The gallbladder is a small but very important element of the digestive system; it stores bile, which is produced by the liver. There are many pathologies in which the functions of the organ are disrupted, which can cause the formation of stones and the development of serious gastrointestinal diseases. Therefore, it is necessary to know which doctor treats the gallbladder, and in what cases should you contact him?
Related articles:
Treatment of gallstones with folk remedies Laparoscopy of the gallbladder: indications and contraindications Stages of gallbladder cancer - first symptoms and treatment Symptoms of gallbladder bending: treatment Symptoms and signs of gallbladder deformation in adults and children
Instructions
The name "hepatologist" comes from the Latin hepar, which means "liver".
The work of a hepatologist includes the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases of the liver and biliary system. There are also pediatric hepatologists who focus on the structural features and development of the gallbladder and liver at an early age. Most often, people with hepatitis turn to a hepatologist. Hepatitis is an inflammatory disease of the liver caused by infection, prolonged alcohol intoxication or medication, food or chemical poisoning, or parasite infestation. The main signs of hepatitis are yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyes, light-colored stools and darkening of the urine.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qg_PnjdMJ0o
However, many liver diseases have symptoms similar to hepatitis. It is the hepatologist, based on knowledge in the field of toxicology, anatomy of internal organs, pharmacology and physiology, who is able to differentiate diseases characterized by itching, sleep disturbances and fatigue from each other.
Other diseases for which patients turn to a hepatologist include: liver cirrhosis, toxoplasmosis, Legionnaires' disease, gallstones, enteroviral hepatitis, hemochromatosis, Gilbert's syndrome, leptospirosis, astheno-vegetative disorder and others.
If during the diagnosis of the disease malignant tumors of the liver and biliary system are discovered, the hepatologist redirects the patient for treatment to an oncologist. Diseases in which a general disorder of the digestive system is diagnosed are grounds for redirecting the patient to a gastroenterologist.
During the initial diagnosis, you will be asked by a hepatologist to take a general blood and urine test and a biochemical blood test. Ultrasound and radiological examinations of the liver and gallbladder are also possible.
Subsequent types of diagnostics, depending on the symptoms of the disease, may also include: stool test for stercobilin - blood test to determine the level of red blood cells and reticulocytes - computed tomography of the liver, magnetic resonance imaging of the liver and gallbladder - blood tests for the presence of herpes, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus - liver biopsy - electroencephalography. And if there is a suspicion of group E viral hepatitis, the patient’s urine and blood are examined for the level of hemoglobin in their composition.
Detection of parasitic diseases
The most common diseases of the biliary system are giardiasis and fluke infection. To clarify the diagnosis, an ultrasound examination is performed to identify parasites. In addition, it is important to conduct a blood test for the presence of antibodies to Giardia, opisthorchid and other flukes. Analysis of feces to identify Giardia and parasite eggs.
If necessary, the bile is examined for the presence of parasites; a duodenal tube or endoscope is used during the examination.
Based on all of the above, diagnosing gastrointestinal tract is a prerequisite for identifying the current state of the organ. Only after a thorough examination will the doctor be able to determine treatment tactics and the necessary preventive measures.
Major diseases of the gallbladder
The first period of disease development is called preclinical. At this time, a favorable background for the formation of stones develops.
The second period is clinical, it consists of three stages. At the first stage, the physical and chemical properties of bile are disrupted. The second stage is characterized by the formation of gallstones. The third stage of the clinical period is surgical.
The first two stages in the development of cholelithiasis are considered a therapeutic problem. Which doctor treats gallstone disease at this stage depends on the clinical manifestations and concomitant diseases. If the patient has few complaints, observation by a family doctor is sufficient; otherwise, the patient should be regularly examined by a gastroenterologist.
In the surgical stage, typical clinical manifestations of cholelithiasis are noticeable. Their nature is determined by the localization, size of the stones, the presence of associations with infection, and the possible spread of the consequences of the pathology to other organs. And, according to the name of this stage, gallstones are treated by a surgeon.
