Ventricular extrasystole (VES) is a type of heart rhythm disorder.
It is characterized by premature excitation of the myocardium under the influence of impulses that can arise in various parts of the conduction system of the ventricles of the heart. Most often, such impulses occur in the branches of the His bundles and Purkinje fibers. It is difficult to talk about the prevalence of ventricular extrasystoles, since the indicators depend on the research method. With a regular ECG, ventricular extrasystole occurs in approximately 5% of people, while in a Holter study (when an electrocardiogram is taken during the day), it is already recorded in half of the subjects.
VES is recorded both in older people and in young people and even in children, but with age the tendency to the occurrence of extrasystoles increases. Men are susceptible to this disease slightly more than women, and after a myocardial infarction - much more.
Without proper treatment, VES under certain conditions can lead to ventricular tachycardia, which in turn often causes ventricular fibrillation, and as a result, death.
Sometimes ventricular extrasystole is called ventricular.
What is ventricular extrasystole
The problem of arrhythmia is familiar to many. At some point, the heart stops, there is a lack of air, and a noticeable cardiac shock is possible.
The cause of unpleasant sensations is extrasystoles or heartbeats out of rhythm. A normal heartbeat begins when the heart impulse comes from the sinus node. This node is sometimes called a natural pacemaker.
For the heart to work correctly, cardiac impulses must be transmitted along a precise route, from the right atrium to all parts of the ventricles. When impulses enter the ventricles, they cause them to contract and pump oxygenated blood into the body. In an adult, a healthy heart beats 60 to 100 times per minute.
The appearance of centers of increased activity, which arise outside the center of the sinus node, cause the heart to beat irregularly, causing additional contractions per minute of myocardial relaxation.
Ventricular extrasystole is a phenomenon that occurs in young, elderly, healthy people, and those with cardiac disorders. It may occur randomly or at predictable intervals.
What is it, why are isolated (single) and frequent extrasystoles dangerous?
With ventricular (ventricular) extrasystole, the impulse can occur in the right and left bundle branches, Purkinje fibers or directly in the ventricular myocardium.
Single contractions of the muscular membrane of the ventricles do not have a significant effect on blood circulation, but paired and group contractions are called ventricular extrasystole, which requires treatment.
This disease can be a harbinger of much more serious rhythm disturbances, so it cannot be ignored.
Unlike atrial extrasystole, with ventricular excitation only the ventricles are involved , therefore on the electrocardiogram they look like dilated and deformed complexes.
Often their appearance is associated with the presence of any organic damage to the heart, a previous myocardial infarction and a decrease in the contractile function of the cardiac muscular layer.
Causes of ventricular extrasystole
The reasons that cause the development of malaise are different, as are its consequences.
The etiology of extrasystole is of two types:
- Organic.
- Neurogenic or functional.
Organic causes
During extrasystole, the irregularity of the heart is due to the small volume of blood entering the aorta from the left ventricle. And also any other source of excitation can disrupt the rhythm of the heart. Cardiac diseases present often worsen the condition. Extrasystoles of an organic nature appear when the myocardium is damaged.
Pathologies that affect the development of tachycardia:
- ischemic disease;
- arterial hypertension;
- cardiosclerosis;
The cause of ventricular extrasystole can be coronary heart disease - chronic heart failure;
- mitral valve prolapse;
- pericarditis;
- myocarditis;
- cardiomyopathy.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or pneumonia, affects the level of oxygen in the bloodstream, causing heart failure.
Functional reasons
Disorders based on functional causes are the most common.
This may be a combination of various factors influencing the occurrence of extrasystole:
- stress loads;
- coffee, strong tea;
- smoking;
- alcohol;
- Food;
- drugs;
- physical exercise;
- medications (decongestants).
In these cases, it is not always possible to determine organic damage to the heart, so “harmless” functional extrasystole leads to the development of many heart diseases.
Classification
The classification of ventricular extrasystoles covers all the characteristics of the phenomenon that has arisen.
This is necessary for specialists in order to adequately assess the threat to health, prescribe effective treatment (if necessary) and make a prognosis.
Consequently, according to the source of occurrence of PVCs there are:
- Monotopic - with one ectopic focus of the impulse (in one ventricle).
- Polytopic - with several secondary foci of impulse (left ventricular and right ventricular at the same time).
According to the duration of the compensatory pause:
- A complete compensatory pause means that the sum of the pre- and post-ectopic interval is equivalent in duration to the two main cardiac cycles.
- Incomplete compensatory pause - if the sum of the intervals is less than the duration of the two main cardiac cycles.
According to Lown-Wolf-Ryan (B. Lown, M. Wolf, M. Ryan), ventricular extrasystoles are divided into 5 degrees to take into account the risk of developing fibrillation:
- 1st degree – monomorphic extrasystoles (less than 30 per hour allowed).
- 2nd degree – monomorphic, more than 30 per hour.
- 3rd degree – polymorphic (group, paired) extraordinary contractions.
- 4th degree – divided into subcategories “a” – twin, “b” – salvo.
- Grade 5 – volley polymorphic PVCs (3-5 in half a minute), fixing paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. In such a situation, a person needs emergency help.
There is also a 0 (zero) degree. It means the complete absence of extrasystoles (single).
Gradation by time of occurrence:
- Early - occurring during the passage of an impulse through the atria.
- Interpolated - simultaneous contraction of the right and left ventricles with the atria occurs.
- Late - extrasystoles during the “rest” of the upper chambers of the heart.
Circadian types of extrasystoles:
- mixed;
- daytime;
- nocturnal
According to their rhythm, they are divided into allorhythms (periodic) and sporadic (single, irregular) extraordinary contractions.
Allorhythmia is divided into:
- Bigeminy - for every second normal contraction there is 1 extrasystole.
- Trigemy - every third.
- Quadrigeminiy - every fourth contraction is interrupted by an extraordinary contraction.
Idiopathic form of extrasystole
Ventricular extrasystole is a disease whose etiology can be causeless. In some cases, doctors are unable to determine cardiac changes after examining the patient. These cases are of unknown etiology. This form occurs in various patients, regardless of age, gender and concomitant diseases.
Doctors admit that the triggering point of the ideopathic form may be:
- disorders of the autonomic nervous system;
- changes in a person’s psycho-emotional background;
- changes in the electrolyte composition of the blood;
- influence of antiarrhythmic drugs.
Forecast
Even if the patient has been diagnosed with ventricular extrasystole due to heart disease, treatment should be started as early as possible, not deviate from the pill regimen prescribed by the doctor, and lead a healthy lifestyle. Only in this case will the prognosis be favorable and the person will be able to cure the pathology and live a long, fulfilling life.
Even if the heart is not bothered by interruptions in its work, it is very important to understand that many pathologies occur hidden and are detected too late (especially in men). Therefore, it is extremely important to undergo a routine medical examination and an ECG every year.
Classification of ventricular extrasystoles
There are two types of ventricular arrhythmias - impulse generation disorder and impulse conduction disorder.
Depending on this, a classification of extrasystole has been carried out in medicine:
- safe, not accompanied by diseases;
- potentially dangerous, asymptomatic, and arising as a result of cardiac diseases;
- malignant.
