Free consultation on treatment in Moscow. Call or fill out the form below:
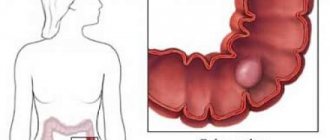
Cecal cancer is a malignant neoplasm of the large intestine located in a designated area. In oncology of the gastrointestinal tract, it is the second on the list of diseases that cause death, after tumors of the sigmoid colon.
According to epidemiology, the main risk group for cecal cancer is elderly people, with the average age of patients being 47.6 years. However, this does not mean that the disease cannot be detected in adolescents - both boys and girls. People with genetic pathologies that are inherited and are capable of triggering the oncological process have a predisposition.
Cancer occurs more often in men than in women. It is provoked by gene mutations, inflammation and trauma to mucosal cells. The incidence in Russia is 1.2–2.7%. The life expectancy of a person with cancer of the cecum is rapidly decreasing, and its consequences can lead to death - this is the urgency of the problem. The incidence of colorectal cancer is increasing, and over the past half century the incidence has increased 7–9 times.
These etiologies indicate an increased risk of cecal cancer in residents of megacities, which may be associated with both quality of life and the level of medicine, detection and treatment.
If you or your loved ones need medical assistance, contact us. The site’s specialists will recommend a clinic where you can get effective treatment:
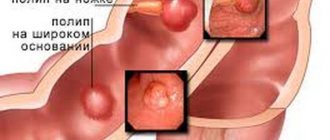
Types of cecal cancer
The TNM classification of cecal cancer makes it possible to determine the stage, but in addition to it, other methods are used to systematize the types of neoplasm. The forms of cancer depend on the location of the main focus—both primary and secondary cancer occur. Moreover, the metastatic variant often occurs with damage to the female genital tract, liver, gallbladder and ducts, and pancreas. According to the cytological picture, the following types are distinguished :
- • adenocarcinoma;
- • signet ring cell;
- • squamous;
- • poorly differentiated;
- • glandular-squamous.
According to the type of growth, they are distinguished:
- • exophytic;
- • endophytic;
- • mixed.
Cecal cancer, symptoms and signs with photos
It is difficult to detect tumor precursors or primary signs in the early stages, since it is often asymptomatic. There are also no characteristic external, visible changes on the body: there are no visible spots, lumps, lumps or other obvious manifestations on the skin and mucous membranes. Cecal cancer rarely progresses quickly—about 10 months pass from the onset of the disease to the appearance of the first symptoms. Often the patient’s very initial complaints are perceived as manifestations of similar diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. For example, when bloody discharge appears during bowel movements, people begin to treat hemorrhoids with home remedies, and if there is pain in the right side of the abdomen, this is perceived as an attack of appendicitis, colitis. Without serious complaints (severe pain or burning), a person is in no hurry to visit a doctor and self-medicates, which delays diagnosis.
Symptoms of cecal cancer:
- • weakness;
- • fatigue;
- • feeling of bloating;
- • nausea;
- • stool disorders, constipation alternating with diarrhea;
- • loss of appetite and weight.
Blood can be seen in the stool; less commonly, so-called “black stool” occurs. A tumor is palpable on the right side of the abdomen. When spreading to neighboring organs, jaundice and ascites occur. Late symptoms include cancer intoxication caused by decay, which is expressed by:
- • low-grade fever;
- • thirst;
- • increased heart rate;
- • shortness of breath, breathing problems;
- • severe pain syndrome.
Narcotic analgesics, intensive infusion therapy and symptomatic medications help to alleviate the condition of a cancer patient with advanced cancer.
Symptoms
Cecal cancer is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Blood in stool. With cancer, damage to the intestinal vessels occurs, which leads to small internal hemorrhages. This symptom is the main one. However, the appearance of blood in the stool is also typical for some other diseases (hemorrhoids, Crohn's disease, etc.), so the diagnosis is made on the basis of differential diagnosis.
- Some neurological disorders - weakness, dizziness, headaches, etc. These symptoms are not independent disorders, but a consequence of internal bleeding.
- The appearance of mild pain in the lower abdomen. There are very few nerve endings in the intestinal area, but as the disease progresses, the tumor can begin to put pressure on the nerve endings of neighboring organs, which will lead to pain.
- Yellowing of the skin and a sharp decrease in body weight. These symptoms usually appear due to the disruption of the synthesis of certain substances in the body due to cancer, which leads to changes in metabolism.
- In case of metastasis, some other symptoms may also appear. Cecal cancer usually affects the lymphatic system, as well as the liver and stomach. Therefore, symptoms of metastases usually include the following disorders: pain in the abdomen, sudden weight loss or weight gain, nausea, vomiting, weakness.
Please note that all of the above symptoms do not appear immediately, but as internal organs are damaged.
Symptoms and first manifestations are most often limited to dizziness and blood in the stool, but sometimes there are no signs of the disease at all. At the middle stage, abdominal pain usually appears (the tumor increases in size, which leads to compression of nerve tissue). In the later stage, yellowing appears and sudden weight loss occurs. This is usually due to the fact that the tumor has metastasized to the liver and stomach.
