Ultrasound diagnostics to determine characteristics
The timing of ultrasound of the appendages and uterus depends on the indications for its conduct.
Diagnostics can be performed on almost any day of the cycle. However, the reliability of the study depends on the phase of the cycle. Gynecologists recommend performing an ultrasound of the appendages and muscular organs during the first phase. The optimal execution time is from 5 to 10 days of the cycle. This is due to the condition of the inner layer of the uterus. After menstruation, the endometrium gradually begins to thicken, which reduces the ability to detect benign formations, such as fibroids or polyps.
For some gynecological pathologies, the doctor may prescribe an ultrasound in the second phase of the cycle. It is advisable to study the uterus and appendages against the background of endometriosis from the 16th day of the cycle.
Important! Often, performing an ultrasound of the appendages and uterus is of an emergency nature. In such cases, the phase of the cycle is not significant.
Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages is ideally performed on days 5-7 of the cycle. This period was not chosen by chance. It is after menstruation that the endometrium is thinnest, which makes it possible to accurately assess pathologies such as hyperplasia of the inner lining of the uterus, fibroids, etc. If the study is carried out in the second half of the cycle, the growing endometrium will hide small tumors and defects, distorting the information.
In addition, from the second half of the cycle, a follicle or cyst of the corpus luteum is normally detected in one of the ovaries. At this point, it is difficult for a specialist to assess the existing cyst - its functional or pathological nature. Small cystic inclusions in the ovaries are present from the beginning of menstruation until days 5-7 of the cycle.
To assess the functionality of the ovaries, the procedure is carried out three times during the cycle on days 8-10, 14-16 and 23-24. If the test does not show pregnancy, and the temperature in the rectum remains elevated for more than 10-14 days, an ultrasound is prescribed to exclude cystic formations.
During pregnancy, three mandatory ultrasound examinations are performed to assess the condition of the uterus and fetus.
Diagnosis of the uterus and ovarian appendages is carried out in order to identify characteristics and anomalies in the functioning of the reproductive system. During the examination, many different factors may be found that require further examination, or immediate hospitalization. For example:
- Atypical location of the ovum during pregnancy. This will allow you to prevent problems caused by incorrect position in advance, as well as correct the course of pregnancy
- Ectopic pregnancy. Early transvaginal ultrasound diagnostics allows you to see in advance the position of the embryo’s attachment, which allows you to terminate a tubal pregnancy in time, or to place the woman in storage in the event of another type of ectopic pregnancy.
- Anomalies of uterine development.
- Tumors. They can only be determined by drawing up a comprehensive picture of all three ultrasound examinations.
- Viral formations.
- Other pathologies.
To choose the best time for a uterine ultrasound, it is important to determine the purpose of the examination. In women capable of reproduction, the uterus and ovaries normally undergo constant changes that repeat each cycle. Each time the body prepares for a possible pregnancy, and if it does not happen, menstruation passes and the cycle repeats all over again.
Every time after menstruation, follicles begin to appear in the ovaries, among them the largest in size is identified - the dominant one, from which the egg is subsequently released. The endometrium (the inner mucous layer of the uterus) changes structure at this time, becomes thicker and prepares to support the development of the fetus if the egg is fertilized.
To monitor the functionality of the ovaries and observe whether the increase in the size of the dominant follicle is normal, several ultrasound examinations are sometimes performed at different periods of the same menstrual cycle. This series of examinations is called ultrasound folliculometry.
How to carry out the procedure
Of the listed methods of carrying out the procedure, the most convenient and comfortable for patients is the method of examination through the abdominal wall. In this case, the woman lies down on the couch, bares her stomach and lowers her trousers. The doctor applies a special gel to the skin and begins the examination.
Transvaginal examination does not cause pain, but sometimes causes discomfort to the patient. To carry out the diagnosis, the woman lies down on the couch and bends her knees. A hypoallergenic condom is put on the sensor and lubricated with a special gel, then carefully inserted into the vagina.
If a girl is to undergo an ultrasound examination through the rectum, she needs to lie on her side. Next, the procedure is the same as for a vaginal examination, only the sensor is inserted into the anus.
