Blood is a liquid connective tissue that performs many functions in the human body: transport, protective, thermoregulatory, etc. It reacts very sensitively to any health problems. Due to the fact that blood parameters change instantly, its analysis makes it possible to identify any pathology at a very early stage. There are many types of research that provide complete information about the course of the disease at any stage.
Clinical (general) analysis
Clinical (general) analysis
blood is prescribed both for preventive purposes and during illness. The required amount of biomaterial can be collected from a finger or a vein. Before the procedure, you must completely avoid eating and drinking 8 hours before the procedure. You can only drink drinking water without gas. The patient is advised to refrain from sports and strenuous physical activity.
A clinical blood test determines:
- The state of the body's immune system.
- Hemoglobin level.
- The presence and severity of the inflammatory process.
- The presence of allergic or parasitic diseases.
- Disorders of the blood clotting process.
What a blood test from a vein shows: deciphering the indicators
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (Hb, HGB) is a complex iron-containing protein, the main function of which is the transport of oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and the removal of carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs.
An increase in hemoglobin concentration is observed with erythremia, heart defects, hydronephrosis, obesity, kidney or liver tumors, dehydration, and smoking. A physiological increase in hemoglobin levels occurs with excessive physical exertion, stay in high mountains, and also in newborns.
Hemoglobin is reduced in bleeding, anemia, chronic kidney disease, liver cirrhosis, hypothyroidism, malignant tumors, chronic infectious diseases, overhydration, and also during pregnancy.
Blood chemistry
Blood chemistry
gives the most complete picture of the functioning of all human organs and systems, as well as the speed of metabolic processes occurring in his body. It is recommended to conduct a biochemical blood test annually. The biomaterial for research is taken from a vein in an amount of no more than 5 ml and distributed into several test tubes. Blood sampling is performed exclusively in the morning. Before analysis it is necessary to prepare:
Sign up for blood tests
Make an appointment
Biochemical research
Not only the previous type of blood test can provide information about the patient’s overall health. What other methods exist for studying biomaterial?
Most often, doctors prescribe a study, the results of which allow us to assess the degree of functioning of all organs and systems. It is called a biochemical blood test - a type of laboratory diagnostics, which also reflects the level of saturation of the body with vital microelements and allows you to find out the speed of metabolic processes.
It is recommended to conduct the study annually to monitor health status. Also, with its help, the doctor has the opportunity to observe changes in existing diseases and, if necessary, adjust the previously prescribed treatment regimen.
For this type of analysis, blood is taken from a vein in a volume not exceeding 5 ml, which is then distributed into several test tubes.
The study requires thorough preparation:
- It is forbidden to eat food 12 hours before collecting biomaterial;
- 24 hours before, you need to exclude coffee and strong tea from your diet;
- for 3 days it is undesirable to eat fatty, fried, spicy, salty foods, drink alcohol-containing drinks;
- within 24 hours you need to reduce the intensity of physical activity;
- It is necessary to donate blood in the morning, before taking medications and performing other medical procedures;
- 24 hours in advance, it is prohibited to take medications that may affect the result (the list is agreed upon with the attending physician);
- Immediately before the test, it is important to avoid stressful situations.
Fulfillment of these conditions is mandatory, since any action performed by a person is reflected in the results of biochemical analysis.
Blood grouping and determination of Rh factor
Blood grouping and determination of the Rh factor is one of the important studies that can save the life of a patient as a result of an accident. This laboratory analysis is also carried out:
Biomaterial is collected from a vein in the morning. Before the procedure, the patient should follow simple recommendations - do not consume food or alcoholic beverages for 4 hours, avoid smoking, and reduce the intensity of physical activity 12 hours before the test.
Blood collection and patient age
If biological fluid is needed for OAC, it is often taken from a capillary. In newborns, the sampling is made from the heel, since the capillary network in this place is thicker. There is a risk of tissue damage when a baby's finger is pierced with a scarifier.
General blood test for children under one year of age - instructions from a pediatrician.
If there are indications for testing from venous biological fluid, it can be taken even from newborns. In this case, the collection is made from a vein on the head, since the vessels in this place are better visible and the risk of tissue damage is reduced.
Important! Venous blood from infants is taken only when indicated. If they are absent, biological fluid is taken from the capillary. This reduces the risk of tissue damage and infection in the general bloodstream.
There are rules for collecting blood from newborns and infants. Both parents and medical staff must adhere to them.
- The donation of biological fluid is performed on an empty stomach. The baby's last meal should be 4 hours before the test.
- The limb from which the sampling is made must be warm so that blood circulates more strongly through the vessels.
- The doctor examines the patient, reveals the degree of translucency of the vessels under the skin. Blood can be taken from the head or elbow.
- The surface to be punctured is treated with an antiseptic or alcohol. If fluid is taken from the elbow, a tourniquet is applied.
- A puncture is made and a little venous blood is taken with a syringe.
- After the procedure is completed, the skin is treated with alcohol or an antiseptic. Apply an adhesive plaster and wrap the elbow with a bandage.
- When collecting biological fluid from the head, no tourniquets are applied. A puncture is made and the liquid is withdrawn. Antiseptic procedures are carried out and a patch is applied.
If all rules for collecting biological fluid are followed, there is no danger to a newborn or infant. If a nurse accidentally punctures a vein, it will cause a small hematoma that will resolve over time. There is no risk to the baby's health, since no medication is administered.
How much blood is taken from the finger and vein for analysis?
To carry out OAC, 1 ml of biological fluid is required. The nurse takes a volume of biological fluid that is 5 ml. This is due to the following factors:
- the possibility of medical error and re-testing if additional blood is available;
- the ability to conduct additional tests that require a larger volume of biological fluid.
Progress of blood sampling from finger and vein
Taking blood from a finger takes place in several stages:
- local disinfection of the skin with an antiseptic or alcohol to prevent the risk of infection;
- puncturing the skin using a scarifier;
- collecting biological fluid using a capillary (a long vessel into which blood is poured at a slight angle);
- treating skin surfaces with an antiseptic or alcohol.
The collection of biological fluid from a vein takes place in several stages:
- treating leather surfaces with antiseptic or alcohol;
- applying a tourniquet to the area above the puncture site to slow down blood circulation through the vessel and accumulate it in the elbow;
- you cannot use your fist while drawing blood, as there is a possibility of damage to the formed elements and penetration of interstitial fluid into the sample (this will change the test result and additional blood donation will be required);
- puncturing the skin with a syringe, removing a small volume of liquid (up to 5 ml for children);
- treating the skin with an antiseptic or alcohol;
- applying adhesive plaster and bandage.
How is a general blood test performed in the laboratory?
Counting blood cells in biological fluid is carried out using two methods.
- Using a semi-automatic analyzer. It requires a liquid volume of no more than 1 ml. Data is calculated with high accuracy. The laboratory doctor places a sample of biological fluid into a machine that automatically counts absolutely all the cells. The risk of medical error is reduced.
- Counting formed elements using a microscope. The doctor counts cells in several fields of view. He will not be able to independently count all the elements, so there are errors.
Attention! At the moment, all hospitals and clinics use semi-automatic analyzers. Doctors only place blood there, the mechanism calculates all the data independently.
Deciphering a child's blood test from a doctor - read in detail.
Doctors recommend OAC for infants and infants using blood sampling from a capillary. This reduces the risk of tissue damage and puncturing the vein. For older patients, it is possible to obtain blood from a vein if there is an indication for this. To obtain reliable data, the patient must be prepared for the study. The choice of location for collecting biological fluid is determined by the doctor, not the parents.
Ekaterina Belikova, laboratory diagnostics doctor, especially for Mirmam.pro
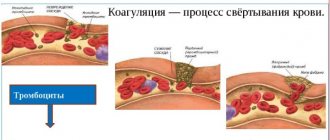
Coagulogram (hemostasiogram) or blood test
A coagulogram (hemostasiogram) or blood clotting test helps determine the quantity and quality of prothrombins, as well as their ability to form blood clots and prevent serious blood loss, as evidenced by the rate of formation of blood clots. If clotting rates are reduced, then there is a possibility of extensive bleeding even with minor injuries, which, in turn, can lead to serious health problems. Excessive blood clotting (increased thickness) can lead to the formation of blood clots that can block the most important vessels and arteries. Most often, a coagulogram is prescribed before surgery, for the diagnosis and treatment of thrombosis, during planning of pregnancy or its pathologies, for diseases of the hematopoietic organs, bleeding, diseases of the liver and cardiovascular system. To obtain reliable parameters for this type of study, the patient must follow some rules:
Blood is drawn from a vein in the morning. Before the procedure, you can drink a glass of plain water without carbon.
Main types of blood tests:
General blood analysis
Testing a few drops of blood under a microscope and using special instruments determines its cellular composition, hemoglobin concentration, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). What do these indicators indicate and what potential problems do they warn about:
- Hemoglobin. An iron-containing protein that carries oxygen and is involved in the transfer of carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs. Low hemoglobin indicates the possible development of anemia (anemia). With this disease, organs experience a chronic lack of oxygen, leading to metabolic disorders.
