Etiology of the disease ICD 10
A ruptured eardrum is an injury to the thin skin that separates the ear canal and the middle ear.
In the International Classification of Diseases, 10th edition, traumatic rupture of the tympanic membrane is coded S09.2. A membrane rupture is said to occur when there is damage, a hole and an obvious wound, that is, a rupture. If there is an eardrum injury, a person suffers from an unpleasant aching sensation, sharp pain, accompanied by tingling inside the ear.
When a rupture occurs, the functions of the eardrum are impaired. Thus, the normal vibrations of the membrane stop, and air vibrations are distorted. This leads to tinnitus, sometimes
partial hearing loss
.
When a rupture occurs, the symptoms are individual in each individual case. Depending on what caused the rupture, the manifestation of accompanying symptoms also depends. Treatment is also prescribed based on symptoms.
What does a perforated eardrum look like?
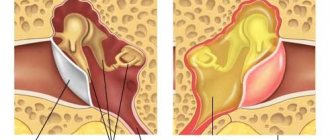
A ruptured eardrum is a hole caused by various reasons in the thin membrane that lies at the border of the middle ear and the ear canal. The International Classification of Diseases, 10th edition (ICD 10) classifies tympanic membrane rupture under code S09.2. This disease is determined by a hole, tissue rupture, crack and other damage to the thin but necessary membrane in the auditory system.
Otoscopy for damage to the eardrum
In case of minor trauma, otoscopy only determines the injection of the vessels of the tympanic membrane. More significant damage is usually visualized in the form of subtotal defects, as well as round and pinpoint perforations, possible slit-like ruptures, up to the complete destruction of the eardrum itself.
A ruptured eardrum is characterized by uneven, scalloped edges. When performing otoscopy in the membrane of the perforation, you can observe the medial wall in the tympanic cavity. Often, otoscopy helps diagnose a hematoma located in the tympanic cavity due to damage to the membrane. If there is acoustic or mechanical damage, the doctor may observe hemorrhages in the tympanic cavity. After a certain time, it is necessary to conduct a control otoscopy, which will be aimed at assessing the reparative processes that occur in the eardrum. It is the control otoscopy that is able to determine scarring or the nature of the perforation hole. Sometimes in the very thickness of the eardrum you can see a dense white formation, which is a deposition of calcium salts on the scar.
Causes
A ruptured eardrum can occur for a variety of reasons. These may include mechanical injuries, consequences after impacts or unsuccessful actions when performing physical work. The main types of reasons include:
- Improper ear cleaning or foreign matter entering the ear canal. If hygiene measures are not taken carefully, it can damage the eardrum. After a piece of cotton wool or a particle of any other object remains inside the canal, infections begin to develop in the ear, which subsequently leads to suppuration and the appearance of otitis media in the middle ear.
- Strong and sharp noise. A sudden explosion, excessively loud music on headphones, or the noise of industrial equipment and machinery can also cause damage to the membrane. Such damage is usually not that significant. For some time, hearing loses its sharpness, but as the membrane heals, it is restored. Sometimes the rupture can be more significant, which is accompanied by the appearance of blood from the auricle and the appearance of pain.
- Pressure. Sudden changes in pressure in the ear canal can easily lead to disruption of air pressure, which is more likely to lead to a rupture of the eardrum. Precautionary measures must be observed by those who are accustomed to sneezing with their nose closed and those who often fly on airplanes.
- Inflammation. The inflammatory process that begins inside the ear can lead to serious complications in the form of suppuration and severe pain. It is this pus that puts pressure on the wall of the eardrum in the future, leading to its damage.
- Exposure to heat. Here we are talking about getting burns, which lead to a violation of pressure, which leads to a rupture. This type of rupture is quite rare and is typical for people working in heavy production.
- Traumatic brain injury of the head. Blows, falls and bruises that result in a fracture or serious damage to the temporal bone can also cause trauma to the tympanic septum.
Do-it-yourself ear cleaners who inadvertently clean the ear canals with cotton swabs, matches, pins and even knitting needles are at significant risk of getting a ruptured eardrum.
A rupture can also occur if you are potentially prone to frequent fluid accumulation in the middle ear.
Rupture of the eardrum with a cotton swab
When there is inflammation in the middle ear—otitis media—discharge accumulates. This discharge may also be purulent. Due to the rather small volume of the middle ear cavity and due to the disruption of the outflow of this discharge through the Eustachian tube (since it is also blocked in this disease), the fluid that accumulates in the middle ear cavity puts pressure on the eardrum.
When fluid accumulates on the inside of the eardrum, it can rupture. However, pressure from its outside can also lead to rupture. This happens, for example, when an open palm is suddenly applied to the ear; sometimes a rupture of the membrane can also occur in flight during the ascent or descent of the plane, when a change in pressure occurs.
Noise trauma
A sudden loud noise (such as an explosion) can also rupture or perforate the eardrum. In addition to a sharp decrease in hearing, severe noise in the ears (tinnitus) may occur. Over time, the tinnitus goes away and hearing is partially restored.
Foreign bodies
Sometimes when cleaning the ear canal, for example, with a cotton swab or other objects, the eardrum can be injured. In addition, this promotes infection in the middle ear.
