;
- if the person's weight is more than the device can support. For such cases, tomographs with increased strength have been developed;
- diagnosis of epilepsy, seizure alertness.
More often, a computed tomography scan of the intestine is done together with contrast. In this case, the contraindications expand:
- Individual allergic reaction to a contrast agent.
- Chronic and acute renal failure.
- Chronic heart failure.
- Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus is not in remission. Because most diabetics take metformin, the use of CT with contrast is limited for them. If it is necessary, it is recommended to stop taking the drug 2 days before the procedure. Otherwise, the iodine-containing drug will slow down the elimination of metformin, which will cause side effects.
- Pregnancy at any stage due to the teratogenic effect.
- Hypothyroidism, thyrotoxicosis, Hashimoto's disease, other thyroid diseases. The contrast agent disrupts the metabolism of iodine-containing hormones.
- Multiple myeloma.
Despite the contraindications, the computed tomography method is certainly relevant. Computed tomography of the large intestine allows you to avoid intervention in the body, but, of course, does not replace colonoscopy.
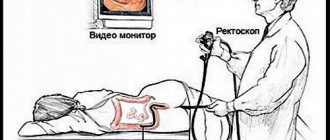
How is the procedure done?
A CT scan of the intestine may be slightly uncomfortable because it requires filling the rectum with air or carbon dioxide. To do this, the patient should lie on the examination table in the desired position as recommended by a specialist. Afterwards, the limbs are secured with special belts to prevent unnecessary movements for clear diagnosis. A thin tube is inserted into the patient's anus, through which gas or air is pumped into the rectum. This is done in order to straighten the intestinal walls, since in its normal state it has many folds. The rectum allows for better diagnosis of the organ along its entire length, even in hard-to-reach places.
The procedure itself takes 15-20 minutes. During the images, the patient will need to hold their breath for 3-4 seconds.
Contrast enhancement
In some cases, contrast enhancement is required to diagnose the intestine. To do this, the patient must take the necessary medication several hours before the examination. Sometimes contrast is administered immediately before the procedure using an enema. This allows you to better visualize the contours of the intestines in the images.
Contrast CT
The administration of contrast is necessary for the diagnosis of oncological formations. The dye is added immediately before the procedure begins. It moves through the body with the bloodstream, accumulating in the organs. This process greatly improves visualization. Metastases and tumors have a fairly developed circulatory system, based on which, with the help of a contrast component, the prevalence of the pathology, its boundaries, structural features and character are determined with high accuracy.
Contrast tomography allows you to detect oncology at the very beginning of its formation
Coloring components do not harm human health. They are removed without residue within 2 days. Extended scanning is indicated in the following cases: to examine the degeneration of cells into cancer cells, to monitor prescribed treatment, during preparation for surgery, if magnetic resonance imaging is not indicated for reasons, then as an alternative method.
Hydro MRI of the intestine
Tip: if you drink more liquid after an extended scan, you can speed up the process of removing the contrast. Computed tomography with contrast suggests the following administration of the substance:
- intravenous. Involves a one-time administration. Most often used to visualize blood vessels;
- oral. Before diagnosis, the patient takes the contrast orally in small portions. After a short time, you can begin research. This method is most often used to diagnose the stomach;
- rectal, when the drug is administered through the anus;
- bolus Allows a more detailed examination of the area under study, is supplied to the body automatically, and regulates the volume of contrast during the study. If necessary, you can increase the supply of the contrast component.
The doctor calculates the dose of the contrast component based on the patient’s personality and weight.
Reviews about the procedures
Nikolai, 45 years old: I have never had any health problems, but I recently learned that after forty you need to check your intestines. I decided to have a colonoscopy to rule out a hereditary predisposition to cancer. Two days before the procedure, I went on a diet and did an intestinal lavage. The procedure went well, no pathology was found.
