Ultrasound examinations are aimed at identifying problems in the heart, kidneys, stomach and other organs. In most cases, if diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are suspected, other diagnostic methods are used. However, in some cases, an ultrasound scan is sufficient. From today's article you will learn about what preparation should be for an ultrasound of the stomach? How is the examination carried out? Are there any contraindications for this procedure? When is an ultrasound of the stomach and intestines performed, what does this study show, and can it replace FGDS?
What is EUS and how does it differ from a transabdominal procedure? What are the advantages or disadvantages of this examination method compared to classical or capsule endoscopy? Should I do an ultrasound on an empty stomach? Is it possible to eat before an ultrasound? Where can I get an ultrasound of the stomach done, and what is the cost of the procedure?
How an ultrasound is performed: step-by-step steps
Many people are interested in learning how an ultrasound of the stomach is performed. The procedure is quite simple and does not require any action on the part of the patient.
- The patient sits on the couch, and the specialist applies a special gel to his stomach and neck.
- The doctor places an ultrasound probe on the abdomen and moves it over selected areas and at the same time examines the affected organ on the screen.
- After the doctor has examined the condition of the patient’s organs, the latter needs to drink a small amount of water. This manipulation is necessary in order to study the characteristics of the flow of fluid into the esophagus.
https://youtu.be/J5v06FtiOXQ
How to examine the stomach using ultrasound
There is no difference between the examination of the gastrointestinal tract in adults and children. Ultrasounds are performed by specially trained medical workers in a separate room at the clinic. A person lying on a couch does not feel pain during the examination. A conductive gel is applied to the abdomen to improve the signal. The ultrasound technician moves the sensor, moving it along the abdominal wall and tilting it left and right at all sorts of angles.
Transabdominal examination
Transabdominal examination is a method of radiological diagnosis of the digestive system. Ultrasound passes through the abdominal surface and is reflected from the internal organs. The image of the examined part of the gastrointestinal tract on the monitor screen is transformed from electrical impulses. The picture is devoid of color, you can see black and white tones.
The diagnostician will suggest doing the procedure in a lying or standing position. This option (when the patient is standing) shows the organs in a different way. But with the same success a functional examination of the anterior and posterior walls of the stomach is carried out. With the patient on the right side, the doctor determines the rate of intestinal peristalsis. The situation helps to draw a conclusion about whether there are neoplasms in the gastrointestinal tract.
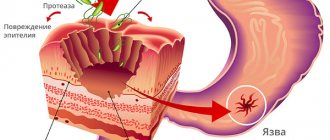
A doctor can identify a stomach ulcer by examining the folds of the epithelial lining of the muscle sac. To see the defect, a contrast examination is performed: the patient drinks a liquid intended for this purpose. An ultrasound image with contrast water shows the intensity of filling and emptying of the stomach. The duodenum also comes under the influence of the staining liquid, which makes it possible to identify ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane of this part of the gastrointestinal tract.
Frequent regurgitation in an infant raises the suspicion of gastroesophageal reflux. To confirm or refute the diagnosis, the baby undergoes a stress ultrasound.
Endoscopy
An examination using a flexible tube with a camera and a light at the end allows you to view the walls of the stomach at close range. The picture is presented in natural colors. The doctor sees an image of the gastrointestinal tract down to the millimeter. The diagnostic method of research recognizes benign and malignant formations at an early stage. Inflammatory processes, ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane and bleeding will not escape the attention of the probe.
Benefits of manipulation
- high information content;
- painlessness of the procedure;
- the result can be found out immediately after the examination;
- can be carried out for newborns and infants;
- Ultrasound is not contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation;
- the procedure can be done several times without worrying about health (unlike the x-ray diagnostic method).
What varieties exist
At the moment, the following examination methods are used in medical practice: transabdominal and endoscopic, ultrasound with water-siphon test and intraesophageal diagnostic method. We will dwell on each of them in more detail.
- The first option involves examination through the anterior wall of the peritoneum on an empty stomach. This is the classic way.
- Ultrasound of the stomach and esophagus with a water-siphon test involves the use of a special concentrated solution (or water). This measure is required for better visualization of the organ being examined and for the doctor to study the motility of the stomach and esophagus.