Let's look at the main causes of damage to the eardrum:
- inflammation observed in the middle ear. In such conditions, otitis media develops. It is observed as a result of the fact that fluid accumulates inside this part of the ear, which is not able to be discharged through the eustachian tube because it is too swollen. As a result of this, the accumulated fluid (it may be mixed with pus) puts strong pressure on the eardrum, causing it to become inflamed. It also becomes thinner. As a result, the membrane ruptures, and pus flows out of the ear;
injury resulting from high pressure on the membrane. It occurs not only from the middle ear, but in some cases it can be caused by an external factor.- These include the sharp application of a slightly clenched palm to the ear;
- sneezing with a closed nose;
- strong fall on the ear;
- movement in an airplane as it descends or ascends sharply. You can avoid negative consequences during a flight by using a simple technique: open your mouth or swallow saliva. Thus, through the auditory tube, air will enter the inner part of the ear, thus relieving the strong pressure occurring on the eardrum;
- injury that occurs as a result of loud noise. This may be a loud sound, a pop, or an explosion that may cause the membrane to rupture or cause a small hole in it. In such cases, tinnitus is often observed, which goes away over time, and hearing gradually returns to normal;
- as a result of cleaning the ear with hard objects. Most often, a cotton swab is used for these purposes, which can not only damage the membrane, but also spread infections into the middle ear;
- mechanical damage, which in most cases is associated with traumatic brain injury or skull fractures;
- Damage caused by burns of varying degrees is sometimes observed. They can occur both in domestic conditions and in production;
- Damage to the membrane can be caused by the action of acids, alkalis, and other chemicals on it. This is one of the most terrible problems, because as a result, hearing completely disappears and numerous burns occur in the inner cavity of the ear.
All of the above reasons, depending on the severity, can provoke deafness.
A ruptured eardrum can be caused by:
- sharp strong sound;
- inflammation;
- foreign bodies entering the ear;
- improper ear cleaning;
- changes in external pressure (on airplanes, when sneezing with a closed nose);
- injuries (bruises, concussions, blows, damage to tissues and bones of the head, etc.).
We invite you to read: Bone fractures are... What are bone fractures?
All causes of membrane damage can be divided into:
- mechanical;
- physical;
- chemical;
- thermal;
- inflammatory in nature.
- mechanical damage - due to careless toileting of the external auditory canal or an attempt to scratch the ear with cotton swabs or other sharp objects.
- a sharp increase in pressure in the external auditory canal - when diving into water, when hitting the ear, sometimes just a slap with your palm on the auricle can cause a rupture of the eardrum.
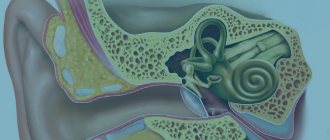
Structure and functions of the eardrum
The eardrum is located deep in the ear canal between the middle and outer ear. It is stretched and most of it is fixed in the groove of the temple bone. The part of the membrane without fixation consists of epidermal (outside), fibrous (in the middle) and mucous (inside) layers. The shape of the membrane is round in children and oval in adults. It is about five millimeters in diameter and one tenth of a millimeter in thickness.
The eardrum performs a protective function and is involved in conducting sound waves. This organ prevents water, air, microorganisms and various foreign objects from entering the inner cavity of the ear. When the eardrum is damaged, it cannot protect the passage and transmit sound vibrations to the ossicles and other structures of the ear. Thus, ear injuries accompanied by perforation lead to disruption of the protective and sound-conducting functions.
Signs of a ruptured eardrum
- Among the primary signs are sharp pain in the ear. In some cases, the pain occurs so unexpectedly and sharply that people can even lose consciousness.
- For some time, the pain remains quite strong, the person feels a pulsation.
- Fluid may appear due to rupture, but not necessarily. Discharge may appear much later.
After detecting such signs, it is better not to delay making an independent diagnosis and urgently go to the doctor for an examination.
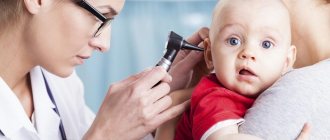
A ruptured eardrum occurs in children according to the same principle as in adults. The only problem is that the child may not orient himself in time and may not understand what happened to him.
This can significantly delay the diagnostic process and diagnosis. Thus, if you find that your child begins to behave restlessly, constantly touching the ear, scratching or holding it, try to find out if he is experiencing pain inside the ear canal.
Even if the child categorically denies everything, do not be lazy and show your baby to a specialist to rule out the possibility of rupture and otitis media.
But for some people, the symptoms are not so pronounced, and for a long time they may not realize that the eardrum has ruptured. They simply feel ringing in the ears, noises and unusual sounds that do not exist in the external environment. The pain symptom may be present during the first 5 minutes after the rupture, and then the pain seems to subside. And besides noises, there are practically no symptoms. But this is not a reason to self-medicate and not see a doctor.
Manifestations of eardrum injury
Patient complaints:
- Sharp pain in the ear at the time of injury, which soon subsides;
- A feeling of congestion in the hearing organ and noise in it of varying degrees of intensity;
- Decreased ability to hear up to complete deafness.
Severe trauma affecting the balance apparatus is accompanied by impaired coordination, nausea, and dizziness.
Objectively, there may be the following symptoms of damage to the eardrum:
- Release of air from the affected ear canal when coughing, sneezing, or strong exhalation;
- Leakage of clear fluid (perilymph) from the damaged organ of balance.
