Home Diseases and treatment Gastroenterology
10 Feb 2020, 20:02 Anna 278 No
Sometimes, when examining the pancreas, you can notice that the organ is deformed. If this happens, then the treating doctor should pay attention to this and find out why the pancreas has changed its shape.
Why does a bend in the pancreas appear?
Among the three factors identified by experts, gland deformation factors truly pose a threat to health.
To prevent the situation from getting worse, it is recommended to visit the doctor regularly and follow his prescriptions. Causes of bending of the pancreas:
- Pancreatitis in acute or chronic form. Under the influence of the inflammatory process, the gland may become more angular and move higher. Acute inflammation is characterized by the following disorders: vomiting, diarrhea, pain radiating to the left hypochondrium, nausea, elevated body temperature, bitter taste in the mouth with a feeling of dry mouth. With timely treatment, the pancreas returns to its place. If you neglect the disease and violate the doctor’s instructions, pancreatitis will go into the chronic stage, and then the deformity may worsen.
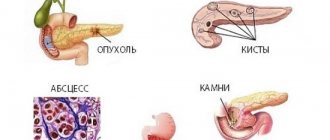
- Cyst formations. A pancreatic cyst itself is not a sign of any pathological process or disease. However, it cannot be ignored. You need to take the examination seriously and find out if there are any deviations. A pancreatic cyst can be recognized on an image; it will have a clear outline, but ultrasound diagnostics is meaningless in determining it.
- Malignant neoplasms. Using an ultrasound, you can suspect a tumor of the gland. If the organ is significantly enlarged in size, and the contours of the pancreas are modified, it may be a neoplasm. The conclusions of ultrasound diagnostics must be supported by other studies, so do not rush to conclusions.
In children, the pancreas is at risk of developing all kinds of serious diseases that can appear due to genetic predisposition, poor or irregular nutrition, as well as many other reasons.
The pancreas can often become deformed when a disease occurs, such as chronic pancreatitis or acute pancreatitis in children.
If a violation is detected in the location of an internal organ, this does not at all indicate the presence of a disease. Meanwhile, the child requires a full examination to prevent the possible development of a particular disease.
In any case, changes in the pancreas in children should be a cause for concern. After the doctor examines the patient and identifies the true cause of the deformation of the internal organ, the child is prescribed the necessary treatment.
The pancreas in children can become deformed either with a displacement to the side or without a change in location. Most often, modification of the internal organ occurs in conjunction with an enlargement of the pancreas.
If a child has a bend in the pancreas, there is no need to worry, since this is a temporary phenomenon that is age-related. It is necessary to carefully monitor the child’s nutrition in order to protect him from the development of any diseases, and carefully monitor the functioning of the digestive system. In case of any deviations, you should consult a doctor.
Diet for a child during illness
Treatment includes diet No. 5 according to Pevzner: it involves a high content of consumed proteins and a low amount of fats and carbohydrates. The child must be fed frequently and in small portions: 6–8 times a day with small portions of warm food. At first it’s a variety of cereals, then the diet expands. Spicy, fatty, fried foods are excluded.
An altered shape or deformation of the pancreas is not always a manifestation of disease. But this is an indication to contact a specialist and conduct a detailed examination of the child. Preventing the onset of the disease and its complications is easier than treating it.
Bibliography
- Ostrovsky A.G., Karashurov E.S. Rare diseases of the pancreas: Textbook. Petrozavodsk, 1988
- Sokolov Yu.Yu. Diagnosis and surgical treatment of duodenopancreatobiliary anomalies in children. Abstract of the dissertation. Moscow, 2002
- Berman R.E. Pediatrics according to Nelson. Edited by A.A. Baranova. T.4. M. LLC "Reed Elsiver", 2009
- Pediatric gastroenterology, ed. Baranova A.A., Klimanskoy E.V., Rimarchuk G.V. M. 2002
- Isakov Yu.F., Dronov A.F. Pediatric surgery. National leadership. M., 2009
- Losev A.A. Pediatric surgery: Textbook. M. 2009
Causes of pancreas deformation
Modern medicine identifies only three reasons why a person’s pancreas can become deformed, and one of the reasons is quite dangerous. For this reason, it is recommended to regularly visit doctors for preventive examinations in order to detect the presence of serious illnesses or complications in time.