Diseases of the digestive organs are very closely related to each other, and dysfunction of one of them can provoke a pathological process in the other. The gallbladder and pancreas play a very important role in the process of digesting food. Enzymes secreted by the pancreas, together with bile, are responsible for the digestion process in the upper gastrointestinal tract. With the help of bile, normal breakdown of fats occurs and intestinal motor function is maintained.
Due to errors in diet or the presence of a hereditary predisposition, the following pathologies of the liver and gallbladder can develop:
- Biliary dyskinesia: this condition is characterized by a violation of the normal tone of the gallbladder and its ducts. The disease can occur in a hypokinetic or hyperkinetic type. The main symptoms are periodic pain in the right hypochondrium and discomfort after eating fatty foods. Doctors consider this pathological condition predisposing to the development of other gallbladder diseases;
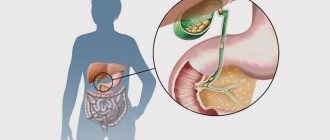
- Gallstone disease: characterized by the formation in the gallbladder or its ducts of stones consisting of bile, bilirubin and other trace elements. If this disease is suspected, the doctor must examine the gallbladder using ultrasound. One of the signs of cholelithiasis is obstructive jaundice. It occurs due to blockage of the bile duct by stones and manifests itself in the form of yellowing of the skin, visible mucous membranes and sclera;
- Inflammatory processes in the gallbladder: cholecystitis can occur in acute or chronic form. The main signs of this pathological condition are pain under the right costal arch, repeated vomiting, and the appearance of bitterness in the oral cavity. Most often, the disease occurs against the background of cholelithiasis due to a violation of the outflow of bile from the gallbladder;
If one of the above symptoms appears, you should contact a gastroenterologist. You can also consult a hepatologist. This doctor specializes in gall bladder and liver diseases.
Pathologies of the gallbladder are quite difficult to determine in the early stages. Symptoms of gallbladder pain usually begin to manifest themselves already in the advanced stage, when the disease becomes acute. But even in this case, the clinical picture of the pathological process may not differ from the symptoms of ailment that a person mistakes for a common disorder.
The main symptoms that may indicate problems with the gallbladder are:
- Painful sensations in the right side, in the area of the liver or under the ribs.
- The appearance of a bitter taste in the mouth in the morning.
- Belching sour.
- Increased body temperature.
- Defecation disorder.
- The occurrence of unpleasant sensations after eating.
- Change in skin color.
- Nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief usually occurs with cholecystitis, gallbladder and liver disease of an inflammatory or infectious nature.
In addition, pathologies such as cholelithiasis can manifest themselves as acute, sharp pain in the right hypochondrium, especially during the period when the stone begins to move along the ducts or blocks the outflow of bile. If problems occur in the functioning of organs, it is necessary to urgently go to the hospital, where a decision will be made to prescribe additional methods of examination and therapy.
Symptoms of acute cholecystitis
Symptoms usually depend on the form of the disease.
Important! More information about the symptoms and treatment of cholecystitis in adults can be found here.
In acute form:
- Sharp pain that occurs immediately after eating.
- Sudden nausea.
- There is a bitter taste in the mouth.
- Vomiting (may occur repeatedly).
- Increased body temperature (up to 39 ͦ).
- Diarrhea (may occur once).
Know: if you have discovered at least one symptom of cholecystitis, then the question of which doctor treats this disease should not arise in your mind. Contact a gastroenterologist immediately. If it is not possible to see a gastroenterologist in your area, go to a physician or surgeon.
In the chronic form of the disease:
- regular pain in the right hypochondrium, becoming aching;
- constant feeling of weakness;
- occasional nausea;
- bloating;
- in rare cases, loose stools occur;
- feeling of dryness and bitterness in the mouth.
Important: all of the above symptoms especially manifest themselves after eating fried or fatty foods. This factor is a kind of provocateur of pain. If you consciously ignore the symptoms that have arisen, this can lead to serious consequences, in particular, to the transition to an acute crisis form.
