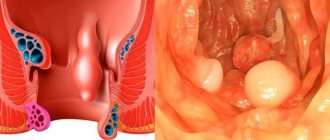
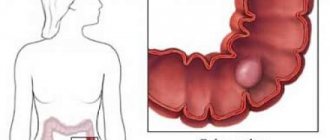
Causes of polyps
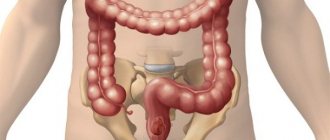
Polyps in the rectum are a multifactorial disease. One thing is known: if the intestinal mucosa is healthy, then growths will not appear in it. Polyps affect the part that has undergone pathological changes.
The main reasons for the appearance of polyps are:
- Genetics. If there is a person in the family who suffered from such a problem, then the likelihood of neoplasms occurring in his descendants increases several times.
- Constipation and poor nutrition. Excessive fat consumption has an extremely negative impact on the state of the gastrointestinal tract. To avoid constipation, and as a result, the formation of polyps, it is recommended to eat foods rich in fiber.
- Gastrointestinal pathologies that are chronic. Ulcerative colitis, colitis vulgaris and proctosigmoiditis cause growths to form.
- Infections. When a person suffers from an infection, the intestines are the first to be affected. This is the root cause of polyp growth.
- Poor environment and physical inactivity. These are the main problems of modern people, because a sedentary lifestyle provokes blood stagnation. Hence - constipation and polyps.
Alarming manifestations
Such bloody discharge may also be accompanied by other symptoms, which must be indicated to the doctor when visiting. This includes pain during bowel movements and a feeling of incomplete bowel emptying, discomfort in the perineal area.
Also, against the background of bloody streaks or bleeding, symptoms such as weakness and constipation, rumbling in the abdomen and flatulence, intestinal tenesmus (false urge to defecate) and heaviness in the stomach, diarrhea and aversion to food should also be alarming.
The reason for visiting a doctor should be streaks in the stool against the background of itching of the skin and a bitter taste in the mouth, dilation of blood vessels in the lower abdomen, asthenia and frequent nausea. This may indicate the manifestation of liver cirrhosis.
Signs of polyps in the rectum
The main and most pronounced signs of rectal polyps are:
- Pain in the lower abdomen. Such sensations are caused by the accumulation of feces, with frequent and long-term constipation. Also, pain in the lower abdomen or ileum can be a consequence of excessive accumulation of gases in the intestinal loops. Excess gases and feces fill the intestinal loops, thereby stretching it, causing discomfort.
- Alternating diarrhea and constipation. Already in the early stages of development, this symptom may appear. This happens because as it develops, the polyp enlarges, reducing the lumen and becoming an obstacle to the evacuation of waste products from the body. More often, clinic patients complain of prolonged constipation, which causes pain.
- The appearance of blood and mucus in the stool. The appearance of pathological impurities in the patient’s stool is a serious reason for going to the hospital. The appearance of mucus is a consequence of the growth of a polyp, which irritates the mucous membrane, causing excessive secretion of the glands. Blood is a sign of damage to the blood vessels of the intestinal mucosa. Or the appearance of blood, the result of polyp necrosis. Small blood losses can lead to anemia.
- Swelling of the skin around the anus. Swelling of the skin around the anus. The appearance of swelling and redness of the skin around the anus occurs due to the frequent secretion of mucus and blood.
Blood during bowel movements in the presence of hemorrhoids
The phenomenon of blood in the form of droplets or even clots in the stool, the presence of scarlet discharge, has many causes. And even isolated episodes cannot be ignored. Most often, this occurs against the background of hemorrhoids. In this case, defecation is accompanied by pain in the anus and rectum. Blood appears immediately after defecation on the stool itself or droplets remain on the toilet paper. Usually, with hemorrhoids, bright scarlet or darker blood is released. Constant blood loss due to such a problem can form chronic iron deficiency anemia, which worsens the patient’s condition. In addition, hemorrhoids become chronic, changes steadily progress, which eventually leads to complications. Loss of nodes and their pinching, necrosis or bleeding may occur, then hemorrhoids require emergency care in the form of surgery.