Where tumors are most often found in colorectal cancer and what symptoms are accompanied, look at the picture:
Causes of cecal cancer
The causes of cecal cancer continue to be studied, but methods are already being developed to prevent the body from being exposed to the main factors that cause the appearance of a malignant tumor. Here are some of them:
- • heredity - this includes hereditary diseases in which precancerous conditions are formed (diverticula, polyps) - familial polyposis, Lynch syndrome;
- • inflammatory processes in the cecum (nonspecific ulcerative colitis);
- • helminthiases (schistosomiasis, giardiasis, amoebiasis), which anyone can become infected with, cause trauma to the mucous membrane, which predisposes to its degeneration;
- • viral infections—for example, human papillomavirus or herpes, which are contagious and widespread; or the same influenza virus, the causative agent of which is spread by airborne droplets and reduces immune defense;
- • unhealthy diet with a high content of fatty, spicy foods and a lack of plant fiber;
- • inactivity, lack of physical activity;
- • overwork and stress, the role of which is considered by psychosomatics;
- • radiation and exposure;
- • smoking, alcohol and drugs;
- • work with carcinogens in the chemical, mining, and oil industries.
https://youtu.be/VGTMYtiZODo
Etiology
Currently, medicine does not fully understand the true causes of the disease. However, a number of predisposing factors have been identified:
- a wide range of digestive system disorders;
- poor nutrition, consuming large amounts of fatty foods and carbohydrates;
- the presence in the medical history of one of the relatives of a similar illness;
- age category over forty-five years;
- regular drinking of alcoholic beverages;
- addiction to nicotine;
- prolonged exposure to stressful situations;
- long-term use of medications;
- work in hazardous production;
- polluted environment;
- excessively high body weight;
- diabetes;
- following strict diets;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- cancer metastases from other nearby organs;
- tendency to chronic constipation and irregular bowel movements.
Stages of cecal cancer
The stage of progression has not only diagnostic value, but also helps to predict the patient’s life expectancy, show the dynamics of the oncological process and choose treatment tactics. At an early stage, survival rate for cancer of the cecum is high, but the latter stage of cancer reduces the effectiveness of therapy, and death occurs within 2–8 months. The following degrees are distinguished:
- • 0 (zero) – only the mucous membrane is affected;
- • 1 (first) - cancer grows through all layers of the cecum:
- • 2 (second) - there is germination into the surrounding tissue, the affected lymph nodes are determined;
- • 3 (third) - metastasizes to regional lymph nodes;
- • 4 (fourth) - characterized by metastases in surrounding tissues and distant organs.
Varieties
There are several classifications of cecal cancer, the main of which are divisions of the disease depending on the histological structure of the tumor and the stage of development of the disease. Thus, the tumor, according to its structure, is divided into:
- adenocarcinoma - formation occurred from the colon mucosa;
- signet ring cell carcinoma – this type of disease has the appearance of vesicles;
- glandular-squamous - based on the name, consists of flat and jelly-like epithelium;
- squamous;
- undifferentiated – characterized by aggressive development, serious condition of the patient, difficulties in treatment and unfavorable prognosis;
- unclassified - consisting of tissues and cells that do not belong to known histological forms.
Division of cecal cancer by stages of progression:
- zero degree or precancerous condition - there is a small tumor that affects the upper layer of the intestinal mucosa. Regional lymph nodes are not damaged, there is no metastasis;
- the first stage – the spread of the oncological process into the deep layers of the organ is observed;
- second stage - germination occurs on the outer wall of the intestine. Lymph nodes are not involved in the pathogenic process, and no metastasis is observed. The prognosis depends on the degree of damage to the outer wall, but in most cases it is quite favorable;
- third stage – the lymph nodes are damaged and the tumor grows into nearby organs. Survival rate is five years;
- fourth stage - not only the surrounding internal organs and regional lymph nodes are damaged, but distant organs are also covered with metastases. The prognosis is extremely unfavorable - death occurs within five years.
The earlier the disease is detected and treated, the more optimistic the outcome will be.
Diagnosis of cecal cancer
Cecal cancer develops asymptomatically for a long time, so in order to check the suspicion, a thorough examination is necessary. A diagnosis, which includes:
- • inspection;
- • laboratory blood tests (erythrocyte sedimentation rate, hematocrit);
- • checking stool for occult blood;
- • finger-rectal examination;
- • Ultrasound to obtain a description of the size and location of tumor formation;
- • plain radiography of the abdominal cavity with contrast, images of which show atypia;
- • colonoscopy with biopsy and cytology to determine the type of benignity or malignancy;
- • test for cancer embryonal antigen;
- • computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging - from their photographs you can determine the prevalence of the oncological process;
- • PET-CT, the purpose of which is to detect metastasis.