Manifestations of acute cholecystitis usually begin with an unexpected sharp pain in the upper abdomen, which can spread to the right shoulder area.
You may experience similar pain with biliary colic, but it usually goes away within a few hours. The pain in acute cholecystitis is long-lasting. Typically, the painful part of the abdomen becomes tense, and deep breathing increases the pain.
In approximately every fourth case of acute cholecystitis, the gallbladder will swell so much that you can feel a bulge in your abdomen. This occurs approximately a day after the onset of pain.
Other symptoms of acute cholecystitis include:
- increased body temperature (fever), usually moderate and not exceeding 38°C;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- loss of appetite;
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice).
If acute cholecystitis is not treated, the risk of complications increases.
note
Many people who are faced with gallbladder or liver dysfunction are wondering what the specialization of a doctor who deals with such problems is. The gallbladder and liver are the most important organs on which the functioning of the digestive system and the entire biliary tract largely depends.
If diseases of these organs occur and there is no timely, competent treatment, there is a high probability that further treatment will not be successful without surgical intervention. If the gallbladder or liver disease progresses to a chronic stage, the possibility of the patient’s death cannot be ruled out, since dysfunction of any of these organs will provoke complications for the entire body, and the consequences may be irreversible.
Treatment of gallbladder and liver pathologies should be supervised by an experienced professional who specializes in these problems. When examining a patient and making a diagnosis, the doctor must take into account many factors, including the patient’s age, his lifestyle and the presence of congenital pathologies.
If gallstones or cirrhosis are treated by a general specialist, the risk of misdiagnosis will be more than 70%. When a patient is prescribed inappropriate medications that have a choleretic effect, neoplasms and stones in the gall bladder may begin to move and clog the ducts. In case of such complications, surgery will be required to save the patient's life.
A specialist who treats pathologies of the gallbladder and liver must take into account many factors, for example, the patient’s lifestyle, congenital disorders, and age. Treating the disease yourself is a waste of time and aggravates the condition. For example, some drugs have a choleretic effect, so gallstones can begin to move and clog the ducts.
In this way, cholelithiasis can be converted into surgical intervention. First, you should contact a general doctor, who will prescribe examinations, tests and determine which doctor will handle further treatment. Let's consider who to contact and in what order to treat hepatobiliary diseases.
For timely detection and treatment of liver and gallbladder diseases, you must contact a hepatologist if the following symptoms occur: bleeding gums, abdominal pain, deterioration in concentration, drowsiness and fatigue, light-colored stool, dark urine, yellow skin and sclera of the eyes, joint pain, nausea, blurred vision, increased temperature and increased abdominal volume.
Attention, TODAY only!
Imagine: you had an ultrasound and, quite unexpectedly, you were diagnosed with gallstones. This situation is close and understandable to many of my readers.
Of course, there is little pleasant in such a find. Therefore, a person first experiences a slight (or not slight) shock, and then, having come to his senses, looks for a way out of the current situation. What could be the solution? Of course, you need to see a doctor. Preferably to someone who is knowledgeable and conscientious.
I can’t recommend a doctor to everyone, but I can tell you which doctor treats gallbladder and cholelithiasis.
Oncological liver lesions | Cancer
It is no secret that in recent decades, cancer has literally taken over humanity. And liver cancer is, according to medical statistics, in 5th place in terms of prevalence. Moreover, primary cancer cells developing directly in the liver are rare; more often, they are metastatic cancer that has taken root in the intestines, lungs or pancreas. Cirrhosis, cholelithiasis, alcohol abuse and toxic hepatitis against this background, as well as, oddly enough, sexually transmitted infections significantly increases the risk of developing cancer.
When fighting cancer, oncologists come to the rescue. In addition to diagnosing and diagnosing, they carry out a complete treatment algorithm. The first signs of liver cancer practically do not appear; most often, symptoms of the disease appear when the tumor has spread beyond the borders of the liver or has metastasized. However, it is customary to highlight the following symptoms of general significance, which, as a rule, patients do not pay too much attention to:
- constant fatigue;
- long-term lack of appetite;
- weight loss;
- slight increases in body temperature;
- nausea;
- itching of the skin and rashes on it.