The last form of pathology occurs against the background of changes in cardiac function and manifests itself in the form of:
- Ventricular flutters. Their frequent and rhythmic contraction (up to 300 beats) is a consequence of unstopped tachycardia, often turning into fibrillation.
- Ventricular fibrillation is a fast heart rate that occurs in the lower chambers of the heart, usually at more than 300 beats per minute. Heart impulses occur chaotically, cardiac muscle cells are activated without coordination, so there is no normal heartbeat. This heart is called "trembling." If resuscitation is not carried out in time, the patient dies within 3–5 minutes. Scattered contraction of the ventricles on the electrocardiogram does not always have clearly defined deviations.
- Ventricular tachycardia is a serious disturbance of heart rhythm that occurs against the background of myocardial damage. The heart rate reaches 250 per minute. Sometimes tachycardia begins with a slow contraction speed ranging from 110-115 beats per minute. This type of extrasystole does not allow the heart to effectively pump blood, which leads to loss of blood in vital organs, including the brain. The occurrence of this type of arrhythmia often leads to loss of consciousness.
Patients with the above signs of tachycardia require immediate medical attention.
Diagnostics
The main method for detecting extrasystole is a resting electrocardiogram and a 24-hour Holter monitor.
Signs of PVC on ECG:
- expansion and deformation of the premature gastric complex;
- the ST segment, extrasystolic T wave and main QRS wave have different directions;
- absence of a P wave before ventricular atypical contraction;
- the occurrence of a compensatory pause after VES (not always);
- the presence of an impulse between two normal contractions.
A daily study of the ECG makes it possible to determine the number and morphology of extrasystoles, how they are distributed over 24 hours depending on various states of the body (sleep, wakefulness, taking medications, etc.). This study is taken into account to determine the prognosis of arrhythmia, clarify the diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
The patient may also be offered other methods of examining the heart:
- electrophysiological study - stimulation of the heart muscle with electronic impulses with simultaneous observation of the reaction to the ECG;
- ultrasound examination (echocardiography) – determination of the cause of arrhythmia, which may be associated with impaired cardiac function;
- taking an electrocardiogram at rest and stress - this helps to find out how the rhythm changes while the body is in a passive and active state.
Laboratory methods include venous blood analysis for the following indicators:
- fast phase protein responsible for the inflammatory process;
- globulin level;
- tropic hormone of the anterior pituitary gland;
- electrolytes – potassium;
- cardiac enzymes - creatine phosphokinase (CPK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and its isoenzyme - LDH-1.
If the results of the study did not show provoking factors and pathological processes in the body, then the extrasystole is designated as “idiopathic,” i.e. not clear in genesis.
Symptoms of ventricular extrasystole
It can be difficult to determine on your own whether there are signs of the disease. Not everything that is perceived as cardiac arrest is an extrasystole. Heart pain and intercostal neuralgia are often confused with arrhythmia.
The following symptoms indicate the development of extrasystole:
- uneven heart rhythms;
- feeling of cardiac arrest;
- lack of air;
- atypical location of chest pain;
- weakness, dizziness;
- strong pulsation (possible in the neck veins);
- in some cases, absence of pulse.
Ventricular extrasystole is a heart rhythm disturbance that is well tolerated by many people. If a person’s vital activity is disrupted and his or her health worsens, then we can talk about heart disease.
Symptoms of pathology
It is not very common to encounter cases where ventricular extrasystole is not subjectively felt at all.
However, almost always the main complaint of patients is a feeling of interruptions in the work of the heart, a feeling of fear or a “lump in the throat” with a sinking heart. During group ES, a feeling of rapid heartbeat is possible, which is often accompanied by severe dizziness and weakness. If at the time of rhythm disturbance the pumping function of the heart muscle is significantly impaired, then fainting and even prolonged loss of consciousness are possible. If such complaints occur for the first time and are accompanied by an increase in heart rate (HR) of more than 120 per minute, you must immediately contact a medical facility or call an ambulance.
Any concomitant heart lesion can add painful sensations behind the sternum or attacks of shortness of breath to the symptoms of ventricular extrasystole. This is often found in chronic heart failure (CHF) and coronary artery disease.
Group or polytopic frequent ventricular ES can lead to ventricular fibrillation. In this case, in addition to loss of consciousness, the patient may experience respiratory arrest with the development of clinical death.
Diagnosis of ventricular extrasystole
At the first sign of irregular heart rhythm, you should visit a cardiologist. Extrasystole is a disease that is very difficult to diagnose based on the patient’s complaints alone. To make a final diagnosis, a full interview with the patient and a series of studies should be carried out.
After a thorough examination, the doctor may suggest that you see other specialists:
- endocrinologist;
- psychotherapist;
- cardiac surgeon;
- neurologist;
- gynecologist.
Inspection
When physically examining patients who complain of irregular rhythms, the doctor does not always find changes in cardiac activity.
Extrasystoles are detected by counting the pulse, measuring blood pressure, and listening to the heart.
Electrocardiography
An ECG confirms the presence of additional heart rhythms. Using the device, a graph of the cyclicity of rhythms is built, which allows you to see the place where impulses are formed.
Holter examination
With the help of Holter equipment, which the patient wears for 24 hours, 24-hour heart rate monitoring is carried out. The device also allows you to find out the impact of external causes on the appearance of extrasystole, rhythm disturbances in a calm state and during physical activity.
Ultrasound
If necessary, a heart examination is prescribed using an ultrasound machine; in case of hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland is examined.
Ultrasound reveals ventricular aneurysm, myocardial disorder, cardiac performance indicators, and determines the size of the atria.
Coronary angiography
Invasive coronary angiography is recommended to confirm or exclude coronary artery stenting. This type of study is performed in patients with life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia.
Blood analysis
Patients with other medical conditions are advised to undergo blood tests to identify transient causes. The results will show the presence of electrolytes and cholesterol levels. The results of immunological and rheumatological tests will help rule out rheumatism, autoimmune and endocrine diseases.
Electrophysiological study
A study using EPI is carried out for patients with heart failure, complaining of fainting, ventricular tachyarrhythmia, and impaired blood flow.
As a rule, patients without structural changes in the heart are examined. Purpose of the study: to study the conduction system of the heart, to detect the pathology of the formation of an electrical impulse.
Symptoms and manifestations
Single ventricular premature contractions are recorded in half of healthy young people during monitoring for 24 hours (Holter ECG monitoring). They do not affect your well-being. Symptoms of ventricular extrasystole appear when premature contractions begin to have a noticeable effect on the normal rhythm of the heart.
Ventricular extrasystole without concomitant heart diseases is very poorly tolerated by the patient. This condition usually develops against the background of bradycardia (slow pulse) and is characterized by the following clinical symptoms:
- a feeling of cardiac arrest, followed by a whole series of beats;
- from time to time, separate strong blows are felt in the chest;
- extrasystole may also occur after eating;
- a feeling of arrhythmia occurs in a calm position (during rest, sleep or after an emotional outburst);
- During physical activity, the disturbance practically does not appear.
Ventricular extrasystoles against the background of organic heart diseases , as a rule, are multiple in nature, but for the patient they are asymptomatic. They develop with physical activity and go away while lying down. Typically, this type of arrhythmia develops against the background of tachycardia.
