Introduction to lymphocytes
What kind of cells are these?
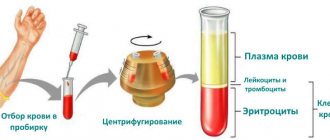
Lymphocytes are blood cells, or more precisely, they are a type of leukocyte - white blood cells.
There are five main types of white blood cells. They are divided into: cells containing granules - basophils, neutrophils, eosinophils, and cells that do not contain granules in the cytoplasm - lymphocytes and monocytes.
Thus, lymphocytes are white blood cells without granules in the cytoplasm.
Like all blood cells, lymphocytes are synthesized in the bone marrow from precursor cells.
Lymphocytes are further divided into two groups: T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes . Each of them has its own place of maturation, that is, an organ that produces mature cells ready to perform their functions.
Thus, the site of synthesis of mature T-lymphocytes is the thymus gland, and B-lymphocytes are the bone marrow. Now it remains to find out whether the roles of these lymphocytes differ.
Functions of lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are the main cells of the immune system. They promote the activation of effector mechanisms, regulate the processes of cell differentiation and their synthesis of necessary substances (cytokines). The main function of these cells is to launch an immune response in response to the introduction of a pathogenic agent, which can be a virus, bacterium, fungus or protozoa. An allergic reaction is also based on the interaction of lymphocytes and an allergen.
So do T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes have different functions? Insignificant. Both types play an important role in the immune response:
- T lymphocytes. There are several subpopulations that perform different functions. For example, there are so-called T-helpers, which help other cells become active, or T-killers, which are capable of destroying other cells. Their main role is participation in the cellular immune response;
- B lymphocytes. There are also several types of them, for example, memory cells. When the pathogen re-enters, the immune response develops faster. The main role of these lymphocytes is to transform them into plasma cells, which are capable of producing antibodies, participating in the humoral immune response.
This is only a small part of the functions that lymphocytes perform in our body.
Why is lymphopenia dangerous?
Reduced lymphocytes indicate the development of pathologies affecting the production of white blood cells against a background of weakened immunity. This condition, called lymphopenia, is already an alarming sign that requires urgent medical intervention. The following types are distinguished:
- Iatrogenic, occurring due to external influence and suppression of the processes of lym formation, for example, after chemotherapy sessions.
- Acquired, in which there are no problems with the formation and “maturing” of structural elements, but there is an accelerated process of their decay.
- Hereditary, when stem cells (precursors) cannot mature and give rise to a new generation of full-fledged lymphocytes.
Examples of congenital lymphopenia:
- Wiskott-Aldrich disease, which is characterized by an insufficient number of blood platelets, as well as skin eczema.
- DiGeorge syndrome is an example of a primary immunodeficiency in which the thymus gland is pathologically small or absent.
- Nezelof's disease with underdevelopment of the thymus gland, resulting in impaired T cell differentiation. Under the onslaught of pathogenic fungi and bacteria, various organ systems and the gastrointestinal tract are affected.
- Louis-Bar syndrome and its characteristic acute shortage of T-lymphocytes. Immunodeficiency leads to frequent respiratory diseases, pathologies of the skin and cerebellum. Death occurs due to complications that develop after infections and cancer.
What is prolactin, the norm in men and women
Antibiotics, immunoglobulins, thymus preparations improve the patient's condition. In all other cases, with congenital lymphopenia, a red bone marrow and thymus gland transplant is performed. In this case, the doctor’s goal is to prolong the patient’s life by supporting his immunity. We are not talking about a complete recovery, since this is impossible in principle.
All of these cases are examples of absolute lymphopenia with values below 1-3 thousand/mC. It is important to perform diagnostic tests and analysis of white blood cell subsets. Therefore, there is another mechanism leading to the deviations in question. This is when the number of lym is within normal limits, but the level, for example, of neutrophils increases and relative to them the content of lymphocytes (in%) turns out to be underestimated.
The norm of lymphocytes in the blood of children
In children, the level of lymphocytes in the blood is not the same as in adults. This is due to the fact that babies' immune systems are in the process of maturation. Therefore, each age has its own framework of reference values.
A table with normal levels of lymphocytes in the blood of children is presented for your reference. Only a doctor should decipher the test results.
Table. The norm of lymphocytes in the blood of children.
| Age | Norm in % | Norm per liter of blood |
| First ten days | 20 – 50 | 1,4 – 6,8 *10*9 |
| Less than one year | 45 – 70 | 2 – 11 *10*9 |
| One year or two | 37 – 60 | 3 — 9,5 *10*9 |
| Two to four years | 33 – 55 | 2 — 8,0 *10*9 |
| Four years – ten years | 30 – 50 | 1,5 — 6,8*10*9 |
| Ten – sixteen years | 30 – 45 | 1,2 — 5,2*10*9 |
| Over sixteen years old | 19 – 37 | 1 — 4,8 *10*9 |
A small explanation: when counting the number of lymphocytes in the leukocyte formula manually, the number of cells is given in relative values (%). When automatically counting blood cells, absolute numbers are given (10*9/l).