At the same time, pain and significant discomfort appear only when treatment has a much lower chance of success than in the first stages. Therefore, it is necessary to contact an oncologist not only when specific symptoms appear, but also for preventive purposes. And the earlier a harmful process is detected, the greater the chance of a favorable treatment outcome.
( 1 ratings, average: 1.00 out of 5)
Diagnostics and tests
To identify the causes of the disease, the specialist needs to collect anamnesis, find out the main complaints and what preceded the onset of symptoms.
For gallbladder diseases, a biochemical blood test is prescribed
- biochemical blood test - the analysis can detect an increase in bilirubin and cholesterol in the patient’s blood;
- clinical blood test - diseases of the gallbladder are characterized by the presence of pathology and signs of inflammatory processes - leukocytosis, increased ESR;
- stool analysis - to accurately formulate a diagnosis and confirm one or another ongoing process in the body;
- urinalysis - in this case, bile pigments are often detected, indicating the development of a pathological process;
- liver tests - allow you to do a biochemical blood test to assess the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- coprogram - examination for the presence of undigested fat deposits in the stool.
These laboratory tests make it clear in which department the pathological process is taking place, and instrumental methods are prescribed to confirm the diagnosis, such as:
- Ultrasound of the peritoneal organs is a method that allows you to examine the state of functioning of tissues and organs using an ultrasound system. This method is the most effective because it allows you to detect dysfunctions of organs and accurately determine the localization of the inflammatory process.
- Cholegraphy is an X-ray examination of the gallbladder.
- Tomography and MRI of the abdominal cavity are quite rare, but very productive diagnostic measures prescribed for a full study of the gallbladder.
After carrying out these activities, the specialist determines the method and method of therapy based on the diagnosis.
Diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
Laboratory diagnostic methods are carried out to assess blood counts, as well as determine the condition of the liver and pancreas. For this purpose, clinical and biochemical blood tests, a general urine test and a stool test are performed.
In some cases, it is possible to conduct bacteriological and biochemical studies of bile. For this purpose, duodenal intubation is used.
Remember: cholecystitis most often affects people with gallstones or those who are obese.
Instrumental methods consist of:
- Ultrasound (detects an increase in the size of the gallbladder, wrinkling of the organ, thickening of the walls of the bladder, etc.);
- cholecystography (detects pathologies in the upper parts of the digestive tract);
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy (determines the presence of stones in the gall bladder).
- laparoscopic diagnostics (used to identify an objective picture of the patient’s condition).
To diagnose acute cholecystitis, your doctor will examine your abdomen. If acute cholecystitis is suspected, you will be admitted to hospital for further examination.
Your doctor will likely do a simple test for what's known as Murphy's sign: He will place his hand firmly against your chest and ask you to take a deep breath. When you inhale, the gallbladder descends. If you have cholecystitis, you will wince from a sharp pain when your gallbladder comes into contact with the doctor's hand.
Your doctor will also give you a blood test to see if your white blood cell count is higher than normal. An increased level of white blood cells usually indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
If both of the tests described indicate a disease, you will likely be referred for an ultrasound. This is a test that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of your internal organs.
Additional studies may be required only when a definitive conclusion cannot be made based on ultrasound or when there is a suspicion that complications have occurred (for example, rupture of the gallbladder).
Additional studies that may be required include:
- an abdominal x-ray (abdominal x-ray) or computed tomography scan, which uses x-rays and a computer to produce a detailed picture of what's happening inside your body
- magnetic resonance imaging, which produces images of organs inside the body using strong magnetic fields and radio waves;
- magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), which is performed when it is suspected that a gallstone has passed out of the gallbladder and blocked the bile duct.
Whether you like it or not, cholelithiasis is still the province of surgeons
Why? Because only surgeons can really and forever rid a person of gallstone disease. Using surgery to remove the gallbladder along with the stones. Doctors call this operation a beautiful and mysterious word: cholecystectomy.
