Home How to stay healthy longer?
Author: Alexey Shevchenko May 07, 2020 12:00 Category: How to stay healthy longer?
Good day, dear readers of Alexey Shevchenko’s blog “Healthy Lifestyle”. Gallstones are a very common and serious problem. Today I want to say a few words about what they are.
- 1 Stones in general terms
- 2 Types of stones
- 3 Mechanism of stone formation
- 4 Reasons for the growth of stones
Therapy for this disease
Diet No. 5
Its main principle is fractional nutrition (frequent (5-7 times a day) meals in small (up to 200 grams) portions) with plenty of fluids (at least two liters of liquid per day) to drink.
This diet strictly prohibits the consumption of: any spicy, fried and fatty foods; lard; products that contain a lot of essential oils (sorrel, spinach, and so on); alcohol; carbonated drinks; sweets; egg yolks (you can only have one egg per week), as well as all types of canned and smoked foods, dishes, legumes, mushrooms and sour types of berries and fruits. All types of spices and herbs and cold dishes (ice cream, jelly, jellied meat) are also prohibited. It is recommended to consume foods that lower cholesterol levels and promote its removal from the body (oatmeal and buckwheat porridge). It is necessary to increase the consumption of plant foods (vegetables and sweet fruits), as well as low-fat varieties of cottage cheese, milk and fermented milk products. The source of protein for this diet is dietary meat (chicken, rabbit, lean veal and lamb, as well as turkey) and low-fat fish (both sea and river).
The necessary fats should only be of vegetable origin (olive, sunflower or flaxseed oil). It is useful to drink non-carbonated mineral water (for example, Borjomi). All food should be warm (in no case cold or hot).
Litholytic therapy (dissolution of stones)
These medications reduce cholesterol levels in bile and also increase the concentration of bile acids, which help dissolve stones.
Shock wave extracorporeal lithotripsy
An increase in pressure causes the destruction of the stone, after which its small remains can be dissolved using the medications described above.
Cholecystectomy
Unfortunately, this method is used more often than others to effectively treat this disease. It is used in cases of acute calculous cholecystitis, with large stones (larger than the diameter of the bile duct), with constant excruciating pain that is not relieved by antispasmodics, as well as to prevent possible serious complications.
Contraindications for cholelithiasis
In case of cholelithiasis, choleretic herbal remedies are strictly contraindicated. They can contribute to the migration of stones, and this is fraught with the most dangerous complications.
For the same reason, you need to be very careful when drinking mineral waters.
If the stones are large and attacks of biliary colic are frequent, then the patient has to lie down on the surgeon’s table.
Often patients with cholelithiasis undergo surgery for emergency reasons, when removal of the gallbladder - cholecystectomy - is vital. This happens in acute cholecystitis, which can be complicated by peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum), as well as in cases of pancreatitis and complete blockage of the bile ducts.
How to treat cholelithiasis?
The gold standard for gallstone disease is laparoscopic surgery, in which the gallbladder is removed through small punctures in the anterior abdominal wall. After the operation, there are practically no traces left on the skin. The patient is usually discharged the next day after the operation and quickly returns to his usual rhythm of life.
Many people are concerned about the question: is it possible to live a full life without a gallbladder?
Doctors say that the quality of life does not suffer from cholecystectomy. The purpose of the gallbladder is to store bile until food is consumed. It was vitally necessary only for primitive people, who sat down to the table only after a successful hunt (and this did not happen every day) and could joyfully eat a good half of the harvested mammoth.
Modern man has no need to eat in reserve. Therefore, the absence of a gallbladder does not affect its functioning in any way.
Integrate “Pravda.Ru” into your information flow if you want to receive prompt comments and news:
Add “Pravda.Ru” to your sources in Yandex.News or News.Google
We will also be glad to see you in our communities on VKontakte, Facebook, Twitter, Odnoklassniki.
Non-surgical treatment
If stones are found in the liver, treatment directly depends on the stage at which the disease is located. Without surgery, it is possible to cure the pathological process only at an early stage of its development. If any alarming symptoms appear, it is very important not to ignore them, but to consult a doctor as early as possible.
Conservative methods of therapy include taking medications and diet. Before leaving the diet, you should definitely undergo re-diagnosis.
The key disadvantage of this therapy is the danger of re-formation of deposits and the need for long-term medication. In addition, conservative treatment does not always bring the desired results. When an attack of biliary colic develops, doctors usually prescribe antispasmodics. If acute cholecystitis is present, surgical treatment is recommended.
Also, for stones, antibacterial medicine, choleretic tablets, and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. A mandatory element of therapy are hepatoprotectors, which are designed to restore damaged liver cells and prevent further development of inflammation. If the formations are small, they may come out on their own.