As can be seen from the table, there are two crossovers in the levels of lymphocytes in children. So, a child is born with one number of cells, then their number increases, and at a certain point begins to decrease, reaching the norm of an adult.
Symptoms
The main manifestation of lymphocytosis is a change in the blood picture. However, if this condition was provoked by an infection, then the patient will be bothered by the signs that are characteristic of an infectious disease - fever, cough, rash, runny nose, etc. However, these symptoms are not directly signs of an increase in the number of lymphocytes.
In some cases, with lymphocytosis, which was caused by non-infectious causes, the spleen and lymph nodes become enlarged.
All other manifestations of the relative type of this condition will depend on the reason that provoked the shift in the person’s blood formula.
If we are talking about a change in the number of lymphocytes in a person who has already had an infectious disease, then his general condition will be relatively normal, without pathological manifestations.
With absolute lymphocytosis, which develops due to a tumor of the hematopoietic tissue, signs will appear indicating the growth of neoplasia . The patient's internal organs - the liver and spleen - become enlarged, bone pain appears, and signs are observed that indicate a blood clotting disorder. Infections become more frequent and more severe due to a general decrease in immunity.
Lymphocytosis in adults is often combined with other abnormalities in the blood count. With viral infections, as well as during the recovery period after them, neutropenia and lymphocytosis . The reasons for this combination may also be associated with the development of certain immunodeficiency syndromes.
In childhood infections - measles , chickenpox , mumps - lymphocytosis and monocytosis .
For what symptoms is it necessary to determine lymphocytes in the blood?
Reduced lymphocytes in the blood are called lymphopenia.
The following symptoms will indicate that lymphocytes are low:
- the occurrence of infectious diseases , or rather their reappearance, for example, frequent pneumonia;
- the presence of skin lesions , leading, for example, to dermatitis.
Usually, when lymphocytes are low in a child, it is difficult to suspect only from clinical manifestations.
The level of lymphocytes decreases during infectious processes, but after recovery everything returns to normal.
Content standards
Knowing the level of lymphocytes (designated “ABC”) makes it possible to conduct a general clinical blood test. The procedure is practically painless, the material is taken in the morning on an empty stomach from a finger, heel (in a child under one year old), sometimes blood from a vein is required.
A small patient should eat in the evening, excluding spicy and fatty foods, because they can affect the result. In the morning you can only drink a little clean water. Before going to the laboratory, you should not brush your teeth; you should stop taking medications in advance or report this nuance to the medical institution.
Fasting blood tests are not performed on infants. You can take the material at any time of the day; you are allowed to feed the baby 2 hours before the procedure.
Important information: What does an increased leukocyte count in a blood test mean?
Sometimes a clinical study is carried out several times to more accurately monitor the patient's condition. In this case, blood sampling should be done at the same time.
The lower limit depends on age:
- newborns - 16%;
- fifth day of life - 30%;
- from the tenth day - 40%
- from 1 month - 45%;
- over 5 years old - 35%;
- over 10 years old - 30%.
If the result turns out that the percentage of lymphocytes in a child is reduced, this condition is called lymphopenia; if abs is increased, it is called lymphocytosis.
How to pass the test correctly?
Proper preparation for analysis will ensure accurate research results. It is worth drawing the attention of parents to a number of basic rules.
- It is best to donate blood on an empty stomach. This rule applies to older children. It is recommended not to feed infants for 2 hours.
- It is advisable to reduce the amount of salted and smoked foods consumed.
- It is advisable that the child does not run along the corridor of the clinic and does not cry in the treatment room. Since stress and physical activity can have an impact on the results of the study.
- If your child is taking medications, it is important to check with your doctor to see if they will affect the test results. Don't do anything on your own!
ethnoscience
To increase immune strength, you can use the following alternative medicine recipes:
- 5 tbsp. pour a tablespoon of fresh pine needles into a liter of hot water, simmer over low heat for 15 minutes, leave for a couple of hours, filter. Add 2 tbsp. spoons of honey, take a glass twice a day;
- Drink ½ cup of fresh pomegranate, beetroot, blackberry, cranberry or apple-carrot juice 3 times a day;
- Mix flower pollen and bee honey in a 2:1 ratio, eat a teaspoon of the mixture on an empty stomach, with ½ glass of whole milk.
