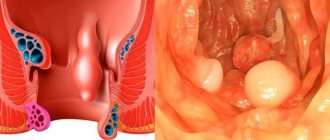
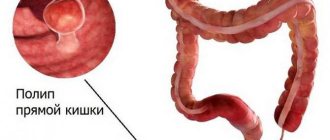
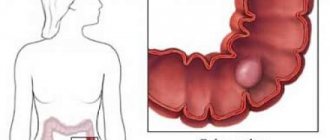
Intestinal polyposis is a disease characterized by the appearance of benign growths on the mucous membrane. The disease is characterized by a constantly relapsing course with the appearance of polyps in different parts of the intestine.
Most often, this pathology occurs in the population over 60 years of age. According to some reports, about half of people of retirement age have growths in their intestines.
Polyps-growths on the mucous membrane of a benign nature appear due to the acceleration of cell division of the mucous membrane. Depending on the type, there are:
- thin stalked polyps;
- broad-based polyps.
The main problem with the presence of polyposis is their ability to develop into malignant tumors. In oncology, intestinal polyposis is classified as an obligate precancerous condition. This means that the chance of benign tissue becoming malignant reaches 40%. Therefore, polyposis must be treated immediately.
Etiology
The causes of polyposis are varied. The main role is played by hereditary predisposition. If close relatives (direct on the father’s and mother’s side) had this pathology, then it is necessary to be constantly examined (according to the recommendation of the European Association of Oncologists, undergo a rectal examination at least once a year).
The quality of nutrition also plays an important role in the development of the disease. Eating large amounts of animal fat increases the chance of developing polyposis, while consuming vegetables and fruits, on the contrary, reduces it.
Chronic diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease predispose to the development of polyposis because they cause constipation. The state of stagnation of feces leads to the development of an inflammatory process, therefore, to an increase in proliferative processes (acceleration of cell division).
Causes of polyps
Why does pathological proliferation of cells in the mucous membrane of internal organs occur? No medical specialist will give an exact answer to this question, since the true causes of the formation of polyps have not yet been identified. It is assumed that the formation of these growths is facilitated by various factors, among which the leading place is occupied by hereditary predisposition and chronic or incompletely cured infectious and inflammatory diseases.
For example, the development of a pathological process in the gastrointestinal tract can be affected by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, and constant allergic inflammation in the nasal mucosa provokes the appearance of nasal polyps. Growths in the urinary system often occur after treatment of advanced urethritis or cystitis.
Hormonal disorders, sexually transmitted diseases, and multiple abortions increase the risk of polyps forming in the uterus or cervix. Also, a favorable background for the development of a pathological process in the mucous membranes is an improper diet, alcohol abuse, various poisonings of the body, a sharp decrease in immunity, and old age.
Pathogenesis
Intestinal polyposis occurs against the background of increased reparative processes. Depending on the reasons for development, it happens:
- inflammatory;
- hyperplastic;
- neoplastic.
Inflammatory polyposis develops against the background of corresponding intestinal diseases (enteritis, colitis). Regenerative cell division leads to the appearance of growths that can increase in size, turning into polyps over time.
Hyperplastic polyposis develops when the intestinal walls are damaged by feces, mainly due to constipation.
Neoplastic polyposis occurs after normal cells mutate into malignant ones. Atypical cells have the ability to rapidly divide, which causes the rapid growth of such polyps.
Factors in the development of intestinal polyps
When the intestinal mucosa loses its ability to renew itself, damaged cells begin to regenerate. The more often inflammation or injury occurs, the more the epithelial layer thickens. As a result, small growths appear. They do not form on healthy tissues, but the exact reasons for their formation have not been established. Doctors believe that polyps in the intestines can appear under the influence of the following factors:
- heredity;
- sedentary lifestyle, obesity;
- chronic inflammatory bowel diseases;
- excess fatty, fried, spicy foods - irritates the mucous membrane;
- surgery on the intestines;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- lack of fiber in the diet;
- hard physical labor;
- strict diets;
- frequent constipation;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- cancerous tumors.
Clinical picture
Polyps appear either singly or in groups. Multiple polyposis is more difficult to treat, since it is necessary to treat a large area of the intestine. The sizes of the outgrowths also vary - from a few millimeters to 5 centimeters.
Clinically small polyps, measuring a couple of millimeters in size, rarely manifest themselves. When the size reaches 1 to 2 centimeters, problems appear with the passage of feces, which become ribbon-shaped, and bloating and heaviness occur in the abdominal area.
When a polyp is localized in the rectum, there is a sensation of a foreign body, symptoms of an intestinal disorder. Large polyps can completely obstruct the intestinal lumen, which leads to the development of acute intestinal obstruction.
Polyps are also prone to ulceration. Constant trauma from passing feces can lead to bleeding - in this case, blood clots will be visible in the stool.
Types of surgery
There are several types of surgical procedures aimed at removing polypoid formations.
Endoscopy
This technique is minimally invasive and is used in the formation of polyps affecting various parts of the intestine. Used for small tumors. In some cases it can be combined with electrocoagulation.