In total, the diagnosis is carried out in 15-20 minutes. The patient immediately receives the research results.
How much does it cost to undergo a gynecological ultrasound?
Ultrasound of the appendages and uterus varies in type and mode of examination. Depending on the indications, a woman is prescribed one of the types of ultrasound in gynecology:
- Transvaginal. The examination of the female genital organs is carried out using a special sophisticated sensor, which is inserted into the vagina. The instrument is first lubricated with gel. Transvaginal ultrasound diagnostics is often used in obstetrics to determine pregnancy in the early stages.
- Transrectal. An ultrasound probe passes through the rectum. The research method is used mainly among virgins.
- Transabdominal. Another procedure is called ultrasound through the abdominal cavity. The gel is squeezed onto the lower abdomen, after which the sensor is passed. The study allows you to thoroughly examine the uterus and appendages. The examination method is used in case of suspicion of the development of tumors, monitoring pregnancy in the 2nd and 3rd trimester.
Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages is carried out in different modes, each of which has its own special capabilities for research:
- Two-dimensional ultrasound diagnostics. The internal organs of the pelvis are visualized in one plane. Using this mode, the shape and size of the uterus, the location of the cervical canal, and the condition of the ovaries and their appendages are determined.
- 3D static mode. The method combines a three-dimensional image in two or more planes at once. Internal organs are examined in layers at different depths up to 1 millimeter. Ultrasound of the uterus in 3D mode during pregnancy in the second trimester determines the sex of the child, reveals the presence of neoplasms and their nature.
- 4D graphics in ultrasound. When examining the uterus and appendages, the image is broadcast in real time. So, during pregnancy, a woman can see the intrauterine movements of the child. 4D mode shows the direction of blood flow and its condition.
Ultrasound devices with 3D and 4D modes are often combined with CID diagnostics and color Doppler mapping (CDC). Sometimes several modes and types of ultrasound of the uterus and appendages are combined simultaneously. This technique is mainly used when examining pregnant women.
In private paid medical institutions, conventional abdominal or transabdominal ultrasound diagnostics costs 600 rubles or more. The transvaginal procedure costs 200–300 rubles more.
Gynecological ultrasound is considered a completely painless procedure, which detects pregnancy or female diseases. This diagnostic method is used throughout pregnancy: if necessary, it is done more than the official three times.
Have you undergone an ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages? Tell us about your feelings in the comments. Share the article with your friends on social networks. Be healthy.
Is it possible to diagnose cancer?
By examining the pelvic organs with ultrasound, it is quite easy to identify a tumor process that affects not only the uterus, but also the cervix. If a space-occupying lesion is detected, it is necessary to conduct an additional examination, namely a biopsy. Having received several fragments of the tumor, a histological examination is carried out, which will render a verdict - what is the nature of the detected formation.
With regular ultrasound examination of the internal genital organs, the risk of detecting advanced cancer diseases is significantly reduced.
https://youtu.be/W5FlxhKnWvU
Errors
Diagnosis using ultrasound is a reliable and accurate method. It has been proven that the scanner error can be no more than 10%. With the help of this device, you can not only determine the fact of pregnancy at an early stage, but also determine its real timing accurate to the day.
The possibilities of ultrasound are vast, but we must not forget about the human factor. The accuracy of the diagnostic result directly depends not on the device itself, but on the professionalism of the specialist. Also, the doctor must inform the patient how to prepare for an ultrasound diagnosis of the uterus and appendages and how the procedure is performed.
What does an ultrasound of the uterus and appendages show?
When conducting a diagnostic study, a specialist may detect the following diseases:
- Uterine fibroids. This is a benign formation from the muscular layer of the organ. There are several fibroid nodes, their sizes vary from a few millimeters to 50 cm. Ultrasound determines the number, size, location and growth dynamics of fibroids.
- Hyperplasia and endometrial polyps. Hyperplasia is characterized by diffuse or focal excessive growth of the endometrium. Its thickness in this disease is more than 7 mm in the first phase of the cycle. Polyps form from focal hyperplasia. There may be several of them, the size of the formations can reach several centimeters. Using ultrasound, these conditions are assessed and the necessary treatment is prescribed.