The patient's pancreas can become deformed:
- Due to acute or chronic pancreatitis. In this case, the internal organ is deformed angularly with a slight upward displacement. If the disease is detected in time and the necessary treatment is started, the pancreas will stop changing or return to its normal location. In the acute form of pancreatitis, a person experiences nausea, vomiting, loose stools, pain in the left side, an unpleasant taste in the mouth, and an increase in body temperature. A transferred and untreated disease becomes chronic, which can also cause deformation of the organ.
- Due to the formation of a cyst. This complex physiological process is not considered a symptom of a disease, but serves as a reason for conducting a full health examination to find out exactly what disorders a person has. The fact that there is a pancreatic cyst is usually indicated by a clearly defined altered zone in the image, which is inaccessible to signals from an ultrasound machine.
- Due to tumor formation. Sometimes a phenomenon such as deformation of the pancreas may indicate that a person is developing a malignant tumor of an internal organ. Basically, this can be said if in the ultrasound image the contours of the pancreas are deformed, and the organ itself is significantly increased in size. Ultrasound data are not the basis for diagnosis, however, changes in the image will be a signal of danger.
Meanwhile, the patient should not immediately panic as soon as he learns about any deviations from the norm in the internal organs. However, the first thing you need to do is see a doctor to undergo a full examination. This will allow you to identify the causes of violations and undergo the required treatment.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment for bending of the pancreas is treated only if the condition poses a threat to the patient's life. The main rule when making a diagnosis is to eliminate those factors that can deform the organ.
First of all, you need to think about proper nutrition. All harmful foods are excluded from the diet in the form of:
- coffee, carbonated and alcoholic drinks;
- fatty meats and fish;
- baking, muffins and confectionery products;
- semi-finished products;
- fresh bread;
- legumes;
- canned food, smoked meats and marinades;
- sour fruits and berries;
- coarse varieties of cereals;
- sausages.
Classification of chronic pancreatitis according to Khazanov
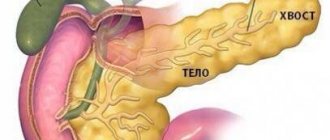
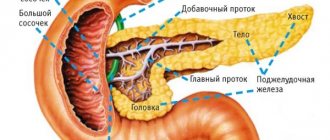
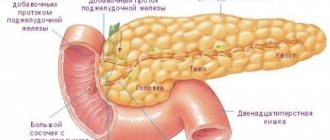
The pancreas consists of a body, head and tail. Classifications do not take into account the location of the inflammatory process. In medicine, forms of sluggish pancreatitis according to Khazanov’s classification are most often used.
Interstitial (edematous form) appearance. Clinical manifestations are closest to the acute phase of the disease. ITS duration is six months. Patients complain of severe pain, nausea and vomiting. During the course of the pathology, the tissue surrounding the pancreas often changes. Complications develop in 30-40% of all morbidity cases.
Recurrent pancreatitis is accompanied by frequent relapses up to 2-3 times a year. The pain syndrome is less pronounced. According to ultrasound examination, the contours of the organ change little, the structure is relatively homogeneous and compacted. Pathology occurs in 50% of cases. It is extremely rare for patients to develop complications. The prognosis is positive with timely and adequate treatment.
Other forms of indolent pancreatitis:
- Fibrous-sclerotic. According to ultrasound, iron rarely increases; in some patients it decreases altogether. There is pain syndrome. The pancreatic ducts dilate. This form of pancreatitis often leads to complications. The course of the pathology is persistent.
- Cystic form. Ultrasound shows uneven contours of the organ, enlargement of the gland, and the presence of small cysts filled with fluid. Large ducts expand. This pathology is diagnosed in 6-10% of patients.
- Hyperplastic appearance. The pain syndrome is severe, patients experience weight loss, and local gland enlargement. Approximately 70% develop complications. The disease is severe.