Many women during pregnancy experience tachycardia and pain in the left side of the chest. The development of PVCs in an expectant mother is not uncommon. This is explained by the fact that the circulatory system and the heart have a double burden. In addition, one should take into account the physiological changes in hormonal levels, which affect the rhythm of impulses. Such extrasystole is not malignant and can be easily treated after childbirth.
Drug treatment of ventricular extrasystole
Ventricular extrasystole, depending on the form and severity of the course, is amenable to treatment, which is carried out in the following areas:
- Simple forms of extrasystole (this is a disorder without hemodynamic abnormalities) do not require special treatment. In these cases there is no organic damage to the heart. If a person does not tolerate arrhythmia well, sedatives, the help of a psychotherapist, and treatment of diseases of internal organs are prescribed.
- An increased number of extrasystoles against the background of cardiovascular diseases without impaired coronary circulation also does not require the use of antiarrhythmic drugs. In this case, the underlying disease is treated.
- In the case of severe forms of arrhythmia against the background of structural heart diseases, drug treatment is offered, including surgical intervention.
The choice of drugs depends on the type of extrasystole and the condition of the myocardium. The doctor’s selection of therapy sometimes takes more than one day.
Treatment
To achieve a good therapeutic effect, you must adhere to a healthy diet and regimen.
Requirements that a patient suffering from cardiac pathology must comply with:
- give up nicotine, alcoholic beverages, strong tea and coffee;
- eat foods with a high concentration of potassium - potatoes, bananas, carrots, prunes, raisins, peanuts, walnuts, rye bread, oatmeal;
- in many cases, the doctor prescribes the drug “Panangin”, which contains “heart” microelements;
- give up physical training and hard work;
- during treatment, do not adhere to strict diets for weight loss;
- if the patient is faced with stress or has restless and intermittent sleep, then light sedatives (motherwort, lemon balm, peony tincture), as well as sedatives (valerian extract, Relanium) are recommended.
If the daily number of extrasystoles is more than 200, then drug treatment is prescribed.
Medicines to restore rhythm
The treatment regimen is prescribed on an individual basis and depends entirely on morphological data, the frequency of arrhythmias and other concomitant cardiac diseases.
Antiarrhythmic drugs used in practice for PVCs are divided into the following categories:
- sodium channel blockers - “Novocainamide” (usually used for first aid), “Giluri”;
- beta-blockers - “Cordinorm”, “Carvedilol”, “Anaprilin”, “Atenolol”;
- potassium channel blockers - Amiodarone, Sotalol;
- calcium channel blockers - Amlodipine, Verapamil, Cinnarizine;
- if the patient’s extrasystole is accompanied by high blood pressure, then antihypertensive drugs are prescribed - “Enaprilin”, “Captopril”, “Ramipril”;
- to prevent blood clots - Aspirin, Clopidogrel.
A patient who has started treatment is recommended to have a control electrocardiogram after 2 months. If extrasystoles become rare or disappear altogether, then the therapeutic course is canceled. In cases where the result has improved slightly during treatment, treatment is continued for several more months. In the case of a malignant course of extrasystole, drugs are taken for life.
Surgical methods of treatment
Surgery is prescribed only in cases of ineffective drug therapy. Often this type of treatment is recommended for patients who have organic ventricular extrasystole.
Types of cardiac surgery:
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA). A small catheter is inserted through a large vessel into the cavity of the heart (in our case, these are the lower chambers) and using radio waves, problem areas are cauterized. The search for the “operated” zone is determined using electrophysiological monitoring. The effectiveness of RFA in many cases is 75-90%.
- Installation of a pacemaker. The device is a box equipped with electronics, as well as a battery that lasts ten years. Electrodes extend from the pacemaker and are attached to the ventricle and atrium during surgery. They send electronic impulses that cause the myocardium to contract. The pacemaker essentially replaces the sinus node, which is responsible for rhythm. An electronic device allows the patient to get rid of extrasystole and return to a full life.
Many cardiologists recommend the installation of a pacemaker for those patients who have to regulate their heart rhythm with medications throughout their lives. As a rule, these are elderly people and such an event as taking the necessary pill on time can be a difficult task for them.
Functional form
For arrhythmia that has a functional form, it is enough to quit smoking, give up alcohol, and drink coffee, and the symptoms may disappear forever. It is necessary to establish the principle of proper nutrition, monitor weight, and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
If arrhythmia is caused by neurogenic causes, then you should beware of stressful situations, change your environment and lifestyle.
In some cases, the doctor will prescribe sedatives and sedatives:
- Organic preparations – motherwort, valerian herb root, lemon balm tincture.
- Chemicals – Diazepam, Rudotel.
What is extrasystole?
Possessing a unique independent innervation system that conducts nerve impulses to the tissues and parts of the heart, the myocardium also has additional nodes and nerve fibers, which, in the event of a failure of the main system, maintain the necessary regularity of heart contractions. Typically, to ensure normal functioning, the heart needs to maintain the functioning of the sinus node, which maintains the most optimal rhythm of contraction of the atria and ventricles.
With any disturbances in both the formation of a nerve impulse and its reception, it is transformed by other nodes, which cause discomfort in the chest area, untimely contraction or missed beat. Moreover, if necessary, even a separate nerve fiber can create the required number of nerve impulses, resulting in contraction of the heart muscle tissue.
The symptoms of this pathological condition, in which there is untimely contraction of heart tissue, may vary slightly. The reasons for the differences usually lie in the relationship of the particular disease manifestation to a particular species. Varieties of this condition have made it possible to create a certain classification of extrasystole, which, in turn, is a convenient basis for drawing up the most effective treatment regimen.
When extrasystole manifests itself, many confuse this condition with signs of serious cardiac pathologies. However, knowledge of the main symptoms will make it possible to make a preliminary diagnosis, without confusing extrasystoles in the heart with other manifestations of heart pathologies, and to take measures that will prevent the likelihood of aggravation of this process.
Organic form
Antiarrhythmic drugs and β-blockers are used to treat this form of arrhythmia.
| Drugs | Indications for use |
| Calcium antagonists β-blockers | For cardiac diseases without signs of heart failure |
| ACE inhibitors β-blockers | Heart diseases with myocardial dysfunction |
| Xanthines | Patients with low heart rate |
| Sodium channel blockers | No signs of cardiac disease |
Complications and probable prognosis
The consequences of ventricular extrasystole are monotonous:
- Heart failure. Requires urgent resuscitation. There are only a few minutes. In an inpatient setting, the chances of recovery are greater.
- Tachycardia. Significantly reduces the quality of life, worsens the outcome of the pathological process significantly.
- Ventricular arrhythmia. Joins almost instantly. Aggravates the development of the underlying disease.
All of these phenomena, one way or another, lead to the death of the patient. It's a question of time. Therefore, there is no point in delaying treatment and diagnosis.
The forecast data is something like this:
- With single extrasystoles, there are almost no risks. The likelihood of complications is about 2-5% for 5 years or more.
- The opposite phenomenon with group contractions is accompanied by severe problems in 65% of situations without therapy, one and a half to two times less with supervision.