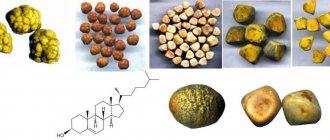
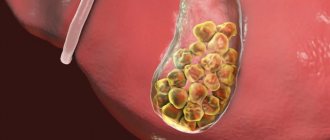
Main types of stones
For the treatment of cholelithiasis, a very important diagnostic indicator is the chemical composition and size of the stone. The fact is that some stones are characterized by a soft, pliable structure. When they are dissolved and removed from the cavity of the bladder, problems usually do not arise. But when large and excessively large stones are crushed, sharp fragments are formed that can seriously damage and even disrupt the integrity of the bile ducts.
Cholesterol stones
This is the most common type of gallstones. Stones may be composed entirely of cholesterol or contain trace amounts of other organic and inorganic ingredients. This type of yellowish stone has a soft structure and fairly large size. They are easily dissolved and crushed, and when removed from the body, they practically do not cause traumatic damage.
Bilirubin stones
This type of stone is formed from bile bilirubin pigment and other insoluble breakdown products of hemoglobin. Bilirubin levels increase significantly if the patient is diagnosed with infectious and autoimmune diseases, chronic intoxication or hemolytic anemia. The enlargement of crystals is facilitated by taking certain pharmacological drugs, about which doctors inform the patient and take preventive measures. Bilirubin stones are not large in size, but rarely form in a single copy.
Lime stones
This is an extremely rare type of stone.
Unlike bilirubin and cholesterol stones, the inflammatory process in the gallbladder takes an important part in the formation of calcareous stones. Mineral calcium compounds begin to gradually be deposited near the epithelial cells, layered on small cholesterol crystals
Typically, calcareous stones have the consistency of clay and are colored in various shades of brown.
Advantages and disadvantages of DL
Remote lithotripsy consists of several procedures that are absolutely accessible and not accompanied by any difficulties.
In modern conditions, they can be carried out by a simple district clinic.
The issue of getting rid of stones in this way is not always resolved positively, due to existing contraindications or late consultation with a doctor for help.
In many cases, treatment is observed when the symptoms have become threatening, and more complex and invasive methods, or at least contact lithotripsy, are required to eliminate them.
To prefer remote treatment, several conditions are required:
- relatively early age of stones;
- their small size;
- absence of a significant amount;
- taking into account existing contraindications (and there are quite a few of them).
Selecting a suitable method without damaging the skin and staying in the hospital is possible only for patients who meet the requirements.
These are, quite often, middle-aged people who closely monitor their health and regularly undergo medical examinations.
For them, one of the existing methods is selected, which requires a preliminary determination of the nature of the stones present and their size.
They may be advised, depending on the subclinical picture, to use ultrasound or shock wave lithotripsy.
It is incorrect to compare the advantages of these methods; they are used for certain cases. There are indispensable features in the purpose of shock wave, and the type of impact is selected taking them into account.
Ultrasonic crushing is less effective and is used for soft stones no larger than 1 cm, and, like any therapeutic method, it has certain disadvantages.
Ultrasound treatment
The use of ultrasonic waves in crushing gallstones is considered less effective and more dangerous in terms of complications.
Waves have less impact force and are only suitable for soft (cholesterol) stones, no more than 10 mm.
An obstacle to the method can also be the patient’s excess weight, when the waves simply go out in the fatty tissue.
Ultrasound can cause burns of soft tissues, provoke inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder and bile ducts, and lead to hemorrhages in soft tissues.
An obstacle to the use of the method is usually chronic cholecystitis and liver diseases, especially those accompanied by inflammatory pathology of hepatocytes.
Before prescribing treatment with ultrasonic waves, as with contact intervention performed in the gallbladder with a laser, all existing contraindications for use must be carefully weighed.
ESW therapy
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy is the safest method for eliminating stones in the gallbladder that are the result of pathological content of bile acids, bilirubin, cholesterol, or a combination of calcifications and cholesterol particles.
To perform wave lithotripsy, three methods are used, each of which involves electrical or electromagnetic waves converted in a different way:
- piezoelectric, with ceramic plates (quite significant in cost precisely because of their use), designed for stones up to 10 mm;
- electromagnetic, where pulses are used, obtained using special coils (they are addressed with a biconvex lens), much stronger, allowing the crushing of 3 cm formations;
- Shock wave lithotripsy is stronger than the first two methods, because it involves water in a special container and electrical impulses (which is why the method is called electrohydraulic).
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy begins after preliminary diagnosis of the location of the stone at a specific point in time, using ultrasound.
At the same time, the entire biliary system and bile ducts are examined for the patency of the residues formed from the operation.
The extracorporeal shock wave procedure may take a long time or require repeated intervention.
It all depends on the composition and size of the stones. If the treatment lasts more than 90 minutes, the patient is usually given anesthesia.
Like any method of hardware treatment, lithotripsy of gallstones has its own indications and contraindications.
Laser fragmentation carried out using a directed beam may not achieve its intended purpose or cause complications.
Shock wave is contraindicated in chronic cholecystitis, pancreatitis, peptic ulcer disease and pathologies of the coagulation system.
In any form, surgery can be hindered by chronic inflammation of the liver, lost patency of the gallbladder ducts, pathologies of the urinary system, and even excess weight (obesity).