Gastroenterologists in Moscow
Gastroenterologists of the Moscow region
Detailed information about each doctor, photo, rating, reviews, quick and convenient appointment.
Anyone who has gallstones has had attacks of acute calculous cholecystitis. For these patients, the only way to relieve themselves from excruciating pain and dangerous complications is surgery.
Therefore, every person who has stones in their gallbladder should see a surgeon to determine whether they need surgery and how urgently it needs to be done.
Or do concomitant serious illnesses prevent it from being done? What if there are no stones in the gallbladder yet, but only thick, stagnant bile? Who treats such a gallbladder? Which doctor should I contact?
In such cases, a gastroenterologist is needed. A doctor who treats the digestive system of the human body. In one of my articles I already talked about this specialty of a doctor. Now I offer you a link to this article if you have not read it yet.
In conclusion, I would like to say one more thing: unfortunately, not every hospital and not every locality has a gastroenterologist.
In such cases, a gastroenterologist is needed. A doctor who treats the digestive system of the human body. In one of my articles I already talked about this specialty of a doctor. Now I offer you a link to this article if you have not read it yet.
Therapist's help
A therapist is a “universal doctor” who determines the degree of the disease and, based on this, gives a referral for consultation with other doctors
First of all, when symptoms of a pathological process are detected, people turn to a therapist for help. This is a “universal doctor” who determines the degree of the disease and, based on this, gives a referral for consultation with other doctors of a narrower specialty. He will help you figure out what other doctors the patient needs - a surgeon, an infectious disease specialist or a gastroenterologist.
Also, the therapist is the main physician who will monitor the patient’s condition in the case of a chronic pathology or in the absence of obvious clinical signs (the so-called stage of active surveillance of the disease).
The therapist’s assistance consists of timely diagnosis and monitoring of the patient’s condition. In addition, the therapist himself has the right to prescribe therapeutic methods of treatment, in the absence of doctors of narrow specialties, or in the case of an uncomplicated process.
But not everyone with stones needs surgery
If the stones lie quietly in the gallbladder without causing attacks of pain, surgery may not be necessary. After all, the stones themselves are not dangerous and do not interfere with the normal functioning of the body. A dangerous situation occurs when a stone becomes wedged into a narrow bile duct. Many articles have been published about this on my website. Today I want to talk about something else. About doctors who treat the gallbladder.
So, if there are stones in the gall bladder, you need to consult a surgeon. A doctor in this particular specialty must determine whether there are indications for surgery to remove the gallbladder. And if there are such indications, then the operation must be performed.
So, if there are stones in the gall bladder, you need to consult a surgeon. A doctor in this particular specialty must determine whether there are indications for surgery to remove the gallbladder. And if there are such indications, then the operation must be performed.
Treatment by a gastroenterologist
This specialist knows everything about the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and its relationship with other organs. Therefore, after a complete diagnosis, he will be able to say what pathology the patient is faced with. Here's what it could be:
- pancreatitis;
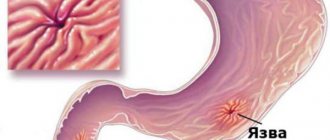
- stomach ulcer;
- gastritis;
- gallstone, cholecystitis.
Such deviations can be caused by banal dysbiosis. In some cases, studies reveal that the patient has problems with the liver, and since this organ is associated not only with digestion, but also with cleansing the body of toxins, synthesizing proteins and hormones, another specialist, a hepatologist, deals with its problems.
A gastroenterologist is a specialist with a narrower profile than a therapist who treats diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including the gastrointestinal tract. Gallbladder diseases are specific to the work of this doctor, in the presence of a chronic course of the pathology, or an uncomplicated course of the disease.
A gastroenterologist can deal with conservative treatment of cholelithiasis and the consequences of the disease either independently or with the help of broader specialists, and in case of complications, the gastroenterologist has the right to transfer the patient to a surgical specialist or infectious disease specialist, issuing a referral and indicating to the person which doctor to see and where to go .
