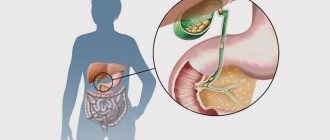
Gallstone disease is a very common pathology, the main danger of which is its hidden asymptomatic onset. While the disease progresses, a person does not experience any signs of illness, and when the clinical picture develops, he already requires long-term treatment.
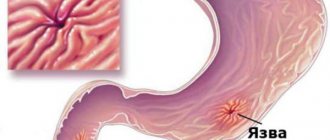
In the vast majority of cases, the disease is caused by cholesterol stones in the gall bladder. This happens by converting cholesterol into cholesterol monohydrate, which is first deposited as sand, then any grain of sand can turn into stone. The process of stone growth takes years: on average, in 12 months the diameter of the stone can increase by 3-5 mm. When the stone reaches a certain size, it can block the duct. Blockage of the bile ducts requires emergency medical intervention.
The process of stone formation
The formation of gallstones is preceded by the appearance of biliary sludge (putty-like bile).
It consists of derivatives of bilirubin, cholesterol and mucin. Sludge tends to dissolve on its own or turn into gallstones, which accumulate in the gallbladder or migrate into the ducts, blocking them and causing symptoms of an attack of hepatic colic. The formation of stones does not occur quickly; it takes many months or years. On average, stones increase by 1-2 mm per year. It takes more than 5-20 years for stones to become large and clinically manifest. Most of them are mainly formed in the cavity of the bladder, but brown pigment-type formations can appear in the bile ducts.
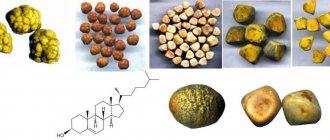
Types of stones
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qg_PnjdMJ0o
There are 4 types of gallstones:
- Cholesterol is the most common formation. They appear due to high levels of cholesterol in bile, when the excess amount settles in the form of solid microcrystals. They connect and form stones.
- Calcareous - mainly from calcium salts.
- Pigmented - divided into black and brown. Black stones are solid formations of calcium salts and bilirubin derivatives. Brown ones have a soft and oily consistency. Include a mixture of fatty acids and other substances.
- Mixed - mostly stones have a combined chemical composition with a predominance of lipids.
One patient may develop stones in the gallbladder of various configurations:
- crystalline;
- with fiber separation;
- layered;
- amorphous.
According to the type of gallstones, there are primary and secondary. Formations that appear in the unchanged biliary tract when the pathological process begins are called primary. If cholesterol stones are the result of a delay in the outflow of bile due to already developed cholelithiasis, these are secondary.
Formations in the gallbladder can be like grains of sand, less than 1 mm, and sometimes reach 60-80 g and fill the entire lumen of the gallbladder. The shape of the stones is also different. There are stones:
- spherical;
- with several edges;
- ovoid;
- awl-shaped;
- barrel-shaped.
By consistency - strong, brittle and soft stones. They have a homogeneous and complex structure. Stones with a complex structure include a core, which can be formed from thick mucus, cholesterol, bilirubin and foreign substances (mercury, fruit pits, helminths, blood clots). The body and bark consist of fat that is insoluble in water. The top layer may also consist of calcium salts.
The following processes lead to the appearance of the first stones in the gall bladder:
- production and stagnation of lithogenic bile (unbalanced in components);
- loss of the ability of the bladder walls to contract normally;
- inflammation in the biliary tract;
- metabolic disorders associated with diseases that are accompanied by high cholesterol levels.
Character and diet play a huge role in the health of the biliary system. Rare meals, fasting, and an unbalanced diet can lead to thickening of bile, increased cholesterol concentrations and the formation of stones.
In addition to poor nutrition, predisposing factors are:
- heredity;
- abuse of protein and fatty foods;
- obesity;
- dyskinesia;
- hormonal contraceptives;
- Crohn's syndrome;
- diseases of the endocrine system (hypothyroidism and others);
- after removal of part of the intestine;
- chronic cholecystitis;
- chronic hemolysis - destruction of red blood cells (erythrocytes);
- parasitic infestations;
- alcoholic liver disease (cirrhosis, hepatitis).