Therefore, there is no point in giving recommendations or advertising a specific method.
To remove stones, the one that most fully corresponds to the current condition of the patient, the presence or absence of chronic pathologies and the stage of the cholelithiasis disease at which the doctor was contacted for treatment is used.
Types of treatment for gallstone disease
If the stones are of a cholesterol nature and their size is small, then drugs based on urso- or chenodeoxycholic acid (Ursofalk, Henofalk) and some traditional medicine are prescribed to help dissolve the stones and then remove them naturally. However, such therapy is applicable only to cholesterol stones and takes a long time (sometimes several years). In addition, this treatment does not eliminate the cause of stone formation, and the risk of relapse is very high.
Single small stones are crushed using ultrasound. This technique is called shock wave lithotripsy. It only applies to small cholesterol gallstones.
The main indications for cholecystectomy for cholelithiasis are:
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | stones larger than 1 centimeter |
| 2 | the localization of these stones threatens to block the bile duct |
| 3 | Cholelithiasis is accompanied by acute cholecystitis |
| 4 | in the gall bladder, in addition to stones, there are polyps |
| 5 | other reasons that, even with an asymptomatic course of the pathology, threaten serious complications in the near future |
Surgery to remove the gallbladder
Treatment and removal of stones
Since the disease is often asymptomatic, it is not treated. The appearance of inflammatory processes and pain in the right hypochondrium entails more detailed studies, which often reveal stones. Stones can be dissolved with acids. This is often a temporary measure. Against the background of disrupted metabolic processes, stones form again. If there is only one stone and there is no inflammation, shock wave crushing (lithotripsy) is suggested. At the clinical stage of cholelithiasis, treatment is carried out surgically (abdominal surgery or laparoscopy). Diet is a good way to prevent stone formation. You can use herbs and folk remedies.
Diet and proper nutrition for gallstones
Diet in case of cholelithiasis is of fundamental importance. In this case, split meals are recommended, which include eating at least 5 times a day, which stimulates the outflow of produced bile and prevents its stagnation.
The food consumed must contain the amount of animal proteins, vegetable fats, and vital microelements (primarily magnesium) required by the body. The following products have a beneficial effect on the biliary system:
- Vegetables: carrots, cauliflower, pumpkin, zucchini.
- Lean meat and fish: beef, rabbit, veal, chicken, river fish.
- Dairy products with low fat content: milk, curd products, cheese, butter (as an additive to porridges).
- Cereals: buckwheat, oatmeal, rice, millet, semolina.
- Fruits and dried fruits: watermelon, apples, grapes, prunes.
- Juices, fruit drinks, compotes: quince, pomegranate, bird cherry, blueberry.
- Chicken eggs (if tolerated).
The diet should not include fatty foods and by-products (meat, fish), canned food, spicy, sour, salty, fried foods, baked goods, caffeine-containing and alcoholic drinks. If you have stones, you should strictly limit or exclude from your diet vegetables high in essential oils (turnips, garlic, radishes, onions, radishes) and oxalic acid (spinach, sorrel).
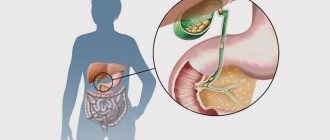
What kind of stones are there in the gall bladder?
Under the influence of various conditions, stones form in the biliary tract, most often in the gallbladder.
Their presence may not be accompanied by a pronounced inflammatory reaction on the part of the bladder wall or ducts, but it causes a number of painful manifestations - dyspeptic disorders, attacks of hepatic colic, and when the bile ducts are blocked - jaundice. If these disorders are caused only by the presence of stones, without inflammation of the bladder or ducts, it is customary to talk about cholelithiasis as such, distinguishing it from cholecystitis and cholangitis. Bladder stones may not cause any pain at all and may be asymptomatic. In such cases, the very definition of “disease” becomes questionable and it is more correct to talk about the presence of gallstones, rather than cholelithiasis. On the other hand, inflammation of the bladder or ducts, most often caused by a pyogenic infection, may not occur as a result of stones and occur without subsequent stone formation (so-called acalculous cholecystitis). Observations of cases of both orders forced us to distinguish between cholelithiasis and cholecystitis, separating them into various nosological headings.
How many stones can there be in the gall bladder?
Sometimes the bladder contains one large stone; more often, multiple stones are observed, numbering in the tens, and less often in the hundreds or even thousands. Diver described a case in which 2252 stones were found in the gall bladder; Rovsing observed 4600 stones, Mayo - 6000, and Otto - 7000. A case was described of the discovery of 10,275 stones in the gallbladder and ducts with a total weight of 58 g (Katamadze).
What are the sizes of gallstones?
The size of the stones is very diverse - from the size of a chicken egg to microscopic size (with a large number of such tiny stones, we no longer have to talk about stones, but about sand).
Usually, when there are a small number of stones, they reach large sizes and, conversely, when there are a huge number, the stones are small. However, there are cases when the bladder contains one or more very large stones and a large number of small ones; In this case, the stones have different compositions, different shapes and, apparently, belong to different periods of formation.