- Red blood cells. Red blood cells containing hemoglobin. Their main function is oxygen transport. A decrease in the number of red blood cells is a symptom of anemia. Too many red blood cells are a sign of blood thickening and also a possible signal of bone marrow disease.
- Leukocytes and lymphocytes. White blood cells responsible for protecting the body from infections. An increase in their number is a sign of an inflammatory process in the body. In some cases, a sharp increase in the number of leukocytes is one of the first markers of tumor diseases of the blood. An isolated increase in any white blood cell population is a sign of possible problems. Thus, an increase in the number of eosinophils signals the presence of an allergy or helminthic infestation. A decrease in the number of white blood cells warns of possible immunosuppression.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate. A parameter that depends on the protein composition of blood plasma. In inflammatory diseases, both acute and chronic, the concentration of proteins in the plasma increases, which leads to an increase in ESR. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which remains at a level of 40–50 mm/hour for a long time, requires further careful examination, as it is a marker of tumor processes.
How often should I take a preventative blood test? In the absence of complaints and chronic diseases - once a year.
Determination of fasting glucose
An increase in blood glucose concentration is one of the first signs of type 2 diabetes. The insidiousness of this disease is that for a long time it occurs without clear specific symptoms. In the initial stages, type 2 diabetes can be treated with diet, without the use of medications. This is why early diagnosis is so important. If a high glucose level is detected, it is necessary to repeat the test and, if the result is confirmed, contact an endocrinologist. Preventive testing is recommended for people over 50 years of age to undergo regular testing. If you are overweight, have metabolic syndrome, or have relatives with diabetes, regular monitoring of blood glucose concentrations begins at 40–45 years of age.
https://youtu.be/7iQemlTmCIY
This is interesting: How giving up sugar for a month can be beneficial
A small practical guide: 9 practical tips on how to eat less sugar
C-reactive protein
The concentration of this protein increases during inflammatory processes in the body. Modern methods for determining C-protein make it possible to detect minimal fluctuations in its amount in the blood. An increase in the concentration of C-protein is a marker of latent endogenous inflammation and the risk of developing thromboembolism and myocardial infarction. It is advisable to take this test at least once a year.
Homocysteine
Metabolism product of the sulfur-containing amino acid methionine. An increase in its concentration in the blood occurs with genetic metabolic disorders, vitamin deficiencies (folic acid, vitamins B6 and B12), diabetes mellitus. High amounts of homocysteine in the blood are toxic to vascular endothelial cells. Determination of homocysteine levels is used to assess the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. An increase in its concentration by 30% increases the risk of heart attack and thromboembolism by 80% in women and by 60% in men.
Lipid metabolism indicators
One of the main tests to assess the risk of developing atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease and the occurrence of vascular accidents (stroke, heart attack, thromboembolism) is a study of fat metabolism in the body. As a rule, not one, but several parameters are tested at once:
- total cholesterol;
- triglycerides;
- low density lipoproteins (LDL);
- high density lipoproteins (HDL);
- atherogenic coefficient.
An increase in the concentration of cholesterol, LDL and atherogenic coefficient indicates a high risk of coronary disease. In this case, it is important to adjust your diet and start taking statin drugs that normalize cholesterol levels.
Who needs to check these indicators and how often:
- for men over 40 years old at least once a year;
- women over 50 years old once a year.
Monitoring thyroid function
The thyroid gland is one of the main instruments in the hormonal ensemble of the body. Thyroid hormones regulate the intensity of metabolism, the functioning of the reproductive and cardiovascular systems. Hypothyroidism (decreased thyroid function) often occurs hidden: weight gain, drowsiness, chilliness, and menstrual irregularities are not always associated with low thyroxine levels. A blood test for thyroid-stimulating hormone and triiodothyronine (thyroxine) can detect organ dysfunction in the early stages. A preventive test is recommended annually after age 40.
Blood sugar test
A blood sugar test determines the level of glucose in a person’s blood, the amount of which affects the well-being and functioning of all internal organs. Conducting such a study is indicated for people suffering from diabetes, as well as those who are at risk for this serious disease. Preparation for analysis is a set of simple activities:
Sign up for blood tests
Make an appointment
The most important types of blood tests depending on gender
Different hormonal profiles, as well as metabolic rates and characteristics, explain the different susceptibility of men and women to the same diseases. Thus, men, due to high concentrations of testosterone, which increases cholesterol levels in the blood, are more prone to cardiovascular diseases. While the incidence of hypercholesterolemia in women is low, thanks to estrogens. Therefore, the point of application of preventive screening will depend on gender.
Important preventive tests for women
- Complete blood count and hemoglobin level. A preventive test can detect hidden anemia. This is especially important for women planning pregnancy, as well as after 45 years during hormonal changes.
- Assessment of thyroid function. Determination of the concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone and thyroxine should be carried out regularly for women after 40 years of age.
- C-reactive protein. The test allows you to identify hidden inflammatory processes in the body. It is recommended to take it not as an isolated indicator, but in conjunction with a general blood test.
- Determination of blood glucose levels. The test allows you to detect latent type 2 diabetes mellitus. The analysis is performed once a year.
Also read on this topic: Clinical minimum for women - what you need to know
Basic preventive tests for men
- Monitoring PSA levels. The purpose of preventive screening is to identify tumor processes in the prostate gland. After 40 years, the test is carried out at least once a year.
- Assessment of the risk of developing atherosclerosis and coronary disease. To get the most complete picture, it is recommended to undergo a set of tests: determine lipid metabolism indicators, the concentration of C-protein and homocysteine. The survey is carried out annually.
- Determination of blood glucose concentration.
Regular monitoring of your health using preventive blood tests, even in the absence of complaints, should become a habit. After all, most diseases are much easier to treat if they are identified at an early stage.
Anastasia Khomyakova, biochemist Illustrations: Anastasia Leman
Blood test for hormones
A blood test for hormones is prescribed by a specialist to determine the condition and correct functioning of many systems of the patient’s body. Hormones are biological active substances that regulate all important biochemical processes - growth, reproduction, metabolism and others. Changes in hormonal balance indicate pathological processes leading to the appearance of various diseases. As a rule, hormonal studies are recommended for suspected malfunctions of the internal secretion organs and associated abnormalities. The most common:
Blood test for hormones
taken in the morning, on an empty stomach. On the eve of the procedure, it is prohibited to drink alcoholic beverages or smoke. Eating should be stopped 8 hours before biomaterial collection. Taking hormonal medications must be stopped 7 days in advance, after consulting with a specialist. Women are advised to remember that hormonal levels change depending on the menstrual cycle. The most favorable days for taking hormonal tests are considered to be from 5 to 7 days from the first day of menstruation.
Health screening. What laboratory tests should be done every year?
GENERAL CONDITION OF THE BODY
General urine test, clinical blood test. The most common tests that each of us has taken at least once in our lives. Despite their familiarity, based on their results, you can draw conclusions about the changes that have affected your body, and, if necessary, prescribe a more targeted examination.
It is important to understand that the data obtained from these tests is general in nature, and the indicators characteristic of a particular disease can vary greatly from person to person.
A number of blood and urine parameters change with age, depending on dietary habits and medications. Therefore, you should not interpret the results yourself and draw hasty conclusions. Only a doctor can do this.
Price: clinical blood test - from 300 rubles, general urine test - from 200 rubles.
LIVER
Bilirubin, ALT and AST. The functioning of the detoxification system as a whole depends on how this organ functions. It is in the liver that substances that are toxic to our body are neutralized. Tests for liver enzymes (ALT and AST), as well as the bile pigment - bilirubin - can determine how effectively the liver copes with such a complex function.
Price: billirubin (full complex) - from 500 rubles, AST, ALT - from 270 rubles. every.
FAT METABOLISM
Lipid profile: total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL, LDL. A test that helps assess the total concentration of cholesterol in the blood. And also the ratio of high-density lipoproteins - LDL ("good" cholesterol) and low-density lipoproteins LPN ("bad" cholesterol). Test results help assess the risks associated with atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease and stroke.
This test should be performed on all people who are overweight, have diabetes, or have a family history of cardiovascular disease.
Often they only look at total cholesterol levels. With a big stretch, such a test can be called informative. It is necessary to check the ratio of HDL and LDL. Paradoxically, both of these substances are important for our body. Thus, the main function of LDL is the delivery of cholesterol to the place of requirement. And HDL removes unclaimed cholesterol from cells, as well as from existing atherosclerotic plaques. All lipoproteins work together.
Price: from 650 rub.
THYROID
TSH, AT-TPO, AT-TG. The thyroid gland is the conductor of all metabolic processes in our body. The work of all other glands of the endocrine system depends on its health. Some women like to go on strict diets with a daily calorie content of 600-700 kcal, and this significantly undermines the functioning of the thyroid gland, reducing the production of its hormones. These tests must be done before planning a pregnancy. Tests are taken for TSH, a hypothalamic hormone that regulates the activity of the thyroid gland, as well as for the sensitivity of the gland itself to these hormones - AT-TPO, AT-TG.