Gallstones often form during prolonged periods of inactivity. Additional risk factors for stone formation in humans are:
- age-related disorders;
- female.
Symptoms of gallstones in women appear during pregnancy and hormonal changes in the body during menopause. The presence of stones can also provoke obstruction or reduction in the lumen of the bile ducts, caused by:
- cancerous tumor;
- formation of adhesions;
- swelling in the biliary tract;
- bending of the gallbladder.
The main prerequisites for the development of the disease:
- Chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal system. These include gastritis, gastroduodenitis, peptic ulcer, chronic ulcerative colitis.
- Endocrine pathologies. Among them, diabetes mellitus plays a leading role, as well as hypofunction of the thyroid gland, dysfunction of the adrenal glands and dysfunction of the female and male gonads.
- Dietary disorders. If a patient consumes large amounts of fatty, fried foods, salt, simple sugars, foods high in stabilizers, dyes, preservatives and flavor enhancers, the likelihood of stone formation increases sharply.
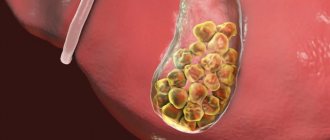
Classification of stones
The gall bladder stones themselves consist of 95% cholesterol, the rest being bilirubin compounds. The shape of the stones is usually round, less often oval, and the color is yellow or green. Cholesterol gallstones are lightweight and do not sink in water.
Most formations in the gallbladder are cholesterol stones. But in approximately 20 cases other deposits occur:
- bilirubin (pigment);
- calcareous (calcium);
- mixed.
Based on the number of stones, the doctor differentiates the disease with single stones from the form with many formations. The stones are classified according to their size: small (diameter up to 1 cm), medium (1–2 cm), large (more than 3 cm).
Symptoms of pathology
A common complaint from patients is a feeling of pain in the right hypochondrium.
The following clinical symptoms are typical for gallstones:
- Pain in the right hypochondrium. It is piercing, cutting, pressing or pulling in nature. Painful sensations are localized mainly in the right epigastric region. They can radiate to the back, neck, right arm and even the pelvic area.
- Yellowness of the skin. Yellowing of the skin occurs when the bilirubin pigment accumulates in the blood due to obstruction of the bile ducts by stones. It concentrates and causes lemon-colored skin, light-colored stool, and dark urine.
- General weakness and malaise. Asthenic symptoms arise as a result of a violation of the general metabolism in the body and the appearance of a large number of toxic metabolic products in the bloodstream.
Most patients do not experience any discomfort when the first stones appear in the gall bladder. This continues until the stones become large, they show themselves with typical signs:
- bitterness in the mouth;
- the appearance of heaviness, pain in the right hypochondrium and abdomen;
- belching;
- hepatic colic, which is accompanied by manifestations of dyspepsia (nausea, rarely vomiting).
If stones leave the gallbladder and move along the biliary tract, an attack of pain and accompanying signs of stones in the gallbladder appear. By blocking the duct or Vater papilla, they create an obstacle to the exit of existing bile, as a result of which the walls of the bladder swell, which is manifested by an attack of biliary colic.
The development of this condition is caused by:
- frequent consumption of spicy, hard-to-digest foods, alcohol, carbonated drinks;
- severe stress;
- carrying heavy objects;
- driving on uneven surfaces.
During an attack of colic in the gallbladder, acute pain is localized under the right rib and can spread to the scapular region, neck, upper limb and epigastric region. Increased pain is observed in the first 15-60 minutes, the duration of colic can reach 12 hours. Blockage of the duct is accompanied by hyperthermia, increased sweating, and convulsive spasms.