What shape are gallstones?
The shape of the stones is to a certain extent determined by their number, size and composition. Large single stones, as a rule, are round - spherical or ovoid, with a smooth or rough, sometimes spiky, surface. Multiple stones, when they reach a certain size, acquire a characteristic multifaceted (faceted) shape due to friction against each other and pressure in the tight container of the gallbladder.
What is the composition of gallstones?
The chemical composition of stones includes cholesterol (the most common and important basis of most stones), lime, and bile pigments. The predominance of one or another chemical component gives the stone specific characteristics, determines its consistency and strength, which is of practical importance in surgery: fragile pigment-calcareous stones easily crumble during surgery and their unremoved fragments, getting into the bile ducts, can cause a relapse. Stones consisting of bilirubin and calcium carbonate, when disintegrating, can acquire a putty-like character, which causes a lot of trouble when clearing the bile ducts from them.
The most common are cholesterol stones, in which the cholesterol content reaches 64-98%. They are easily recognized by their characteristic pearl color, sometimes acquiring a brownish tint from the presence of bile pigments, low specific gravity (they do not sink in water) and flammability (they are burned with almost no residue). Less common are pigment and calcareous stones; usually they are of a mixed nature.
Protein components, which originate from exfoliated cells of the bile ducts and participate in the formation of the structural basis of the calculus, also play a known role in the composition of stones. This basis acquires particular importance in case of inflammation of the biliary tract, being the center of formation of the resulting calculus.
The slow growth of gallstones with uneven crystallization processes and the participation of various chemical formations in it creates a heterogeneous structure of stones, often having a radial or layered structure, less often - a homogeneous one.
Stones form mainly in the bladder, but stone formation is also possible in the hepatic and common bile ducts. Stones in the hepatic ducts are found in 7% of all cases of cholelithiasis.
Folk remedies
There are a number of folk recipes for removing liver stones. But these drugs have a more preventive effect and prevent the progression of the disease. Most often, herbalists advise drinking vegetable juices (carrots, cucumbers, zucchini, tomatoes, celery), radish juice (50 ml three times a day), infusion of immortelle and birch leaves. There is also a technique for drinking ten glasses of warm tea for 15 minutes, which supposedly should “soften” the stones. However, therapy with folk remedies is ineffective, and the lack of timely medical assistance will only lead to progression of the disease.
Stones in the liver are a consequence of cholelithiasis of the biliary tract and liver.
Cholelithiasis is a disease of the biliary system, which is based on a violation of the exchange of bilirubin and cholesterol in the body. As a result, stones form in some part of the biliary system.
Stones are made up of bile components such as cholesterol, bilirubin and calcium. They are classified into cholesterol, pigment and mixed types. Cholesterol stones are formed due to the oversaturation of bile with cholesterol, from the precipitation of which similar stones are formed. Pigment stones contain a lot of bilirubin.
The shape may resemble a round ball, a polyhedron or an irregular oval. The sizes vary from the smallest (sand) to several centimeters. In terms of density, they can be fragile (crumble at the slightest pressure of the fingers, or soft - the consistency of putty or clay) to very hard, reminiscent of real stone. The surface of the stones varies from smooth, polished to rough, covered with spines. They grow for quite a long time: it takes at least six months to form a stone 1 cm in size.
The most typical location is the gallbladder (calculous cholecystitis), but cases of stones in the liver ducts (choledocholithiasis) cannot be excluded. During examination, from one single stone to many may be detected; the gallbladder may be completely clogged with stones. There are usually no large numbers of stones in the bile ducts, but this does not indicate a milder version of the disease, since a small stone can cause more significant harm to the body than a large one. Small pebbles are more mobile and can block the duct, causing a serious condition of the body and the urgency of surgical intervention.
Diet
If a person has a tendency to form stones in the bile ducts or the formations appeared but were removed, it is extremely important to adhere to a special diet. You need to eat often (6 times per day) in small portions
With such a diet, the release of bile through the duodenal papilla is constantly stimulated, the secretion does not stagnate. If the portion is too large, the motility of the gallbladder increases, which, in the presence of a calculus, can lead to inflammation.
The diet is supposed to be balanced, filled with nutrients, vitamins and microelements. It is recommended to consume low-fat varieties of meat and seafood, low-fat dairy products, cereals, especially oatmeal and buckwheat, plant foods (fruits, vegetables, herbs, dried fruits), compotes, juices, mineral waters. It is not recommended to consume fatty, fried, spicy foods, foods high in caffeine, smoked foods, canned foods, garlic, cucumbers, and beans.
Useful video
Increasingly, the world's population is faced with such a problem as cholelithiasis (GSD). If earlier this pathology was characteristic mainly of older people, now there is a noticeable rejuvenation of it.
Cholelithiasis can occur even in children. Before starting treatment, the specialist prescribes diagnostic measures.
They will help determine the types of gallstones, their structure, shape and other characteristics. Such knowledge will help you cope with the disease more effectively.