A complete cure never occurs, but there are chances to improve the quality of life and prolong one’s existence. From a prognostic point of view, types 3,4,5 of the process are the least favorable. 1 and 2 do not pose a danger to life and health.
Traditional methods of treatment: recipes
There are several methods you can try at home:
- increase your intake of nutrients that support the heart (potassium, magnesium);
- practice breathing exercises to reduce stress levels;
- do yoga to strengthen the body and mind;
- try running, cycling, swimming.
Recipes for arrhythmia control:
- Grind the motherwort leaves into an extract. Pour hot water, strain the mixture and drink as needed.
- Add 1 tsp to boiling water. dried valerian herb. Brew, strain, drink as needed.
- Brew 160–200 grams of hawthorn with hot water. Let it brew, strain, then drink throughout the day.
- Grind 40 grams of lovage roots. Fill with hot water (1 l). Let it brew for 8 hours. Drink the infusion throughout the day.
- Add 1 tbsp to 4 cups of boiling water. l. dried horsetail herb. Leave for 4 hours. Take 1 tbsp. l. 5 times a day.
- Infuse calendula flowers (30 g) in two glasses of boiling water for 1 hour. Filter, drink 100 ml every two hours.
Development mechanism
Normally, the impulse generator that controls the contraction of the heart is the sinus node. While it is functioning normally, backup sources of impulse are suppressed.
An extrasystole indicates that such a (secondary) source of impulse has intensified its activity.
It is in the intraventricular system (Purkinje fibers, trunk of the His bundle, its branches or legs) that extraordinary impulses arise, causing the ventricles to contract without prior contraction of the atria. This can be seen on the electrocardiogram: there is no full-fledged P wave, indicating the functioning of the atria.
Experts have given a name to this phenomenon – the reentry mechanism. This means that the impulse conducting the excitation passes along a closed path and repeats its action. This mechanism, according to scientists, often causes various forms of arrhythmias.
During an extraordinary contraction, the ventricles do not pump blood, and the transient function does not occur. This is a fruitless waste of the strength of the heart, which at that moment should have been “resting”, but as a result – “working for wear and tear”.
There are relative norms for the number of extrasystoles outside sinus rhythm occurring during the day:
- 600-950 - are considered a non-life-threatening condition if there are no other abnormalities in the heart and disturbing symptoms (tachycardia, causeless shortness of breath).
- 1000-1200 are polymorphic extrasystoles. They are accompanied by a noticeable failure of the heart, which is not only displayed on the ECG, but also felt by the patient himself.
- 1200 or more extraordinary contractions of the ventricles per day are a direct threat to human life and health.
In healthy people, up to one hundred rare extraordinary extrasystoles can occur during the day, which do not in any way affect the overall functioning of the heart or the person’s well-being. In a child, PVCs and other heart rhythm disturbances (abbreviated as HRS) are often observed during puberty.
Indications for surgery
Operations are prescribed when frequent extrasystoles are detected - more than 800 per day.
Ventricular extrasystole, in some cases supraventricular, combined with atrial fibrillation - these forms often require surgical intervention:
- High frequency catheter ablation . This is minimally invasive surgery in the heart area, performed under ECG control. The basis of a widely used treatment method is the effect of high-frequency current on the area where ari occurs. "700″ height="485″[/img]
- Open heart surgery , in which areas that produce additional impulses are excised. A permanent pacemaker implant may be inserted.
Symptoms
If the patient does not have underlying cardiac pathologies, then, paradoxically, ventricular extrasystole is more difficult for them to tolerate than with the presence of diseases.
This is due to some compensatory capabilities of the body.
In a young, relatively healthy person, VES will manifest itself:
- A feeling of “cardiac arrest” followed by a series of palpable beats. Trying to describe their condition, patients say that their heart is sinking.
- Several strong heartbeats against the background of a calm state.
Women during pregnancy also often experience a sensation of extraordinary shocks in the heart area. This is due to hormonal changes, but if the symptoms are alarming, you need to consult a doctor and measure all indicators.
Even in the presence of all the above symptoms and signs, it is possible to assert the presence of ventricular extrasystole only on the basis of diagnostic results.
Important: if any interruptions in the functioning of the heart occur, you must consult a general practitioner or cardiologist.
Preparation and progress of the operation
Ventricular extrasystole is a pathological disorder for which doctors are increasingly prescribing minimally invasive radiofrequency ablation. The area in the heart that will be affected by electrical charges is preliminarily determined. The operation is performed using electrode catheters.
Indications for its implementation:
- congenital anomaly of the heart structure;
- flutter, atrial fibrillation;
- ventricular tachycardia;
- reciprocal nodal tachycardia (supraventricular);
- ventricular extrasystole.
Before the operation, the patient undergoes a thorough examination using an ECG, laboratory blood tests, and ultrasound of the heart.
Preoperative rules:
- The last meal is 12 hours before the procedure.
- Colon cleansing the night before surgery.
- Discontinuation of antiarrhythmic drugs 2–3 days before the procedure.
Ablation of arrhythmogenic zones is performed by a cardiovascular surgeon. The procedure takes place in an operating room equipped with an X-ray unit, an ECG machine, EPI, and an ablation generator.
Progress of the operation:
- Catheterization of the great vessels under local anesthesia.
- Advancement of diagnostic catheters and ablation electrode towards the heart.
- Ablation (delivery of electrical impulses) to the area of the heart causing the arrhythmia.
- Removing catheters. Applying pressure bandages.
The postoperative period lasts 12 hours, during which you should lie on your back without bending your knees.
ECG and other diagnostic methods
The following methods are used to diagnose the disease:
- ECG. Allows you to record everything that happens to the human heart during systole (contraction) and diastole (relaxation). When deciphering the cardiogram, the appearance of an expanded and deformed ventricular QRS complex, a complete compensatory pause, the absence of a P wave before an extraordinary contraction, and a change in the refractory period are observed.
- ECG monitoring according to Holter. This is a diagnostic method during which a special device with sensors is attached to a person, with which he must live his normal day. It is this daily observation that gives specialists the opportunity to track the periods and frequency of occurrence of extraordinary contractions of the ventricles. Holter monitoring is the main method for diagnosing PVCs.
- Bicycle ergometry. The method is used to confirm or refute the relationship between pathology and physical activity.
Additional diagnostic methods are used:
- General and biochemical blood test (to detect cholesterol levels, which could trigger the development of atherosclerosis).
- Blood test for thyroid hormones.
- Treadmill test.
- Echocardiography.
- Polycardiography.
- Rhythmocardiography.
- Transesophageal ECG.
- Sphygmography.
Usually, to determine the correct diagnosis, the patient only needs to undergo an ECG and a Holter study, but in some cases a detailed blood test and stress tests may be required.
Recovery
Postoperative complications are rare and are mainly associated with thrombotic complications. Anticoagulants are prescribed for prevention in the preoperative period. Also after the procedure, the patient must take anticoagulants for 3 months, while maintaining sinus rhythm.
After the operation, the patient spends 2–3 days in the hospital. A course of antiarrhythmic drugs is prescribed to reduce the rapid heartbeat. The recovery period at home can last from one to several months. In the first days, bed rest is indicated.