Visit to a hepatologist
A hepatologist is a specialist who deals only with the pathology of the liver and gallbladder.
If a therapist discovers or suspects a person has liver problems, he can give him a referral for examination by a hepatologist who deals with these ailments. A hepatologist is a specialist who deals only with the pathology of the liver and gallbladder. He also performs diagnostics if there is a suspicion of pathology of the bile-forming and bile-excreting organs.
The hepatologist has the right to carry out preventive measures to prevent recurrence of the disease. Most often, patients come to this doctor with complaints such as yellowing of the skin, changes in stool, pain in the liver. A hepatologist can help solve such human problems as hepatitis, stones in the biliary tract, cirrhosis, inflammation in the gallbladder and many other pathologies.
Summing up, we can come to the conclusion that today there are quite a large number of doctors who help prevent and detect in time, and most importantly, cure gallbladder diseases, based on the cause of the disease.
This attending physician will examine the liver and gallbladder in detail using hardware and laboratory techniques, and if abnormalities are detected, he will tell you which treatment method will be optimal. What medications you will be prescribed to take, and whether you will need to follow a diet, depends on the disease itself. Here are the most likely ones:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- hepatitis;
- infectious diseases;
- cholelithiasis;
- inflammatory diseases;
- helminthic infestations.
Cirrhosis of the liver
All these pathologies require not only urgent, but also competent treatment, otherwise they can become chronic or provoke complications, especially for gallstones. The danger is that they increase in size every day and, for example, with a diameter of 3 mm, you can get rid of them by taking modern medications and herbal decoctions; if they reach large sizes, then the likelihood of such an easy elimination of the disease decreases several times .
Nutrition for cholelithiasis
After stone removal, a diet is usually needed, since after surgery stones can appear in the bile ducts, and special nutrition is designed to prevent recurrence of the disease. Apply diet (table) No. 5. The essence of the diet is to limit fat in food and eat frequent, but small portions, which promotes uniform separation of bile, better absorption of nutrients, and good intestinal function. It is especially good to train yourself to eat at a strictly defined time. To reduce the load on the gallbladder, it is better to chop food. It is recommended to boil, bake (but without crust) or steam the products. To prevent bile from thickening, you need to drink enough fluid - at least two liters a day - and limit your salt intake. But you need to give up alcohol completely, as it causes spasms of the bile ducts.
Despite some general principles, therapeutic diets for gallbladder disease are prescribed individually, based on the characteristics of the body, nervous system, and metabolic processes. Sometimes such diets include recommendations for losing excess weight.
In any case, more effective than any diet, taking care of yourself will help you avoid illness. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, preventive examinations with doctors and fighting stress - such simple actions significantly increase the chances of preventing gallstone disease and living in peace.
What to do then?
You need to contact your local doctor. A local physician can also help in treating the gallbladder. If the situation is complex, and the knowledge or capabilities of the local doctor are not enough, you can always get a consultation with a gastroenterologist in the regional center. For this, you also need the help of a local therapist, who will prescribe the necessary tests and give a referral for consultation.
Previous article – Diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract, symptoms
Next article –
TO THE TOP OF THE ARTICLE
Consultation with a therapist is the first stage of diagnosis
It is logical to start your initial visit to the hospital with a therapist. This specialist has sufficient knowledge and skills to suspect liver damage and make a preliminary diagnosis. He has available laboratory and instrumental research methods at his disposal.
Liver diseases can be an accidental discovery precisely after these examinations. This is explained by the absence of specific complaints in the initial stages of the pathology; during this period the organ does not hurt due to its structural features.
Correct interpretation of the results obtained will allow us to determine further tactics for patient management. If the process does not threaten the patient’s life, does not involve other organs and systems, and does not require further examination or hospital treatment, then the doctor himself can prescribe rational therapy.
Other specialists
If you experience nettle fever, itching and redness on the skin, you should consult a dermatologist. This specialist will conduct diagnostics, identify functional liver failure and refer the patient to a doctor with a more specialized profile. It is important to properly prepare for diagnosis in order to obtain reliable results. Only in this case will it be possible to detect the disease at an early stage and cure it.