What are there
The classification of formations depends on their size:
- a small stone (no more than 11 mm) - does not cause discomfort in the patient, since it can easily leave the duct, enter the intestines and exit the body;
- a medium-sized stone (no more than 19 mm and no less than 11 mm) can lead to negative consequences, even worsening well-being. The patient experiences symptoms of cholelithiasis - a stone blocks the duct, and the outflow of bile becomes difficult;
- a large stone (more than 19 mm) may not cause discomfort and may not move through the gallbladder, but if it moves, the duct becomes completely blocked, which requires mandatory surgery.
Diagnostic methods
When conducting such a study, single or multiple stones formed there are clearly visible in the gallbladder. Ultrasound data allows you to estimate the size of the stones, determine their location, and also provide information about the general condition of this organ (for example, if its walls are thickened, this is a sure sign of developing cholecystitis).
These diagnostic methods include:
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | oral cholecystography (examination of the gallbladder using bile contrast agents) |
| 2 | retrograde cholangiopancreatography (examination by injecting a contrast agent into the bile ducts) |
| 3 | MRI and so on |
Abdominal ultrasound
Prevention of pathology
To prevent the formation of stones in the liver, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, avoid fatty and fried foods, and drink plenty of fluids. If there is a hereditary predisposition to the pathology, you should carefully monitor your health. It is recommended to periodically do blind probing - eating food or medications that promote the expansion of the bile ducts, the release of bile and small stones. But this type of prevention should be discussed with your doctor.
Contraindications to laparoscopic intervention
Laparoscopy is not performed on women in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. Surgical intervention is prohibited in the presence of diseases of the respiratory tract and cardiovascular system in the acute severe stage. Contraindications for laparoscopy are:
- the presence of abscesses in the organ;
- difficulties in determining the location of organs inside the abdominal cavity;
- abdominal operations previously performed in the abdominal cavity;
- the gallbladder is located inside the liver;
- state of acute stage of inflammation of the pancreas;
- jaundice formed due to a failure of the bile ducts;
- development of a cancerous tumor in the gallbladder or suspicion of cancer;
- gangrenous and porcelain cholecystitis in the acute stage;
- the presence of significant scars in the intestines, liver or neck of the gallbladder.
Surgical intervention is impossible if there are malfunctions in the blood clotting mechanism, the presence of fistulas in the biliary tract, or the presence of a pacemaker in the patient.
Useful video
Lithotripsy of gallstones is a collective term for different techniques for removing stones.
Previously, it meant certain interventions. With the development of non-invasive and minimally invasive methods, lithotripsy began to refer to all methods of crushing or otherwise destroying formations in the urinary and gall bladder without and with a scalpel.
Over time, methods and possibilities for providing assistance in the presence of stones in the genitourinary system and gall bladder began to prevail over traditional cholecystectomy.
The term lithotripsy began to mean any manipulation where stones were removed.
In modern medicine, these are several types of interventions carried out using different techniques and using destructive forces of variable origin.
The choice of method for removing stones is now made taking into account their composition, size, condition of the patient’s body and existing contraindications.
Methods for treating cholelithiasis
Gallstone disease is not uncommon, since any person can have a stone in the gall bladder. In some cases, if its size is less than 10 mm, then it is easily excreted from the body without any consequences.
If the stone is more than 10 mm, then clinical symptoms may occur, which are expressed as follows:
- aching or boring pain in the liver area, which radiates to the right shoulder or shoulder blade (in case of obstruction of the bile duct);
- nausea and vomiting of bile (in case of poor outflow of bile or complete closure of the duct);
- sweating, fever and general weakness;
- belching of bile or a bitter taste of food (caused by the fact that it enters the stomach).
The presence of such symptoms suggests that you urgently need to consult a doctor and undergo an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, which will show the size of the stone or stones in mm.
After which the doctor will prescribe the necessary treatment. Treatment for this disease is as follows:
- Medication.
- Operations.
- Ultrasonic crushing.
- Insertion of a special catheter.
- Special diet.
Surgeries to remove the gallbladder are very common.
Such operations are carried out when the stone is large and cannot be crushed. In this case, the entire gallbladder is removed. Such operations are prescribed as a last resort. Such operations do not cause much harm to the body, and after a few days the patient is discharged. Ultrasonic crushing of stones involves the impact of a special shock wave on them, and crushing them into small elements that are easily removed from the body naturally. But this method of treatment is contraindicated for those who have ulcers, poor blood clotting, respiratory tract diseases, or heart diseases.
The introduction of a special catheter involves a procedure in which a catheter is inserted into the gallbladder, through which a special liquid is infused, dissolving these solid formations. This method is not effective if they are large.
It is important to know that after removing existing stones, new ones will form. To prevent this from happening, you must strictly follow a diet that will prevent too much bile formation and stagnation.
Stones that form in the gall bladder are small, up to 10 mm, medium and large. In some cases, they are eliminated from the body on their own and do not cause clinical symptoms. But if a person begins to feel a sharp pain in the liver area, which appears periodically, then he needs to see a doctor.