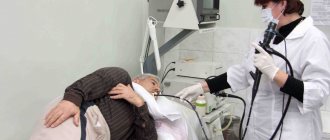
- For endoscopic ultrasound, it is necessary to use a special device with an ultrasound sensor, which is inserted through the pharynx into the stomach cavity. A procedure called endosonography allows you to examine suspicious areas of the organ in detail and identify changes and lesions up to 1 mm in size. This is not possible during a transabdominal examination.
- During the intraesophageal diagnostic method, a special sensor is inserted directly into the lumen of the esophagus. With its help, a specialist has the opportunity to study all layers of the walls of the esophagus and identify changes of various etymologies.
The latter diagnostic method is used only when examining adults. In children, intraesophageal ultrasound is not used, since there is a high risk of mechanical damage to the stomach and esophagus.
Decoding the results
Preliminary adherence to therapeutic nutrition is necessary in order to properly prepare for diagnosis. Without preventive measures, the results of the study will be inaccurate, the picture of the organs will be blurry. A special diet will help relieve increased gas formation. The patient begins to consume the following products three days before the scheduled procedure:
- Porridge on the water;
- Soft-boiled eggs (one per day);
- Skim cheese;
- Low-fat varieties of beef, poultry, fish, boiled, baked or steamed.
What foods are prohibited in a person’s diet before an ultrasound examination:
- Peas and legumes;
- Milk products;
- Fresh vegetables and fruits;
- Brown bread, baked goods, pastries;
- Pickles, pickled vegetables;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Alcohol, coffee, tea;
- Juices.
The doctor prescribes the patient to take medications in addition to a special diet. Preparing the body consists of using the following drugs:
- To eliminate gases.
- Laxative for bowel cleansing. Prolonged constipation can be relieved with an enema.
- Sorbents (activated carbon, lactofiltrum).
- Enzyme medications for disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
To thoroughly prepare for the procedure, a person observes a number of conditions on the day of the ultrasound:
- You should not smoke, eat sweets or chewing gum (digestive juice is stimulated and digestion is activated).
- Refrain from brushing your teeth to prevent the toothpaste from entering your body.
- Warn the doctor who sent the patient for an ultrasound about chronic diseases and medications.
- 15 minutes before the examination, drink at least a liter of clean water to straighten the stomach. Water allows you to informatively interpret what you see on the monitor, as it is the best conductor of ultrasound.
- In some cases, the doctor sends the patient to the toilet. After a while, a second ultrasound may be performed to determine the rate of gastric emptying and gastrointestinal motility.
- Some patients undergo the procedure without first drinking water.
After diagnosing the abdominal organs, the diagnostician makes a conclusion about the presence of normality or pathology in the patient. A mandatory element of the study is the conclusion about the condition of the retroperitoneal lymph nodes. Enlarged lymph nodes are a reason to refer the patient for further examination (CT or MRI); the risk of developing oncology is high. The doctor indicates in the patient’s chart the structural and dimensional parameters of the gastrointestinal tract, whether there is fluid in the hollow sections.
An increase in size indicates a developing infection, beginning inflammation. Deviation from the norm in ultrasound when describing the thickness of the walls of organs prompts the doctor to think about the proliferation of the epithelial layer or the presence of a tumor formation. An enlarged abdominal aorta is a dangerous indicator. Thinning of the vessel wall can lead to an aneurysm; “smoker’s disease” is eliminated surgically.
How to properly prepare for an ultrasound of the stomach? First of all, it is necessary to follow a certain diet several days before an ultrasound examination of the stomach. To eliminate the possibility of gas formation in the abdominal cavity, it is necessary to exclude the following foods from the diet:
- Rye bread
- any legumes
- any fresh vegetables or fruits
- carbonated liquid
- don't eat fried food
- fermented milk drinks such as kefir, ayran or kumiss
You can eat any porridge made from grain crops (buckwheat, oats, etc.), which should be cooked only in water (in no case with milk). It is better to exclude dairy products from the diet when preparing for an ultrasound. You can eat boiled or steamed lean meat, bake lean fish in the oven.
Be sure to soft-boil one egg for your afternoon snack. It is also recommended to include cheese in your diet, but not spicy varieties. A few days before this procedure, you need to drink fluid in larger quantities than usual (about one and a half liters per day). It must be remembered that an ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as a similar examination of the entire abdominal cavity, must be done on an empty stomach.