Trauma to the skull and a sharp change in atmospheric pressure (barotrauma) may be accompanied by bleeding from the ear canal.
If the membrane rupture is complicated by otitis or labyrinthitis, purulent discharge will be detected.
In young children under 2 years of age, diagnosis is complicated by the lack of meaningful complaints and parents’ silence about a previous ear injury or ignorance about it. Usually they go to the doctor with suspicion of congenital deafness in the baby.
Diagnostics
How can you tell if your eardrum is damaged? To diagnose this problem, first of all, an otoscopy is performed. For this purpose, the doctor inserts a special funnel made of plastic or metal into the ear opening - an otoscope. The ear is then retracted in either the superior or inferior direction.
This method allows you to make the movement in the ear opening more even - so that the membrane appears at its end. The ear canal is lightened to allow details to be seen. If there really is a rupture or crack, the doctor will be able to clearly see the hole in the membrane. If it is completely torn, the auditory ossicles can be easily observed in the middle ear area.
In addition, in some cases, if the eardrum is damaged, the symptoms are reduced to the discharge of pus and blood from the auricle. If the doctor notices purulent discharge, he will take a sample of it for analysis in order to identify the pathogen as quickly as possible and, accordingly, begin effective antibiotic therapy.
When you visit the doctor on the first day of your appointment, you will be given an accurate diagnosis. This will be possible thanks to an integrated approach to diagnosis for hearing problems. This complex includes:
- a confidential conversation with a doctor, answers to all his questions, which will help in collecting an anamnesis of the disease;
- external examination: skin, temperature measurement, pressure, etc.;
- examination of the ears with an otoscope or endoscope;
- laboratory tests - taking the necessary tests;
- audiometry – measurements of sound perception;
- Computed tomography is a study inside the head.
As you know, an accurate diagnosis is half the success in treatment. Thanks to modern innovative diagnostic methods and modern new generation equipment, all diagnostic procedures are carried out without pain and discomfort. And the results obtained allow us to make an accurate diagnosis.
If there is damage to the eardrum, then in most clinical cases this problem is dealt with by a traumatologist. However, an additional consultation with an otolaryngologist will not hurt.
As a rule, with this diagnosis, visual examination and palpation alone are not enough, and the attending physician additionally resorts to instrumental examination. First of all, this is an endoscopic examination, represented by otoscopy and microotoscopy. In the first case, it is possible to visualize the ear canal, determine the source of pathology and the degree of damage to the eardrum. The second determines the presence of pus, potential complications and possible clinical outcome.
If making a final diagnosis is still difficult, then among additional clinical examinations it is recommended to resort to the services of audiometry, threshold audiometry, tuning fork examination, acoustic impedance measurement, electrocochleography, stabilography, vestibulometry and caloric test. It is not at all necessary to carry out all these procedures, but two or three indicators are quite enough.
As for laboratory tests, in the event of damage to the eardrum, bacterial culture is mandatory, which makes it possible to examine the fluid released from the ear for the activity of pathogenic microorganisms.
An otoscopy is performed to determine damage to the eardrum. It is performed by an ENT doctor. However, first of all, the doctor learns about all the possible factors that could affect the ruptures.
Then a special plastic or metal cone is installed in the ear canal, into which light is directed. After this, with both hands, the doctor pulls the upper and lower parts of the ear back. Thus, the eardrum becomes clearly visible.
Having carried out such manipulations, the doctor will see either a hole in the membrane or its complete rupture (in this case, even the bones located behind it can be seen).
During an otoscopy, the ENT doctor will also see pus or blood accumulated in the ear. If it is pus, then using a special instrument the doctor will take a small amount of it to determine the causative agent of the infection.
Only after carrying out all the above measures will it be possible to prescribe effective and efficient drugs and treatment methods.
In addition to collecting anamnesis, the doctor must perform an otoscopy.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Arthritis of the elbow joint, symptoms and treatment, traditional methods of treatment
This simple and completely painless procedure allows you to identify the presence of a rupture or any other changes in the ear canal.
Inspection allows you to determine the extent of the tear. If there is pus or any other suspicious discharge, the doctor takes a small amount of fluid for analysis.
This allows you to identify the potential causative agent of the infection and prescribe effective antibiotics when drawing up a treatment plan.
Diagnosis of eardrum damage
The primary diagnosis of a damaged eardrum is carried out by a traumatologist. The latter can be explained precisely by the fact that the damage is often associated with ear trauma. To establish a final diagnosis and determine the correct treatment, consultation with an otolaryngologist is necessary. An effective method for diagnosing damage to the eardrum is endoscopic examination, which includes otoscopy and microotoscopy. To determine the assessment of the indicators of the hearing aid, as well as the vestibular one, audiometry, tuning fork studies, threshold audiometry, electrocochleography, vestibulometry, stabilography and caloric test are performed. Bacteriological examination of ear discharge is carried out if damage to the eardrum is complicated by secondary infection.
Treatment
If the damage to the eardrum is not complicated by other pathological processes in the characteristic area, then surgical intervention is not required in this clinical picture. The doctor first removes the foreign body from the ear canal, and then uses a cotton swab dislodged with peroxide or ethyl alcohol as an antiseptic. Such careful treatment of a characteristic area helps prevent pathogenic infection from entering the auditory tube and, accordingly, extremely unwanted infection. But the complicated form of the characteristic disease is treated in the same way as acute otitis media of various localizations.