Innovative diagnostic methods used in clinics in Belgium
Virtual colonoscopy (CT colonography) is a method of non-invasive visualization of the mucous membrane of the large intestine by constructing a three-dimensional computer model. Its diagnostic value approaches that of conventional colonoscopy, without causing any discomfort to the patient.
PET-MRI is a hybrid of magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography. The method allows you to obtain a detailed image of the intestine with visualization of areas of abnormally increased metabolism (cancer tumor).
Treatment of cecal cancer
The myth that cancer is incurable is a thing of the past. An effective remedy against tumors of the cecum - surgical removal - is offered by surgery. You should not take herbal infusions and decoctions, wasting precious time in the hope of getting rid of cancer. Painkillers will also not help stop the process - only surgery will give a real chance to survive and defeat cancer.
In the case of an operable neoplasm of the cecum, the surgeon’s actions are aimed at excision of the pathological focus with a section of healthy tissue under general anesthesia (for example, in case of extensive lesions, a right hemicolectomy is indicated). Unlike other localizations, cecal cancer does not require a colostomy. The doctor removes the tumor, restoring intestinal patency.
Contraindications to surgical intervention are an inoperable tumor, the patient’s serious condition and the presence of lesions in distant organs, but even in these cases it is possible to fight. Radiation and chemotherapy help slow progression, lead to clinical remission, and also prevent re-formation of pathology, relapse, after surgery.
Recovery with timely detection is 82–94%. Although the disease is deadly, cancer is curable. Mortality is only high if the cancer is left untreated or if the patient seeks medical help late.
Chemotherapy
In the initial stages of the disease (stage 0, well-differentiated carcinoma stage 2 without screening out to lymph nodes), chemotherapy is not performed.
Adjuvant (postoperative) chemotherapy is prescribed to patients with stages 2-3 cancer when metastases are detected in regional lymph nodes, tumor has invaded the serous membrane, and in a number of other cases.
Chemotherapy should begin as early as possible within a month after surgery. Courses are conducted according to standard schemes, the total duration is at least 6 months. The drugs can be used infusionally or orally.
Prevention of cecal cancer
Cancer prevention allows in some cases to prevent and completely avoid the development of cancer. On the recommendation of oncologists, you should adjust your daily routine and sleep, get rid of bad habits, eliminate the effects of carcinogens on the body, promptly treat precancerous intestinal diseases, and undergo preventive examinations.
An active lifestyle and a healthy diet protect against cecal cancer - a large amount of fiber in the diet promotes normal food passage, which has a beneficial effect on the intestines. It is recommended to enrich the diet with natural immunomodulators and vitamins to improve immunity.
Forecast
If treatment was carried out at stage zero and was successful, then the survival rate predicted by doctors is 95%. Due to mild symptoms, the disease cannot be diagnosed immediately.
When treatment is carried out at the first stage, the prognosis is 91%. This is due to the fact that cancer cells affect the second and third layers of the intestine.
If treatment was carried out at the second stage, then survival rate varies from 70 to 82%. This depends on how deeply the tumor has grown into neighboring tissues.
Treatment at the third stage guarantees patient survival only in 42–63%. These indicators depend on how badly the organs near the tumor are damaged and whether the lymph nodes are affected.
Therapy at the last (fourth) stage guarantees survival of only 6–10% for 6–7 years after therapy.
The figures given were obtained during the study.
To prevent people from having problems with cecal cancer, it is necessary to:
- completely give up bad habits;
- eat right and enrich your diet with microelements necessary for the body;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- maintain normal body weight;
- take only those medications prescribed by the clinician;
- promptly treat infectious and inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases;
- regularly visit a gastroenterologist for a preventive examination - this will help diagnose the disease at an early stage.
How long people live after surgery to excise cecal cancer depends on the severity of the cancer and the presence of complications.
Cecal cancer is a slow-growing tumor. Therefore, if a tumor is detected in the initial stages, the patient has every chance of a complete cure.
Five-year survival of patients after treatment depending on stage:
- I – 96%.
- II – 70-75%.
- III – 50%.
- Stage IV – no more than 6%.
The disease is highly treatable in the first three stages. The main danger is that nerve cells are almost completely absent in the cecum, which significantly complicates diagnosis.
Basic treatment methods:
- The main treatment for intestinal cancer is surgery. In this case, the surgeon removes the cancerous tumor. If necessary, the doctor can perform resection of the lymph nodes if the tumor has metastasized.
- Radiotherapy. The tumor is exposed to radiation, which destroys the cancer. The danger of the method is that radioactive particles also damage healthy cells, so radiotherapy is used only in cases of cancer with extensive metastasis.
- Chemical therapy. Special drugs are injected into the person’s body to destroy the tumor. These drugs are toxins that poison not only the affected cells, but the entire body, so this method is used only as a last resort.
If the disease is at stage 1 or 2 of development, then the doctor may prescribe surgical intervention. At stages 2, 3 and 4, radiation therapy or chemotherapy is used for treatment.
| Stage | Survival at 5 years after treatment |
| 1 | 95% |
| 2 | 85% |
| Prognosis for stage 3 | 50% |
| 4 | 15% |