Symptoms of cholelithiasis are very diverse and depend on the size and location of the stones. Symptoms of gallstones in men are the same as in women, and often manifest themselves with characteristic manifestations:
- vomiting mixed with bile;
- obstructive jaundice - the skin turns yellow;
- light stool and dark urine;
- intestinal dysfunction - diarrhea, constipation, flatulence;
- poor appetite;
- intolerance to certain foods;
- the appearance of a white or brown coating on the tongue;
- the appearance of pain in the liver area during shaking;
- low-grade fever – temperature rise to 37.1-37.3 degrees;
- weakness, chronic fatigue.
Reasons for the formation of stones in the gallbladder
The etiology of this pathology usually includes the following:
- the presence of excessive amounts of calcium, cholesterol or bile pigments in the bile;
- inflammatory process in the gallbladder;
- stagnation of bile due to impaired contractile function of the bladder.
Favorable factors for the formation of stones are also considered:
- heredity;
- treatment with certain drugs (for example, Cyclosporine);
- in women, stones are found more often, which can be associated with the influence of estrogens and the use of hormonal contraceptive pills; In addition, during pregnancy, the absorption of cholesterol is much more active, which becomes the cause of the formation of stones;
- rapid weight loss or vice versa obesity;
- some diseases (for example, hemolytic anemia, liver cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus);
- consumption of high-calorie foods and foods high in animal fats;
- physical inactivity.
How is it diagnosed?
This type of stone is easily visualized using ultrasound.
- Ultrasound scanning. A thorough examination of the abdominal organs is carried out in order to identify the presence, size, quantity and characteristics of stones. In parallel, the patient is excluded from other pathologies.
- General blood analysis. Leukocytosis and accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation indicate an inflammatory process.
- Biochemistry of blood. An increase in the direct fraction of bilirubin and other liver parameters indicates in favor of stone formation.
- Computerized or magnetic resonance imaging of the gallbladder. Anomalies of the structure and anatomical defects of this organ will be more accurately determined.
- Cholecystography. This method is also hardware based. It allows you to diagnose impaired contractility of the gallbladder walls.
- Endosonography. This instrumental technique is an analogue of ultrasound examination.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. The method is invasive and involves inserting a special tube with a camera into the patient's esophagus.
Diagnosis of cholelithiasis
The basis for successful treatment of the disease is a correct diagnosis. Initially, differential diagnosis of cholelithiasis is carried out. The main task is to confirm that the patient’s complaints are caused by the specified disease, ensuring effective treatment. A number of diseases - chronic pancreatitis, hepatitis, cholecystitis and others - show similar symptoms. How to determine the disease that caused the attack? You cannot rely solely on patient complaints and laboratory tests. Additional procedures are required. These include:
- Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder (ultrasound).
- Computed tomography (CT).
- Magnetic resonance cholangiography.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).
Diagnosis of gallstone disease involves the use of other, less common methods, for example, radiography or duodenal intubation.
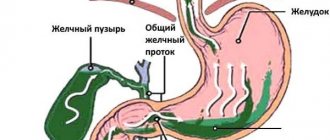
Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder
It is considered an accessible and safe diagnostic method. The patient is not exposed to radiation; if necessary, the study can be repeated several times. An ultrasound examination allows you to fully see the inside of the gallbladder and the walls of the organ. The ducts, due to their small thickness, are not always identified. Ultrasound has no contraindications and is widely used in the diagnosis of abdominal organs, including the gallbladder.
Preparations for the study begin two to three days in advance. It is recommended to exclude from the diet foods that cause flatulence and complicate diagnosis. It is recommended to take drugs that help remove gases - activated carbon, Motilium. The last meal before the study occurs eight hours before. It is recommended to cleanse the intestines using an enema or laxatives. Ultrasound is done strictly on an empty stomach. It is forbidden to drink tea, water, or chew gum to prevent the release of bile.