If, after conservative therapy, an abnormal opening still remains in the structure of the eardrum, then a surgical approach to the problem is clearly required. Such procedures are the well-known myringoplasty and tympanoplasty, which provide a positive therapeutic effect for the prevailing disease.
In modern medicine, otolaryngologists recommend transplantation of cultured allofibroblasts from the patient, but such a procedure is appropriate only in those clinical situations where there is no ear congestion for more than two weeks after injury.
So do not be upset, since the clinical effect is quite favorable, especially if you immediately respond to a painful sensation in the auricle after an unconscious injury. That is why it is best not to hesitate, but to immediately contact an otolaryngologist or traumatologist.
A ruptured eardrum requires mandatory treatment. But treatment methods depend on the form of the disease, the stage, complexity of the disease, the age of the patient, etc. Important: If you consult a doctor at the first symptoms, the treatment will be quick and minimal. As a rule, the doctor will prescribe medications, possibly antibiotics, herbal medicine, rest and diet.
Rupture of the membrane, especially in children, is often associated with a foreign body entering the auricle. It usually penetrates the ear canal and rolls into the middle ear. In this case, the rupture of the membrane will depend on the size of the object. And if this damage is large, then surgery is simply necessary; medications, drops and herbal teas alone cannot solve this problem
Myringoplasty
An operation to apply skin at the site of a ruptured membrane using an endoscope is myringoplasty. A piece of skin is inserted through the ear canal (which can be taken from any part of the patient’s skin) and, using a special medical device, is attached to the torn area of the membrane. After which the application site is washed with agents that disinfect the diseased area.
Ossiculoplasty
This is a more complex operation, which is prescribed to patients after diagnosis. Typically, the cause of such a complex rupture of the eardrum is a head injury. Ossiculoplasty involves tissue augmentation, insertion of cartilage and small bones and other elements necessary to achieve the integrity of the eardrum.
Medication
The most common type of treatment for eardrum disorders is medication. It may include: antibiotics in tablets, injections, antibiotics in external applications, anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins that enhance immunity, gels and ointments based on natural ingredients, etc.
Physiotherapy
UHF heating of the ears
Along with medications for damage to the membrane, the complex of treatment procedures often includes physical therapy. It can be recommended as:
- ultrasound therapy;
- low frequency therapy;
- short-wave UV therapy;
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- UHF;
- magnetic therapy.
For each patient, the doctor selects the most effective physical treatment, which depends on:
- medical history;
- duration of the disease;
- patient's age;
- stages;
- the nature of the disease;
- physiology of the patient;
- personal intolerance by the patient to any drugs and techniques.
The patient himself cannot prescribe this or that procedure, since this is possible only after extensive diagnosis and analysis of the course of the disease.
There are actually a huge number of physical procedures that help restore hearing. Experts classify them into 3 large groups:
- cleansing (blowing, rinsing, etc.);
- stimulating (improves blood circulation, increases local immunity);
- warming (promote the regeneration of healthy tissue).
Folk remedies
As part of complex medical therapy, doctors often recommend herbal treatment - herbal medicine. Treatment of a ruptured eardrum can be either internal - using decoctions, teas, juices, herbal infusions, or externally - compresses, lotions, drops, baths. Herbs that help:
- relieve pain;
- relieve inflammation;
- have antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, restorative effects.
The quantity and composition of herbal infusions and decoctions depends on: the stage of the disease; forms of the disease; your age; the presence of chronic diseases of other organs and systems; heredity; features of physiology.
It is enough to list the most effective herbs, which are rich in vitamins of all groups, tannins, and beneficial bacteria: fireweed is the second name for fireweed; marigold; strawberries; chamomile; St. John's wort; nettle; toadflax; ginseng; Kalanchoe; celandine; ginger.
The list goes on. So, for example, strawberry leaves, marigold flowers and chamomile have a good therapeutic effect. Nettle has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. Dandelion leaves and flaxseed reduce pain and relieve spasms. Clover and sweet clover improve blood circulation and cleanse blood vessels.
If it is necessary for herbs to simultaneously perform several medicinal functions, then doctors often recommend herbal ones, which can be purchased at a pharmacy or made by yourself, taking into account the compatibility and complementarity of plants. But all this is after the doctor’s recommendations.
In most cases, membrane perforation heals on its own without complications within a few weeks. If the membrane does not heal, treatment is necessary.
If there is a small tear or perforation, the doctor may close it with a paper patch. Before this, the edges of the tear are treated with a drug to stimulate growth, after which a paper patch is applied to the tear site. Three or four such procedures may be required to completely close the gap.
In case of a larger rupture or perforation of the membrane and if the above method is ineffective, surgical intervention may be required. An operation to restore the integrity of the eardrum is called tympanoplasty or myringoplasty. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes a small skin incision above the ear. A thin piece of skin is taken from it. It is used to stitch the hole in the eardrum.
The surgeon inserts a special microscope into the ear canal and then the entire operation is carried out with its help through the ear canal. The eardrum is lifted and the flap is placed over the hole in the eardrum. Special absorbable materials are placed on both sides of the membrane to help hold the flap in the desired position until it heals completely.