In the future, you should limit yourself to:
- in drinking coffee, tea;
- alcohol, tobacco;
- salt;
- physical activity;
- stressful situations.
In rare cases, a repeat operation is performed.
Gradation of PVCs
Although adults are more likely to have ventricular arrhythmia, children should also be checked to prevent possible complications. For a child and an adult, the same gradation of ventricular extrasystole is used. In total, there are several stages of PVCs, which determine how dangerous the arrhythmia is and whether treatment is necessary to eliminate it. The first stage (or 0) indicates the absence of extrasystole. The condition is normal and does not pose any danger. That’s why they start from the first class.
- The first class (1) indicates arrhythmia in the amount of up to 30 extra impulses per hour. This is a common ventricular extrasystole. It is a normal health condition, does not pose a threat and does not require treatment.
- Second class (2). This is a single ventricular extrasystole, manifested in the form of more than 30 extra impulses per hour. It’s worth paying attention to and slightly adjusting your lifestyle. But it does not pose a serious threat.
- Third grade (3). Polymorphic extrasystoles, having different shapes during one ECG. If there are multiple episodes of ventricular arrhythmia, special treatment will be required.
- The fourth class (4a) refers to paired ventricular extrasystoles following each other.
- The fourth class (4c) is called volley extrasystoles, manifested in the form of 3 - 5 extrasystoles one after another.
- Fifth grade (5). This is already ventricular tachycardia, requiring mandatory surgical intervention.
The last three classes of PVCs can lead to dangerous and serious consequences for human health, including fibrillation and tachycardia. The result of such complications is sudden cardiac arrest with all the ensuing consequences, including the death of a person. How dangerous a PVC is depends directly on its type. To determine the nature of the lesion and the number of unnecessary contractions (impulses), it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient in the cardiology department. It is dangerous to ignore the manifestations of frequent ventricular extrasystole, so at the first sign or suspicion of abnormal heart function, seek help.
Lifestyle with pathology
In case of heart rhythm disorders, especially those associated with various heart diseases, special attention should be paid to lifestyle. It is necessary to walk in the fresh air more often, relax, and not overload the body.
The malignant type requires limiting life situations that contribute to the development of an attack. Emotional and physical stress should be excluded, and lifestyle also needs to be reconsidered. If ventricular extrasystole has a benign sign, then there is no need to limit physical activity, but it should be within normal limits.
Some tips:
- monitor blood pressure;
- limit salt intake;
- give up caffeine and coffee-containing drinks;
- eat foods that are good for the heart: flaxseed oil, fish oil, vitamins with potassium and magnesium supplements;
- take Resveratol, Coenzyme Q10 (as agreed with your doctor);
- include dried apricots, grapes, dried fruits, bananas, and hawthorn in your daily menu;
- stop smoking;
- avoid excess weight;
- stop uncontrolled use of medications.
By changing your lifestyle, you can prevent many pathologies.
Causes
The causes of ventricular extrasystole can be divided into two large groups: cardiac and extracardiac.
Cardiac causes – as the name suggests, these are causes associated with heart disease. It can be:
- cardiac ischemia;
- myocardial infarction;
- cardiomyopathy;
- cardiosclerosis;
- acquired heart defects and some other pathologies.
Extracardiac (non-cardiac) factors can cause extrasystole even with a healthy cardiovascular system:
- disturbances in the electrolyte balance in the body - a decrease in the amount of potassium, magnesium, an increase in calcium content;
- overdose of certain medications - cardiac glycosides (digoxin), aminophylline, some antidepressants and other groups of drugs;
- taking drugs - cocaine, amphetamines;
- excessive consumption of coffee and caffeinated drinks;
- alcohol consumption;
- some infectious diseases;
- increased emotional excitement, stress.
Possible complications
With a healthy heart with a normal rhythm, but isolated cases of failure occurring, there is no cause for concern.
Repeated extrasystoles can give impetus to the development of diseases:
- heart failure;
- renal;
- cerebrovascular insufficiency.
Reluctance to be examined and treated leads to complicated forms:
- heart rhythm failure (atrial fibrillation src=»https://healthperfect.ru/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/zheludochkovaya-ekstrasistoliya-14.jpg» class=»aligncenter» width=»700″ height=»427″ [/img]
- paroxysm of ventricular tachycardia;
- flutter, atrial fibrillation.
These diseases increase the risk of sudden death.
Prevention
The consequences of ventricular extrasystoles can be extremely dangerous, even fatal, so their prevention is important. It includes:
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle. It is necessary to maintain a daily routine, allocate enough time for sleep and rest, and avoid excessive physical and emotional stress;
- Balanced diet. You should not eat a lot of fried, salty, spicy foods. It is useful to include foods containing large amounts of fiber in your diet;
- Rejection of bad habits. Alcohol and smoking aggravate many diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- Periodic examination of the body. It is necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner if any complaints arise, and also periodically undergo age-related medical examinations;
- Treatment of diseases, compliance with all doctor’s prescriptions. You should not treat diseases yourself, using folk remedies, or voluntarily cancel or change the dosage of medications prescribed by a cardiologist.
Prognosis for ventricular extrasystole
The prognosis of the disease is positive if the course of the disease is benign and there is no concomitant cardiac complication. Malignant arrhythmias, organic damage to the myocardium, create an unpredictable and often unfavorable outlook.
Taking antiarrhythmic drugs and beta blockers will help improve your health. The tandem of these medications will improve the quality of life and reduce the risk of complications.
In many cases, ventricular extrasystole does not cause concern. The appearance of irregular myocardial function is a reason to conduct a full examination. Taking good care of your health will help prevent many diseases.
Author: Belyaeva Anna
Article design: Mila Friedan
Classification and severity
To begin with, we invite you to familiarize yourself with what types of ventricular extrasystoles exist:
| Classification of pathology | What are extrasystoles? |
| By number | Single, pair (two in a row), group (three or more in a row). Group extrasystoles are also called unstable paroxysmal tachycardia |
| By frequency | Rare, medium, frequent |
| By nature | Monomorphic (one source of impulse due to which the ventricles contract untimely), polymorphic (several sources) |
| By rhythm | Periodic, bigeminy (each normal contraction is followed by an extrasystole), trigeminy (two normal contractions - an extrasystole), quadrigeminy (three normal contractions - an extrasystole). |
Three scientists (Lown, Wolf and Ryan) proposed the following classification of ventricular extrasystole (from mildest to most severe):
- 1 type Up to 30 single ventricular extrasystoles per hour (up to 720 units per day with a Holter study). Most often, such extrasystole is functional or idiopathic in nature and does not indicate any diseases.
- Type 2 More than 30 single untimely contractions per hour. It may indicate heart disease, or it may be functional. In itself, such extrasystole is not very dangerous.
- Type 3 Polymorphic ventricular extrasystoles. May indicate the presence of additional conduction bundles in the heart.
- 4A type. Paired extrasystoles. More often they are not functional, but organic in nature.
- 4B type. Group extrasystoles (unsustainable paroxysmal tachycardia). This form occurs due to cardiovascular diseases. Dangerous of developing complications.