CT scan
With this examination method, a detailed image of the internal organs is obtained using X-rays. The patient is placed on a table that slowly slides inside the tomograph. Rotating, the device takes pictures of the desired organ layer by layer. To obtain a clearer picture, the patient first takes a contrast agent containing iodine. Pictures taken before and after taking the drug allow you to clearly see foci of inflammation.
A computed tomography scan reveals the presence of stones in the ducts and neck of the gallbladder. Computed tomography allows you to determine the density of stones and differentiate formations by origin, which is important when choosing a treatment method. It is known that cholesterol stones can be dissolved with the help of medications, and pigment stones are crushed by a shock wave. Calcareous or X-ray-positive stones are considered dangerous; removal of such deposits is possible only by surgical methods.
Possible complications
In the case of advanced cholelithiasis, without proper treatment or untimely contact with a doctor, a number of complications may appear:
- acute cholangitis is an inflammatory process of an infectious nature;
- sepsis – general blood infection when microorganisms enter the bloodstream;
- abscess in the liver;
- perforation of the gallbladder due to its thinning;
- peritonitis when the bladder ruptures;
- the formation of a fistula between the duodenum and the bladder;
- intestinal obstruction in case of stone penetration into the intestines;
- calculous cholecystitis;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- secondary cirrhosis of the liver.
If stones remain in the gall bladder for a long time, the pathological process can lead to the appearance of an oncological tumor. Each of the secondary pathologies is life-threatening and requires emergency medical care.
Diagnostic methods
Cholesterol plaques in the gallbladder are diagnosed using a set of laboratory and functional methods. The examination begins with examining the patient: assessing skin color for jaundice. When pressing on the area where the gallbladder is located, the patient feels pain.
Then the doctor prescribes a set of tests:
- Ultrasound - to detect cholesterol polyps in the gallbladder;
- radionuclide scanning - to determine the degree of patency of the bile ducts;
- tomography to identify anomalies in the anatomical structure of the organ;
- X-ray of the bladder and liver with a contrast agent;
- endoscopic cholangiopankeatography.
Laboratory studies include conducting a biochemical study of blood composition, which evaluates indicators such as cholesterol, ALT, AST, and bilirubin. In a clinical analysis, markers of the inflammatory process are assessed: ESR, leukocyte count. Usually, stone diagnosis quickly confirms the diagnosis, and no lengthy investigation is required.
Treatment of the disease
The dissolution of stones is facilitated by ursodeoxycholic acid preparations.
Stones can be dissolved using medications - ursocholic and ursodeoxycholic acids. Folk remedies are used less frequently in medical practice. If the process has already reached decompensation, and the stones are too large to be lysed and removed, surgical removal is resorted to.
The underlying disease may be complicated by diverticulosis of the organ.
Gall stones lead to the following complications:
- Gallbladder diverticulum. This is a protrusion of the entire organ or part of it with disruption of the passage of bile into the duct.
- Formation of ulcers. Due to the chronic mechanical impact of the calculus on the wall of the bladder, ulcerative defects are formed.
- Cholecystitis. This is inflammation of the gallbladder followed by infection.
- Peritonitis. It is already a complication of cholecystitis. This is a purulent process in the abdominal cavity that can be fatal.
- Subhepatic or subphrenic abscesses.
Pigmented gallstones
Pigment stones account for 10-25% of all gallstones in patients in Europe and the USA, but their frequency is much higher among the population of Asian countries. As with cholesterol stones, pigment stones are more common in women and are usually small, fragile, black or dark brown in color, and their incidence increases with age.
Black pigment stones
Black pigment stones consist either of a black polymer - calcium bilirubinate, or of polymer-like compounds of calcium, copper, and a large amount of mucin glycoproteins. Does not contain cholesterol. It is not possible to identify a clear crystalline structure in the stones. They are more often found in patients with cirrhosis of the liver, in chronic hemolytic conditions (hereditary spherocytic or sickle cell anemia, vascular prostheses, artificial heart valves, etc.). They make up approximately 20-25% of gallstones and can migrate into the bile ducts.