How is an ultrasound of the stomach done? There is a special device in which a special sensor is moved across the abdomen, and with the help of ultrasound, certain abdominal organs are displayed on the monitor. With this study, you can see some defects in the gastrointestinal tract. Unfortunately, such an examination of the stomach is not as effective as gastroscopy, because it is not possible to take a biopsy. This procedure is performed on an empty stomach. The patient is usually asked to either lie in a supine or semi-sitting position.
For the screening results to be reliable, the patient must follow the preparation rules:
- It is recommended to go on a diet 3 days before the ultrasound. The patient should avoid foods that cause excessive gas production in the intestines. To do this, you should exclude rye bread, confectionery, fresh fruits and vegetables, white cabbage, and legumes from the daily menu. In addition, you should give up carbonated drinks, alcoholic drinks, coffee;
- It is necessary to cleanse the body as much as possible. To do this, you should take a laxative or sorbents. However, the latter drug is contraindicated in patients who suffer from constipation;
- The day before the procedure you need to follow a strict diet. A light dinner made from permitted foods is allowed. Drinking kefir is strictly not recommended, as this drink causes bloating;
- On the day of the study, it is forbidden to eat or drink. If necessary, the doctor will offer the patient to drink a small amount of cooled boiled water.
As a rule, ultrasound is performed in the morning on an empty stomach. The doctor first examines the empty esophagus, stomach and intestines. Then the patient is asked to drink some water, after which the diagnosis continues. You should also not smoke before the test. You can read more about preparing for an abdominal ultrasound here.
As a rule, a comprehensive examination of the abdominal organs is performed. Many patients are interested in the question of how to decipher ultrasound results. If a person is healthy, then an ultrasound of the esophagus and stomach will show the following results:
- The edges of the organs have a rounded shape with rims that are poorly displayed and a clearly visualized center;
- The walls have a thickness of 4 to 6 mm, and closer to the central part of the organ - from 6 to 8 mm;
- The wall consists of 5 layers that have different echogenicity;
- The outer shell has a lower density compared to the surrounding tissues;
- The thickness of the muscular layer is from 2 to 2.5 cm, it is also hypoechoic (low-density structure);
- The thickness of the submucosal membrane is about 3 mm, the echogenicity is average;
- The mucosal plate is about 1 mm thick with low density;
- The thickness of the mucous membrane is about 1.5 mm, has a hyperechoic character (increased density);
- 220 ml of liquid passes in 20 minutes, while the initial evacuation takes 3 minutes.
The presence of pathological changes in the esophagus and stomach during ultrasound can be judged by the following signs:
- Fluid in the cardiac region indicates gastroesophageal reflux. After several turns of the body, the fluid returns to the esophagus in the form of an anechoic formation;
- If fluid is present in the stomach, this indicates a diaphragmatic hernia;
- If the mucous membrane is echogenic, and the muscular membrane is hypoechoic, then this indicates the presence of a cyst;
- When the pylorus of the stomach thickens, we are talking about hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, which provokes a narrowing of the walls of the stomach.
With abdominal ultrasound, it is impossible to identify many pathologies of the mucous membrane of the digestive organs. Therefore, most often after the study, doctors use the term “Hollow Organ Lesion Syndrome.” Doctors recommend gastroscopy, as this method is more informative.
Ultrasound of the stomach cannot replace endoscopic or x-ray examination. However, it gives an idea of the condition of the walls of the organ, its external contours, and helps control regression or relapse of the pathological process.
So, what will a stomach ultrasound show? It fully studies functions and reveals reflexivity. An ultrasound will provide information about the thickness of the stomach walls, inflammatory processes, and tumors. The study will reliably clarify the localization of the pathology, allow you to study blood flow, and distinguish small structures. Such a survey provides answers to many questions.
Ultrasound of the stomach can detect the following conditions:
- neoplastic diffuse wall thickening;
- hypertrophic congenital pyloric stenosis;
- swelling of the walls;
- varicose veins;
- tumor aberrant vessels;
- stomach ulcer;
- acquired pyloric stenosis;
- tumors;
- lack of wall delimitation;
- gastric carcinoma;
- mesenchymal tumor;
- lymphoma of the stomach.