We invite you to read: The importance of marigolds for the pancreas and other systems in the body
If there is a cyst in the pancreas or a pseudotumorous form of pancreatitis, you can palpate tumor growths that are associated with the pancreas.
Therapy of the disease
Therapeutic treatment is necessary only in case of acute inflammatory process. Tumors are observed from the first days and treated by oncologists. In case of injury, tumor, compression of the duodenal bulb by the parenchyma of the gland and the development of intestinal obstruction in this place, treatment is surgical.
Medicines
Pancreatitis is a common cause of the appearance of an angular bend, which appears with an acute onset. With timely and adequate treatment, the iron returns to its normal position. Therefore, it is necessary to begin therapy as early as possible using:
- antispasmodics,
- painkillers,
- antibacterial,
- anti-enzyme,
- enzymatic agents.
Phytotherapy
Herbal medicine is not suitable as a method of treating pathology that has caused bending or deformation of the pancreas. In acute pancreatitis or during exacerbation of a chronic process, it is contraindicated: it can worsen the course by adding an allergic component. The disease is too serious and can cause severe complications, often leading to death, so the use of medicinal plants for its treatment is not recommended. Similarly - when a gland tumor is detected.
In other cases (in case of injuries, congenital anomalies, cysts), the method is ineffective.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment are used only for pancreatitis: in the acute phase, when the child cannot eat, warm mineral alkaline water without gas is used. The frequency and volume of fluid you drink is determined by your doctor. After 2–3 weeks, in the phase of unstable remission, symptomatic physiotherapy is used to:
- relieving spasms,
- improving the outflow of pancreatic juice,
- anti-inflammatory action,
- restoration of blood circulation in the affected organ,
- improving motility of the stomach and duodenum.
An effective method is:
- electrophoresis with novocaine, antispasmodics (papaverine, platiphylline, No-Shpa), liquid mud preparations (medicinal mud, peloidin, humisol),
- Ultrasound in pulsed mode relieves pain well and normalizes gastric secretion.
Disease severity
The chronic form can constantly recur, which leads to an exacerbation of the pathological process. Inflammation can lead to severe organ failure in a short period of time.
With a long-term disease, irreversible changes are observed in the organ, leading to complete dysfunction of it. In medical practice, the disease is divided depending on the severity.
The initial (first stage) lasts no more than ten years. It is characterized by long periods of remission, however, no less long periods of exacerbation. The pain at this stage is wandering, most often the pain syndrome is localized on the left hypochondrium. Dyspeptic syndrome after treatment is completely leveled.
Subsequently, the disease progresses. Signs of exocrine insufficiency are observed; they are intense. The pain syndrome decreases slightly, but doctors note that this is bad, since new foci of inflammatory processes form in the pancreas.
In severe forms of the pathological process, various complications develop. There is severe pain; usually painkillers do not help relieve them. The stability of the dyspeptic syndrome is noted.
Complications arise (according to Ivashkin’s classification):
- The flow of bile is disrupted.
- Portal form of hypertension.
- Infectious abscesses.
- Inflammatory transformations - cysts, cholecystitis, acute form of renal failure, bleeding in the stomach, etc.
- Endocrine disorders: pancreatic diabetes mellitus, hypoglycemia.
Gland deformation in children
Hereditary factors, unbalanced irregular diet and other reasons can lead to bending of the pancreas in children. Diseases of the digestive system, in particular pancreatitis in all its diversity, are often to blame for the deformation of the gland.
When specialists conclude that a child’s organ is deformed, do not panic. In most cases, as mentioned above, this will pass over time as it develops and grows. But first, it’s still worth visiting a doctor and undergoing a full examination; this will help prevent the development of complications if any diseases occur. Treatment consists primarily of proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle.
Bend of the pancreas is one of the possible organ disorders. This deviation is not always considered a pathology. The pancreas is responsible for insulin synthesis and digestive activity. Therefore, any ailment of the gland can lead to dysfunction. To prevent negative consequences, you need to take care of your health and undergo regular examinations. If you feel unwell, you should consult a doctor rather than ignore the symptoms.