The ailment of the body's biliary system lacks a single solution that will be the key to healing. According to many signs, the treatment of the biliary tract has fulcrum with determining the diagnosis and establishing the origin of the disease. The study of gallstones is of great help in this.
The size of the gallstones determines the nature of the treatment. Pain and discomfort can be caused not only by visible stones, but also by small grains of sand, which together form a suspension. Therefore, many people wonder which gallstones are considered large.
A gallstone does not just appear. In itself, its occurrence occurs gradually and indicates incorrect, disrupted functioning of not only the gallbladder, but also the liver. Cleansing the body of toxins and working as a natural filter in a complex human system is the task of the liver. It is also responsible for the production of bile, which is designed to process heavy foods.
If a harmful diet and passive lifestyle are not corrected in a positive direction, then the health situation does not change. This scenario is dangerous due to the appearance of several stones in the gall bladder or the growth of one stone into one large specimen, occupying the entire volume and reaching the diameter of a tennis ball.
Causes of stone growth
If bile for some reason does not leave the gallbladder for too long, then the substances contained in it begin to transform and partially disintegrate. Microscopic crystals and clots appear, which are gradually saturated with the salts present in the bile. This is how stone formation begins.
If there is no food in the intestines, then bile will not be released from the gallbladder. Therefore, too long breaks between meals create favorable conditions for the growth of stones. Fasting is another powerful trigger for stone formation. Unclaimed bile gets stuck in the gallbladder for a long time and intensively crystallizes.
Overeating, excess weight, and especially obesity also contribute to the accelerated growth of stones. Despite the fact that in this case a lot of bile is required, and in theory there is simply no time for it to linger in the bladder, the stones grow very quickly.
Ideal conditions for the formation of stones are created during sudden weight loss. If the rate of weight loss exceeds 3 kilograms per month (that’s 100 grams per day), then the risk of developing gallstone disease increases tenfold. If weight loss is carried out regularly, alternating with “belly festivals,” then cholelithiasis is almost inevitable.
Other factors that create a threat of increased stone formation are:
- hereditary structural features of the liver and gall bladder;
- inflammatory liver diseases;
- undergone extensive surgical operations;
- pregnancy;
- forced long-term immobility (for example, with fractures);
- sedentary lifestyle, physical inactivity;
- taking certain medications (for example, proton pump inhibitors used to treat peptic ulcers, chronic gastritis and pancreatitis, coronary heart disease);
- abuse of oral contraceptives;
- elderly and senile age;
- chronic constipation;
- lack of vitamin C.
It is interesting to note that Caucasians are significantly more susceptible to gallstones than other races. Low levels of melatonin in the body, which gives the skin a dark color, contributes to the formation of stones, since melatonin is a natural antioxidant that protects the gallbladder from oxidative stress.
Lack of clean water in the diet also provokes the formation of stones. An adult needs to drink about 2 liters of water per day. Precisely water, not juice, coffee, tea, beer or other drinks. But this rule is often violated, because if you drink the prescribed amount of water, then an extra cup of coffee or glass of beer simply “doesn’t fit.” Therefore, lovers of these drinks drink them with water, which exposes their liver to double the risk.
An excess of carbohydrates and sugar in the diet also makes stone formation almost inevitable.
The effect of alcohol on stones is controversial. Small consumption of quality wine reduces the risk of stone formation. And systematic indulgence in any alcoholic beverages, and especially their abuse, accelerates the growth of stones.
Dear readers, I invite you to share the story about the types of gallstones with your friends on social networks. For this we have a number of convenient buttons. With their help, a link can be placed in one click.
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks:
This blog is read and used by 6,939 adherents of a healthy lifestyle and uses its advice and recommendations, so their health is in order, their mood is good, and their work is going well. Read it too.
I agree to the newsletter and accept the privacy policy.
You may also be interested
PREVENTIVE EYE TREATMENT ACCORDING TO PEOPLE’S RECIPES…
TREATMENT WITH HERBS AND FOOD EYE DISEASES In the list of diseases...
8 Read more
How to remove flux - complex treatment
Good day, dear readers of Alexey Shevchenko’s blog “Healthy image...
14 Read more
Flu and traditional medicine
Flu and a healthy lifestyle Every time a cold season approaches...
12 Read more
REACTIVE ARTHRITIS IN ITS CAUSES AND EFFECTS
IMMUNE SYSTEM AND REACTIVE ARTHRITIS Reactive arthritis is triggered by infection, a disease, ...
39 Read more
Possible complications of gallstone disease
The lack of timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment of cholelithiasis can cause the development of various complications (including severe diseases and their transition to a chronic form):
- Phlegmon of the bladder wall.
- Cholecystitis.
- Pancreatitis (biliary form).
- Dropsy.
- Cholangitis.
- Empyema of the gallbladder and, as a consequence, its gangrene.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Oncological diseases of the biliary system.
- Bladder perforation.