Indications for ultrasound
Most often, this diagnostic method is indicated for problems such as:
- gastritis and stomach ulcers;
- suspicion of malignant formation in the digestive tract;
- in case of intestinal obstruction (an ultrasound examination of the entire gastrointestinal tract is recommended);
- for pathological and abnormal phenomena.
It is necessary to do an ultrasound for the following symptoms:
- attacks of heartburn, frequent belching;
- excessive regurgitation (more than 3-5 tablespoons at a time) in newborns and infants;
- frequent constipation;
- colitis;
- weight loss for an unknown reason (in this case, an x-ray of the stomach with barium is also prescribed);
- suspicion of the presence of polyps on the walls of the mucous membrane;
- pain localized in the upper part of the stomach, in the solar plexus;
- Thanks to the examination, it is possible to clarify the safety of surgical interventions.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe an examination for patients who complain of hunger pain in the stomach (both in the morning and at night).
Since ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and stomach does not cause the patient any pain or the slightest discomfort, it is recommended to conduct an ultrasound examination in order to prevent diseases of the stomach and the entire gastrointestinal tract.
For example, a patient may not immediately pay attention to a disease such as reflux esophagitis, which is characterized by the entry of gastric juice into the esophagus. Thanks to a simple ultrasound, the doctor will be able to detect the development of the disease in time and prevent its complications.
Indications and to whom it is prescribed
It is advisable to do an ultrasound of the stomach for comprehensive primary diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of the course of the pathological process for the following complaints and diseases:
- Pain syndrome localized in the stomach area;
- Frequent nausea with bitterness in the mouth and vomiting;
- Poor appetite, aversion to certain types of food;
- Belching of foul-smelling or unpleasant air;
- Marked weight loss with a simultaneous increase in the size of the abdomen and indigestion;
- Children of younger age groups and the first days of life with severe long-term vomiting that cannot be corrected with medication;
- Periodic slight vomiting with blood in people of any age;
- Chronic diseases of the stomach, when it is necessary to monitor the dynamics of their course. These may be patients with peptic ulcer disease, compensated pyloric stenosis, gastric polyps and other diseases that require assessment of the effectiveness of their treatment, preparation for surgery or the postoperative period.
Is preparation necessary for the procedure?
As is the case with other methods of diagnosing the stomach, before an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, it is necessary to foresee some nuances in advance.
How to prepare for an ultrasound of the stomach:
- 2 days before the ultrasound examination, it is recommended to start following a special diet. Avoid eating legumes, cabbage, dairy products, rye bread and fresh vegetables. Drinking caffeine-containing and alcoholic beverages is also contraindicated. It is advisable to avoid drinking store-bought packaged juices and kvass. All kinds of carbonated drinks are also prohibited.
- It is not advisable to eat food later than 7-8 pm. By the way, in everyday life you should also adhere to this rule. Or try to eat 3-4 hours before bedtime.
- On the day of the ultrasound of the stomach and esophagus, it is forbidden to eat or smoke. However, if you suffer from severe hunger pains, it is recommended to drink a cup of tea and eat a cracker early in the morning.
- If the examination is carried out on an infant, it is not allowed to feed the baby several hours before the examination. In this case, it is not at all necessary to carry out the diagnosis on an empty stomach. However, you should take some formula or diluted apple juice with you to give to your child later.
- On the day of the procedure (or the day before), you must have a bowel movement.
- To prepare for an ultrasound of the stomach, it is sometimes recommended to use adsorbents (for example, Lactofiltrum) or activated carbon (black or white). Sometimes Mezim or Festal may be prescribed - medications that stimulate the digestive tract.
Following these rules will help improve diagnostic accuracy.
Are there any contraindications?
The classic version of ultrasound of the stomach and intestines has no contraindications, so it is recommended even for small children and women during pregnancy.
However, there is also endoscopic ultrasound, during which part of the apparatus is inserted into the body. This type of ultrasound examination has a number of contraindications.
It is prohibited to perform endosonography if:
- the presence of mechanical injuries and burns localized in the digestive tract;
- stenosis (so-called narrowing of the esophagus). This pathological process is caused by tumor changes;
- poor blood clotting;
- acute and chronic processes in the oral cavity, as well as the pharynx;
- aortic aneurysm.