- Cysts and tumors of the ovaries. Cysts can be functional or pathological. The former appear and disappear again during the cycle without any intervention. Pathological cysts require treatment. Ovarian tumors may indicate oncology. Therefore, decoding an ultrasound image of a neoplasm in the ovary is a responsible task that is solved by more than one specialist.
- Apoplexy or rupture of the ovary. This is a dangerous condition that occurs spontaneously, for example as a result of injury. Ultrasound allows you to distinguish apoplexy from ectopic pregnancy or appendicitis, evaluate bleeding, and make the correct diagnosis.
- Tuboovarian formations - hydrosalpings. Appear against the background of inflammation in the pelvic organs. Ultrasound of the appendages and uterus not only reveals this abnormal condition, but also helps eliminate it using hydrotubation of obstructed fallopian tubes under ultrasound guidance.
- Pathologies associated with pregnancy. It could be an ectopic pregnancy, a frozen pregnancy, or a hydatidiform mole. A placental polyp may be detected: if an ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries after a cesarean section, natural birth or abortion reveals a remnant of placental tissue in the organ cavity, its urgent removal is necessary.
Reliable results of decoding an ultrasound of the uterus and its appendages require a specialist to have excellent knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the female body, as well as the clinical situation. The results of the study can only be assessed by a person with a medical education. You cannot independently decipher the ultrasound protocol and determine the diagnosis, as some women do.
The appendages are the formations on the side of the uterus. Echo-positive inclusions in their structure contain echo-negative elements of round or oval shape.
Ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages is performed to diagnose physiological and pathological conditions. The method is indispensable for identifying diseases in girls before sexual activity begins. Using ultrasound, you can observe the maturation of the follicle and confirm ovulation and intrauterine pregnancy. Ultrasound allows you to identify the threat of spontaneous abortion and prescribe adequate therapy to prevent miscarriage.
Important! During pregnancy, screening ultrasounds are performed to assess fetal development.
Typically, the first ultrasound is performed after the onset of puberty. Diagnostics helps to identify pathologies of uterine development by determining the size of the muscular organ and appendages. The specialist also evaluates their structure, position and functioning.
Anomalies in the development of the uterus often lead to infertility. Ultrasound can reveal the saddle-shaped, bicornuate, horseshoe-shaped nature of the muscular organ, and the presence of a septum. In adolescence, a specialist sometimes diagnoses ductal atresia, complete and incomplete duplication of the uterus.
When performing an ultrasound of the appendages and uterus, the following pathologies are determined:
- Neoplasms (fibroids, cysts, polyps). The method complements the gynecological examination and allows you to assess the size of the nodes, their location, and approximate composition. Blood flow analysis is a differential diagnosis of benign and malignant formations. Poor circulation usually indicates necrosis and the need for surgery.
- Endometriosis. The lesions are located in the area of the appendages, uterus, cervix and other parts of the small pelvis. The presence of endometriosis is indicated by areas of reduced echogenicity, as well as an increase in the volume of the uterine body and the friability of its structure. Endometriosis of the appendages is most often represented by cystic changes.
- Cysts. Pathology of the appendages is usually detected by ultrasound. An ovarian cyst can be suspected by ultrasound when determining the size of the appendages and the number of follicles. Thickening of the capsule of the paired organ and the absence of ovulation are essential in the diagnosis of PCOS.
Important! The study is necessary to determine hyperplasia and hypoplasia. In these pathological conditions, there is a disruption in the maturation of the endometrium, which contributes to infertility and the growth of tumor-like neoplasms.
Ultrasound of the female organs allows you to monitor the presence of diseases in the early stages and the state of pregnancy. If it is impossible to get pregnant, a woman often turns to this method of studying the reproductive system. Follow-up ultrasounds are prescribed to check the effectiveness of treatment for gynecological diseases.