- Type 5 Early group ventricular extrasystoles (visible on the cardiogram in the first 4/5 of the T wave). This is the most dangerous form of ventricular extrasystole, as it often causes life-threatening forms of arrhythmias.
Classification of ventricular extrasystole
Types of systolic arrhythmia
The presented type of arrhythmia is not classified separately, but in clinical practice it is customary to conventionally distinguish different types of changes in heart rate. These can be tachycardia, bradycardia and extrasystoles.
Tachycardia
Characterized by an increase in heart rate more than 90 times per minute. Some patients do not feel a change in heart rate, but as a rule, older people are very sensitive, so for them every rhythm disorder is a whole unpleasant event. Therefore, tachycardia is often experienced in combination with headaches and heart pain, increased fatigue and weakness.
Tachycardia in itself is not dangerous, but in combination with other disorders of cardiac origin it can lead to a number of serious complications - myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiac arrest.
Tachycardia often develops after overeating. This is due to increased digestion, which contributes to an increase in heart rate. Also, physical activity can increase the number of heart contractions, but unlike the pathological condition, physiological tachycardia normalizes over time. Therefore, the presence of a heartbeat at rest is a serious sign of severe organic heart damage.
Bradycardia
It is a sign of slow heart function and is determined by measuring heart rate, which in case of bradycardia is less than 60 times per minute. In some people, most often athletes, physiological bradycardia is determined. This option is considered normal because it does not cause health problems for humans.
Pathological bradycardia is characteristic of a number of diseases, primarily heart failure. With this pathology, the left ventricle cannot release blood normally, which leads to a weakening of all vital functions of the heart. Therefore, systolic arrhythmia in the form of bradycardia can be one of the first signs of deterioration in heart function.
Extrasystole
Heart rhythm disturbance is quite common for all age groups. It manifests itself as sudden interruptions in cardiac activity, sometimes accompanied by cramping pain or pressure in the heart area. Most often, especially in the case of young people and children, they are practically not felt.
In the case of systolic arrhythmia, which manifests itself on the ECG in the form of extrasystole, it can be noted that its development against the background of heart failure is also an unfavorable sign. This may indicate ongoing processes of myocardial damage, leading to the development of ectopic foci. Their occurrence most often provokes premature contractions.
Expert advice
Detection of ventricular extrasystoles on an ECG is not yet a sign of a serious problem and does not require special treatment.
Functional rhythm disturbances are often accompanied by symptoms that do not correspond to the severity of the condition. To eliminate them, it is enough to remove alcohol from your diet, quit smoking and drink caffeinated drinks. Among the drugs you can drink valerian tincture, Corvalol. When extrasystole is accompanied by coronary disease or other disorders, you must immediately contact a cardiologist and undergo a full examination. All medications should be taken as scheduled and should never be discontinued on your own.
Diagnosis of extrasystole
The presence of extrasystoles can be suspected after collecting patient complaints and a physical examination. Here it is necessary to find out whether a person constantly or periodically feels interruptions in the functioning of the heart, the time of their occurrence (during sleep, in the morning, etc.), the circumstances that provoke extrasystoles (anxiety, physical activity or, conversely, a state of rest).
When collecting anamnesis, it is important to note whether the patient has heart and vascular diseases or previous diseases that cause complications on the heart. All this information makes it possible to preliminarily determine the shape of the extrasystoles, the frequency, the time of occurrence of unscheduled “beats,” as well as the sequence of extrasystoles relative to normal heart contractions.
Laboratory research:
- Clinical and biochemical blood tests.
- Analysis with calculation of thyroid hormone levels.
Based on the results of laboratory diagnostics, it is possible to identify an extracardiac (not related to cardiac pathology) cause of extrasystole.
Instrumental studies:
- Electrocardiography (ECG) is a non-invasive method of studying the heart, which consists of graphically reproducing the recorded bioelectric potentials of the organ using several cutaneous electrodes. By studying the electrocardiographic curve, one can understand the nature of extrasystoles, frequency, etc. Due to the fact that extrasystoles can only occur during exercise, an ECG performed at rest will not record them in all cases.
- Holter monitoring, or 24-hour ECG monitoring , is a heart study that allows, thanks to a portable device, to record an ECG throughout the day. The advantage of this technique is that the electrocardiographic waveform is recorded and stored in the device's memory during the patient's daily physical activity. During the daily examination, the patient makes a list of recorded time periods of physical activity (climbing stairs, walking), as well as the time of taking medications and the appearance of pain or other sensations in the heart area. To detect extrasystoles, full-scale Holter monitoring is more often used, carried out continuously for 1–3 days, but generally no more than 24 hours. Another type - fragmentary - is prescribed for recording irregular and rare extrasystoles. The study is carried out either continuously or intermittently for a longer period of time than full-scale monitoring.
- Bicycle ergometry is a diagnostic method that consists of recording ECG and blood pressure indicators against the background of constantly increasing physical activity (the subject pedals the bicycle ergometer at different speeds) and after its completion.
- Treadmill test is a functional load test, consisting of recording blood pressure and ECG while walking on a treadmill.
The last two studies help to identify extrasystole that occurs only during active physical activity, which may not be detected with a regular ECG and Holter monitoring.
To diagnose concomitant cardiac pathology, standard echocardiography (Echo CG) and transesophageal, as well as MRI or stress Echo CG are performed.
Clinical picture of the disease
Heart rhythm disturbances such as ventricular extrasystole in practice are manifested by the following symptoms:
- with ventricular extrasystole, patients experience a feeling of interruptions in cardiac activity, the appearance of an irregular beat and a feeling of revolutions;
- extraordinary contractions of the myocardium are accompanied by weakness and general malaise, as well as anxiety and dizziness;
- Often patients with extrasystole complain of the development of shortness of breath or a sharp feeling of lack of air;
- in this pathological condition, there is a feeling of fear of death, panic attacks, anxiety and many other disorders of the psycho-emotional sphere;
- fainting conditions are possible.
Often, ventricular extrasystole occurs without visible subjective manifestations, so such patients have no complaints in principle, and the disease is diagnosed exclusively by electrocardiographic examination. Symptoms of ventricular extrasystole with frequent episodes of extraordinary contractions, which occur mainly against the background of heart diseases of organic origin (the so-called organics), can be accompanied by cardiac pain, severe shortness of breath and weakness, as well as loss of consciousness and nausea.
Ventricular extrasystole in children is a fairly common phenomenon, which is recorded in most cases in combination with congenital defects, myocarditis and cardiomyopathies. The severity of manifestations in a child depends on factors such as the age of the young patient, the type and form of the pathological process, as well as the timeliness of diagnosis of rhythm disturbances and the causes of its occurrence.
Objectively, in a patient with diagnosed extrasystole of ventricular origin, the following are determined:
- pronounced pulsation of the veins of the neck;
- arrhythmia of arterial pulse;
- change in sonority of the first tone and bifurcation of the second tone;
- long compensatory pause after an extraordinary contraction.
Symptoms
Many patients are not even aware of their problem, since there are no manifestations. Others suffer from:
- Feelings that the heart is working intermittently. It either freezes or an increased shock occurs.