It is also not recommended to perform an ultrasound examination of the stomach in cases of damage to the central nervous system and severe asthma.
It must be said that the endoscopic version of abdominal ultrasound is performed if non-invasive diagnostic methods do not make it possible to understand the complete picture of the condition and functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. All procedures have both their advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, several diagnostic tools should be used.
How is an intestinal ultrasound performed?
How is diagnostics such as intestinal ultrasound performed? When performing an ultrasound, the patient lies on his back and during the examination turns over to different sides to improve the visualization process. Endorectal ultrasound of the intestines and stomach is performed using a special thin catheter, which is inserted into the rectum at a distance of 5 cm. Then a special solution is passed through it, which acts as a contrast agent when examining the colon.
Next, the doctor evaluates the condition of the intestines and stomach when fluid enters them. Diagnosis of the rectum is carried out by filling not only the organ itself, but also the bladder.
An ultrasound procedure using a solution protects it from the loops of the small intestine and improves visualization on the monitor of the condition of the rectum and sigmoid colon, as well as the space between them and the bladder or uterus. It all depends on the gender of the patient.
Ultrasound using Doppler sonography will show the presence of oncological tumors at the earliest stage of their development. This diagnosis is prescribed in cases where colonoscopy is contraindicated.
An ultrasound is performed if acute appendicitis is suspected, since this study allows not only to see the condition of the appendix, but also to examine other organs to determine the source of extraneous pain.
https://youtu.be/Od69zMuxKrE
Ultrasound examination of the stomach and intestines is carried out to assess the performance of organs, their hypotension, to identify the degree of development of malignant tumors and their locations. This diagnosis also shows where erosions occur, which over time develop into ulcers and cancer.
Pregnancy may also be a reason for an ultrasound scan.
to determine the developmental features of the fetus and its hyperechoic intestine. This may indicate the presence of various pathological abnormalities in the development of the embryo, both congenital and genetically acquired.
What does an ultrasound of the stomach show?
During an ultrasound examination of the stomach, you can identify:
- Diaphragmatic hernia, which is detected only if there is fluid in the cavity of the diseased organ. By the way, this diagnostic method does not make it possible to determine the size of the formation.
- Changes in the stomach of oncological etymology. The problem is indicated by such factors as: enlargement of the lymph nodes of the abdominal wall, deformation of the digestive tract, decreased or, conversely, increased echogenicity of some parts of the organ. If at least one sign is detected during the manipulation, then a gastroscopy will be required, during which a piece of the affected tissue will be taken for subsequent examination - a biopsy.
- In the process of performing an ultrasound with a water-siphon test in children, gastroesophageal reflux can be determined. Doctors often send infants for diagnostics if they regurgitate frequently and profusely.
- Also, according to the results of an ultrasound of the peritoneum and stomach, the price of which is very affordable, the presence of cysts and the structure of the anomaly are visible.
- Ultrasound examinations of the pancreas are also intended to identify disorders caused by a disease such as diabetes.
- Using diagnostics, you can identify varicose veins, swelling of the stomach walls and a number of other problems that negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Modern ultrasound diagnostic devices make it possible to identify pathologies whose dimensions do not exceed 4 mm.
When drawing up a conclusion based on the results of the study, the doctor writes down the following data:
- tissue structures;
- features of blood flow in the organ;
- the presence of tumors, foci of inflammation;
- thickness of the stomach walls.
Ultrasound of the stomach or FGDS - which is better?
Many patients are afraid of the FGDS procedure like fire, so they think for a long time about what to choose - ultrasound of the stomach or gastroscopy. Ultrasound and FGDS have different purposes and do not replace, but complement each other. Doctors usually prescribe both examinations to accurately identify gastrointestinal diseases.
Endoscopic ultrasound is not available in all cities, and the classic study involves studying the pancreas, liver and spleen. The stomach and intestines are not visible during this examination, therefore it is impossible to identify gastrointestinal pathologies (such as ulcers, gastritis, gastroduodenitis, etc.) with this type of diagnosis.
At FGDS, the internal state of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum is carefully studied. This procedure will not replace any other diagnostic method. In addition, in its process it is possible to measure the pH of gastric juice, take an analysis for Helicobacter pylori and take the affected tissue for further histological examination.