Ultrasound diagnostics reveals:
- single cysts in the uterine cavity;
- endometrioid lesion;
- inflammation in the appendages, uterus;
- polycystic disease, polyps;
- twisting of cyst pedicles;
- increased uterine tone during pregnancy, the condition requires medical supervision;
- fibroids;
- malignant neoplasms;
- diffuse changes in the uterus, more often diagnosed in the myometrium;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- the presence or absence of pathologies, hypoxia in the fetus;
- a picture of the female reproductive system after childbirth;
- condition of the uterus, appendages after abortions, miscarriages and frozen pregnancies;
- excessive accumulation of fluid in the pelvis.
Ultrasound results: What can an ultrasound show?
The most important conditions:
- uterine fibroids
- malignant neoplasms
- cervical cancer
- pathology of the fallopian tubes
- ovarian cysts
- benign neoplasms
- ovarian cancer
Uterine fibroids
Myomas look like round formations with a diameter of 0.5-10 cm. They are located in the myometrium and can protrude into the uterine cavity; larger fibroids look like a thickening of the uterine wall or hang down like a “backpack”. Myomatous nodes can undergo calcification, then they have the appearance of hyperechoic structures capable of casting an acoustic shadow.
Leimomyoma was discovered in a 46-year-old patient who complained of vaginal bleeding. The image clearly shows an isoechoic formation.
If there are several myomatous formations, this can increase the size of the uterus and change its echostructure. It is often impossible to distinguish individual nodes from each other. It is important to find out that the node originates specifically from the uterine wall and not to confuse it with the formation of ovarian tissue. The likelihood of such an error is high, especially if the fibroids are located laterally. The main diagnostic criterion for fibroids is that the wide surface of the node is in contact with the wall of the uterus.
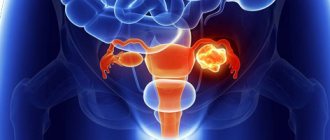
Malignant neoplasms
Cancer of the body or cervix in the early stages is difficult to diagnose using ultrasound. Limited areas of hypoechoic or heterogeneous structure are suspicious. Large formations are clearly visible on the screen, but determining their primary location is quite difficult.
Fallopian tube pathologies
Pathology of the fallopian tubes may manifest as their obstruction. During an ultrasound examination, various constrictions and adhesions are detected. Also, pregnancy can develop in the cavity of the fallopian tube, then a fertilized egg can be seen in the tube.
Ovarian cysts
It is necessary to distinguish follicular cysts from true cysts and cystic tumors. Any cyst less than 2.5 cm in diameter found in a woman before menopause should be considered normal unless proven otherwise. Cystic changes in the period of follicle maturation are physiological and temporary.
Follicular ovarian cyst
If these cysts are identified, it is enough to advise the patient to repeat the ultrasound examination at the next visit. If the cyst is more than 2.5 cm in diameter, it is recommended to undergo regular additional examination with a transvaginal sensor. Often such cysts disappear on their own. True cysts are harmless. They can reach significant sizes and even fill the entire small pelvis.
True cysts differ from cancer, cystadenoma, and cystadenocarcinoma in that they do not contain a tissue component . If the examination reveals additional growth in the wall of the cyst, or their group accumulation, multi-chamber structure, increased vascularization, it is recommended to remove the ovary. MRI is used to clarify the diagnosis.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
The scan reveals numerous small cysts formed from immature follicles, the occurrence of which is associated with prolonged stimulation with gonadotropin. There are pronounced fibrous changes in the ovarian tissue, the capsules are compacted. On ultrasound, ovarian tissue is heterogeneous, often hyperechoic.
Polycystic ovary syndrome in section
Cancer and benign neoplasms
Cancer is asymptomatic for a long time; often, by the time the diagnosis is made, the tumor usually turns out to be inoperable. Patients note an enlarged abdomen due to the significant size of the tumor and/or cancerous ascites. Ultrasound reveals a mass formation of tissue, cystic or mixed type, which can reach even 20 cm in combination with or without ascites. Abundant blood supply also indicates a malignant nature. If the formation is large, it can be difficult to determine the primary location . Ovarian cancer is quite rare. Not every tumor of this organ is malignant; benign processes can be found much more often. MRI is usually used to clarify the diagnosis.