Depending on the location and size of adjacent organs, the pancreas can be of one form or another:
- Dumbbell-shaped;
- Evenly oblong;
- With thickening in the head area.
All these are variations of the norm. Moreover, organ movement also occurs and is not considered a pathology. When a person lies down, the organ is located under the stomach, in accordance with its name. While in a standing position, the gland moves closer to the back.
In medical terminology, there is no such thing as a bend/kink/bend of the pancreas due to the ability of the organ to change location and have an individual shape. The tissues allow the gland to bend, straighten, and even curl into a ring.
The diagnosis of a bent pancreas in a child is fundamentally incorrect. This deviation does not pose a threat. The only thing that can be dangerous about a bend is strong compression of the duodenum, when the resulting ring from the organ begins to negatively affect the digestive process, causing intestinal obstruction.
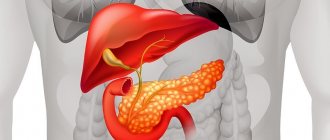
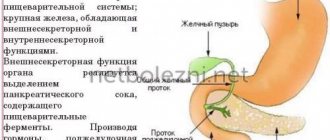
The pancreas is an important organ responsible for normal human digestion. It is located behind the stomach in its lower part and has an alveolar-tubular structure. In terms of size, iron in the human body ranks second after the liver. It produces special enzymes that promote complete absorption and digestion of food.
Pancreas shape
The pancreas can have different shapes. For some people it is bent, for others it resembles the letter “L”, for others it has an elongated shape. This factor depends on the location of neighboring organs, as well as the presence of angles and thickenings in various sections.
When examining a child or an adult, you can see that the pancreas even tends to shift. So, in a lying position, it moves downwards, under the stomach. If a person is standing, then the organ is located closer to the back, only a small part of it is “hidden” behind the stomach.
Bend or bend
In medicine, there is no such thing as a “bend” of the pancreas.
Since an organ can have different shapes, that is, its tissues allow it to bend, straighten and even curl into a ring, then such a pathology does not exist. However, many parents, when examining their child, hear that the baby has a kink in the pancreas. This phenomenon does not pose a danger to health in general or to digestion in particular.
An exception is a strong bend of the organ when it is folded into a ring, inside of which is the duodenum. In this case, difficulties with digestion, or rather, obstruction, may occur. This pathology is very rare.
In most cases, bending of the pancreas is a temporary phenomenon. In newborn babies, the organ is wedge-shaped with a small head. As the gland grows, it changes its shape and often becomes elongated or forms bends.
We suggest you read: Treatment of acute and chronic pancreatitis
Deformation
If the bend of the pancreas is not a pathology, then the deformation of the organ requires observation by specialists. In a child, this phenomenon becomes a consequence of the following diseases:
- Pancreatitis suffered in acute form. This disease poses a danger to the pancreas. With pancreatitis, there is an upward displacement of the organ and its slight deformation. This can be either an angular bend or multiple bends. If the disease is detected at an early stage, treatment of the child is effective and helps prevent negative consequences. It is difficult to see pancreatitis - in its acute form it is manifested by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pain in the left side, an unpleasant taste in the mouth, and an increase in body temperature. A transferred and untreated disease becomes chronic, which can also cause deformation of the organ.
- Cyst. Unfortunately, it is impossible to examine the pancreas in detail even with ultrasound. However, a cyst-like formation can be detected by the uncharacteristic outline of the deformation site for the organ. Treatment is conservative with timely diagnosis of the disease.
- Tumor. An unusual bend in the pancreas, characterized by protruding edges that do not have clear boundaries, may indicate a tumor. In children, this phenomenon is extremely rare, but still occurs.
Deformation of the pancreas in a child should be carefully examined to identify the disease at an early stage. Often the cause is heredity, poor nutrition and acute pancreatitis.
The detected deformation does not always indicate the pathology of the organ and the presence of a disease. This factor should only become an impetus for a thorough examination of the child.