Price: AT-TPO - from 1500 rubles, AT-TG - from 600 rubles, TTG - from 300 rubles.
If any test reveals abnormalities, then a repeat analysis must be done. This eliminates laboratory error. If deviations from the norm are confirmed, a specific treatment regimen is prescribed. After 2-3 months, the diagnosis is repeated to assess the effectiveness of therapy.
IMMUNITY, MOOD, BONES
Blood test for vitamin D3 (25-OH-choleciferol). 98% of residents of central Russia suffer from a deficiency of this vitamin. It regulates the functioning of the immune system, maintains normal levels of immunity and our mood. Responsible for emotional balance and control of eating behavior. With its deficiency, there is a tendency to overeat.
Price: from 1000 rub.
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Blood test for homocysteine. This substance is an indicator of vascular health. The analysis helps determine the risks of cardiovascular disease. Moreover, its concentration shows how well the pregnancy will go: the level is higher than normal, the risks of preeclampsia, gestosis and possible pregnancy loss increase.
Price: from 1000 rub.
HEATING SYSTEM
Iron, ferritin. The presence or absence of iron deficiency anemia is an important indicator of health. Due to the regular loss of this valuable microelement during the menstrual cycle, women need much more of it. The need for iron also increases among those who engage in fitness. It is important not only to measure the concentration of iron in the blood, but also to take into account its reserves in tissues. Determining the level of ferritin makes it possible to detect a decrease in iron stores as early as possible. This condition is called latent iron deficiency.
Price: iron - from 130 rubles, ferritin - from 600 rubles.
SYSTEMIC INFLAMMATION
C-reactive protein is ultrasensitive. Shows the degree of systemic inflammation in the body (acute diseases and exacerbation of chronic diseases, trauma) and food allergies. The analysis will show how suitable the food you usually eat is for you. If the concentration is increased, advanced tests can be done to determine specific products that cause allergies.
Price: from 500 rub.
SEX HORMONES
On the 5th day of the cycle: estradiol, testosterone, prolactin, LH, FSH, DHEA. On the 21st day of the cycle: progesterone. Both how a woman feels and how she looks depends on their level. Sex hormones affect the condition of the skin, hair and nails, all metabolic processes, on which our weight also depends. Regular examination of sex hormones helps to catch diseases of the reproductive system and the initial manifestations of menopause in time. This test is required when planning pregnancy, selecting oral contraceptives, and hormone replacement therapy.
Price: full complex - from 2500 rubles.
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
Glucose, insulin, glycated hemoglobin. Allows early detection of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. WHO experts note that every 10 years the number of patients with this disease increases by 20%. Type 2 diabetes mellitus develops due to a decrease in the sensitivity of body tissues to insulin. It is usually provoked by lifestyle features: poor diet, lack of exercise and bad habits. Testing the level of fasting glucose, the level of the hormone insulin, as well as a test for glycated hemoglobin - the average number of glucose concentrations in the blood for a month - will help to detect the disease in a timely manner at the initial stage.
Price: glucose - from 125 rubles, insulin - from 450 rubles, glycated hemoglobin - from 600 rubles.
EXCRETORY SYSTEM
Urea. The level of its concentration in the blood is an indicator of kidney function. The first symptom of its excess is a tendency to swelling. Very often, an increase in its concentration is associated with nutrition - abuse of protein foods.
Price: from 250 rub.
Immunological blood test and allergological studies
Immunological blood tests and allergological tests help assess the state of a person’s immune system, the presence of antibodies in his blood, and also determine the allergological status. This research method is recommended for use in cases where the patient is concerned about:
Blood is taken for examination from a vein in the morning, on an empty stomach. It is recommended to stop eating 12 hours before the procedure, and one day to exclude fatty and spicy foods, as well as alcohol, from the menu. Women should not get tested during their period. If the patient is prescribed special medications, then the doctor should be warned about this.
Which blood test is better to take?
Using a blood test by taking a sample from a finger or a vein, various hematopoietic disorders are identified, the condition and functionality of the human body is assessed, and pathological changes in organs and tissues are detected.
Thus, human blood testing is an important element in diagnosing diseases, allowing, based on complaints and the general clinical picture, to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
The cellular composition of the blood of a healthy person has a constant composition. With certain diseases, the opposite picture occurs - the composition of the patient’s blood changes. Exactly what changes are taking place can only be determined after a blood test. For those wishing to get tested in Zhukovsky, we recommend a good medical center https://nsclinic.ru/.
Type of blood tests
There are many types of blood tests. The most common of them are : general clinical, blood tests for sugar, hormones, allergens, biochemical, immunological, serological blood tests, blood for tumor markers, for determining the group and Rh factor, for infections (HIV, hepatitis, syphilis, etc. ). Some blood tests are taken from a finger prick (clinical, for sugar), but most are taken from a vein.
Clinical blood test is a study that can be used to evaluate the level of hemoglobin, color index, number of leukocytes (white blood cells), erythrocytes (red blood cells), platelets (blood platelets) in human blood, determine their parameters, leukocyte formula (percentage of lymphocytes) , neutrophils, monocytes, basophils, eosinophils), cell mass to plasma ratio, erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
This blood test allows you to assess the general picture of the state of the human body, the condition and effectiveness of drug therapy, identify anemia, inflammatory processes, the presence of an allergic reaction, and distinguish a viral or bacterial infection.
A biochemical blood test is more informative The following indicators :
- Proteins (total protein, Albumin, C-reactive protein, Myoglobin, Glycated hemoglobin, Transferrin, Ferritin, ZhS, Rheumatoid factor)
- Carbohydrates (Glucose, Fructosamine)
- Lipids (total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol)
- Pigments (Bilirubin, total Bilirubin, Direct Bilirubin), Enzymes (AST - Aspartate aminotransferase, ALT - Alanine aminotransferase, Amylase, Lipase, Alkaline phosphatase, Cholinesterase, Creatine kinase, Lactate, Gamma GT - Gamma-glutamyltransferase, LDH - Lactate dehydrogenase)
- Low molecular weight nitrogenous substances (Creatinine, Urea, Uric acid)
- Inorganic substances and vitamins (Potassium, Calcium, Sodium, Magnesium, Chlorine, Iron, Phosphorus, Vitamin B12, Folic acid).
The specificity of a biochemical blood test lies in a comprehensive assessment of the activity and functional state of the entire organism, its internal organs, and metabolism. With the help of blood biochemistry, you can detect a lack of essential microelements, diagnose diabetes mellitus, malignant tumors, dysfunction of internal organs or water-salt balance, recognize the disease in time and prescribe the correct treatment.
Quite often, patients are prescribed a blood test for sugar . This test allows you to determine the level of glucose in a person's blood. Its concentration is regulated by hormones, the main of which is insulin, and depends on the ratio of the rate of glucose formation in the pancreas, its absorption from the gastrointestinal tract and further utilization. Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism in the body are expressed in an increase or decrease in blood glucose levels (hyper- or hypoglycemia).
A study of a person's hormonal status is carried out by taking a blood test for hormones. Hormonal indicators are assessed :
- thyroid gland: T3 - Triiodothyronine total and free, T4 - Thyroxine total and free, AT-TG - Antibodies to thyroglobulin, AT-TPO - Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase
- pituitary gland: TSH - Thyroid-stimulating hormone (stimulates the formation of thyroid hormones), Prolactin (responsible for stimulating the growth and development of the mammary glands and milk production in women), LH - Luteinizing hormone (ensures the proper functioning of the sex glands and hormones), FSH - Follicle-stimulating hormone ( hormone responsible for the growth and maturation of the follicle in women and the maturation of sperm in men)
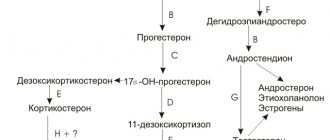
- adrenal hormones: ACTH - Adrenocorticotropic hormone (an important stimulator of the adrenal cortex), DHEA sulfate - Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, DHEA sulfate - Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (androgenic hormones of the adrenal glands), Progesterone (steroid hormone of the corpus luteum of the ovaries), Cortisol
- sex hormones: Testosterone (the main sex hormone in men), Estradiol (the main female sex hormone), Estriol (a minor sex hormone in women)
- prenatal diagnosis: hCG - Chorionic gonadotropin (specific pregnancy hormone), SHPG - Sex hormone binding globulin, 17-CS - 17-ketosteroids, 17-OH progesterone -17-hydroxyprogesterone (the result of chemical and biological reactions of progesterone), STH - somatotropic hormone (growth hormone), Parathyroid hormone - Parathyroid hormone (regulates the level of calcium and phosphorus in the blood), etc.
This study makes it possible to diagnose various hormonal disorders in the human body caused by changes in the functioning of the gonads, adrenal glands, pancreas and thyroid glands, etc.