Interpretation of ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries
When deciphering the examination results, the normal sizes of the uterus and ovaries with appendages are compared with the woman’s organs. The normal size of the uterus according to ultrasound and the condition of the appendages consists of several parameters:
- When conducting diagnostics in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, there is no free fluid in the pelvis. A small accumulation of fluid is possible during the onset of the ovulation phase.
- In the ultrasound image, the ovaries look voluminous. This indicator is influenced by the reproductive period. Normally, the contour of the ovaries is always clear.
- The neck has clear contours. During the examination, the cervical canal is visualized. The cervix becomes longer under normal conditions only during pregnancy (see Ultrasound of the cervix during pregnancy). In nulliparous women, the thickness according to a special table does not exceed 3 centimeters.
- The uterine cavity is shown as a homogeneous structure with a bright outline. In a woman who has given birth, the normal size of the uterus on ultrasound suggests a slight dilatation of the uterus.
- The size of the endometrium during examination is assessed differently. This is influenced by the age of the subject and the phase of the menstrual cycle. So, in girls under 10 years of age, the endometrium is thinner, since they have not yet had their periods.
- The full size of the uterus according to the norms is calculated individually: the presence of menstruation, age, pregnancy, and childbirth are taken into account. In nulliparous women, the body of the uterus does not exceed 4.5 centimeters.
- The shape of the organ should look like a pear.
Ultrasound diagnostics can reveal diseases:
- Myoma. It is a benign formation. Ultrasound finds myomatous nodes with a diameter of 2 millimeters. In the picture, the pathology looks like an outlined capsule with uneven dots.
- Adenomyosis. Appears when the endometrioid layer grows inside the muscle. During the study, the disease appears as a diffuse heterogeneous area of the myometrium with small zones that differ sharply in the degree of echogenicity and ability to reflect ultrasound waves.
- Inflammatory process in the ovaries. An ultrasound is diagnosed when the ovaries and appendages are enlarged (more than 9 cubic centimeters). The outline of the organ becomes unclear due to swelling. An accumulation of fluid is detected in the retrouterine space.
- Cyst in the ovary. During the examination, the doctor records round-shaped formations filled with liquid. The latter consists of fat, blood, pus, and hair accumulations.
- Polycystic. It is diagnosed when more than 12 follicles are detected, which are less than 1 centimeter in diameter. On an ultrasound image they look like pearl beads.
Inflammation of the appendages is very difficult to detect with ultrasound. Typically, a woman is referred for examination with a suspected diagnosis due to persistent pain in the lower abdomen outside of menstruation, increased body temperature, and the presence of purulent discharge with blood from the vagina.
The inflammatory process in the appendages is often accompanied by a vague outline of the ovaries during ultrasound diagnostics. During the procedure, the woman feels discomfort, sometimes pain.
Errors during ultrasound of internal female organs occur in rare cases. This happens if the sonologist is inexperienced or the procedure is performed at the wrong time. It is important to consider the day of the menstrual cycle.
Usually, the doctor gives the results of the examination to the woman on the day of the procedure. The interpretation of the ultrasound includes data on the shape and size of the uterus, the thickness of the endometrium, the structure of the cervix, the size and structure of the ovaries, and the presence of follicles.
Uterine cavity
The structure of the uterus should normally be homogeneous. The contours of the organ must have clear boundaries. If the picture is blurry, the specialist draws conclusions about the inflammatory process. The detection of hyperechoic inclusions may indicate polyps, fibroids and organ cancer.
In a nulliparous woman, the uterus has a length of 43-47 mm, a width of 42-50 mm, and a thickness of 32-34 mm. For those who have given birth, the sizes will be larger, within 10 mm.
Cervix
The normal length of the cervix is 20-40 mm, the anterior-posterior size is 25-35 mm. According to ultrasound, its structure should be homogeneous.
The cervical canal, filled with mucous contents, has a diameter of up to 3 mm. If the neck or canal is enlarged, we may be talking about inflammation.
Immediately after ovulation, a small amount of fluid is detected behind the uterus. This is the norm. If the fluid is detected at another time, most likely we are talking about inflammation in the pelvic organs.