We invite you to read: What is the difference between osteochondrosis and intercostal neuralgia
During the first time after surgery, you may experience some pain and discomfort. It is recommended not to blow your nose or make sudden sucking movements through your nose. This is due to the fact that on the back wall of the nasopharynx there are openings of the auditory (Eustachian) tubes, which connect the nasopharynx cavity with the tympanic cavity.
Discussion on the forum
In case of an ordinary rupture of the eardrum, the most gentle treatment is prescribed. In most cases, the damage heals on its own without outside help. Quite rarely, the doctor can use an auxiliary remedy that will speed up this process.
Sometimes lotions may be needed; they can relieve discomfort and reduce itching. During treatment, you should not take sharp breaths and exhale through your nose. You should also control the urge to sneeze. Active movements are also prohibited until the membrane is completely restored.
Medication
If there is an inflammatory process, a course of antibiotics and auxiliary drugs is prescribed. Such a need occurs only in the presence of thick pus and bloody discharge, which is also accompanied by severe itching and unpleasant sensations inside.
In case of inflammation, the ear must be covered with a sterile patch, which is changed about 3 or 4 times. In the process of changing patches, the ear must be treated with a special solution or ordinary alcohol.
Treatment of eardrum damage
If the damage to the eardrum is not complicated by anything, then unnecessary intervention will only cause harm. There is no need to rinse the ear canal yourself, or put drops in your ear. If this is necessary, then the doctor removes the foreign body from the ear canal. Blood clots must also be removed - they are removed using a dry cotton swab. To prevent the disease, treat the ear canal with ethyl alcohol. In case of development of an inflammatory complication of the middle ear, a whole range of antibiotics is usually prescribed. If the damage to the eardrum was complicated further, then treatment is carried out in accordance with the treatment of ordinary otitis.
If, after treatment, a hole still remains in the previously damaged eardrum, then the doctor prescribes surgery to permanently close this hole. The latter involves tympanoplasty or myringoplasty. The material used to close such a perforation hole is chicken amnion or meatotympanic flap. In recent years, the method of transplanting specially cultured allofibroblasts has been used in operations to close the hole. This method is applicable when the perforation is larger than half the size of the eardrum itself and does not heal within 2 weeks.
Prevention
To prevent damage to the eardrum, you need to follow these preventive measures:
- do not clean your ears with small objects or cotton swabs;
- treats your ears with care;
- At home, do not remove wax plugs from your ears using tweezers or other sharp objects, as this can also damage the eardrum.
- Acute pain in the ear can go away quite quickly.
- Noise in the ear, an unpleasant sound sensation, lasts longer, up to 2 weeks, until the healing process begins.
- Hearing loss continues until the perforation heals completely.
Injuries of any nature are often accompanied by membrane rupture. This is especially true for any head injury. Even with a strong shock, deformation of the ear membrane can occur. Symptoms after injuries are not long in coming. Dizziness, tinnitus, and pain immediately appear. In addition to the main head injury, membrane rupture occurs as a concomitant disease, but which must be identified and treated together with the main injury.
As for injuring children, all responsibility lies with the parents. You should not leave your child alone with small toys and objects. he will definitely want to taste them or stick them in his ear. Monitoring the activities of a small child every minute is the responsibility of the parents.
It is quite possible to avoid this diagnosis, but to do this you should take preventive measures. These rules have been known since kindergarten, but for some reason some young patients forget to adhere to them.
Firstly, there is no need to “stuff” foreign objects, small parts and spare parts from toys into the ear canal, since such foreign objects contribute to extremely unwanted injury.
Secondly, it is recommended to take special care and attention when cleaning your ears, since the eardrum can be damaged and even torn with a regular cotton swab. This problem is especially relevant when cleaning the ears of restless children.
Thirdly, it is strictly forbidden to pull out wax plugs using tweezers and forceps, since such metal tools can also cause extremely unwanted injury and deafness, respectively.
If a problem does arise, then solve it not by self-medication, but by going to a specialist for an individual consultation.
Complications caused by a rupture are directly related to how quickly the damage is discovered. The main danger lies in the ability of microorganisms to penetrate deep into the ear, which provokes the development of serious inflammation.
At the initial stage, a person experiences hearing loss. Further, even deeper penetration of the infection is possible. This in turn causes a series of inflammations in the structures of the ear. They are accompanied by human weakness, nausea and vomiting.
With the deepest penetration of the infection, a person develops diseases such as encephalitis and meningitis. In the absence of qualified assistance, the patient may face death or lifelong disability.
When an object that injures it gets into the ear, the integrity of the membrane or any of its individual fragments may be disrupted. If the impact was weak, the victim will escape with only congestion of the membrane vessels. If it turns out to be more powerful, blood vessels rupture and hemorrhage occurs in the membrane tissue.
When injured by a firearm, the symptoms of perforation appear most clearly. After all, it is accompanied by a violation of the structure of the tissues that surround it. This significantly increases the pain syndrome.
If a burn occurs with a chemical substance, most often only fragments remain of the membrane. In the absence of a barrier, toxins penetrate into the deep parts of the ear, destroying their structure. Signs of damage to the eardrum in adults in this case are reduced mainly to severe pain and persistent hearing problems.