The method involves inserting a colonoscope or rectoscope into the canal through the anus. Excision of the abnormal growth is carried out using a loop that is placed around the base or stem of the growth. If the tumor is large, it is removed in parts.
In terms of duration, endoscopic polypectomy lasts no more than half an hour, depending on the location of the growth, its size and quantitative indicator.
Since the operation involves minor damage, the recovery period takes a minimum of time.
Abdominal excision
It is used if multiple growths or large tumors are diagnosed. Since the operation involves removing part of the affected intestine along with the tumor, the patient is given general anesthesia. When familial polyposis is detected, complete excision of the large intestine occurs.
This type of surgery requires a long period of rehabilitation. In most situations, the patient is assigned a disability group.
Transanal polypectomy
Polyps are removed with special scissors or a scalpel. Upon completion of the procedure, the mucous membrane is sutured. It is worth noting that such operations are prescribed only when polypoid growths are located near the anus.
The patient is given a local anesthetic. To ensure that nothing interferes with the operation, the anus is spread apart with a rectal speculum.
Laser
It is used if benign tumors with a wide or thick base are diagnosed. The lesion is exposed to a laser beam. After the moisture evaporates, the base and the growth itself are destroyed.
Electrocoagulation
It is used for polyps that are not prone to degeneration into malignant tumors. Removal of the tumor occurs through cauterization.
Polyps can be treated simultaneously using several surgical techniques. This tactic is especially advisable for purposes when it is necessary to maintain the patient’s health or speed up the recovery period.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing polyposis in the early stages is difficult, since small polyps rarely manifest themselves in the initial stages. The only method is an annual examination for polyposis. Persons who are hereditarily susceptible to this pathology and people over 60 years of age should undergo routine examination methods (digital rectal examination) annually.
It is also necessary to take into account that if one polyp is found, there is a high chance of finding several more in the overlying parts of the intestine.
For a more accurate diagnosis, irrigoscopy and colonoscopy are prescribed, followed by histological examination of a tissue sample for malignancy. In the case of polyposis, preference should be given to magnetic resonance imaging, since it allows you to identify even small areas of hyperplasia (the direct sources of polyps).
What worries people when polyps occur in the intestines?
When polyps appear in the colon or rectum, the patient experiences unpleasant symptoms. However, the clinical picture manifests itself with certain features. It is noted that the signs in the initial stages of the disease do not cause discomfort. Therefore, polyps can go unnoticed for a long time.
To immediately consult a doctor, you need to know the signs of emerging tumors in order to begin treatment:
- pain throughout the entire abdominal area or only in one part;
- frequent trips to the toilet;
- pain during bowel movements;
- inclusions of blood or mucus are observed in the stool;
- difficulties in moving stool through the intestine;
- loose stools;
- constipation
Symptoms of the disease depend on the degree of the tumor. In particular, special importance is attached to the size, type and number of compactions and growths. In addition, you need to know in which intestine the polypous formation is located. Growths can appear not only in the stomach, but also in the esophagus.
Treatment
There are 2 main methods of treating polyps:
- Surgical method.
- Treatment with traditional methods.
Surgical treatment is most effective in removing polyps. The operation is called polypectomy. It is performed using electrocoagulation knives under colonoscopy control. In the case of villous polyposis (multiple polyps in a particular area of the intestine), a section of the intestine may need to be removed.
Also, the surgical method is the only method for large polyps that block the intestinal lumen, as this can lead to the development of acute complications.
The surgical method allows you to get rid of polyps, but does not prevent the possibility of their recurrence in the future. Also, removed polyps are examined for malignancy.
Walnuts
Another effective and time-tested medicine is nut balm, which is made from green fruits:
- Each nut is cut into 4 parts.
- The raw materials are placed in a glass jar, which is filled 1/3 with vodka (40%).
- Cover with a lid and leave for 3 weeks in a dark place. During this period, the contents of the jar are shaken several times.
- Then the nut tincture is decanted and stored in the refrigerator.
- Use the drug 3 times a day, 1 tsp. 15 minutes before meals.
- Treatment is a month, then a break of 30 days and repeat.
At home, you can make ointments from herbal ingredients. They help to effectively cope with the disease. The most popular folk recipes:
- Grind the dried celandine herb. Mix it with Vaseline in equal proportions. Dip a cotton swab into the resulting mass and insert it into the anus. Change the tampon 7 times a day (the one that was installed at night is changed in the morning). Perform the procedures throughout the week.
- Wash sea buckthorn berries (1 kg), cook for 3 hours over low heat, after mixing with sunflower oil (liter). Pour the hot liquid into a glass jar. Moisten your little finger with the medicine and lubricate the anal canal of the rectum in the morning, afternoon and evening. The approximate duration of the procedures is 2-3 weeks.
Baking soda is often used to treat polyps. To get rid of the disease, the following methods are used:
- Soda (1 tsp), apple cider vinegar (1 tsp) are diluted with boiled warm water (liter). The resulting liquid is used for enemas in the morning and before bedtime. The duration of treatment is determined individually.