Blood tests for various types of household, food, medicinal, industrial and other allergens are very common these days . It is necessary to identify the causative agent of an allergic reaction by detecting in the blood specific antibodies of class E immunogobulin proteins (IgE), which are produced in the body in response to an allergen. The results of the analysis are presented in the form of a table, which indicates the type of allergen tested and the degree of immune response that it was able to provoke.
It is possible to identify the characteristics of a person’s blood clotting disorder by taking a coagulogram. This study is necessary for problems with the liver, cardiovascular system, varicose veins, autoimmune diseases, pregnancy, planned operations, and taking oral contraceptives. Using a coagulogram, you can detect insufficient or excessive blood clotting ability.
The main parameters of a blood clotting test include:
- PTT - Prothrombin time (characterizes blood clotting along the external pathway)
- APTT - Activated partial thrombin time (testing the internal pathway to stop bleeding)
- Fibrinogen (a protein produced in the liver and later converted into the basis of a clot during blood clotting)
- TV - Thrombin time (time of clot formation)
Additional Analysis Options:
- Antithrombin III (anticoagulant factor)
- Protein C (vitamin K-dependent protein synthesized in the liver)
- Protein S free (vitamin K-dependent plasma glycoprotein)
- D-dimer (indicator of thrombus formation)
- VA - Lupus anticoagulant (if the development of antiphospholipid syndrome is suspected)
Blood tests for tumor markers occupy an important place in the diagnosis of cancer. This study is aimed at detecting specific proteins in the body that are produced by various tumor cells. The presence of a tumor marker in the blood of an adult is an alarming signal and a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
Most often, blood is tested for the following types of tumor markers:
- CEA - Carcinoembryonic antigen (marker of various tumors)
- AFP - Alpha-fetoprotein (liver cancer marker)
- PSA – Prostate specific antigen (prostate cancer marker)
- B-2-MG - Beta-2-microglobulin (marker of leukemia, lymphoma)
- CA 19-9 - Carbohydrate antigen (marker of pancreatic cancer
- CA – 125 – Carbohydrate antigen (marker of ovarian cancer)
- CA 15-3 - Carbohydrate antigen (breast cancer marker)
PCR blood testing for various infections, including sexually transmitted infections, has become very popular in recent years This diagnostic method allows you to detect not only acute, but also latent diseases, has high specificity and sensitivity, which guarantees almost 100% reliability of the results. Using PCR, you can detect bacteria and viruses at any stage of activity in the body.
There is also an immunological blood test, according to the results of which the doctor can assess the state of a person’s immunity as a whole and its strength, i.e. how active the body’s defenses are at the time of the test. Using this study, primary and secondary immunodeficiency, infectious, hematological, and autoimmune diseases are determined. By the presence of a class of immunoglobulins, an acute (IgM) or latent (IgG) infection process can be identified.
Main parameters of the study:
- Immunoglobulin A (IgA) – is responsible for local immunity of the mucous membranes;
- Immunoglobulin E (IgE) – takes part in allergic reactions;
- Immunoglobulin G (IgG) – responsible for long-term immunity; Immunoglobulin M (IgM) – reacts to the initial penetration of infection into the body;
- Alloimmune antibodies are antibodies to the clinically most important erythrocyte antigens. Antinuclear factor is a marker of systemic connective tissue diseases;
- ASAT - Antisperm antibodies - antibodies to sperm membrane antigens, etc.
A very important study is to determine the blood group and Rh factor. These are tests that can be used to identify whether a person belongs to a group of people who have certain immunogenetic blood characteristics, which in turn means that they are compatible with each other based on these characteristics.
There are several types of blood groups: I (0) group - first (zero); II (A) group - second group; III (B) group - third group; IV (AB) group - the fourth blood group.
The Rh factor is an antigen found on the surface of red blood cells - erythrocytes. The vast majority of people have this same Rh factor and are considered Rh positive. Those who do not have it are called Rh negative. Determination of blood group and Rh status is necessary during pregnancy, blood transfusion, and preoperative preparation.
Do I need to prepare in any way before donating blood?
On the eve of donating blood, you should not eat fried, spicy, fatty or smoked foods so that the viscosity of the blood remains unchanged. It is necessary to donate blood strictly on an empty stomach, preferably in the morning and before the start of drug therapy, endoscopic, ultrasound, X-ray and other types of examination, unless otherwise prescribed by the attending physician.
A couple of hours before your blood test is taken, you need to stop smoking and not drink tea, coffee, or juice. You should not drink alcohol for at least three days before taking the tests, because... it influences the action of the human nervous system, which regulates all physiological processes. Under the influence of alcohol, the water-salt balance, enzyme and respiratory systems, biochemical parameters and hormonal levels change. The results may not be reliable.
For 15-20 minutes, relax and eliminate physical activity, since any physical stress leads to the activation of a number of hormones and enzymes, which can lead to changes in metabolism and also affect test results. A number of studies for women (for hormones, for example) are taken on certain days corresponding to the physiological cycle. The day of blood donation is determined according to which hormones need to be tested.
The better you prepare, the more reliable the results will be, according to which the doctor will be able to prescribe correct and effective treatment.
Blood test for PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
A PCR (polymerase chain reaction) blood test allows you to correctly diagnose any viral or bacterial infection at an early stage of the disease. Typically, this laboratory test is prescribed for serious pathological conditions:
You can undergo a similar study to determine the likelihood of infection after accidental unprotected sexual contact.
and during pregnancy in order to prevent diseases that can cause abnormalities in the development of the fetus. Preparation for a PCR blood test depends on the type of pathogen and the nature of the suspected disease. General recommendations are to exclude spicy and fatty foods and alcohol from the menu the day before the procedure. Blood is drawn from a vein in the morning, on an empty stomach. However, it is believed that the accuracy of the results does not depend on whether the patient had breakfast before the test or not.
Sign up for blood tests
Make an appointment
What does the CBC (complete blood count) show?
Clinical blood testing is a basic diagnostic method, which is most often prescribed during a preventive examination. And the procedure is also carried out if a person comes to the clinic with complaints of poor health.
The main objective of the study is to determine the concentration of major blood cells, the content of normal and pathological forms, and also to identify foreign agents. Based on the results of the analysis, the doctor will be able to make a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe additional studies that will help make a reliable diagnosis.
What a general blood test from a vein shows, why it is prescribed, and whether it is possible to eat before the procedure, the doctor must explain to the patient. And also the doctor must explain what values should be normal and what indicators indicate a deviation. But in any case, interpretation of the analysis should be carried out only by a qualified physician.
Using UAC you can obtain the following information:
- color index;
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate);
- hemoglobin concentration;
- hematocrit content;
- quantitative and qualitative assessment of red blood cells, platelets, granulocytes and agranulocytes;
- leukocyte formula.
For healthy adults, the following BAC indicators are considered normal:
| Index | Women | Men |
| Hemoglobin | 120–140 g/l. | 130–160 g/l. |
| Red blood cells | 3.5–4.5*1012 g/l. | 4–5*1012g/l. |
| Hematocrine (HCT) | 37–46% | 43–50% |
| Platelets | 180–320*109g/l. | |
| Leukocytes | 4–9*109g/l. | |
| Leukocyte formula | ||
| Neutrophils | until 6% | |
| Eosinophils | 0,5–5% | |
| Basophils | no higher than 1% | |
| Lymphocytes | 20–40% | |
| Monocytes | 3–10% | |
| ESR | 2–15 mm per hour | 1–10 mm per hour |
| Reticulocytes | 0,5–2% | |
The leukocyte formula can only be calculated through a detailed blood test. Such testing is usually prescribed for suspected infectious diseases, severe damage to internal organs, or oncology.
Blood test for hCG
A blood test for hCG is the most popular test among women today. This method allows you to quickly and accurately determine whether a patient is pregnant at the earliest stages.
HCG is a human chorionic gonadotropin hormone that is produced by the chorion of the embryo. The level of this hormone in the blood indicates the onset of pregnancy or its absence. You can take the test starting from the first day of missed menstruation, or 14 days after sexual intercourse. You should refrain from eating 3 hours before the procedure. Blood is drawn from a vein. The results of the analysis can be known within a few hours.
Preparing for a blood test
The doctor should tell the patient how to properly take blood tests. Donating blood for testing requires some simple preparation. What is this connected with? The blood composition is not always stable. To ensure that the results of the biochemical analysis are not distorted, factors that contribute to changes in the ratio of blood cells should be excluded.
This indicator is influenced by:
- recent viral infection;
- heavy physical activity;
- playing sports;
- alcoholic drinks.
The doctor who determines which tests should be taken should tell the patient about the measures necessary to ensure the integrity of the tests. Some of these recommendations may be of a purely individual nature. For example, if a person is already taking certain medications, especially antibiotics, they should be temporarily stopped. Therefore, it is so important that the patient has information on how to take a blood test.
To determine the concentration of the drug in the blood, you cannot stop taking it. The issue of preparing for tests must be taken very seriously and follow all the doctor’s recommendations at the preparatory stage.