In most cases, a more effective diagnostic method is gastroendoscopy.
If we talk about the use of diagnostic tools in the form of an endoscope with an ultrasound sensor, then the accuracy of the procedure increases several times. However, this method of examining a diseased stomach has a number of contraindications, which we will talk about a little later.
What pathologies does ultrasound diagnose?
Ultrasound of the stomach and intestines provides the diagnostician with detailed information about the condition of the organs, allowing him to track all possible changes indicating the presence of gastrointestinal diseases. After the procedure, it is not difficult for the attending physician to make the correct diagnosis, because an ultrasound of the stomach shows clear signs of pathologies such as:
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system
- gastroesophageal reflux (reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus);
- duodenogastric reflux (ingestion of duodenal contents into the stomach);
- violation of the motor-evacuation function of the esophagus and stomach;
- inflammation of the esophagus - esophagitis;
- tumors in the lower esophagus;
- inflammation of the gastric mucosa - gastritis;
- erosive lesions of the mucous membrane, peptic ulcer, polyps;
- neoplasms of the stomach lining;
- prolapse of the stomach - gastroptosis;
- the presence of foreign bodies in the esophagus and stomach;
- hyperplasia (thickening) of the walls of the digestive organs;
- dilation of large blood vessels in the gastrointestinal tract.
In addition to all of the above, ultrasound examination makes it possible to diagnose pyloric stenosis in infants - a decrease in the patency of the pyloric section of the stomach. Ultrasound diagnostics, in the presence of abdominal pain of unknown etiology, often becomes decisive in identifying acute appendicitis and determining the boundaries of malignant neoplasms. Studying the sections of the small and large intestine using ultrasonic vibrations is no less informative technique, and is prescribed as often as the previous one.
Doctors often resort to it, as ultrasound of the intestine shows a fairly wide range of pathologies, which includes:
- dolichosigma – increase in the size of the sigmoid colon;
- colitis - an inflammatory process of the intestinal mucosa;
- ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, formation of fecal stones;
- violation of intestinal motility and evacuation function;
- neoplasms of benign and malignant nature;
- irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), decreased tone;
- fluid in the intestines and establishing the causes of its accumulation.
The procedure determines a congenital anomaly of the sigmoid colon - Hirschsprung's disease, which is manifested by a violation of the innervation of its area, leading to chronic constipation. During the examination, the doctor is able to detect thickening of the intestinal walls, which is evidence of the development of oncological processes. In addition, the method allows you to study the functional state of blood vessels and track the spread of cancer tumors beyond the boundaries of the organ.
One of the intestinal diseases characterized by damage to the tissue structure is diverticulosis.
Ultrasound is also successfully used to assess the effectiveness of prescribed therapy, allowing you to keep the situation under control and, if necessary, take appropriate measures to prevent relapses.
What is the price
Ultrasound examination as a method of primary diagnosis is carried out in clinics and medical centers. The average cost of diagnostics is 400-600 rubles. If you are interested in the cost of an endoscopic ultrasound procedure, then count on 2500-5000 rubles.
It must be said that you can sign up for an ultrasound with an endoscope only in medical centers in large cities. In rural hospitals, most likely, this diagnostic method is not yet available.
Now you know in what cases an ultrasound procedure is permissible, and what problems can be identified with its help, how an ultrasound of the stomach is performed and what types exist. Do not forget that treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract must be combined with a balanced diet and the eradication of bad habits.
Indications for prescribing an examination
The basis for prescribing an ultrasound is the patient’s complaints about manifestations that indicate a dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, but due to the non-specificity of the symptoms, they do not allow an accurate diagnosis of the disease. In adult patients, ultrasound examination is prescribed to clarify the diagnosis if:
- gastritis;
- stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- cancer;
- pyloric stenosis;
- congenital anomalies of organ development;
- intestinal obstruction.
For children, the non-invasive transabdominal method is preferable to the endoscopic method, since it has no age restrictions, can be used from the first days of life, and does not cause physical and psychological discomfort. In children, ultrasound is prescribed for asthma and asthmatic bronchitis, increased gas formation, regurgitation, loose stools, complaints of pain in the epigastrium, weight loss for no apparent reason.