Ovaries
Normally, the ovaries measure 25x30x15. The volume of the ovary is 5-8 mm³. If these parameters are higher than normal, we may be talking about polycystic disease or oophoritis.
Normally, the ovary contains several follicles 4-6 mm and one dominant follicle up to 25 mm. If its diameter exceeds 25 mm, we are talking about a functional cyst.
The fallopian tubes
Ultrasound of the fallopian tubes is performed as a separate study, allowing an accurate assessment of their functionality. It is prescribed to women who suffer from infertility.
During the procedure, the doctor fills the uterine cavity and tubes with a contrast agent, after which he evaluates the patency of the latter on the monitor. With a regular ultrasound, it is impossible to assess the condition of the fallopian tubes, since their lumen will not be visible.
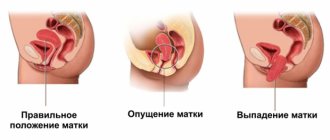
Bicornuate uterus
It is a consequence of the pathology of the patient’s intrauterine development. This condition is fraught with infertility, miscarriages, and intermenstrual bleeding.
Ultrasound determines a bicornuate uterus in the form of division of its cavity into two sections. Other anomalies that usually accompany it are also identified.
After an ultrasound scan of the uterus, the results should be interpreted by your attending physician. The diagnostician usually makes only a preliminary diagnosis in his conclusion. Your doctor may disagree. The normal sizes of the uterus and ovaries according to ultrasound and their condition may vary depending on the age of the woman, the diseases she has suffered, and the day of the menstrual cycle. Usually they focus on average values.
Uterine cavity
It should look structurally homogeneous. The contours are without irregularities and are clearly visible. Their blurriness during an ultrasound scan of the uterus may indicate that an inflammatory process is underway. The detection of hyperechoic formations during data decoding indicates the presence of problems such as polyps, fibroids, and possibly uterine cancer, which can be seen on ultrasound. The uterine cavity may be split into two sections. This phenomenon is called a bicornuate uterus. Below we will look at it in detail.
| Group of women | Length, mm | Width, mm | Thickness, mm |
| Those who have not given birth | 45 ± 3 | 46 ± 4 | 34 ± 1 |
| Those who gave birth | 58 ± 3 | 54 ± 6 | 40 ± 2 |
Cervix
According to healthy indicators, it should be from 20 to 40 mm. in length, the anterior-posterior size should be 25-30 mm. During ultrasound of the cervix, its echostructure should be homogeneous.
Visual differences between healthy and inflamed cervical tissue
The cervical canal usually has a diameter of up to 2-3 mm. and filled with mucus. If, during an ultrasound scan of the cervix, the cervix itself or its canal is dilated, an inflammatory process may be occurring.
When performing an ultrasound, a specialist assesses the condition of the organs of the reproductive system, excludes structural anomalies and neoplasms that can be benign or malignant:
- Uterus. The muscular organ is located in the midline, the normal deviation is no more than 30 degrees. Anterior or posterior inclination is essential, indicating adhesions or abnormalities. The shape of the uterus can be pear-shaped or round. The dimensions of the uterine body in nulliparous patients are 45-34-46 mm. In the presence of pregnancies without subsequent births, the size of the organ reaches 51-37-50 mm. In women who have given birth, the uterus corresponds to values of 58-40-54 mm.
- Cervix. The dimensions depend on the surgical interventions performed, the method of delivery, and the presence of inflammatory processes. The cervix is normally a homogeneous structure with a length of 25 to 45 mm. The width is 30 mm. An increase in thickness may be observed when the uterus is bent (up to 45 mm).
- Appendages. The amount varies depending on the age period. The phase of the cycle and the intake of certain medications are essential. The permissible length is 40 mm, width – 30 mm. After the onset of menopause, the volume of the ovaries decreases.
In the absence of pathologies, the tubes may not be visualized on ultrasound. Sometimes they are defined as thin strands of a uniform structure. A change in the volume of the tubes requires an examination to exclude ectopic pregnancy and inflammation.
Attention! If an ectopic pregnancy is detected, emergency surgical intervention is performed, since the pathology is a threat to the patient’s life.