You need to learn in detail about the blood test and how to take it correctly. This will help to see an objective picture of the patient’s health condition, determine the diagnosis and draw up the correct treatment regimen.
There are general rules for preparing for a blood test:
- The patient should give up fatty and fried foods 2 days before the study.
- Some types of procedures are done in the morning on an empty stomach (for example, biochemical research), so those who like to smoke in the morning should give up this habit.
- It is better not to even do exercises this morning, but to postpone it to a later time.
- Even anxiety and stress can affect test results. Protect yourself from such situations and try to calm your nerves.
- If the patient is scheduled for any other tests on this day (x-rays, physical procedures, etc.), they should be postponed until a later time.
- A general blood test allows you to avoid fasting for a long time. It can be done at least 1 hour after eating. Drinking water is allowed.
- A biochemical blood test requires abstaining from food from the evening of the previous day (it can be done 12 or more hours after a meal), only water is allowed.
Everyone should know the rules for taking tests in order to achieve reliable information and subsequently receive quality treatment.
.
Blood test for parasites
A blood test for parasites is the most accurate diagnostic method, allowing you to prevent serious inflammation of internal organs caused by various types of parasites entering the body. Studies are prescribed for adults and children. The material is taken from a vein. Preparing for analysis:
What can a general (clinical) blood test show?
This analysis is an integral laboratory diagnostic method for any disease, as well as during preparation for surgery. This procedure allows the specialist to draw a conclusion about the condition of the patient who contacted him.
This analysis allows us to form an idea of:
- blood color index;
- hemoglobin level;
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
- hematocrit volume;
- the number of red blood cells and platelets, as well as their quality;
- leucoformula.
What indicators can be determined by a general blood test:
https://youtu.be/AKfXMsbrn1k
Study for the presence of tumor markers
Testing for the presence of tumor markers is one of the methods that determines the likelihood of a tumor process developing in the body. Using this analysis, it is possible to detect oncological diseases in the early stages, as well as prevent their relapses. A study for the presence of tumor markers is prescribed by a specialist. Preparation for the procedure includes excluding spicy and fat-rich foods from the diet, smoking and alcohol 3 days before the analysis. The patient is prescribed rest and minimal physical activity. You should not take medications other than vital ones prescribed by your doctor. Blood is drawn from a vein in the morning.
The importance of blood for humans
Blood is a special liquid that is the first indicator of the slightest changes in the human body. Its ability to react with lightning speed to the appearance of pathology in any organ of the human body allows doctors to find the epicenter of the disease in time, determine the stage of its development and possible consequences. This liquid tissue in the human body plays a huge role in his life.
Thanks to her:
- gases and nutrients are delivered through vessels to the cells;
- cells can breathe with the help of oxygen delivered to them through the circulatory system;
- cells receive glucose, vitamins, fats, water, amino acids;
- the body is cleansed and gets rid of unnecessary substances (urea, uric acid);
- the temperature of internal organs is regulated;
- water-salt exchange occurs;
- the internal environment of the body is constantly maintained in the same state;
- the body is protected from viruses, germs and infections;
- ensures uninterrupted operation of organs and systems.
Therefore, if at least one of these points is violated, the liquid connective tissue changes its composition. It passes through all organs and carries information about pathologies, even if they have just begun to develop.
Blood test for trace elements
A blood test for microelements allows you to most accurately determine the reserves of useful substances in the human body, identify disturbances in water-salt balance and various types of rheumatic conditions. Insufficient content of certain groups of vitamins and enzymes or their excess can cause the development of pathologies or deterioration of well-being. When testing blood for microelements, biomaterial is taken from a vein, exclusively in the morning and on an “empty” stomach. Before the procedure, eating and drinking alcohol is prohibited; it is recommended to limit physical activity 24 hours before. It is important to remember that a blood test for trace elements should be performed before starting a course of taking any medications or two weeks after stopping them.
Modern medicine offers a large selection of various blood tests that make it possible to identify various diseases even before the first clinical symptoms appear. With their help, the effectiveness of treatment and the correctness of selected medications for existing pathologies are assessed. For a correct diagnosis and accurate results, you need to know what blood tests exist, how and when they need to be taken.
Anti-Age screening. What examinations will help delay aging?
Aging is an inevitable process. Changes associated with aging affect all organs and systems. But it is still possible to prolong youth for as long as possible. And the first thing worth thinking about is diagnosing those processes that accelerate fading. Moreover, in some cases, well-known analyzes and tests are suitable.
LEVEL OF SYSTEMIC INFLAMMATION
Aging is always associated with an increase in the overall inflammatory response. This, in turn, leads to disruption of the body’s functioning at all levels: organs, tissues and cells. The level of systemic inflammation can be measured. ESR is the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. This indicator is usually included in a standard clinical blood test. In the case of acute and chronic processes, as well as with systemic inflammation, the value of this marker increases.
C-reactive protein is ultrasensitive. Gives a general picture of the inflammatory response. All indicators related to carbohydrate metabolism. Sugar is the very substance that activates general inflammation. It is necessary to monitor the dynamics of fasting glucose levels, the amount of insulin and measure glycated hemoglobin. Some laboratories calculate the HOMA index. It shows the ratio of glucose and insulin. Additionally, you can donate blood for insulin-like factor, the value of which also reflects the general inflammatory response. Important! Test results are assessed in conjunction with other factors. For example, taking aspirin prescribed to thin your blood may increase your ESR levels. This needs to be taken into account.
HORMONAL CHANGES
An anti-age specialist will primarily be concerned with the functioning of the thyroid gland. It is she who is responsible for protein and water-salt metabolism. To do this, a blood test is taken to determine the level of TSH, a hormone of the hypothalamus. Both high and low levels indicate an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. Screening of the thyroid hormones themselves is also done. Another important test is to determine the level of antibodies to the thyroid gland. It happens that the level of hormones is normal, but due to the increased activity of the immune system, its cells begin to attack the cells of the thyroid gland, disrupting its functions.
ANTIOXIDANT STATUS
Free radicals oxidize fats in cell membranes and destroy cell structures, in particular mitochondria (the main energy depot) and DNA. Modern tests allow you to assess the level of oxidation, as well as see how well the body can protect itself from the effects of free radicals. The analysis determines the concentration in the blood of glutathione, coenzyme Q10, vitamins E and C, and some substances that accumulate when there is an excess of free radicals.
ANALYSIS OF SALIVA FOR SEX HORMONE METABOLITES
One of the most modern tests that helps doctors prescribe treatment to correct hormonal status. The concentration of sex hormones in the blood may be within normal limits. But in order to perform its function, the hormone must connect with a specific cell receptor and trigger a whole cascade of reactions. Alas, a blood test for sex hormones does not give us the full picture. But the study of saliva for the breakdown products of one or another hormone is very informative. The test gives an idea of how the sex hormone worked and what forms of substances were ultimately obtained. If among them there is a high concentration of so-called bad forms, then the risks of developing endometriosis, mastopathy, and tumors increase. This analysis is very important for women after 40, especially when it comes to prescribing hormone replacement therapy.
Healthy heart
Do you want to reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease? Note the additional splashing of the carotid arteries. This test allows you to study the condition of the middle lining of blood vessels. If it thickens, the risks of strokes and heart attacks increase. It is advisable to do such an analysis every year after 40 years! By the way, it is possible to restore the elasticity of the vascular wall. Physical activity, diet and individually selected supplements will help you.
DETOXIFICATION PROCESSES
Biological age largely depends on how well the body copes with harmful substances. The accumulation of so-called toxins in the body sufficiently undermines the functioning of all organs and systems.
What indicators are assessed in this case? Liver function. This organ plays a leading role in the detoxification system. It is enough to take a test for liver enzymes and bilirubin. Glutathione levels. This is an antioxidant necessary to neutralize toxic substances. The amount of B vitamins. They take part in the construction of enzymes that are involved in detox processes.
STRESS
If the stress level goes off scale, the body wears out faster. You can evaluate your body's ability to withstand stress by taking a saliva test for cortisol (a hormone produced by the adrenal glands). The test shows how exhausted your adrenal glands are and whether your response to stress is adequate.
Cortisol is a moody hormone. Its concentration in the blood changes throughout the day and depends on physical activity and food. You can most accurately assess its level by examining saliva taken in the morning on an empty stomach. You can determine your daily cortisol concentration by collecting several portions of saliva throughout the day.
At the same time, it makes sense to evaluate the levels of dopamine and serotonin (saliva is also suitable in this case). They are responsible for our behavioral reactions, mood, eating behavior. Often, emotional swings and chronic fatigue syndrome are associated with an imbalance of these substances.