Therapy for damage to the tympanic membrane
Some time after the hole is formed, spontaneous restoration of the eardrum is possible with virtually no disruption of its functions. This can happen with shallow damage affecting no more than 25% of the organ area. The regenerative capabilities of connective tissue are relatively high, which allows the auditory membrane to heal even with more severe injuries, but in such situations a scar forms on it and calcium salts are deposited. Scarring and calcification tighten the membrane, changing its shape and configuration, which affects the quality of its functioning as an organ.
If the doctor, having assessed the extent of the damage, sees that spontaneous regeneration of the membrane is impossible without subsequent disruption of its functions, then he immediately offers plastic surgical treatment methods. Both own tissues (fascia, muscle flaps) and foreign ones (chicken embryo amnion) are used as material.
Conservative therapy
Important! It is prohibited to use ear drops when the eardrum is perforated, since it can cause infection in the “open” middle ear.
If the lesion is not severe, the patient is instructed not to do anything, just keep the ears and the outer part of the ear canals clean. If there is blood in the ear canal, it should be carefully removed with a cotton swab moistened with alcohol, without penetrating deep into the ear. A foreign body, if found in the passage, is also removed. This should be done by a doctor. If necessary, he will place a sterile cotton swab in the affected ear canal to protect the tympanic membrane and underlying tissue. The doctor also decides on the need for surgical intervention (suturing the hole in the membrane) in cases where conservative treatment for some time has not produced results and the damaged membrane has not healed.
When purulent inflammation develops, systemic antibiotics are used, selected taking into account the sensitivity of microbes to them.
In most cases, young children, even with uncomplicated rupture of the auditory membrane, are required to be hospitalized to avoid inflammation and other consequences.
In patients with complicated damage to the tympanic membrane in the event of sensorineural or conductive hearing loss, surgical interventions are performed to restore hearing (implantation of high-tech hearing devices). Modern hearing aids are also used.
Consequences
A perforated eardrum means there is a hole or tear in the eardrum. If the eardrum is ruptured or has a hole in it, its vibrations may be disrupted, which in turn leads to hearing impairment. In addition, the presence of a hole in this membrane allows infection to enter the middle ear cavity, which is fraught with its inflammation - otitis media.
For many people, the fear of a ruptured membrane is so strong that they prefer to withdraw into themselves and not listen to anyone’s advice. This is fundamentally wrong. No need to panic. Stress will only aggravate the situation, because every disease also has a psychosomatic nature, when the disease is aggravated by bad thoughts.
If you have consulted with a doctor and strictly follow all his recommendations, then with minimal rupture, it will take only 2 weeks to restore the auditory membrane. For more extensive disorders, longer time and intensive therapy.
Prognosis and prevention
If a rupture of the eardrum is diagnosed in time, and treatment is carried out adequately and in full, then in most cases a complete recovery occurs and hearing is completely restored.
With secondary bacterial complications, the prognosis is somewhat less optimistic, and treatment continues for quite a long time.
Basic preventive measures:
You should not use air transport for ENT diseases in the acute phase;
- no need to try to remove wax plugs yourself;
- For ear canal hygiene, it is permissible to use only special cotton swabs (with caution);
- inflammation of the middle ear (otitis media) is important to treat immediately after the first signs of the disease appear;
- If possible, avoid being in places with high noise levels or use earplugs;
- do not self-medicate - this almost always leads to complications.
Please note: While in the aircraft cabin, wear headphones during acceleration and takeoff. Suck on a lollipop (on most airlines, flight attendants hand them out right away); With each swallowing movement, air enters the middle ear cavity through the Eustachian tubes. It is important to follow similar tactics when decreasing, when the pressure equalizes. The easiest way to avoid barotrauma is to open your mouth slightly.
Plisov Vladimir, medical observer
13, total, today
( 182 votes, average: 4.67 out of 5)
Pharyngeal neurosis: causes, symptoms, treatment, prevention
Sensorineural hearing loss
Related Posts
Which doctor should I contact?
Hearing problems are dealt with by an otolaryngologist or an ENT doctor. It is he who will be able to conduct professional diagnostics, make a clear diagnosis, and develop a comprehensive individual treatment program. Your job is only to strictly follow everything that the ENT advises you.
Take care of your hearing, take preventative measures and lead a healthy lifestyle. But if you still couldn’t avoid a ruptured eardrum, then don’t panic and go to the doctor. Today, medicine for the treatment of “ear diseases” has a high level. The latest effective drugs, innovative techniques and high-precision equipment are used in diagnosis and treatment.
Tags: tympanic, treatment, membrane, damage, role, symptom
About the author: admin4ik
« Previous entry
Symptoms
Signs of a ruptured eardrum include:
- Ear pain that may come on and go quickly.
- Clear, purulent or bloody discharge from the ear.
- Hearing loss.
- Ringing in the ear (tinnitus).
- Dizziness (vertigo).
- Nausea or vomiting as a result of dizziness.
What does the eardrum look like?