What diseases cause a decrease in the level of lymphocytes in the blood of children?
There are two groups of reasons that lead to a low level of lymphocytes in the blood: congenital and acquired.
Congenital - associated with a violation of the synthesis of lymphocytes as a result of some genetic defect.
Acquired – low lymphocyte count is caused by some disease. This disease may be:
- flu;
- autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus;
- acute infections caused by bacteria;
- immunodeficiency states and others.
Lymphocytopenia
A condition in which there is a low level of lymphocytes in the blood is called lymphocytopenia. The abbreviated name is lymphopenia. The opposite condition, when lymphocytes in the blood are elevated, is called lymphocytosis.
Lymphocytopenia
If lymphocytes are reduced by several percent, there is no need to sound the alarm and give the child a diagnosis. Even different laboratories claim standards that differ by these percentages. If lymphocytes are greatly reduced, or you note that the child’s condition is unsatisfactory, then consult a doctor. The danger of lymphocytopenia is that with this state of the immune system, your child can easily pick up various viruses, and antitumor protection is reduced.
Lymphocytopenia is dangerous because the child’s immunity decreases, which means the risk of catching various viruses increases.
Lymphocytopenia is not necessarily an indicator of an existing disease. Often it can indicate a predisposition to this kind of disease. Lymphocytopenia can also occur due to disturbances in the child’s nutrition – lack of protein.
Lymphocytopenia can occur due to improper nutrition of the child
Lymphocytopenia occurs:
- congenital. It happens in children born to cancer patients or HIV-infected mothers. Poses a threat to the life of a child;
Congenital lymphocytopenia is a consequence of the disease in mothers
- acquired. Appears due to external factors: viruses, bacteria, diet or medications.
Taking medications (even as prescribed by a doctor) can cause lymphocytopenia
Also divided into:
- absolute. Associated with low production of lymphocytes and other immune cells in the blood. It happens with congenital immunodeficiency conditions, blood cancers and other serious diseases;
- relative . In this case, the decrease in the number of lymphocytes is associated with an increase in the number of another type of white blood cells - neutrophils. Occurs mainly due to infections in the acute or chronic stage.
Additional examination of children
Listed above are just a few possible reasons why lymphocytes in the blood may be low. To clarify the diagnosis, a number of additional studies are required depending on the type of suspected pathology:
- for congenital diseases - detection of a genetic defect using molecular genetic methods;
- for autoimmune pathology - detection of autoantibodies;
- determination of the type of causative agent of an acute infectious process, for example, by bacteriological (culture of material) or serological method (pathogen antigens).
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for leukopenia. To alleviate the patient's condition, drugs that stimulate the immune system are prescribed. Antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs are also selected, since low lymphocytes can be a sign of inflammatory processes.
In most cases, a complete medical examination is required to make an accurate diagnosis. Only after this is treatment prescribed for the underlying disease.
And the list of necessary medications and other types of influence depends on the specific violations. Self-administration of medications can cause complications, which can even lead to death.
Causes
The risk group for lymphopenia includes patients with congenital autoimmune pathologies, chronic viral or infectious diseases, as well as those who expose their body to radiation or chemotherapy.
A serious factor that increases the likelihood of developing the disease is poor nutrition combined with the abuse of bad habits .
Exposure to constant stressful situations, taking potent medications and lack of timely treatment for chronic diseases increase the risk of lymphopenia.
The causes of lymphopenia are the following factors:
- congenital pathologies of the immune system;
- insufficient protein nutrition;
- infectious diseases (including AIDS);
- damage to the structure of the lymph nodes or thymus gland;
- purulent-inflammatory diseases of the acute period;
- long-term or uncontrolled use of drugs from the psoralen group;
- development of cancer;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs;
- diseases associated with changes in blood composition;
- long-term therapy with potent drugs;
- development of intestinal obstruction;
- progression of rheumatic diseases;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome;
- consequences of viral diseases.
Preventive actions
The development of congenital lymphopenia cannot be prevented. Regular examinations during pregnancy will help reduce the risk of its development.
In order to prevent relapses after treatment of the acquired form of the disease, the following recommendations should be followed:
- include protein foods in the diet, as well as foods containing zinc and vitamins;
- stop drinking alcohol and smoking;
- carry out preventive measures aimed at protecting against various infectious diseases;
- Avoid stressful situations whenever possible.
You should also not forget about regular medical examinations, which will reveal a decrease in the level of lymphocytes in the blood. It is necessary to avoid casual relationships, including sexual ones, which pose a risk of contracting AIDS, tuberculosis and hepatitis.