Kinking and bending of the pancreas is not a problem or even a diagnosis. Parents have only one task: to provide the child with proper, healthy nutrition and carefully monitor his digestion. Any deviations should be consulted with a specialist.
The most important organ of digestion is the pancreas, which ensures the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The organ is located in the lower posterior part of the stomach and has an alveolar-tubular structure. The glandular tissue has a shape slightly smaller in volume than the liver. The main purpose is the production of specific digestive enzymes. Bend of the pancreas, especially in a child, is a pathology that requires treatment.
The pancreas has a different shape, which depends on the location of the organ relative to other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, the presence of thickenings or angles in different parts of the mucosal tissue. It can be bent or oblong, or it can resemble the letter “L”.
The glandular tissue can shift depending on the body position of the child or adult being examined. For example, when lying down, the pancreas moves downwards, under the stomach. When positioned vertically, the gland is adjacent to the back and partially hidden behind the stomach.
Children's pancreas is susceptible to many serious diseases due to hereditary factors, dietary disorders and other influences. Often the deformation is caused by the consequences of pancreatitis in acute and/or chronic form, which manifests itself with clearly defined symptoms.
Changes in the shape of the pancreas can occur with or without its displacement. Sometimes deformation is accompanied by a change in size.
Acute pancreatitis can cause organ deformation.
The effectiveness of treating pathology in children depends on the degree of deformation, displacement and the stage at which the process is detected. Deformation in the gland can be caused by:
- Acute pancreatitis, in which the organ moves upward and is slightly deformed. You can observe an angular bend or multiple bends. Detecting a problem early in its development helps avoid complications. Symptoms of pancreatitis include nausea with vomiting, loose stools, left abdominal pain, metallic taste in the mouth, and fever. More often it causes deformation of the organ, the transition from the acute stage to the chronic stage.
- Cystic formations detected on ultrasound in the form of uncharacteristic outlines of the organ lining.
- Tumors characterized by kinks of a non-standard shape with protruding edges without a clear edge. Rarely occurs in childhood.
There is no medical term for “bending” of the pancreas. This is explained by the ability of the organ to change its shape depending on its location. Glandular tissue can take various forms - straighten or bend, wrap itself in a ring. Therefore, a kink or bend in the pancreas should not be a cause for concern if:
- does not harm the health of a child or adult;
- does not cause discomfort;
- does not interfere with digestive function.
You should worry when the gland is bent into a ring, when the duodenum is captured. This process causes digestive problems and intestinal obstruction.
Often, bends of the gland in children are temporary. The gland of newborns has a small head and a pointed body. As it matures, it changes shape, stretches out or bends slightly. When a child is diagnosed with a kinked or bent gland, parents are required to provide:
- proper selection of a healthy diet;
- Digestive control.
Heredity, violation of rules and regularity of nutrition can cause serious diseases. For example, due to acute or chronic pancreatitis resulting from poor diet, a child more often has gland deformities. Sometimes disturbances or changes in the position of the child's pancreas have nothing to do with the disease. But in order to prevent the risks of developing diseases, the child needs to undergo a general examination.
Any transformation of glandular tissue in children should be a reason to consult a doctor, who will conduct an examination to identify the true cause of the deformation of the organ and select the necessary treatment. Deformation of the child's glandular tissue can occur with or without displacement in any direction. Typically, modification of the organ is accompanied by an increase in the size and volume of the pancreas.
Symptoms of pathology
Deformation of the pancreas can occur due to acute pancreatitis. In this case, the organ moves upward and changes its shape. Bending may occur in several areas. Characteristic symptoms arise, accompanied by pain to the left of the navel and slightly above, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. The temperature may rise, there is always no appetite.
A bend in the pancreas may not always cause discomfort. However, many parents are scared, because not everyone knows what it is. The fact is that it is not the organ itself that is deformed, but the glandular tissue. However, such a process does not always require intervention. If changes in the gland are not accompanied by discomfort or disturbances in digestive function, then you can simply do an ultrasound periodically to monitor the situation.