The appearance of the eardrum is an important diagnostic criterion by which one can judge the condition of the inner ear and its organs. Through the handle of the hammer, the sound that vibrates is transmitted to the anvil, then through a long process it is transmitted to the stirrup, and the next link in the chain is the cochlea. The cochlea consists of two and a half turns of the channel, inside of which there is liquid, divided into compartments by membranes. The liquid is not homogeneous: part of it is represented by endolymph with an increased concentration of potassium ions, and part by paralymph, which contains a large amount of sodium ions. Between the oppositely charged parts of the liquid there is a separation membrane, which amplifies the incoming vibrations by discharging the electrical voltage.
The membrane contains a transformer that converts sound vibrations into the electrical potential of a nerve impulse. This transformer is called the Organ of Corti. A canal extending down from the middle ear cavity is called the Eustachian tube. Thanks to this passage, the difference in internal and external pressure is smoothed out. If the pressure in the environment suddenly increases or decreases, a person yawns reflexively, which helps restore the balance necessary for normal hearing.
There is another way to relieve ear congestion; to do this, you should tightly close your nostrils with your hand, seal the nasal cavity, and then take air into your mouth and blow it forcefully into your nose.
Reconstructive surgery
This technique is aimed at restoring the function of the middle ear. The purpose of the operation is to replace or restore the eardrum and improve hearing.
Alternatives to surgery
It is impossible to close a hole after a large rupture using methods other than surgery. The risk of delay is represented by deterioration of hearing and the possibility of infection entering the middle ear. Other complications may occur relatively rarely:
- meningitis,
- sepsis,
- purulent inflammation of the brain,
- facial nerve paralysis,
- deafness,
- imbalances.
Uncontrolled growth of the eardrum into the middle ear often leads to septic inflammation of the bone. There is a risk of more serious complications.
The course of the operation and its consequences, possible variations
The operation is performed under general anesthesia, less often under local anesthesia.
A skin incision is made along the upper wall of the ear canal through the auricle, sometimes behind it. Under the control of a microscope, the eardrum and middle ear are opened, and the condition of the auditory ossicles is checked. Cartilage is taken from the protrusion in front of the ear or directly from it, from which the material for replacing the eardrum is made.
If the auditory ossicles are damaged, they are replaced with plastic prostheses or pieces of bone and cartilage. The sound passage is lined with fatty tissue.
Risks and complications
In 10–15%, surgery may result in significant ear discharge.
After surgery you may experience:
- whistling in the ears,
- taste disturbance,
- dizziness,
- impaired mobility in conditions of swelling of the facial nerve.
These disturbances are temporary. Severe postoperative complications are exceptional.
Absolute success of treatment and a completely risk-free operation cannot be guaranteed by any doctor. General risks of surgery, such as heart and circulatory disorders and pulmonary complications, cannot be excluded, despite all the advances of modern medicine.
Lifestyle and home treatment
If you have trouble with your ear, try combining treatment with the following measures, which will protect the eardrum during healing:
- Keep your ears dry during treatment. When swimming, use silicone earplugs or a piece of cotton cloth coated with petroleum jelly.
- Avoid cleaning your ears yourself. Give your eardrum time to heal completely.
- Avoid sharp blowing of your nose. The pressure created by this can lead to damage to the already healing membrane,
- Warm compresses or over-the-counter pain relievers (eg, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen) can be used to relieve pain.
Diagnosis of organ condition
Only an otolaryngologist can accurately determine the presence of a problem. During diagnosis, a history is taken from the patient and, without fail, an examination using an otoscope. An examination will help identify additional signs indicating a violation:
- discoloration or clouding of the membrane;
- protrusion of the process of the malleus;
- thinning of tissues;
- presence of perforation;
- change in the light reflex or its absence at all;
- different types of discharge.
If necessary, additional studies may be prescribed:
- Audiometry and tuning fork testing to detect decreased hearing acuity at certain frequencies.
- Impedance measurement, which determines the compliance of the membrane and the presence of accumulation of liquid of any kind behind it.
- The Politzer blowing procedure, with which it will be possible to determine the obstruction of the Eustachian tube.
- A smear test to determine possible infection.
Complications and consequences
The most common complications of eardrum injury are inflammation of the middle and inner ear. A damaged membrane cannot prevent infection from entering. A microbial agent can also penetrate into the cranial fossa - meningitis develops (inflammatory changes in the meninges) or encephalitis (the substance of the brain is involved in the inflammatory process).
The most serious consequence of eardrum injury is deafness, complete or partial. This is observed if the area of damage is significant and the membrane cannot heal completely.
Traditional methods
Treatment can be supplemented with traditional methods. Such recipes have a general strengthening effect and speed up recovery. To speed up the regeneration of damaged tissues, you should consume more products rich in vitamin C. This includes fresh vegetables and fruits, berries, and sauerkraut. In addition, the patient is recommended to drink rosehip decoction, grape juice and tea with the addition of hawthorn.
During the recovery stage, you can place a cotton wool soaked in an infusion of nightshade or pine needles into the ear canal . All procedures must be agreed with the attending physician.
A ruptured eardrum should be treated as early as possible. Only in this case is it possible to avoid serious complications, which include labyrinthitis and meningitis. Treatment can be carried out both conservatively and surgically. Therapy is always supplemented by taking antibacterial drugs.
Clinical symptoms
Signs of damage to the integrity of the eardrum depend on the cause of the injury. For example, a rupture of the eardrum from a blow is accompanied by severe pain at the site of its application. In inflammatory processes of the middle ear at the time of pus breakthrough, on the contrary, pain decreases.