- Excessive fatigue, irritability, headaches and dizziness. This indicates extrasystole in combination with vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air. This suggests that the rhythm disturbance occurred as a result of heart pathologies. Some patients lose consciousness.
During the examination, they may find that the veins in the neck are pulsating. Instrumental techniques are required to confirm the diagnosis.
Also read: Extrasystole of the heart: causes, types, diagnosis, treatment
Extrasystole in children
Previously, it was believed that the more common form of extrasystole in children was ventricular. But now all types of extrasystoles occur with almost the same frequency.
This is due to the fact that the child’s body grows quickly, and the heart, unable to cope with such a load, “turns on” compensatory functions due to the same extraordinary contractions. Usually, once the child's growth slows down, the disease disappears on its own.
But extrasystole cannot be ignored: it may be a sign of a serious disease of the heart, lungs or thyroid gland. Children usually present the same complaints as adults, that is, they complain of “interruptions” in the functioning of the heart, dizziness, and weakness. Therefore, if such symptoms occur, the child must be carefully examined.
If a child has been diagnosed with ventricular extrasystole, then it is quite possible that treatment will not be required. The child must be registered with a dispensary and examined once a year. This is necessary in order not to miss the deterioration of his condition and the appearance of complications.
Drug treatment of extrasystoles in children is prescribed only if the number of extrasystoles per day reaches 15,000. Then metabolic and antiarrhythmic therapy is prescribed. Source "sosudinfo.ru"
Consequences and prognosis
The prognosis depends on how disturbed the heart rhythm is, whether there are heart pathologies and circulatory disorders. With functional extrasystoles that occur in healthy people, there is no risk. But, if a person suffers from heart disease, the likelihood of sudden cardiac arrest increases. Among the complications of ventricular extrasystole are:
- sudden cessation of heart activity;
- the development of heart failure, when the organ cannot fully perform its work;
- worsening of existing pathologies;
- violation of the structure of the ventricle;
- ventricular fibrillation.
These are dangerous conditions that in some cases lead to human death.
Features of the pathology
The development of extrasystole is observed in people of different ages. An ectopic focus that sends abnormal impulses may be located in the atria or ventricles. In this case, extraordinary contractions of the heart appear. At these moments the patient suffers from dizziness, weakness, and pain in the chest.
To detect the problem, you need to undergo a detailed examination. Medications are usually used to normalize the rhythm.
More than half of the patients have a ventricular form of extrasystole. Using a cardiogram, the presence of extrasystoles is determined in 5% of people who do not have health problems. With age, the number of patients increases, which means that such rhythm disturbances are most typical for people over 45 years of age.
The problem can develop in benign and life-threatening forms. In the first case, antiarrhythmic drugs are sufficient to correct the situation. In case of malignant extrasystoles, it is necessary to eliminate the main cause of the disorder, namely heart pathology.
The danger of this condition is that it can cause ventricular fibrillation and cause sudden cardiac death.
Diagnosis of pathology
The classic method for recognizing arrhythmias is electrocardiography. Depending on the source of the pathological impulse causing premature contraction of the heart, supraventricular (supraventricular) and ventricular extrasystoles are distinguished. The supraventricular ones include atrial, extrasystoles from the A-V junction, as well as the much rarer sinus. One of the types of ventricular extrasystoles are stem ones.
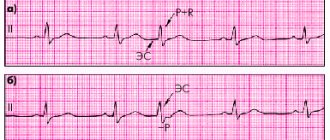
Variants of extrasystoles from the AV node. a) the P wave has merged with the QRS complex, b) an altered P wave is visible after the QRS complex
All of them have specific ECG signs, which in most cases make it possible to confidently distinguish them from each other. But on a regular resting ECG, recorded within a few seconds, rhythm disturbances are often not detected.
Ventricular extrasystole
Therefore, the main method for diagnosing extrasystole is daily Holter ECG monitoring . Special equipment allows you to record all the electrical activity of the heart during the day, diagnose the type of extrasystoles, their number, distribution over time, connection with exercise, sleep, medication and other important characteristics. Only after this should drugs be prescribed for the treatment of cardiac extrasystole.
Treadmill test or bicycle ergometry
An additional method that helps determine the relationship between arrhythmia and exercise is a treadmill test or bicycle ergometry. This is a type of physical activity (respectively, walking on a moving path or simulating cycling), accompanied by constant ECG monitoring.
If a large number of extrasystoles appear during exercise or at rest, the functional diagnostics doctor reflects this in the conclusion based on the results of the load test.
The method of rhythmocardiography is becoming a thing of the past as it has not found any justified application in the clinic. However, in many medical institutions it is used and also allows you to detect extrasystoles.
Only after receiving a complete description of the extrasystole does the doctor begin treatment.
We recommend reading about atrial extrasystole. You will learn about the causes of its appearance, signs and symptoms in adults and children, diagnosis and basic treatment methods. And here is more information about emergency measures during an attack of atrial fibrillation.
What do extrasystoles look like on an ECG?
On a normal ECG, the relationship between the five main waves, their size and direction is always observed. The correctness of the rhythm is judged by the distance between the R waves. By the presence of the P wave - by the origin of contractions from the sinus node.
Extrasystoles can be from the left or right ventricle. Then we will see a change in the shape of the QRS complex in the corresponding leads. The form of extraordinary contraction differs from normal:
- in width,
- notch at the top
- subsequent extended pause.
The P wave (shape, place before or after the ventricular wave) indicates the location of the focus of excitability in the upper, middle or lower part of the atrioventricular node.
The ECG shows in detail the conditions for the occurrence of rhythm disturbances:
- tachycardia,
- bradycardia,
- atrial fibrillation,
- myocardial pathology.
Consequences for the patient
If there is no concomitant disease of the heart or nervous system, or an uncompensated disturbance in the production of hormones, then such extrasystole can be easily corrected by normalizing the lifestyle and taking recommended medications. The prognosis for recovery in such patients is favorable.
If there is a persistent neuroendocrine failure in the regulation of heart contractions, then in the future (if untreated) extrasystole can transform into ventricular tachycardia, which is accompanied by more serious consequences.
We recommend reading the article about ventricular extrasystole and methods of its treatment. From it you will learn about the classification of pathology, causes of development, signs and symptoms, as well as the diagnosis and treatment of ventricular extrasystole.
And here is more about parasystole.
Functional extrasystole occurs in patients in the absence of heart disease. It is provoked by stress, bad habits, infections, hormonal and electrolyte imbalances in the body. With neurocirculatory dystonia, extrasystole is accompanied by vegetative manifestations.
For diagnosis, an ECG is performed, including stress tests and Holter monitoring. Treatment is aimed at restoring rhythm and reducing excitation of the nervous system.
Kinds
Depending on the number of ectopic foci, extrasystole can be monotopic or polytopic.
Extraordinary contractions may occur during atrial contraction or at the border with the ventricles. In this case, the extrasystoles will be early, interpolated and late.
Depending on the frequency of occurrence, the following may occur:
- Single ventricular extrasystole. In this case, no more than five extraordinary contractions are observed within a minute.
- Multiple extrasystole. In this case, more than five contractions are observed.
- Steam room. Between normal contractions there are two extrasystoles at once.