Photo: Legion Media
Blood test cost
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 090001 | Total protein | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090002 | Albumen | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090003 | Protein fractions | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 600.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090004 | Creatinine | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090005 | Urea | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090006 | Uric acid | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090007 | Total bilirubin (TB) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090008 | Direct bilirubin (DB) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090009 | Total cholesterol | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090010 | HDL cholesterol | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090011 | LDL cholesterol | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 600.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090012 | Triglycerides | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090014 | Alanine aminotransferase (ALT, GPT) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090015 | Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, GOT) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090016 | Gamma glutamine transferase (GGT) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090017 | Alkaline phosphatase (ALCP) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090018 | Acid phosphatase* | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 600.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090019 | Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090020 | Alpha amylase | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 600.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090021 | Creatine kinase | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090022 | Creatine kinase-MB* | blood (serum) | count | 5-6 hours**** | 1500.00 rub. | CITO only | |
| 090023 | LDH 1st fraction (a-HBDH) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090024 | Myoglobin | blood (serum) | count | 5-6 hours**** | RUR 2000.00 | CITO only | |
| 090025 | Lipase | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 600.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090026 | Cholinesterase* | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090027 | Iron | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090028 | Total iron binding capacity of serum (TIBC) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090029 | Vitamin B 12 (Cyanocobalamin)* | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 900.00 rub. | 1800.00rub | 0 |
| 090030 | Folic acid* | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 900.00 rub. | 1800.00rub | 0 |
| 090031 | Ferritin | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 800.00 rub. | 1600.00rub | 0 |
| 090032 | Transferrin* | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 600.00 rub. | 1200.00rub | 0 |
| 090033 | Calcium | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090034 | Phosphorus | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090035 | Magnesium | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090036 | Ca2+/Na+/K+/Cl- | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 600.00 rub. | 1200.00rub | 0 |
| 090037 | Glucose | blood with sodium fluoride | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090040 | Rheumatoid factor RF | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 500.00 rub. | 1000.00rub | 0 |
| 090041 | Antistreptolysin-0 Asl-0 | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 500.00 rub. | 1000.00rub | 0 |
| 090042 | Glycosylated hemoglobin (HB A1C) | blood with EDTA | count | 1-2 k.d. | 600.00 rub. | 1200.00rub | 0 |
| 090043 | Zinc | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 600.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090044 | Fructosamine | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 1200.00 rub. | 2400.00rub | |
| 090045 | Troponin I | blood (serum) | count | 5-6 hours**** | 2200.00rub | CITO only | |
| 090046 | Apolipoprotein AI (ApoAI) | blood (serum) | count | 3-5 k.d. | 600.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 090047 | Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) | blood (serum) | count | 3-5 k.d. | 600.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 090048 | Pancreatic amylase | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 400.00rub | 800.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090049 | Erythropoietin | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 1200.00 rub. | 2400.00rub | 0 |
| 090051 | Lactic acid (lactate)* | blood with sodium fluoride | count | 1 k.d. | 800.00 rub. | 1600.00rub | 0 |
| 090052 | Unsaturated iron binding capacity of serum (IBC) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 400.00 rub. | 800.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090053 | Haptoglobin | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 1200.00 rub. | 2400.00rub | 0 |
| 090054 | Ceruloplasmin | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 900.00 rub. | 1800.00rub | 0 |
| 090055 | Alpha-2 macroglobulin | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 900.00 rub. | 1800.00rub | 0 |
| 090057 | Lipoprotein(a) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 2000.00 rub. | 4000.00rub | 0 |
| 090059 | C-reactive protein (Highly sensitive method) | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 700.00 rub. | 1400.00rub | 0 |
| 090061 | VLDL - cholesterol | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 200.00 rub. | 400.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090068 | Ca2+ | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 400.00rub | 800.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090069 | Na+/K+/Cl- | blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 400.00rub | 800.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090070 | Cystatin C | blood (serum) | count | 3-5 k.d. | 4000.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 090078 | Vitamin B12, active (holotranscobalamin) | blood (serum) | count | 1-2 k.d. | 2000.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
All our services and prices
Sign up for blood tests
Make an appointment
Types of blood tests
When a patient comes to the doctor, the first step the specialist takes is to give a referral for a blood test. This is an important and most correct way to diagnose all diseases. What tests are there?
There are several types of blood tests. For different conditions of the patient, different tests are taken. Usually the first blood test prescribed to a patient is a general examination.
It is carried out in two cases:
- When you need to identify any disease.
- For preventive purposes.
Such an analysis also provides information about possible pathologies in the future. This is important to prevent the development of the disease in the very first stages.
Another equally frequent analysis is a biochemical blood test. It involves a detailed description of the chemical composition of the patient's blood.
Only a doctor can determine which blood test (or tests) a patient needs. Moreover, even if two different people have the same symptoms, the doctor can individually prescribe a specific blood test and their number.
Sometimes doctors resort to a series of such studies. This is necessary in order to track the disease over time and assess the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy.
General analysis
A general blood test allows you to see:
- how much immunity is maintained in the body;
- whether the cells are properly supplied with oxygen and nutrients;
- what is blood clotting?
- whether homeostasis is maintained.
In the blood of a person there are blood cells of different natures and shapes that perform different functions in the body (leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets). Each of them has its own quantitative value, strictly maintained in a healthy body.
In a general analysis, all quantitative indicators of these components are calculated and compared with the norm. Deviations in any direction indicate the presence of a disease.
https://youtu.be/HFVp7euw7Oo
What else is included in the analysis?
- The degree of erythrocyte sedimentation is determined, which is designated as ESR.
- The color of the blood is also taken into account (hemoglobin plays an important role here: the more of it in the blood, the darker it is). Hemoglobin level is also an important indicator of human health. Its deficiency, as well as its excess, provide information about diseases of the blood, heart, bone marrow, kidneys and other organs and systems.
- Such an important indicator as the leukocyte index helps determine the degree of intoxication and the severity of the inflammatory process.
Biochemical analysis
The next type of analysis is biochemical.
He is called upon:
- evaluate the functioning of internal organs;
- provide information about metabolic processes occurring in the body;
- show how much the body needs microelements.
What can you learn from the results of this laboratory test?
- The test taken can help conduct an important test in diagnosing such a serious disease as diabetes. This is determined by the level of glucose in the blood. If there is a deficiency of this substance in the blood, this indicates that the person has problems with the endocrine system or the liver is not functioning well.
- Assessment of the following indicator - bilirubin (total, direct and indirect) - allows you to recognize cirrhosis, anemia, cholelithiasis, malaria, the presence of hemorrhages, as well as jaundice, the cause of which is poor outflow of bile.
- A feature of the biochemical blood test is that it evaluates the state of enzymes that are synthesized in the liver: aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyltransferase. The amount of these enzymes in blood serum is normally small, since they are synthesized mainly in liver cells. A blood test reveals changes in their quantity, which allows one to draw a conclusion about the development of cirrhosis, hepatitis, heart disease, blood disease, and pancreas disease.
- As a result of donating blood for biochemistry, the doctor receives data on the presence of alkaline phosphatase, cholesterol, and lipoproteins. These enzymes and lipids ensure normal vital processes of the body.
Indications for donating blood for the amount of thyroid hormone
They are as follows:
- Living in an area with known iodine deficiency.
- After any surgical treatment.
- For problems with conceiving and bearing a child.
- When using hormonal means of protection against pregnancy (TSH control once a year).
In case of previously identified disorders in the functioning of the gland, to monitor the course of the disease and select medications.
Deviations from the norm in this analysis may indicate problems such as:
- Hypothyroidism (low thyroid function).
- Hyperthyroidism (increased gland function).
Minor deviations from the norm detected in time can be easily corrected with medication, but serious and late detected pathologies may require surgical treatment. If a patient is found to have an excess of thyroid-stimulating hormone, he is required to undergo an ultrasound of the thyroid gland and, most likely, life-long hormone replacement therapy.
What do red blood cells tell you?
These red blood cells bring oxygen to every cell in the body and remove carbon dioxide. Norm:
- newborns – (3.9–5.5)*1012/l;
- children from 2 months to 6 years – (2.7–4.9)* 1012/l;
- 6–12 years – (4.0–5.2)*1012/l;
- women – (3.7–4.7)*1012/l;
- men – (4.0–5.5)*1012/l.
A physiological increase in the number of red blood cells occurs due to:
- physical activity;
- emotional excitement;
- large loss of water (intense sweating).
Such increases are short-term and occur due to the redistribution of red blood cells in the body. Since they are deposited in the spleen, if necessary (physical activity, stress) they are released into the blood, because oxygen consumption in the body increases and it is necessary to increase the number of blood cells supplying this element to the entire body. Due to thickening of the blood due to loss of water, the concentration of red blood cells also increases.
A physiological decrease is observed with excessive fluid intake after meals.
Deviations from the norm also indicate various pathologies. Erythrocytosis (increased level of red blood cells) occurs:
- primary;
- secondary.
With primary erythrocytosis, their concentration increases to (8–12)*1012/l. This is the main symptom of polycythemia vera.
Secondary – associated with oxygen starvation. In response to hypoxia, the body begins to produce more red blood cells. Erythrocytosis indicates:
- lung diseases;
- some heart defects;
- circulatory disorders;
- pathology of hemoglobin structure.
In healthy people, erythrocytosis appears due to smoking and prolonged exposure to altitude.