Nina, 52 years old: For several years I suffered from diarrhea, which always produced blood. The temperature rose frequently. I went to the clinic and were advised to have an ultrasound check of the intestines. To do this I had to clean it completely. The result showed the presence of polyps in the colon. To eliminate them, I had a coloscopy. Operation was successfully completed.
Tatyana, 36 years old: After giving birth, I couldn’t go to the toilet normally, so I decided to go for an intestinal examination. To do this, I had to take blood, urine, and stool tests. The proctologist said that they show the presence of pathology. I had to do a computer colonography, which revealed a large presence of polyps and hemorrhoids.
An important computer diagnostic is a CT scan of the abdominal cavity with contrast of internal organs, which is necessary to show suspected foci of pathology. In this way, the condition of the peritoneum and retroperitoneal space can be assessed, along with the vessels and abdominal lymph nodes. Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity with a contrast agent is performed in the hospital, facilitating the final diagnosis.
Advantages and disadvantages of CT scan of the stomach and small intestine
Using computed tomography, specialists study the deepest parts of the intestines, stomach and other vital organs. This procedure helps to identify various hidden diseases in the early stages of their occurrence. CT allows you to detect pathologies at stages when symptoms have not yet appeared and the disease has not reached the chronic stage.
A tomograph with the widest technical capabilities allows you to obtain a series of informative images and display them on the monitor screen. All images together help the doctor see a holistic picture of the disease that has affected the intestines or stomach. All 3D images are saved on the computer, so the treating doctor can view them at any time.
The advantages of diagnostics using a computed tomograph are:
- detailed study and analysis of the structure, properties and parameters of the intestinal section under study;
- obtaining high-precision 3D images;
- quick and accurate detection of pathologies and anomalies in organs;
- control over pathologies and their effects on other tissues and organs;
- minimal exposure to the human body;
- painlessness of the procedure and absence of any discomfort during diagnosis.
Disadvantages of computed tomography:
- although in small quantities, the human body is irradiated, which has a detrimental effect on the patient’s well-being;
- It is prohibited to conduct research during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- people weighing more than 200 kilograms need to have their organs diagnosed only if the device is designed for that weight.
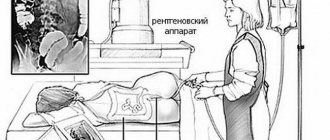
How is an abdominal CT scan done?
Virtual colonoscopy is performed with or without a contrast agent; the information content of the computer method depends on this. Native CT is performed without the use of contrast and shows the general condition of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity. The sequence of actions during a clinical trial is as follows:
- The patient is required to remove all metal objects and jewelry.
- The patient should lie on the extendable table on his back.
- The table moves into the tunnel of the device, and communication with the patient takes place using a microphone and speakers.
- When the table rotates, the tomograph takes several informative images.
- If the image quality is decent, the table moves out of the tomograph ring.
CT scan of the abdomen with contrast
When a contrast agent is administered intravenously, the internal organs are additionally illuminated, which is especially appropriate if metastases, malignant tumors, or cysts are suspected. The resulting image shows the exact shape and size of the progressing tumor, the location of the pathology. Reviews from specialists who regularly use bolus contrast to make a final diagnosis are positive and report that this diagnostic method is more informative for the upcoming treatment.
Which is better MRI or CT?
To understand which method is better, let's look at the advantages of each of them:
https://youtu.be/bfHAbeB616w
Advantages of MRI:
- high accuracy;
- does not bring discomfort, unpleasant or painful sensations;
- minimum contraindications, practically does not harm the body;
- It is impossible to make an incorrect diagnosis using this technique.
As for CT scanning of the stomach, this method also has many advantages, which we discussed above; when compared with MRI, the first diagnostic method is cheaper, and it provides maximum information. The safety of CT is a controversial issue because there is a radiation dose involved and it is not appropriate to perform the procedure repeatedly within a short period of time. MRI can be done as many times as the diagnostician needs to make the correct diagnosis. In general, deciding which method will be preferable is the doctor’s task.