One of the classification options is the Ryan gradation, based on which the development of ventricular extrasystole occurs in several stages:
- ventricular extrasystole grade 1 according to Ryan is the first stage of arrhythmia. At the same time, no more than 30 episodes of extraordinary contractions are observed over the course of an hour.
- in the second stage there are more than 30 extrasystoles per hour;
- the third stage is characterized by multifocal extrasystoles;
- there is stage 4a, in which paired monotropic extrasystoles are observed;
- at stage 4b, with polymorphic extrasystoles, ventricular fibrillation and flutter develops;
- The fifth stage is characterized by the presence of ventricular tachycardia with three or more extrasystoles.
Main causes
There are a number of factors that can provoke disturbances in the functioning of the heart and the rhythm of its contractions. Bad habits combined with an incorrect and unhealthy lifestyle can cause significant changes in the condition of the heart tissues, for example, extrasystole and alcohol are incompatible concepts: alcoholic drinks in significant quantities can cause pathological changes in the tissues of the heart muscle, causing interruptions in the normal contraction of the atria and ventricles .
Also, the reasons that can cause the appearance of signs of extrasystole include the following:
- smoking, which causes sclerosis of blood vessels, which can impair the circulatory process, deteriorate tissue nutrition and oxygen supply;
- lack of motor activity - this can worsen both the processes of blood circulation and nutrition of heart tissue, and cause a decrease in tissue conductivity due to a decrease in the number of the entire area of blood vessels in the heart;
- frequent stressful situations that provoke increased heart rate and increased blood pressure, which negatively affects the general condition of the myocardium;
- food that does not meet the standards of a healthy lifestyle. Consuming fast food, carbonated drinks such as Fanta and Pepsi-Cola can provoke sclerotic manifestations in the blood vessels;
- changes in the hormonal system that can occur during menopause, puberty, and pregnancy;
- too frequent use of energy drinks and strong coffee;
- prolonged hard physical work that causes increased fatigue and exceeds the capabilities of the human body.
There is also a type of extrasystole, the causes of which cannot be identified. In this case, idiopathic extrasystole is diagnosed.
The listed reasons can affect the body with negative results, both independently and when they are present in combination. However, even one of the factors listed above can significantly disrupt the normal functioning of the cardiac system and change blood circulation with deterioration in tissue nutrition.
At the initial stage of exposure to the listed negative factors, with their timely elimination, a rapid restoration of the normal functioning of the heart muscle is observed. Therefore, it is recommended, in the presence of hereditary factors and a tendency to develop disturbances in the functioning of the cardiac system, to eliminate the causes of the risk and restore a healthy diet and healthy lifestyle, eliminating bad habits. After all, even irregular fibrillations (ineffective contractions of the heart muscle), when repeated for a long time, can not only worsen the general condition, but also cause death if the pathological condition is neglected.
What it is?
Ventricular extrasystole is one of the types of arrhythmias, which are premature, out-of-order contractions of the ventricles. Ventricular extrasystole is characterized by a feeling of disturbances in the functioning of the heart in the form of failures, weakness, dizziness, anginal pain and lack of air.
This type of arrhythmia is established after listening to the heart, electrocardiogram and Holter monitoring. And to treat extraordinary contraction of the ventricles, sedatives, beta-blockers and antiarrhythmic drugs are used.
How to treat premature myocardial contractions?
Treatment of ventricular extrasystole in practice is carried out using conservative and surgical methods and has several main goals:
- elimination of extraordinary layoffs;
- preventing the transformation of the disease into more complex forms;
- prevention of disease complications.
Treatment measures should be started as early as possible, which will avoid the development of undesirable consequences of the pathological condition and, as far as possible, prevent the occurrence of its complications.
For patients with single extrasystoles who do not have any symptoms of the disease, doctors do not recommend treating the disease with medications . In such cases, experts suggest that patients give up bad habits, normalize their diet and adjust their daily routine, as well as normalize their emotional state and, if possible, avoid the influence of provoking factors. Doctors warn that treating ventricular extrasystole with folk remedies may be dangerous to their health and provoke an exacerbation of the pathological process.
In most clinical options, conservative correction of the disease is carried out through the use of such groups of drugs as:
- sedatives to normalize the nervous system;
- beta blockers, which are prescribed to prevent the development of myocardial ischemia;
- antiarrhythmic drugs that block the activity of ectopic foci.
Surgical treatment is used in cases where there is no effect from drug therapy and the disease is malignant. The most commonly used method for such patients is RFA of the heart (radiofrequency catheter ablation). This surgical intervention involves cauterization of ectopic foci by inserting a special catheter through a large vessel into the cavity of the heart. Much less often, a more radical operation is performed using direct access to the heart with subsequent excision of ectopic foci.
Treatment of cardiac systole: modern methods
Standard treatment for extrasystole lasts approximately three months. Then you need to take a break and continue active therapy. During the selected treatment, you should not forget about maintaining a healthy lifestyle. It is recommended to give up all bad habits that affect the heart and, of course, the body as a whole.
Treatment of systole with drugs is used when the pathology severely disrupts the functioning of the heart and also causes secondary pathological changes in the structure of the brain and internal organs.
In severe cases of cardiac extrasystole, treatment is carried out in a supervised hospital with intravenous administration of drugs that help restore heart rhythm and systole. If there is no positive effect, surgical treatment of extrasystole is performed. It consists of direct catheterization through the coronary vessel to administer a coagulator.
The heart is affected by drugs that completely eliminate the focus of ectopic signals for extraordinary myocardial contractions. This technique is used in the case of a monotropic form of heartbeat disorder. This is what helps to establish the systole process.
Medicines for acute extrasystole can be used from several pharmacological groups, each of which has its own specific purpose. A combined scheme can also be used to stabilize systole. This therapy involves the use of medications from completely different groups.
The main types of drugs for the treatment of extrasystole:
- Medicines to completely eliminate signs of arrhythmia.
- Beta blockers.
- ACE production inhibitors.
For the active treatment of extrasystole and the establishment of systole rhythm, various sedatives, for example, of natural herbal origin, are widely used. This can be a regular tincture of valerian, peppermint or motherwort. In more complex cases of extrasystole, treatment is carried out with stronger drugs, which can be purchased at any pharmacy exclusively with a prescription from your attending physician. Basically, these drugs belong to the barbiturate group. Active treatment with magnesium and potassium preparations is indicated.
Also relevant are vitamins that help stabilize the functioning of the heart, as well as the body as a whole. It is contraindicated to be nervous during extrasystole, so do not worry about the diagnosis – it can be treated. If you approach the chosen therapy and your lifestyle correctly, problems associated with heart rhythm disturbances will be forgotten quite quickly. Follow the doctor’s recommendations and your feelings, then the success of the treatment is guaranteed.
Extrasystole is the most common type of arrhythmia: according to statistics, it periodically occurs in 60-70% of people. In itself, this rhythm disturbance is not dangerous, but in patients with chronic heart diseases (post-infarction cardiosclerosis, myocardial hypertrophy), it can be an additional risk factor for the development of complications.
In our review and video in this article, we will understand what extrasystoles are, why they occur, and how they are treated.