A decrease in the number of red blood cells is a sign of anemia. Due to acute blood loss, hemolytic anemia and other forms of anemia, the level is below 1*1012/l.
With chronic blood loss, the level of red blood cells is normal or slightly reduced (3–3.6)*1012/l. To establish an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to determine the color indicator, hemoglobin level, and conduct a cytochemical study. Study the size and shape of red blood cells. They become larger after severe blood loss or due to a lack of vitamin B12. And the shape changes with sickle cell anemia.
Thyroid hormone
Now almost every fifth resident of our large country can experience some kind of malfunctions and disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland. If during the examination the doctor suspects changes, the patient will be sent for an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland, as well as a blood test for TSH (the amount of thyroid-stimulating hormone). After all, disturbances in the functioning of this organ lead to infertility, libido disorders, problems with mental work, and accelerate and aggravate the course of any infectious and inflammatory process in the body.
Immunological blood tests
This test determines the number of immune cells and immune systems in the body. The study provides information about the state of numerous parts of the immune system and makes it possible to diagnose immunodeficiency at the primary and secondary stages. Based on the content of immunoglobulin classes, acute (IgM) and chronic (IgG) types of infectious diseases are distinguished. Determine the content of lymphocytes, the number of leukocytes, monocytes (absolute and percentage), granulocytes; populations of suppressors, lymphocytes - hellers, nullers, killers; proliferative and phagocytic activity of leukocytes; immunoglobulins IgA, IgM, Ig.
What it is
Before moving on to how to take general blood tests, it is worth considering general information that will help you understand why a general blood test should be performed at all. When blood is taken from the fingers for testing, the analysis allows you to calculate the general parameters of blood cells. Hemoglobin is counted and the leukocyte formula is determined. The ratio of plasma to blood cells is checked.
If there are any deviations from the norm in the biological fluid taken, the doctor will be able to suspect disturbances in the body, and therefore take timely measures. How is a general blood test done? The sample is taken on an empty stomach. Blood is donated from the ring finger. However, sometimes the rules for donation change, and biomaterial is taken from a vein. Why is blood taken from a vein? Donate blood from fingers only if checking the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is not required. If it is important for a doctor to know this indicator, then by taking a sample from a finger, the laboratory assistant will not be able to carry out a correct calculation. In addition, doctors often offer to donate blood for a whole range of tests, within which there is a whole list of studies carried out. In this situation, a venous sample is suggested for a general blood test.
What blood tests are there?10807
Depending on where the blood is taken from, there will be a different way of testing. So, when taking blood from a finger on an empty stomach, a small puncture is made on the skin, and the protruding drops are taken into a test tube with a pipette. From there a sample is taken for research.
Blood clotting
It happens that during a routine medical examination or during a test, a violation of blood density is accidentally detected. If this disorder was detected during a biochemical analysis, the therapist will give a referral for an additional blood clotting test. You need to remember what it is called scientifically - coagulogram.
Also indications for analysis are:
- Signs of prolonged bleeding, bruising even from slight pressure.
- Upcoming surgery.
- Diseases of the heart, liver, blood vessels.
- Pregnancy.
- Reduced immunity.
Complete blood count where is blood taken from?
There is no strictly defined place where a general blood test is taken. For an adult, the number of elements being studied is important; for a child, the minimum amount of trauma for the baby is important.
Important! An indispensable condition for taking the OAC is an empty stomach, but this rule does not apply to infants.
How is a general clinical blood test taken? Most often, biomaterial is collected from a puncture on the ring finger, and, if extensive analysis is necessary, from a vein. The decision remains with the doctor who issued the referral for the study.
To fully and accurately reflect information in the UAC before taking the test, you must adhere to the following rules:
- take the UAC on an empty stomach,
- one hour before blood sampling, you should not smoke or physically overexert yourself,
- for 3 hours, refrain from food, liquid intake (even pure still water),
- the previous day, exclude the consumption of fatty and smoked foods, sweet carbonated and alcohol-containing drinks, for 24 hours you cannot undergo instrumental examination or physical procedures,
- Stop taking medications 48 hours before the test.
If, before the manipulation, for objective reasons it is not possible to fulfill the requirements (for example, not to take medications), then notify the doctor in advance.
Where is a clinical blood test taken from children?
According to the plan for monitoring the growth and development of children, OAC is prescribed by a pediatrician during the following periods of a child’s life:
- newborn babies (up to 1 day),
- month old babies,
- in six months,
- one year old,
- up to six years old,
- from seven to twelve,
- from thirteen to fifteen.
This frequency of OAC is necessary to prevent iron deficiency anemia, identify allergens, study the biochemical and serological composition of the blood, before scheduled vaccinations and according to doctor’s indications, if complaints arise.
In very young children (up to six months), venous blood is taken for OBC, but sometimes difficulties arise with collecting biological fluid due to small veins. Therefore, blood can be taken for analysis from:
- forearm or elbow,
- back of the hand,
- calf area, head or forehead.
During the procedure, parents may be asked to leave, which is recommended to listen to, since this method of work will allow you to quickly take the necessary blood without traumatizing the psyche of mother and baby.
Important! After the procedure, a bright toy or rocking in the arms of a loved one will help calm the child.
Where do they get a complete blood count in adults?
Blood sampling in adults occurs from the fourth finger of the hand (counting from the thumb), which is disinfected with alcohol, pierced with a 2.5 mm scarifier, the escaping blood is collected with a pipette, and then poured into a test tube. First, the serum is examined for hemoglobin concentration and ESR, then for leukocyte and erythrocyte composition, and then applied to a glass slide to study the cellular composition. The modern level of medical devices makes the procedure painless.
If it is necessary to expand the analysis and examine the blood in detail, a sample is taken from a vein in the elbow. Before this, a tourniquet is applied to the shoulder, squeezing the vein, and blood is drawn into a disposable syringe with a sterile needle.
https://youtu.be/ke0uhPD24JI
Preparing for analysis
A general blood test is often taken from a finger, less often from the earlobe. If a laboratory conducts research using automatic hematology analyzers (they determine from 5 to 24 different indicators), they can take venous blood rather than capillary blood. By the way, depending on the research method, the standards vary somewhat, and the indicators in different laboratories differ. Therefore, repeated studies must be carried out in the same place where the initial study was carried out.
And be sure to prepare properly. There are several recommendations for patients to limit the influence of various factors on the result:
- Since daily fluctuations in the content of blood cells have been detected, they take the test in the morning.
- Food and nutrition also have an impact on the outcome. This means that 8–12 hours before taking blood, the patient should not eat or drink much (the blood will thin out and as a result there will be a lower level of red blood cells and platelets).
- Before the study, you should not engage in excessive physical activity. You can spend one day without charging.
- Try to avoid emotional excitement. Preferably without sedatives, as they can also affect the results.
- If you are taking medications, be sure to tell your doctor. He will either cancel them for a while, or take this factor into account when decrypting them.
- Do not smoke, do not drink alcohol. They not only harm health, but also affect the composition of the blood and, accordingly, the results of the study.
If you follow these recommendations, the result of the study will be the most accurate, and this will make it easier for the doctor to identify the cause of the disease.
Norms of biochemical blood analysis in adults: table
| Index | Unit | Lower limit of normal | Upper limit of normal |
| Sugar/glucose | mmol/l | 3,3 | 5,5 |
| Urea | mmol/l | 2,5 | 8,3 |
| Non-protein blood nitrogen (residual) | mmol/l | 14,3 | 28,6 |
| Creatinine | micromol/l | 44 | 106 |
| General lipids | g/l | 4 | 8 |
| Cholesterol | mmol/l | 3,6 | 7,8 |
| Low-density lipoprotein, LDL/LDL cholesterol | mmol/l | men: 2.02 women: 1.92 | men: 4.79 women: 4.51 |
| High Density Lipoprotein, HDL/HDL Cholesterol | mmol/l | Men: 0.72 women: 0.68 | men: 1.63 women: 2.28 |
| Atherogenic coefficient | 0 | 3 | |
| Triglycerides (the norm strongly depends on gender and age. Values are given for the age of 35-40 years) | mmol/l | men: 0.61 women: 0.45 | men: 3.62 women: 1.99 |
| Phospholipids | mmol/l | 2,51 | 2,92 |
| Bilirubin | µmol/liter | 8,5 | 20,55 |
| Protein | g/l | 65 | 85 |
| Albumen | g/l | 35 | 50 |
| AST (aspartate aminotransferase) | Chalk | 10 | 38 |
| ALT (alanine aminotransferase) | Chalk | 7 | 41 |
| Gamma glutamyl transpeptidase | µmol/l | men: 15 women: 10 | men: 106 women: 66 |
| Alkaline phosphatase | Chalk | 20 | 140 |
| Calcium | mmol/l | 2,15 | 2,50 |
| Potassium | mmol/l | 3,5 | 5,5 |
| Sodium | mmol/l | 136 | 145 |
| Chlorine | mmol/l | 98 | 107 |
| Iron | µmol/l | men: 11.64 women: 8.95 | men: 30,43 women: 30,43 |
Due to savings in our regional hospitals, doctors often do not consider it necessary to send patients for a generally accepted full-fledged analysis, and then certain types of biochemical blood tests are formed, the directions of which will highlight only some characteristics.