A dangerous type of organ bending in children is twisting it into a ring. In this case, the duodenum is involved in the process, which creates obstruction. This creates a clear clinical picture. If such a process is not detected in time, the prognosis is extremely unfavorable.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Succinic acid - properties, benefits for various diseases, instructions for use (tablets, capsules, solution, powder), weight loss with the help of succinic acid preparations, reviews, price
A sign of deformation in a child can be detected at an early age, but gradually the gland acquires the correct shape. However, if the irregular shape persists, then such children need proper nutrition without errors.
What is pancreatic deformation and how dangerous is it to health? Patients may ask this question after undergoing an ultrasound scan. Any changes in the structure of organs that occur in the human body indicate the presence of some kind of disorder. Such manifestations refer to the symptoms on the basis of which the disease is diagnosed.
If an ultrasound examination reveals deformation of the gland, it is important to pay special attention to this and visit a doctor for a full examination. This will avoid the development of serious diseases that can be caused by organ deformation.
The pancreas is responsible for the proper process of digesting food by the digestive system, producing special enzymes. This organ is located next to the lower part of the stomach and is second in size after the liver among all human internal organs.
The pancreas comes in completely different shapes, depending on the individual characteristics of the location of nearby organs in a person. For some it is elongated, for others it may have the shape of an angle.
In this case, the pancreas can shift when a person changes position. In a lying position, the organ will be placed lower, while it will move towards the back if the person is standing.
Since the pancreas has the ability to change shape, its tissues can bend, straighten or curl. Accordingly, the process of changing the shape of this internal organ does not relate to pathology.
Many parents, hearing from a doctor that their child has a bend in the pancreas, begin to worry. However, this phenomenon does not pose any danger to children and adults.
As an exception, pathology may include the case when the pancreas tightly curls into a ring, wrapping around the duodenum. For this reason, the patient may experience digestive problems as food cannot pass through the normal route. However, such a problem is extremely rare.
In general, the bending of an internal organ is usually temporary, since during the process of human growth and development it unfolds and often takes on an elongated shape.
Diagnosis of pathology
In contrast to bending and kinking, deformation of the pancreas occurs as a result of some disease. Illnesses suffered by the child can lead to this phenomenon:
- Pancreatitis in acute form. There is an upward displacement of the organ and slight deformation. If a problem is detected in the initial stage, there are no complications. The onset of pancreatitis can be determined by the symptoms: pain in the left side of the abdomen, loose stools, nausea and vomiting, fever and a feeling of metal in the mouth.
- A cyst on the pancreas can be congenital or acquired. The first is small in size and is usually discovered by chance during an ultrasound scan of another organ.
- Tumors of irregular shape appearing on the gland. Rarely occur in childhood.
Deformation of the pancreas must be given attention and examination so as not to miss the onset of the disease. This does not always indicate the presence of a disease, but a thorough check of the child’s condition will only be beneficial.
Treatment of the child's gland should be aimed at eliminating the causes of deformation and eliminating the unpleasant symptoms accompanying the disease. The purpose involves complex therapy with the use of medications and the use of traditional medicine. Considerable attention is paid to nutrition and preventive measures to prevent diseases of the gastrointestinal organs. Surgery is used only as a last resort.
Kink and bend are not anomalies of the pancreas. It is important that parents provide their child with a nutritious, healthy diet and, if they see signs of indigestion, promptly seek advice from a doctor.
Symptomatic picture
Symptoms of bending of the pancreas are absent or mild. Often this pathological process is confused with a bend in the gallbladder. But this is not true, because deformation of the pancreas can be congenital.
If the bend of the pancreas in a child is accompanied by severe curvature or compression of the duodenum, then the first signs will begin to appear in the form of:
- strong painful feeling in the abdominal area. The pain can be sharp, sharp, aching or dull;
- rapid breathing;
- gastric reflux. This process can lead to the formation of ulcers on the stomach and intestinal walls;
- nausea and vomiting;
- strong secretion of saliva.
Some patients report pain and cramping after eating. Others complain of heartburn and belching of sour matter or air. In most cases, constipation is observed, since when the pancreas bends, the function of the pancreas is partially limited.