The following symptoms indicate a violation of the integrity of this membrane in the ear:
- hearing loss - immediately after a blow or breakthrough of pus, a person feels a decrease in hearing acuity on the side of the damage;
- dizziness and nausea – especially if there is combined damage to the eardrum and vestibular apparatus;
- leakage of pus (during inflammatory processes), blood (combined traumatic damage to the ear and other tissues);
- noise of varying severity in the damaged ear (from moderate to unbearable hum).
All of the above means that you need to contact an otolaryngologist as soon as possible. In case of combined head injury, a medical consultation will act (otolaryngologist, neurosurgeon, neurologist, infectious disease specialist).
Procedures and drugs used in treatment
If the eardrum does not heal on its own, treatment includes procedures to close the tear. Such methods include:
- using a patch
- surgical intervention,
- taking antibiotics.
Patch
If healing complications occur, a paper patch may be used. In this procedure, the doctor treats the edges of the tear with a chemical to stimulate cell and tissue growth and then covers the area with a bandage. The procedure must be repeated several times until complete healing.
Surgery
If the paper patch does not have the desired effect, your doctor may recommend surgery.
The most common surgical procedure is tympanoplasty. The doctor transplants a small piece of the patient's own tissue to close the hole in the eardrum. This procedure is performed on an outpatient basis, so the person can go home the same day unless their condition requires a long hospital stay.
Treatment of membrane rupture
Medical and surgical treatment
In most cases, injuries heal on their own, especially if only a small part was damaged. In this case, it is recommended to maintain a rest regime and also avoid any manipulation of the ear canals.
There are two methods for treating a ruptured eardrum, each of which will be used depending on the degree of damage:
Medication method. If there is a small tear, the doctor may apply a patch (paper) to close it. After about a few days, he will call a person to change and apply a new, sterile one. It will take about three or four treatments to eliminate the possibility of infection and also speed up the healing process.
If there are blood clots or residual dirt, particles of dust or other foreign objects in the wound, the doctor will carefully clean the ear with a cotton swab and then treat the walls of the cavity with alcohol.
Treatment with alcohol is necessary to disinfect the wound and eliminate the possibility of developing an inflammatory process.
After these procedures, a twisted cotton swab is inserted into the ear. In addition to the above procedures, the doctor will perform cauterization with special solutions, such as silver nitrate, chromic acid. Moreover, they are not poured inside the ear, but only the edges are processed with them.
Why is there pressure on my ears and a headache?
A video from which you can learn a lot of information about the structure of the eardrum in the human body.
And at the very end, in order to avoid infection, the specialist will prescribe ear drops (antibiotics), the main task of which will be to eliminate unfavorable microflora.
Surgical method. In the event that treatment with medications does not give the desired effect, or the gap is so large that it is useless to use conservative methods of treatment, you have to resort to surgical intervention. Myringoplasty or surgical intervention:
- It is performed under general anesthesia, since a person, even with a high pain threshold, is not able to withstand the pain when using local anesthesia.
- A small incision is made behind the person's ear. It is from this place that a piece of tissue is taken to cover the damage.
- Then, the taken flap is sewn to the damaged membrane using an endoscope and self-absorbing threads. Such threads will dissolve on their own in about a couple of weeks, and during this time the wound will completely heal.
- After surgery, a swab soaked in antibiotics is inserted into the person's ear to prevent infection. In addition, the patient is prohibited from taking deep breaths in and out through the nose, as this can move the patch and it will take root in the wrong place.
The prognosis for people who have suffered a ruptured eardrum is quite optimistic, except in cases where treatment was not carried out on time and the infection spread deep into the tissue.
First aid for perforation
If the membrane is damaged, there is a high risk of infection, so the patient is contraindicated:
- various warm-ups in a bathhouse, sauna, application of compresses and heating pads;
- independent removal of purulent discharge, blood clots and foreign objects;
- rinsing the ear with cold water;
- traveling by plane and parachute jumping;
- diving deep into water;
- listening to music on headphones;
- applying cold.
First aid consists of introducing a dry sterile turunda into the external passage. Then the patient should be transported to the nearest hospital, and if the pain is severe, give him a diclofenac or paracetamol tablet. During transportation, ensure that the patient does not shake. Do not tilt or tilt your head.
If a foreign body gets in, you should not remove it yourself - this can further injure the ear and cause infection. In such cases, a specialist uses a special hook. The instrument is inserted into the affected ear and gently pushed between the wall of the ear canal and the foreign body until the hook is behind it. Then the hook is hooked onto the object and removed.
In case of emergency admission, bleeding is first stopped using tamponade and a bandage. In case of mucopurulent discharge, the doctor takes actions aimed at ensuring the unhindered outflow of pus. Then a sterile swab is inserted into the ear canal and replaced after a while. To liquefy the pus, a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide is poured into the ear. After this, the purulent secretion is removed using a special probe.
Next, the doctor uses a catheter to infuse the following medications into the ear:
- Dioxidin solution (0.5-1%) - the product has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
- Tsipromed (0.3%) - antimicrobial drops with a wide spectrum of action.
- Otofa (2.6%) - antibacterial drops.
The above drugs promote tissue restoration and faster wound cleansing.