Diagnostics
If stone formation occurs, the patient is first examined by a therapist. The doctor listens to complaints, conducts an examination, and collects an anamnesis of the disease. To exclude diseases with similar symptoms, laboratory tests are prescribed:
- do a blood test for liver function tests;
- general urine analysis;
- stool examination;
- analysis for hemoglobin, ESR, leukocytes.
After a presumptive diagnosis, the patient requires additional consultation with a gastroenterologist, who performs hardware diagnostics of the gallbladder:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- radiography - this method detects calcified stones;
- MRI and CT;
- oral cholecystography;
- Endoscopic ultrasound helps identify small stones (3 mm).
Why are stones formed?
There are actually many reasons for the formation of stones:
- unhealthy diet (consuming large amounts of fatty and fried foods, alcohol, carbonated drinks, fasting, dieting, overeating);
- stress;
- chronic infections;
- pregnancy and childbirth (the risk increases in proportion to the number of children);
- surgical interventions in the abdominal cavity;
- smoking;
- excess weight (body mass index greater than 25);
- sedentary lifestyle;
- diseases of the endocrine system or gastrointestinal tract.
Traditional methods
The choice of treatment for gallstones greatly depends on the clinical symptoms and examination results. Only a medical specialist decides whether surgery is necessary for the patient or whether litholytic methods are sufficient for the disease to go away.
Methods without surgery are effective in identifying solid formations in the gallbladder at the initial stage of their formation, if the size is less than 1 cm. In this case, it is possible to preserve the organ and ducts without resorting to surgery.
For this purpose, medications are used, as well as the destruction of stone nuclei with ultrasound. Some patients use alternative medicine methods, but such recipes should only be used under the strict supervision of a physician.
Drug treatment with the use of drugs for dissolving stones, which are based on bile acids, can achieve good results. They effectively dissolve small cholesterol stones, and also normalize the composition of bile and increase the level of bile acids.
This method will help if the following important conditions are met:
- the walls of the gallbladder contract well;
- the ducts are not blocked;
- prevalence of cholesterol stones;
- cholesterol stones no more than 1.5 cm;
- the cavity is filled with stones less than half;
- the possibility of taking medications for a long time.
Treatment of gallstones in this way lasts up to 2 years. At this time, it is necessary to abandon drugs that contribute to the formation of stones.
Preparations for dissolving formations in the gallbladder:
- Ursosan;
- Ursofalk;
- Ursoliv;
- Ursodex.
To eliminate the signs and causes of stones in men and women, the doctor prescribes medications:
- for timely evacuation of bile - Allohol, Holosas, Flamin;
- to relieve severe spasms - No-shpa, Drotaverine, Spazmalgon;
- elimination of pain – Tempalgin, Novigan;
- means to relieve inflammation - Ibuprofen, Indomethacin.
According to indications, the complex is often complemented by antibiotic therapy. The correct selection of medications and impeccable adherence to the doctor’s recommendations will significantly facilitate the course of the pathological process.
The destruction of solid formations is carried out using extracorporeal shock wave therapy. Often prescribed for crushing large stones before removing stones by dissolving them. This treatment method is based on the use of the ability of ultrasonic waves to crush large stones into small sizes. The same effect can be achieved with a surgical laser.
When can you do the manipulation:
- free bile ducts;
- stones no more than 3 cm;
- cholesterol stones.
This option is contraindicated for patients suffering from chronic gastrointestinal pathologies, as well as with blood clotting disorders.
The solution to the problem through surgery is to remove the gallbladder along with stones or only solid formations. The need for surgery arises in cases where:
- large stones occupying a third of the organ;
- repeatedly recurring attacks of biliary colic;
- bladder dysfunction;
- there is no effect from non-surgical treatment after two years of taking the drugs;
- complicated cholelithiasis.
Cholecystectomy is resorted to last, when all possible methods have already been used. There are several options for surgery if it is necessary to remove stones:
- Removal of the gallbladder in the classical way - resection is carried out through a 15-20 cm incision. The disadvantage of the open method is high trauma, a high risk of postoperative complications and a long rehabilitation period.