- You can also prepare a healing solution from table salt and soda (1:1), diluted in water (liter). You will also need dried fruit compote, but not sweet. Take the medicinal drug in small sips for 15 minutes, wash it down with compote. Continue therapy for 1-2 months.
Treatment of intestinal polyps with folk remedies
It is a fairly effective method of treating polyps. Due to the healing effect of the herbs used, the body's immune system is mobilized. Local exposure allows you to inhibit cell growth, which inhibits, and in some cases stops, the growth of polyps. Treatment of rectal polyps with folk remedies is easier to carry out, since it is easier to reach. More difficult is the treatment of polyposis of the colon and sigmoid colon.
When treating with traditional methods, it is recommended to notify your doctor. You should also strictly follow the method of preparation and use of the products, as they have a hepatotoxic effect.
Application of celandine
Since the Middle Ages, celandine tincture has been used in the treatment of neoplasms on the skin and mucous membranes. This folk method has proven its effectiveness. Thanks to its antitumor, antispasmodic, antimicrobial effects, celandine is a popular and widespread remedy.
It is also able to stimulate gastrointestinal motility, thereby preventing the formation of constipation. The antitumor effect is achieved due to the alkaloids contained in celandine - their cytostatic effect leads to inhibition of cell division.
To treat polyps, an aqueous solution of celandine is used - it is used topically and administered through enemas.
Preparing for a therapeutic enema
Before performing a therapeutic enema, it is necessary to do a cleansing enema. To do this, using an Esmarch mug, about 2 liters of liquid (1-2 tablespoons of table salt per 2 liters of water) with a temperature of 38-40 degrees are injected into the rectum.
The procedure is carried out in a lying position - on the right or left side. It is recommended to hold the liquid for 5-6 minutes, which will allow you to maximally cleanse the intestinal mucosa, and the effect of the tincture will be greater.
Preparation of aqueous infusion of celandine and treatment
In order to prepare an aqueous infusion of celandine, you need to add 1 tablespoon of dry matter to 200 ml of boiled water. Leave for 1-2 hours. After this, the infusion is decanted through gauze to obtain a liquid without impurities.
Enemas should be performed when the infusion reaches a temperature of 38-40 degrees - to avoid intestinal burns. Treatment should begin with small volumes (50 ml will be enough). The course is 10 days. During this period, the amount of fluid administered is increased daily by 10 ml. After 10 days, you should temporarily stop using microenemas to avoid the development of side effects.
If after administration there is a strong feeling of discomfort, bursting pain or bloody discharge appears, you should consult a specialist.
There is another option for infusion with celandine. Calendula and yarrow are also used to prepare it. Mix 2 teaspoons of calendula, add 1 teaspoon each of celandine and yarrow. The resulting mixture is poured with boiled water in a volume of 200 ml and administered in a similar way.
Celandine juice in the treatment of intestinal polyposis
- To achieve greater effect, it is recommended to combine local treatment with enteral treatment (taking celandine juice). It is important to strictly follow the technique of preparing the drink.
- Sections of stems with flowers are crushed using a blender. The resulting mass is frozen for 3-5 days in the refrigerator. After defrosting, squeeze out the juice and mix with alcohol or vodka in a ratio of 1 to 2. After 2 weeks, the juice can be used.
- Treatment is carried out by ingesting a solution with celandine. Add 5-10 drops of the resulting juice to a glass of water and take 2-3 per day, combining with microenemas with water infusions.
- For better control of treatment, it is recommended to take a biochemical blood test once a month, which will allow you to monitor the hepatotoxic effect of the drug.
Additional folk remedies
Often in the treatment of colon polyposis, an infusion of viburnum fruits in alcohol . To do this, fresh fruits are preserved in 0.5 liters of alcohol for 5-6 months. Subsequently taken 3 times a day. If there is no infusion, regular tea with viburnum will do.
Tampons soaked in sea buckthorn oil also provide benefits by eliminating the development of the inflammatory process. They should be used when the process is localized directly in the rectum.
Chamomile decoctions have an anti-inflammatory effect and stimulate gastrointestinal motility. Taking them allows you to relieve the unpleasant sensations of heaviness and discomfort in the intestines.
Traditional methods have been practiced for many hundreds of years and legitimately occupy their niche in the treatment of diseases. It is worth noting that the effect of any means is an individual process, and before carrying out non-pharmacological procedures you should consult with your doctor. Any changes in the general condition while taking folk remedies should not be ignored.
Kalina
Decoctions are prepared from the beneficial berries of the plant or its leaves.
Viburnum contains valuable chemicals that can prevent the degeneration of a polyp from a benign formation into a malignant tumor
A few proven recipes:
- Wash viburnum berries (250-300 g), place in a saucepan, add cold water (700 ml). Bring to a boil, keep on low heat for an hour. Cool, strain well with gauze. Drink fruit drink four times a day, 100 ml. To improve the taste, you can add a little sugar. The duration of the procedures is about 6 months.
- Mix berries (200 g) with natural honey (1 tbsp). Leave for 2 hours. Take orally (inside), morning and evening on an empty stomach. Drink the medicine for 2-4 months.