Free fluid determined during ultrasound does not always indicate ovulation. After the release of the egg, a small amount of fluid is noted in the posterior fornix. With an increase in the amount of fluid, differential diagnosis of inflammation, ectopic pregnancy, ascites and malignant neoplasms is carried out.
Gynecological ultrasound: vaginal or transabdominal?
The main advantage of transvaginal ultrasound in gynecology is its high accuracy in displaying the structure of the tissues of the pelvic organs, giving the doctor the necessary information about their functional state. Intravaginal sonography allows you to obtain detailed data on the condition of the tissues of the cervix and body of the uterus, ovaries, and visualize both fallopian tubes, while transabdominal examination allows you to examine only the left one.
Unlike transabdominal ultrasound, vaginal ultrasound makes it possible to detect and study areas of altered endometrium, which in many cases makes it possible to recognize endometriosis without performing a diagnostic operation - laparoscopy.
Despite the high information content of vaginal ultrasound, its use is not always possible. Transvaginal ultrasound is not prescribed for virgins due to the likelihood of damage to the integrity of the hymen. Vaginal ultrasound examination also cannot be used:
- if the patient is allergic to latex;
- in the later stages of diagnosed cervical cancer (due to the risk of bleeding);
- in the acute phase of diseases accompanied by inflammation, tissue swelling and severe pain (the study should be postponed until recovery or alternative methods should be used);
- in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy (due to the risk of premature contractions).
If there are contraindications to vaginal ultrasound, the doctor may prescribe transabdominal sonography or other diagnostic methods. Also, both types of examinations can be prescribed simultaneously to obtain the maximum amount of data on the condition of the pelvic organs through examination in different planes.
The results obtained during the study are interpreted by a sonologist, after which he gives his opinion and refers to the appropriate doctor to prescribe the necessary treatment.
Restrictions and contraindications
Indications for ultrasound examination of the uterus and ovarian appendages are:
- absence of menstruation if pregnancy is suspected;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle, periods may be completely absent or be more abundant and painful;
- complications that arose after childbirth, miscarriage or missed pregnancy;
- suspicion of infertility, which is caused by the abnormal structure of the uterus, ovaries and their appendages;
- setting the timing of pregnancy, assessing the condition and intrauterine development of the fetus;
- periodic pain in the lower abdomen, often occurs during the inflammatory process in the pelvic organs;
- the presence of neoplasms in the uterine cavity of various types;
- pathological changes in neighboring organs and systems - impaired defecation, pain when urinating.
A woman undergoes a gynecological ultrasound annually for preventive purposes to identify hidden diseases. It is better to detect the disease early. This way the treatment will bring quick and effective results.
Ultrasound gynecological diagnostics are performed mainly according to indications and for the prevention of diseases. During pregnancy, according to the plan, a woman undergoes 3 ultrasound screenings: in the first, second and third trimester. In case of illness, the gynecologist himself prescribes the frequency of examinations: this is how the condition of the woman’s reproductive system is monitored.
It is optimal to do an ultrasound of the uterine cavity and appendages in gynecology in the first phase of the menstrual cycle. Recommended days: from the 5th to the 10th day. This way, the result of the study will be as accurate as possible: the inner layer of the uterus with appendages is very thin at this time.
You can undergo ultrasound diagnostics during menstruation, but the result will be less reliable. At this time, the endometrium thickens. This reduces the possibility of detecting benign tumors in the uterus - polyps, fibroids.
It is better to do an ultrasound on the recommendation of a doctor. Sometimes the gynecologist sends a woman for examination in the second half of the menstrual cycle. The procedure is relevant if there is a suspicion of endometrioid damage to the uterine cavity and appendages. The second phase begins on the 16th–17th day of the cycle.
There are practically no contraindications to transvaginal scanning. The limitation is the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy - at this stage, inserting a sensor into the vagina can provoke an increase in the tone of the uterus.
For virgins, the transducer is inserted not into the vagina, but into the anus - in order to avoid mechanical damage to the hymen.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
How the procedure is done and its types
In modern gynecology, various methods of scanning the internal genital organs are used to obtain reliable information. The option of ultrasound examination is chosen by the attending physician. After performing an ultrasound of the uterus, the results are deciphered by a sonologist.