Women should remember that lymphopenia can be transmitted from mother to unborn child. Therefore, when planning pregnancy, it is necessary to exclude the presence of this disease.
About some diseases leading to lymphopenia
Hodgkin's lymphoma
This malignant disease is also called lymphogranulomatosis. Tumor cells are localized mainly in the lymph nodes. Main signs of the disease:
- anemia;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- bleeding;
- weight loss;
- sweating;
- fever.
The main treatment is radiation therapy and cytostatics. In more severe cases, a bone marrow transplant is performed.
Bone marrow diseases
With such pathologies, not only lymphocytes, but also other blood cells can be reduced. Such diseases include Fanconi anemia. With this congenital disease, the bone marrow is depleted and the hematopoietic function is inhibited, the level of all leukocytes, as well as platelets and red blood cells, decreases. With this pathology, various developmental anomalies are observed, as well as massive bleeding, a tendency to severe infections and cancer. The most effective treatment is a bone marrow transplant.
The full name is severe combined immunodeficiency. It is based on gene mutations that lead to severe consequences. This is a congenital disorder of both cellular and humoral immunity. Symptoms appear in the first days of a child’s life (ear and skin infections, pneumonia, diarrhea, and others). Some microorganisms that are harmless to healthy people can become fatal for a patient with immunodeficiency.
Treatment for SCID involves a bone marrow transplant. There is a chance of recovery if surgery is performed in the first three months of life. Without treatment, children live no more than two years.
note
Please note:
- if lymphocytes are low in an adult or child, then an extensive examination should be carried out using various diagnostic methods;
- compliance with the preparation rules is of decisive importance for obtaining reliable test results: blood is donated on an empty stomach, alcohol is excluded 1 day before, any medications 2 days before, smoking 30 minutes before;
- a slight deviation from standard values, as a rule, has no diagnostic significance;
- the causes of low lymphocytes can be: infectious or autoimmune diseases, oncopathologies, bone marrow disorders, immunodeficiency states;
- attempts at self-diagnosis and treatment can lead to a worsening of the severity of the disease, even death.
Yulia Martynovich (Peshkova)
Certified specialist, in 2019 she graduated with honors from the Orenburg State University with a degree in microbiologist. Graduate of the graduate school of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education Orenburg State Agrarian University.
In 2019 At the Institute of Cellular and Intracellular Symbiosis of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, she completed advanced training in the additional professional program “Bacteriology”.
Laureate of the All-Russian competition for the best scientific work in the category “Biological Sciences” 2019.
Lymphocytes are white blood cells (a type of leukocyte), the main function of which is to provide immune protection. Lymphocytes are engaged in the destruction of harmful microorganisms and mutated cells of their own body. For the immune system to function correctly, a certain number of these cells is necessary. A table of the norm of lymphocytes in women by age will be given below and will allow us to identify possible deviations. After all, a lot in the normal functioning of the body depends on these small blood cells.
Possible complications in the child
If treatment is untreated or ineffective, a sick child may experience dangerous complications. In newborn children, whose body is not ready for such serious pathological processes, a small number of white blood cells sometimes ends in death.
Possible complications in older children when lymphocytes are low:
- HIV AIDS;
- oncological diseases;
- frequently recurring infections of a viral and bacterial nature.
Diagnostics
Clinical blood test as a method for diagnosing lymphopenia
As a rule, lymphopenia is detected during a planned regular blood test for a general analysis.
To calculate the leukocyte formula, peripheral (from the finger or heel) or venous blood is needed. On hematological analyzers, a general blood test is performed and the formula is calculated, and the device also calculates not the percentage, but the quantitative (absolute) content of each type of leukocyte in the blood. For a more thorough diagnosis, a thin smear is prepared from the blood, stained with a special paint and examined under a microscope by a specialist. Under a microscope, you can calculate the percentage and evaluate the size and shape of each cell.
Prevention
To maintain normal white blood cell levels, take care of your health
To reduce the risk of changes in the circulatory formula, patients should adhere to the following recommendations:
- avoid hypothermia;
- do not stay in places where large numbers of people gather during epidemics;
- regularly eat protein foods;
- try to drink up to 2 liters of clean water daily;
- take vitamin complexes as recommended by your doctor.
You should not self-medicate. The dosage of drugs should be determined by a specialist, and treatment should be carried out under his close supervision. Some sulfonamides and antibiotics have a powerful effect on the human body. To avoid harm, such drugs are taken only after a full examination and as prescribed by a doctor.
Both an increased and decreased number of lymphocytes may indicate the development of a number of severe pathologies in the body. Therefore, if you notice the first signs of such a failure, you should immediately visit a specialist.