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a minimally invasive, gentle operation using a special endoscopic device.
- Laparoscopic cholecystolithotomy - to remove stones of different sizes from the organ, but not to remove it.
Removal of the gallbladder negatively affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which is manifested by the development of various diseases of the digestive system. Therefore, it is correct to strictly follow your doctor’s instructions, eat right and often, and visit a specialist regularly.
Traditional medicine recipes should be used only after prior consultation with a doctor with a mandatory ultrasound of the gallbladder and abdominal cavity to determine the composition of gallstones and how to treat them. In the absence of contraindications, you can use effective recipes:
- Drink sauerkraut juice 3 times a day for 2 months. A single serving is half a glass.
- Take fresh rowan berries (200 g) daily, you can add honey, sugar (if there is no allergy), 1 month.
- Pour a full tablespoon of chopped lingonberry leaves into 1 tbsp. boiling water After 30 minutes, strain the infusion and drink 50 ml 5 times a day before meals.
- Olive oil is good to take on an empty stomach. The first portion is half a teaspoon and gradually the single volume should be increased to 10 ml.
- Beetroot broth is prepared by boiling 5 small root vegetables for a long time. Drink the resulting solution half a glass in the morning, afternoon and evening.
It is possible to include alternative treatment if there is no allergic reaction to the components, which manifests itself as a rash on the body, itching and other typical symptoms.
How to treat patients after acute symptoms have resolved?
If possible, conservative therapy is carried out. It includes the following points.
- Diet food. Patients are recommended to eat 6 times a day. Fatty, spicy and fried foods, carbonated drinks, chocolate and alcohol are excluded. It is recommended to consume dairy products, wheat bran and foods of plant origin. It is useful to include more vegetables and fruits in your diet, as they contain fiber, which stimulates intestinal motility and helps reduce the size of stones. Ginger is also considered beneficial, as it stimulates the processing of lipids. In addition, it is important for patients not to overeat and drink plenty of water.
- Drug therapy - treatment with special tablets that contain ursodeoxycholic and chenodeoxycholic acid and help dissolve stones in the gallbladder. This method of treatment is effective only in the presence of small cholesterol stones. In addition, such drugs are prescribed only when the contractility of the gallbladder is normal and in the absence of obstructions in the patency of the bile ducts. During treatment, it is prohibited to take certain other medications (for example, estrogens or antacids). A special feature of this therapy is that to achieve a positive result, medications should be taken regularly and for a long time (from 6 to 24 months).
Prevention
To normalize the functioning of the biliary system, to prevent exacerbations of cholelithiasis and the reappearance of gallstones, men and women should adhere to the following recommendations:
- it is worth following a diet;
- avoid a sedentary lifestyle;
- you can exercise moderately;
- for obesity, get rid of excess weight with its gradual reduction;
- take medications as prescribed by your doctor;
- be regularly examined by a specialist (once a year).
In order to prevent lithogenesis in the gallbladder, potential patients at risk should adhere to certain rules. These include dietary fractional meals, moderate physical activity, avoidance of fatty foods, salt and foods rich in simple sugars. Such patients should undergo regular medical examinations.
Causes of gallstone disease
Gallstone disease is a fairly common disease. Older women and people with excess body weight are more often affected. The causes of the disease include:
- Poor nutrition – irregular eating, fasting, overeating.
- Sedentary lifestyle, physical inactivity.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy.
- Heredity.
- Diseases of the pancreas.
Recently, it was believed that removing the gallbladder was a simple method of getting rid of stones. Recent studies have proven that if possible, it is better to try to preserve the organ. The gallbladder accumulates excess cholesterol; when the organ is removed, the substance enters the blood vessels, increasing the risk of developing atherosclerosis. After removal of the gallbladder, a person is doomed to a lifelong adherence to a strict diet.