Women and girls
Ultrasound of the uterus in girls is of a preventive nature and is aimed at identifying congenital malformations and hormonal disorders during puberty. To comply with these requirements, the periods of girls’ lives before the onset of sexual activity are defined:
- within 12 months from the date of birth;
- age from 5 to 6 years;
- age from 9 to 12 years;
- age from 14 to 15 years.
Girls who are sexually active and women should, for their own peace of mind, visit a gynecologist once a year and undergo an ultrasound examination. If necessary, such visits and examinations may occur more frequently.
Transvaginal
This type of ultrasound examination of the uterus is performed using a vaginal sensor, and absolutely all pelvic organs are accessible for examination. A special condom is first placed on the sensor, then it is inserted into the vagina to a shallow depth. The procedure is painless, the woman does not experience any negative feelings.
Transabdominal
If you do not take into account the rather lengthy preparation for transabdominal ultrasound of the uterus, then this technique can be called the fastest, most convenient for screening and easiest to implement. A special gel is applied to the skin in the lower abdomen, then a sensor is installed and an examination is performed. Can be performed on girls, young women and women.
Intrauterine
This is a rather specific ultrasound technique called intrauterine, and the sensor passes the internal os, entering the uterine cavity. This type of research is aimed at a more accurate study of the disease of the uterine walls. In this case, the myomatous node or nodes, as well as the mucous layer of the uterus affected by endometriosis, are examined.
How often can you do an ultrasound of the uterus?
For an adult woman, an ultrasound examination of the uterus should become an annual procedure, even in the absence of complaints and chronic diseases.
If symptoms of diseases arise that belong to the group of indications for ultrasound of the uterus, then scanning is performed as often as required by the treatment process. The number of ultrasound examinations is determined by the attending physician. It should be remembered that the uterine ultrasound technique is absolutely safe and does not have a damaging effect on the body.
How do you prepare for the study?
Basic recommendations for preparing for ultrasound diagnostics of the uterus and appendages include an empty intestine and no gases. Such conditions ensure maximum penetration of ultrasonic waves, which affects the accuracy of the research result. It is necessary to prepare for an ultrasound 3-4 days in advance.
At this time, food that takes a long time to digest is excluded from the diet. These include fatty dishes - fried pork, smoked meats. Before an ultrasound scan of the uterus and appendages, you should not eat food that causes severe gas formation in the intestines. This applies to soda, caffeine-containing drinks, legumes, and flour.
2–3 hours before the examination, it is better to take the enzyme preparation “Festal” or “Creon” to improve the digestion process. To eliminate gases, take Espumisan or an infusion of chamomile flowers. If a woman often experiences constipation, she will have to take a laxative to empty her bowels.
With a transabdominal ultrasound, through the abdominal cavity, you need to fill the bladder. Therefore, an hour before diagnosis, a woman drinks at least 1 liter of liquid. In the early stages of pregnancy, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed. In this case, the pregnant woman is asked to empty her bladder before the procedure.
Indications for use
Gynecologists identify certain indications for performing ultrasound diagnostics of the appendages and uterus. In addition, ultrasound is performed as part of a preventive study, which is a necessary condition for the early detection of various gynecological pathologies.
https://youtu.be/4tcOU86tT3E
General indications for ultrasound of the uterus and appendages include:
- absence of menstruation or menstrual irregularities,
- confirmation or exclusion of the fact of pregnancy, anomalies of the pelvic organs,
- determination of gestational age,
- identification of pathologies in the development of the embryo and fetus,
- pain syndrome,
- suspicion of an inflammatory process of the internal genital organs,
- disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the excretory system,
- exclusion of malignant and benign tumors,
- complications arising from abortion and childbirth,
- bleeding of varying intensity,
- infertility.
Important! Experts emphasize that annual ultrasound of the appendages and uterus is a mandatory diagnostic method. Many gynecological diseases progress asymptomatically. Their identification is possible exclusively through instrumental research.