Dermatologist helps identify skin manifestations of liver disease
According to doctors, the liver has regenerative properties, thanks to which it is able to repair itself. But with regular poisoning of the body, iron is deprived of this ability. In this case, you should visit a surgeon who will perform a partial or complete liver transplant. It is this doctor who treats severe cases of organ damage.
Thus, if characteristic symptoms of liver disease regularly appear (yellowness of the sclera and skin, discomfort in the right side, change in the color of stool), it is necessary to visit a therapist. The doctor will conduct a thorough examination, determine the causes of the disorders, and make a diagnosis. If necessary, the doctor will refer the patient to a specialized specialist.
Who deals with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract?
A gastroenterologist deals with combined pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. Patients whose condition requires clarification are also referred to him. Often patients cannot determine which organ in the abdominal cavity hurts. Thanks to a complex of in-depth laboratory and instrumental diagnostic techniques, the localization and nature of the pathology are significantly clarified. Consultation with this doctor is necessary in case of digestive dysfunction.
Pathogenetically based therapy will help improve the patient’s condition, normalize the functional activity of damaged organs and slow down further progression of the disease.
Surgeon and oncologist
If the functions of the “filtering” organ are impaired due to tissue replacement and the development of irreversible processes in it, the help of a surgeon is required. It eliminates cysts and benign formations, restoring the functionality of the liver. The help of a surgeon is necessary for partial or complete organ replacement.
In the event of the development of malignant tumors, the oncologist provides first aid in treatment. He studies the condition of the organ, performs a biopsy and determines the type of tumor. Based on the data obtained, a treatment regimen is prescribed, including chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery.
Important: if abnormalities in the functioning of the liver appear, it is advisable to contact a therapist, who, based on the patient’s complaints, will send him to a highly specialized specialist. It is not recommended to delay visiting a doctor; in 90% of cases this is dangerous to human life and health.
Which specialist treats severe liver pathology?
If the disease is isolated, then such a patient will be treated by a hepatologist - a doctor who specializes in the problems of this organ. Due to the functional connection of the liver and gallbladder, their pathology is considered together.
The list of diseases for which people turn to a hepatologist is very extensive. These can be: hepatitis of various etiologies (viral, toxic, autoimmune), cirrhosis, cholecystitis, congenital pathology of the liver and gallbladder, neoplasms in these organs.
For this purpose, specialized hepatology centers have been organized. There, patients can undergo specialized laboratory and instrumental examinations to make a final diagnosis. Indeed, depending on the severity of the lesion (hepatosis, hepatitis, cirrhosis), adequate therapy is prescribed.
Complications of cirrhosis include bleeding from dilated veins of the esophagus. If such a condition develops, urgent hospitalization in a surgical hospital is necessary. There, specialists carry out a complex of hemostatic measures, starting with infusion therapy and ending with the installation of a special probe that mechanically compresses the damaged vessels.
Surgeons deal with another complication of liver disease – ascites. Excess fluid is usually removed with diuretics. If ascites does not respond to drug treatment, then paracentesis is performed: using a special tube inserted into the abdominal cavity, excess exudative fluid is pumped out.
Viral hepatitis: who to get advice from?
There are currently 6 types of viral hepatitis known. Some of them have a good prognosis (A and E). The rest (B, C, D, G) often lead to chronicity of the process and the development of complications - cirrhosis, carcinoma.
Symptoms of the disease are similar for all types of hepatitis and do not depend on its name. The patient has pain in the right hypochondrium, jaundice appears, a rash on the skin, the color of urine and feces changes. If these signs appear, you need to contact an infectious disease specialist.
Treatment of such hepatitis is carried out in a hospital. An infectious disease specialist prescribes antiviral therapy that acts on the cause of the disease. In this case, it is necessary to monitor the functional state of the liver. Very often, an active inflammatory process leads to liver failure.