For example, if a patient complains of liver problems, they will take blood samples for bilirubin (total) and total protein, albumin, alanine aminotransferase, gamma GTP, C-reactive protein, and alkaline phosphatase.
If the doctor suspects that the patient has diabetes, he will first conduct a biochemical test for sugar (glucose) to confirm or refute the assumption.
Patients are all different and an experienced doctor, if there are direct symptoms of the disease, will not waste the patient’s money and hospital resources in vain. After all, it is not at all necessary to conduct a complete general blood test several times a year, without special indications.
Serological blood test
This method consists of studying certain antigens or antibodies and is based on the immune response. Patients' blood serum is used for research. A serological blood test is used to detect infectious diseases to determine the presence of antibodies in the blood to a specific type of virus or bacteria and to determine the blood type.
This analysis reveals the presence of specific antibodies to various viruses and infections (herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus, mycoplasmosis, mumps, measles, rubella, chlamydia, toxoplasmosis, HIV, hepatitis A, B, C, D, E, syphilis).
When certain specific proteins (antibodies) are detected, a diagnosis of the disease is made.
Hormonal profile analysis
Hormones are presented in the form of biologically active substances produced by specialized organs or a community of cells (endocrine glands - adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid and pancreas). The number of hormones contained in the blood, in comparison with other components of the blood, is insignificant.
However, hormones have a huge impact on the human body. For it to function properly, a certain ratio of all hormones in the blood must be observed. Using hormone analysis, specialists are able to diagnose all kinds of diseases of individual organs and entire systems.
There are certain standards for the amount of hormones in the blood. They depend on the age and gender of the patient. Significant deviations from established norms (lack or excess of hormone levels) lead to quite serious changes in the human body, which can lead to the emergence of a number of diseases.
What do platelets tell you?
Platelets are the smallest blood cells. Normally they contain 180–320*109/l. They are necessary for blood to clot. Their increase may be physiological:
- in pregnant women;
- during menstruation;
- after physical activity.
Daily and seasonal fluctuations in the number of blood platelets are characteristic.
Pathological increase is typical for:
- blood diseases;
- acute blood loss;
- anemia;
- malignant tumors;
- inflammatory processes;
- after removal of the spleen.
At the same time, the number of platelets increases several times. The decrease shows:
- purpura;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- malignant tumors with metastases to the bone marrow;
- hemolytic disease of newborns;
- pathology of the thyroid gland;
- liver diseases.
If the platelet count becomes less than 60*109/l, the patient experiences symptoms of bleeding. This is an extremely difficult condition.
If the platelet count reveals a deviation from the norm, the doctor will recommend additional examination (biochemical blood test, coagulogram).
Mandatory annual tests for women
The female body is designed in such a way that many serious gynecological diseases in the early stages are completely asymptomatic. For this reason, women are recommended not only to visit a gynecologist annually, but also to undergo a number of mandatory tests:
- Flora smear : a study showing the quantitative and qualitative composition of the microflora of the vagina, cervix and urethra. It is the main technique that detects the presence of pathogenic agents in scraping the surface of these areas. It is the deviations in the flora smear that serve as the basis for prescribing additional high-precision tests.
- Bacterial culture determines the presence and type of causative agent of a bacterial infection. In addition, the analysis shows to which antibacterial substance the pathogenic agent detected in the analysis is sensitive.
- PCR diagnostics detects the presence of STIs: ureaplasmosis, genital herpes, chlamydia and others.
- A blood test for TORCH infection allows you to determine antibodies to the rubella virus, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis and herpes simplex virus.
The state of health in the future largely depends on what measures a person takes to preserve it today. Therefore, you should not ignore the recommendations of doctors, but on your own initiative undergo a full range of diagnostic studies that describe a full picture of the coordinated work of all organs and systems of the body.
The introduction of this contraceptive is carried out in the last days of the menstrual cycle or in the first days after it. After an abortion or childbirth without complications, the procedure is carried out immediately after the operation or after 5-6 weeks. After a caesarean section, the IUD can be installed only after 10-12 weeks.
As a rule, the installation is performed without anesthesia. Of course, each type of spiral has its own characteristics, but the basic principle is the same. The woman is placed on a gynecological chair, the external genital organs are treated with an antiseptic, and then the cervix. After this, the neck is fixed with bullet forceps and straightened. A conductor with a closed contraceptive is inserted into the cervical canal and moves into the uterine cavity to the required distance. Then, by moving the piston, the spiral opens and is located inside. Threads - antennae are placed in the vagina and cut to the desired length. The procedure is virtually painless and takes about 5-7 minutes.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Is it possible to independently decipher a general blood test?
Laboratory studies of biological material are carried out by experienced specialists. The results contain a huge number of terms and indicators that are not understandable to patients without certain knowledge. Special online services can help you get an answer to the question of what a general blood test shows, thanks to which anyone can prepare in advance for a visit to a medical facility.
To find out what a general blood test can show, you need the following information:
- gender (in men and women, the same test results may mean different deviations);
- age (in children and adult patients, the levels of certain substances differ);
- general information about the substances whose levels are being studied (for example, to understand what hemoglobin or leukocytes are, you can use special literature or the Internet);
- norms of various substances in the blood (this information can be easily found in similar sources).
To understand the nuances of decoding, it is important to understand in advance what a clinical blood test is. In a broad sense, CCA is the study of the composition of a material in a laboratory setting to determine the level of certain substances. The number of items on the sheet that the patient receives depends on the sampling method and the type of research being carried out and their purpose.
The clotting analysis includes a large set of indicators:
| Index | Norm |
| Prothrombin index | 12-20 sec. |
| APTT | 38-55 sec. |
| Plasma fibrinogen | 2.0-3.5 g/l |
| Thrombin time | 11-17.8 sec. |
| Plasma recalcification | 60-120 sec. |
| Heparin tolerance | 3-11 min |
| Blood clot retraction | from 44% to 65% |
If a person is prescribed a blood clotting test, you don’t have to remember what it’s called. Each patient is given a special referral, which will indicate the time, name of the study and the necessary requirements for its implementation, depending on the expected diagnosis:
- Material is taken from the finger to assess capillary blood clotting.
- Material is taken from a vein to evaluate venous blood.
This test, like many others, must be taken on an empty stomach.
What else needs to be checked after 45 years
At this age, the risk of developing various diseases increases, so doctors recommend undergoing an annual medical examination, which involves taking additional tests and undergoing highly informative studies:
- Every year it is necessary to do an analysis for tumor markers: men are prescribed a test for tumor markers of the prostate gland, rectum and large intestine, women are prescribed a test for tumor markers of the mammary glands, ovaries, as well as the rectum and large intestine.
- Women should be tested for sex hormones and C-peptide.
- Conducting a colonoscopy - examination of the large intestine.
- Gastroscopy allows you to identify pathologies of the stomach, esophagus and duodenum in the early stages.
- Blood test to determine lipid profile and cholesterol levels in particular. The main goal of such a study is the timely detection of atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels. With its help, you can prevent the occurrence of vascular thrombosis, sudden stroke or heart attack.
At this age, it is recommended to do an electrocardiogram with physical activity. Such a study will most informatively describe the condition of the blood vessels and heart.
General clinical blood test, what are the prerequisites?
The most common method in medicine. It includes the determination of hemoglobin, the number of erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes (white blood cells), leukocyte formula (each type of leukocyte is counted), platelets (blood platelets), determination of ESR.
The changes that occur in the peripheral blood are not specific; they reflect general changes occurring in the body. Without this analysis, it is impossible to diagnose blood diseases, infectious and inflammatory diseases, no matter what they are.
However, there are changes that have occurred in the leukocyte formula that are not characteristic of a particular disease; they may be similar in different pathological processes. Or, conversely, the same disease in different patients may be accompanied by changes that differ from each other.
The leukocyte formula changes with a person’s age, so it is necessary to take into account its shifts from the position of the age norm (special attention should be paid to it when examining children). Blood for analysis is taken from a finger; at least 8 hours must pass between the last meal and blood sampling. There is no need to stretch your fingers before taking the material; this may increase the level of leukocytes.
How long are the results valid?
Each of the blood tests has a certain expiration date, which doctors rely on when they need to check a person’s health status, for example, during a preventive examination or after a therapeutic course. For ordinary people not related to medicine, it is also important to know how long blood tests are valid, so as not to visit the laboratory again without a special reason.
The validity period of the examination results is as follows:
- UAC – 10–14 days;
- BAK – 10–14 days;
- immunological – 2 months;
- coagulogram – 6 months (in a healthy person).
Reference! Sugar test results are valid depending on the patient's condition. A healthy person after 40 years of age needs to be examined every six months, while a diabetic determines the glucose level several times a day.