- Formation of biliary fistulas.
- The emergence of Mirizzi syndrome.
- Rupture of the bladder walls with subsequent development of peritonitis.
- Toxic hepatitis.
In the event of the development of one or another complication, appropriate treatment is required, which is carried out in parallel with the treatment of cholelithiasis. In severe cases, in the absence of adequate therapy, death cannot be ruled out.
Symptoms of gallstone disease
In medical practice, there are cases where patients lived with stones in this organ all their lives, and they were discovered after the death of such people, which occurred for a completely different reason.
The main symptoms of cholelithiasis:
- hepatic colic. Occurs due to blockage of the bile duct by a stone. The external manifestation of this symptom is a sudden pain attack, which is often provoked by alcohol, fatty or fried foods, shaking in transport, and so on. The pain syndrome is localized in the right hypochondrium and can echo in the right arm, in the right shoulder blade or on the right side of the neck. You can stop such an attack by applying a warm heating pad to the right side of the abdomen. Usually such attacks last no more than six hours;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- bitterness in the mouth (appears when bile enters the stomach, which should not happen in the normal digestive process);
- bloating (flatulence);
- constant stool disorders in the form of alternating diarrhea and constipation;
- The acute course of the disease is characterized by a slight increase in temperature (usually no more than 37 degrees) no higher than 37°C, which serves as a signal that an infection has joined this disease, and most likely the patient develops chronic cholecystitis (in other words, the mucous membrane becomes inflamed this body).
Causes and symptoms
Such a conglomerate in the liver cavity cannot appear suddenly; usually its predecessors are an unbalanced diet or chronic diseases of the digestive system .
The reasons for the formation of stones in the liver ducts are as follows:
- Disorders of the metabolism of bilirubin and cholesterol structures.
- Congestion in the bile duct or liver.
- Common bile duct in the bile ducts.
- Inflammatory processes in the organs of the digestive system.
- Violation of general metabolism.
- Blockage of channels.
- Presence of anemia.
- Dysfunctions in the hormonal environment.
- Helminth infections in the digestive system.
- Damage by viral agents.
- Improper nutrition for cholecystitis of the gallbladder.
- Inflammatory or infectious processes in the liver (hepatitis).
- Abuse of ethanol-containing products.
- Long-term use of certain medications - hormonal, antibiotics, oral contraceptives.
What causes stones to form is related to clinical manifestations. There are also certain predisposing factors that provoke the formation of deposits:
- Improper diet, the presence of a large amount of animal fats in the menu. Fried food lovers are also at risk. To avoid the problem, it is recommended to adjust the diet and include vegetable fats in the daily menu instead of animal fats.
- Another important predisposing factor is dysfunction in the metabolism of hormonal substances. Usually these are disruptions in sex hormones or disorders in the thyroid gland.
- Sharp weight gain due to consumption of large amounts of animal fats and carbohydrate compounds.
- Viral, parasitic, bacterial diseases of the digestive system.
- Changes in the composition of bile, the predominance of any component in it.
- Inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system.
You can also add to the listed factors: long-term use of oral contraceptives, alcohol abuse, leading a sedentary lifestyle .
Stones in the liver cavity are a chronic disease; their formation occurs over a long period of time.
In the chronic course of the disease, symptoms in women and men may be as follows:
- The presence of constant aching pain. Most often they are located on the right under the rib. Appear after eating fatty foods.
- Other symptoms are discomfort, a feeling of fullness in the right side of the abdomen.
- The presence of constant nausea, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, increased gas formation.
- An increase in the diameter of the gallbladder, its increased sensitivity during examination.
- The skin and mucous membranes become slightly yellowish in color.
The listed symptoms can be one at a time or in combination.
The acute course of the disease is characterized by its own clinical picture:
- the occurrence of an attack of biliary colic, which is accompanied by sharp, spastic, intense pain on the right side, attacks of vomiting and yellowing of the epidermis,
- exacerbation of cholecystitis, which is accompanied by intense pain in the right iliac region, nausea, vomiting, hyperthermia, jaundice of the skin and mucous membranes.
The size of the stones also affects the intensity of symptoms and the duration of the attack. It must be remembered that if these symptoms appear, it is very important to consult a doctor as soon as possible and take treatment as prescribed by the treating specialist.
Methods of conservative therapy
Methods for dissolving and/or crushing stones depend on their size and composition. Currently, the following main methods are used for this purpose:
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | drug dissolution of stones |
| 2 | shock wave lithotripsy (crushing stones using ultrasound) |
| 3 | laser crushing of stones |
Let's take a closer look at these three methods.
Drug therapy
The duration of such treatment is very long (up to several years), so its use is not recommended in cases where there is a risk of complications of this pathology.
The process of drug therapy constantly requires monitoring using ultrasound. If the treatment has a positive effect and the size of the stones allows them to be painlessly removed from the body naturally, the doctor prescribes choleretic, anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic medications.