Symptoms of polyps
The main signs of the presence of polyps are highlighted:
- Itching and burning in the anal area.
- There is blood and mucus in the stool.
- Increased body temperature, chills or fever.
- The number of urges to go to the toilet increases.
- Exhaustion of the body and sudden weight loss.
- Abnormal stool, constant constipation.
The disease can pass without noticeable symptoms, and noticeable signs appear with direct impact on the polyp itself, and the appearance of a concomitant disease can reveal the presence of a polyp in the rectum.
The symptoms of this disease are similar to those of hemorrhoids. And the inflammatory process of hemorrhoids can cause polyps. In case of serious complications, anemia and exhaustion may develop; if symptoms of these diseases appear, the presence of formations in the body cannot be ruled out.
In children, these growths can appear as early as three years of age. They will not cause any significant harm to health, but constant monitoring is necessary.
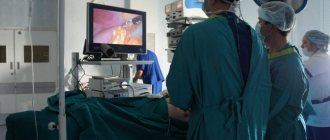
Polyposis therapy
Unlike hemorrhoids, treatment of polyps is carried out only surgically, while conservative therapy or treatment with folk remedies and medications is unacceptable.
The only method to get rid of polyps is to remove them using an endoscopic or surgical method.
If the location of the polyp in the anus is too low, therapy can occur through the anus. If the polyps are located high in the large intestine, then treatment occurs using endoscopic electroexcision, through the action of electric current.
In the presence of large polyps, removal is carried out gradually, in parts.
After the polyp has been surgically removed, it must be sent for histological examination. This is done to confirm or refute the oncological process in the body. Therapy for diffuse polyposis is carried out by removing the affected part of the intestine.
Treatment of polyps
For pathologies such as rectal polyps, treatment is carried out with surgery. Operations can be completely different. It all depends on where the polyps are located, what type they are, and what sizes are most prevalent. As a result, all benign tumors are removed, and then undergo various studies in histological laboratories.
There are about two types of surgical cases practiced in clinics. The first is called a minimally invasive procedure (polyps are removed while preserving the organ), and the second is called rectal resection. Also, some treatments are applied depending on the pathological problem itself.
With endoscopic intervention, the growth is removed with a sigmoidoscope or colonoscope. In this case, the patient is put on a strict weekly diet in order to reduce inflammation.
With electrocoagulation, polyps are removed using a proctoscope, which can burn through some types of tumors. In cases where the growths are quite wide at the base, then they refrain from surgery, because in this situation, perforation of the intestine can occur.
It would be wrong to derive a single mechanism for the formation of anal polyps. Considering the variety of types of AP, pathogenesis should be determined for each type.
“True” polyps , which are benign tumors, develop in stages similar to all tumors: chronic inflammation → dysplasia (pathological changes) of mucosal cells → the appearance of atypical cells with a high malignancy index.
The intestinal epithelium is quite intensively renewed at the cellular level. With complete health, the intestinal walls undergo a “correct” and timely alternation of phases:
- proliferation (increase in number);
- differentiation (maturation and appearance of properties specific to a given type of epithelium);
- apoptosis (death).
Universal pathogenesis in tissue dysplasia
With any damage to the epithelium, the processes of cell proliferation and migration are activated. This regeneration helps bring tissues to their original state. In the presence of chronic inflammation, there is constant mononuclear and neutrophilic infiltration of tissues. Because of this, a large, even excessive amount of pro-inflammatory agents (interleukins 8, tumor necrosis factor, HLA) appears here. Cytokine gene polymorphism during dysregenerative processes changes the severity of the inflammatory response.[4] All of the above leads to an imbalance in the appearance, maturation and death of cells. There is a disruption in the normal course of tissue renewal.
Epithelial cells from the generative zone move too early to the upper layers of the epithelium; they may not be sufficiently differentiated. This leads to the appearance of cells with altered histoarchitecture (cellular atypia). The frequency of gene mutations is increasing, which can also contribute to an increased risk of developing malignant properties in them. With an unchanged basement membrane in atypical cells, the following are noted:
- increased polymorphism and cell size;
- increase in the number of mitotic figures;
- the appearance of atypical mitoses;
- an increase in the size of the nuclei, their hyperchromia.
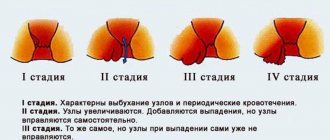
The degrees of atypia (dysplasia) are conventionally divided into three degrees:
- I - light (small);
- II - moderate (average);
- III - severe (significant). Sometimes this stage is difficult to distinguish from stage 0 carcinoma. (so-called cancer in situ).
Hyperplastic polyps appear due to an imbalance in the stages of cell differentiation and apoptosis. With a significant prolongation of these phases, an excess amount of tissue appears with the formation of a hyperplastic polyp.
Nonepithelial polyps can appear as a result of disorders of embryonic development, when heterotopic embryonic tissue remains in the mucous membrane of the anal canal.
Hamartomas , which are often mentioned in hereditary polyposis (Pates-Jeghers syndrome, juvenile polyposis syndrome, Cowden's disease), appear as a result of genetically determined structural features of the intestinal wall: the ratio of its structural elements - stroma and muscle fibers - is disturbed and their unusual location occurs / combination. There is no cellular atypia of the epithelium and no disruption of proliferation processes. With hamartomas, the stroma prolapses the muscular layer of the intestinal wall, smooth muscle fibers branch abnormally in it, which creates the appearance of invasive epithelial growth into the intestinal thickness.[5]
Hypertrophied anal papillae , which are often mistaken for polyps, are just abnormally large (up to 4 cm) outgrowths on the semilunar valves of the Morgani columns and crypts (tubular ingrowths of the epithelium). The crypts are located in the most distal part of the rectal ampulla. The pathogenesis of the appearance of tissue hypertrophy in this area has not been precisely established, but most sources indicate the presence of chronic inflammation of the mucosa [6], which probably leads to a failure of the processes of proliferation and repair in general and to the resulting growth of excess tissue on the semilunar valves.
Prevention of occurrence
Prevention of rectal polyps is the prevention or reduction of the causes that contribute to the formation and growth of polyps. It is necessary to perform simple preventive actions to avoid cancerous tumors. These include:
- Treatment of diseases that become chronic;
- Replenishing the lack of vitamins and nutrients in the body;
- Eating the right nutritious food;
- Elimination of constipation;
- Visiting medical institutions for tests.
Diseases that contribute to the development of polyp-like growth include colitis, proctitis, Crohn's disease, colon dyskinesia, enteritis, and hemorrhoids. In case of inflammatory processes of these diseases, it is necessary to consult a specialist in a timely manner. This will favorably facilitate the correct diagnosis and treatment in the early stages of the disease.
- An important role is played by replenishing missing elements in the human body, such as vitamins A, C, D, E, folic acid, calcium, selenium and others.
- Eating whole grains (brown rice) and high fiber content (white cabbage) will be good for your health. Lean varieties of meat products (turkey) are more valuable than the abuse of “red meat” (smoked products). Vegetable fats (linseed oil) should replace animal fats.
- To avoid constipation, avoid fast food, play sports, do not use enemas, eat prunes and dried apricots, they contain potassium.
- After 40 years, it is recommended to periodically examine the colon and take a test for occult blood in the stool. The risks increase in males, those with a hereditary predisposition, and those living in large cities and industrial areas.
If you have already had surgery to remove the tumor, to avoid a recurrence, you must be monitored by a doctor. It is advisable to conduct a full examination once a year.