However, the use of stone-dissolving drugs, like any other therapy, has a number of contraindications, which include:
- pregnancy;
- the presence of inflammatory processes in the gallbladder;
- some types of liver pathologies;
- inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Crushing stones using ultrasound
Ultrasound of the gallbladder
The advantage of this method is that such shock waves do not damage the tissues and organs surrounding the bubble. Their impact is focused specifically on the stones themselves.
Contraindications to crushing stones using ultrasound are as follows:
- systemic pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- pathologies associated with blood clotting;
- pregnancy;
- inflammation of a chronic or acute nature (especially of the digestive system).
Another significant disadvantage of this method is the high probability of uncontrolled release of a stone fragment with sharp edges from the bladder cavity into its duct. In this case, damage to the internal surfaces of the bile ducts is possible.
The most dangerous complication after such a procedure is blockage of the bile duct, which, as a rule, is accompanied by severe pain and obstructive jaundice, and is most often treated only by surgery.
Laser crushing of stones
This technique is considered the most effective and modern. Its main advantage is the ability to crush stones on any basis, but their sizes are still limited (no more than two and a half centimeters).
At its core, such grinding of stones is a minimally invasive surgical intervention, since it involves an incision in the wall of the abdominal cavity to insert a special device into the gallbladder, with the help of which doctors can observe the progress of the process on an external monitor.
After introducing a device that visualizes the process, a catheter is inserted, through which the laser is delivered to the stone itself.
The use of this method allows you to ignore the composition of the stone, and to crush it to the required size you need a significantly smaller number of sessions than with shock wave lithotripsy. And the size of the crushed stones themselves is close to the size of grains of sand, which greatly simplifies their natural removal without damaging the walls of the bile ducts.
In conclusion, I would like to say that, alas, any of the listed methods is characterized by a high percentage of relapses (up to 30%), since they do not eliminate the root cause of stone formation. That is why the most effective method for curing cholelithiasis to this day remains removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy).
How to remove liver stones
During the period of exacerbation of cholelithiasis, drugs are prescribed that relieve pain and improve the quality characteristics of bile. For renal colic, analgesics (Metamizole), cholespasmolytics (No-Shpa, Papaverine) and cholinergic drugs (Atropine) are administered. Medical recommendations outside of exacerbation will depend on the stage of the disease. There are three stages of gallstone disease.
First stage
Physico-chemical. Liver secretions contain too much cholesterol and few bile acids and phospholipids. There are no clinical manifestations of the disease, and the diagnosis is made based on the results of an analysis of duodenal contents. The first stage can develop over several years.
Therapeutic measures consist of understanding the causes of bile lithogenicity, systematic physical activity, fractional balanced nutrition, normalization of gastrointestinal functions, elimination of stagnation of hepatic bile are prescribed, and, if necessary, drug therapy is indicated.
After completing the medication course, stones may form again in the gland
Second stage
It is asymptomatic, but the process of stone formation has already begun. The transition of the disease to the second stage may be due to stagnation of bile, damage to the mucous membrane, inflammation, increased permeability of the bladder to bile acids, and disruption of the intestinal-hepatic movement of bile acids.
The diagnosis is made based on the results of ultrasound and cholecystography. Predisposing factors are also taken into account, such as female gender, age over 40 years, hemolytic anemia, increased weight, diabetes mellitus, pregnancy, long-term course of medications (nicotinic acid or clofibrate). Stones containing calcium are visible even on a plain X-ray.
During the latent stage, patients are advised to adhere to a balanced diet, give preference to vegetarian and fiber-rich foods, move more, and avoid weight gain. Drugs that can dissolve stones are also prescribed.
Types of gallstones
Stones that form in the biliary system are divided into primary and secondary. The first type is formed in the bladder cavity over a long period of time due to changes in the structural composition of bile. The disease in this case does not show obvious symptoms.
Secondary stones occur when there is a violation of the outflow of bile: with cholestasis, biliary hypertension, as a result of blockage of the ducts by previously formed primary stones. They can be localized in the bladder and ducts. In addition, stones are classified into the following types:
- Calcareous. Appear during inflammatory phenomena affecting the walls of the gallbladder. The core of this type of stones is cholesterol crystals, pathogenic bacteria or scales of desquamated epithelium.
- Cholesterol. They are represented by rounded homogeneous structures reaching 1.8 cm in diameter. They arise as a result of metabolic disorders and are found in the bladder cavity of obese people.
- Bilirubin, or pigment. Like the previous species, they are non-infectious in nature. They are formed as a result of changes in blood proteins or in the presence of congenital pathologies that accelerate the destruction of red blood cells. These stones are localized in the cavity of the bladder, ducts and are characterized by small sizes.
- Concretions of mixed composition. They are formed on the basis of pigment or cholesterol stones due to the layering of calcifications on the main core. These processes occur against the background of the development of inflammatory phenomena.
The size of the stones can vary over a wide range - from 2 - 3 mm to 4 - 5 cm, consistency - from waxy to hard, configuration - from spherical to irregular shapes. The weight of one stone is from 0.5 g to 80 g.
Share the article on social media. networks: