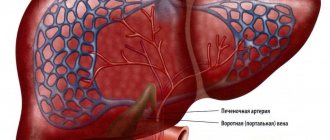
Among the internal organs, the liver is the largest. She has a lot of physiological functions and an excellent ability to restore on her own. Despite such regeneration, this organ cannot cope with serious diseases on its own, so computed tomography is needed - it will identify existing problems in order to prescribe appropriate treatment.
A CT scan can show disorders and diseases that a person does not even feel, since this gland has a minimum of nerve endings, which means there may not be one of the main symptoms - pain. Human anatomy is such that CT scans of the liver and gallbladder are usually performed together, since the bile that enters the gallbladder is produced by the liver.
What it is?
Liver CT is a diagnostic method that allows you to determine liver pathology. The method is effective and informative in identifying the early stages. The procedure is carried out through radiation scanning to obtain complete and detailed data on the condition of the liver. Computed tomography of the liver can detect the disease at an asymptomatic stage. When diagnosing a liver tumor using the method, it is possible to determine the type. For example, a hemangioma is detected when its size has not yet reached 10 mm.
Liver tomography consists of scanning the organ to identify abnormalities.
Liver tomography capabilities:
- determination of the state of the liver parenchyma;
- clear visualization of tumors of various types;
- establishing the reasons for organ enlargement;
- determining the type of pathology that caused jaundice;
- visualization of internal bleeding, degree of danger, place of blood accumulation in liver injury.
CT as a method for diagnosing the liver
The principle of studying the liver using CT is based on X-ray exposure - electromagnetic waves penetrate deep into the tissues and detect differences in densities. As a result, about 10–12 slices (pictures) are taken, which are sent to the matrix and read by a computer. In a healthy person, the liver tissue is homogeneous and dense, and areas with less density correspond to the location of large blood vessels. The hepatic and bile ducts are clearly visible on the tomogram, but the intrahepatic vessels and arteries are invisible, so to visualize them the patient is injected with a contrast agent.
In addition to comparing tissue density, other diagnostic markers are used during liver CT. For example, tumors and thrombi at an early stage of formation have a density similar to parenchyma, but they are also indicated by distorted contours of the liver. And if the bile ducts are dilated, then we can say by 70% that the patient has obstruction of the bile ducts (obstruction of the bile ducts). A study was conducted to compare the diagnostic capabilities of CT and MRI:
| Diagnosis | CT | MRI | ||
| Cyst (non-parasitic) | large cysts have a liquid density, while small (solid) cysts can be recognized by ultrasound | 82,1% | low intensity for T1 signal and high for T2 signal | 90,4% |
| Cyst (hydatid cyst) | multilocular fluid formations with calcifications on the walls and with bone density | hypointense signal of multiple calcifications | ||
| Abscess | reduced density and accumulation of contrast around the hollow capsule | 88,2% | T1 low and T2 high | 90,8% |
| Hemangioma | low density, round shape of the formation with a homogeneous structure and clear contours | 79,6% | accumulation of contrast towards the center from the periphery, characteristic imbalance of T1/T2 signals, formation without capsule and edema | 97,3% |
Percentage values are the maximum diagnostic accuracy of the method when studying certain pathologies. Pathological formations are arranged in the table in order of increasing density coefficient relative to each other.
The contrast agent makes it possible to distinguish ordinary cysts from cystic metastases, which accumulate contrast at the edges.
The results showed that MRI diagnostics is more effective for detecting tumors, but CT has its advantages over magnetic resonance:
- better visualization of the walls of blood vessels and ducts, making it more likely to detect blood clots and obstruction;
- ease of identifying pathology at an early stage of development;
- speed of the procedure (only a few minutes compared to the 60–120 minutes required for MRI);
- imaging provides a three-dimensional image of the liver;
- when studying the abdominal organs, CT is more informative;
- the gallbladder is less amenable to MRI examination;
- affordable price.
It is the speed of the procedure and lower cost compared to MRI that has led to the widespread use of computed tomography. In addition, it can be used to examine patients for whom magnetic resonance is contraindicated. These are people suffering from claustrophobia and overweight (more than 110 kg), as well as patients who have metal prostheses and implants in their bodies.
People over 50 years of age who have tattoos, even if an MRI is indicated, undergo a CT scan, since tattoo dyes previously contained iron. A strong magnetic effect causes attraction of Fe particles, causing enormous pain in the patient.
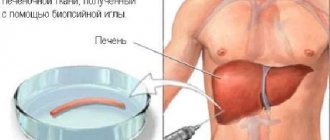
When diagnosing liver tumors, an integrated approach is very important, since sometimes even the combined use of MRI and CT does not make it possible to distinguish a benign tumor from a malignant one. In this case, a biopsy is indicated. Most often, doctors first prescribe an ultrasound as the first stage of diagnosis, and then a CT scan. This is due to the fact that if the echogenicity of the tumor is the same as the parenchyma, it can only be visible on CT and vice versa.
Advantages
The possibility of early detection of any liver pathology makes CT a popular diagnostic method that stands out among other diagnostic procedures. Radiation scanning allows you to determine even functional abnormalities in the liver through the use of a contrast agent. As a result, the doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, determine a treatment regimen or adjust therapeutic tactics. By recognizing the disease at an early stage, the chances of curing the patient without surgery increase. Thus, the advantages of the procedure are:
Tomography allows you to identify liver diseases at the earliest stages.
- accurate diagnosis of diseases of any etiology;
- possibility of simultaneous examination of the liver and regional organs;
- possibility of emergency scanning without preparation and obtaining quick results;
- the use of less sensitive motion sensors, which allows you to obtain higher quality images;
- the ability to create a 3D image for viewing from different angles in the original and enlarged version;
- minimum side effects;
- minimal sensitivity to metal implants, insulin pumps, pacemakers in the patient’s body and no effect on their operation;
- painlessness.
How the research is carried out
The patient lies down on a movable table, which will be placed in the tunnel of the device. It is very important to lie still, so the patient’s position is fixed using fastening straps and a bolster.
Next, the medical staff leaves the room and the scanning process begins. To ensure clearer images, the patient may be asked to hold their breath briefly during the procedure. Medical staff monitors the process through a special window, and to communicate with the patient, the tomograph has a built-in two-way communication system.
A metallic taste in the mouth and hot flashes are normal after contrast injection, and if pain or nausea occurs, the patient should immediately inform the doctor.
The research process lasts 10–30 minutes.
After the scan is completed, the diagnostic specialist deciphers the images taken during the study and transmits the conclusion to either the patient or his attending physician to determine treatment tactics. The patient may also request that the result be recorded on digital media.
Normal or pathological?
To increase the effectiveness of the method, the use of contrast is recommended. With the help of an auxiliary substance, standards are determined for the shape, size, structure, contours of the organ, the structure of the lobules, the condition of the fat capsule, intrahepatic vessels and bile channels. Normal indicators based on CT results of liver tissue are visualized as follows:
- structural homogeneity of parenchymal tissue;
- greater tissue density than the pancreas, kidneys, spleen, gall bladder;
- less dense areas in the structure of parenchymal tissue, corresponding to the hepatic vessels;
- lack of visualization of the hepatic artery and bile ducts inside the lobules;
- identification of the portal vein, common hepatic and bile ducts.
Liver diseases according to CT results are displayed in color saturation and expansion in certain areas of the organ.
Pathology is determined by the following characteristics:
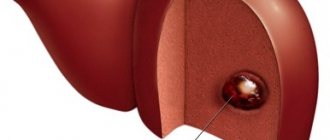
- Benign tumors (classic cysts, adenomas, hemangiomas) CT shows as darkening with smooth edges with clear boundaries, but a wavy structure. Type of growth: slow to small amounts.
- Malignant neoplasms CT shows as shadows with uneven, fuzzy, bumpy edges. Type of growth - fast, aggressive to large sizes.
- Problems with the ducts for blood supply and bile outflow are visualized by changes in color saturation (more often by intensification) in certain places, as well as by the disappearance of some ducts and the visualization of others.
Indications for the study
There are many indications that indicate the need for CT:
- signs of cirrhosis, tumor lesions, cysts, abscess;
- signs of hemangioma (benign tumor in infants);
- gallbladder disease, jaundice of unknown origin;
- hepatomegaly (pathologically enlarged liver);
- clarification of the nuances of a disease identified in another study;
- metallic taste in the mouth, bitterness;
- heaviness and aching pain in the right side;
- nausea after meals;
- trauma, dark urine;
- discoloration of stool.
Techniques used
To scan the liver on a tomograph, a beam of X-rays is used, which illuminates the body from all sides. The device records the speed of radiation passing through the liver tissue, and then processes it using special software. Three-dimensional color images of the organ are created on a computer with clear visualization of the pathological area. To make an accurate diagnosis, one of the following types of CT scans can be used:
Tomography is carried out in hardware, followed by software processing of the primary data.
- SCT (spiral tomogram) is a classic technique using rotating X-ray beams in a spiral, which allows you to obtain one or several images per revolution. The rotation speed is selected by the doctor individually.
- MSCT of the liver is a multispiral technique (modernized SCT) with increased resolution. Scanning speed - 300 images/revolution. Often used in emergency diagnostics.
- CT scan of the liver with contrast is a technique often used to identify problems with blood vessels and bile ducts. To do this, a contrast agent with the main component, iodine, is injected into the patient’s cubital vein and can accumulate in structures with increased blood supply.
- SPECT of the liver is a single-photon emission technique that allows one to obtain layer-by-layer images of parenchymal tissue after intravenous administration of a radiotracer (Technetium isotope). The technique makes it possible to identify tumors of different nature and etiology based on insufficient or excessive accumulation of isotopes. Color layer-by-layer images can be combined into a 3D picture.
CT results: what is considered pathology
A specialist, interpreting the results of a liver CT scan with or without contrast, will be able to see the presence of pathological formations in the organ. Having a lower density than the parenchyma of the gland, they will be clearly visible on the resulting images. The doctor will not only be able to see absolutely all neoplasms, but also understand their nature.
CT scan of the liver allows you to exclude or confirm the presence in its parenchyma of:
- tumors (adenomas or other types) - inclusions that have a round shape and low density (which is a deviation from the norm), having different sizes and clear or blurred outlines;
- abscesses – homogeneous formations of a round shape;
- cysts - benign neoplasms of an elongated shape, with a lower density than tumors and abscesses;
- blood clots - fresh, more dense, or just forming clots, less dense than the parenchyma of the gland;
- hematomas – severe damage to an organ of various sizes and shapes.
Indications
The procedure is prescribed to diagnose a disease or as a control after surgery on the gland, after transplantation or excision of part of the liver, after chemotherapy or radiation due to cancer in order to detect changes in the organ and monitor its condition. CT scan of the hepatic lobules is recommended if the following pathologies and conditions are suspected:
Tomographic examination makes it possible to diagnose cysts, oncology, inflammation, and injuries to internal organs.
- cystic metastases;
- polycystic disease;
- portal vein hypertension, disturbances of general blood flow in the organ or liver infarction;
- pathological enlargement of the liver of unknown etiology;
- all types of cirrhosis;
- fatty infiltration;
- radiation injury;
- tuberculosis, hepatitis, abscesses;
- thrombosis, venous obstruction;
- cancer, blastomas;
- lymphoma, focal metastases;
- hemangiomas, echinococcosis, lipomas;
- peritoneal injuries.
Indications and contraindications for CT scan of the liver
An unpleasant feature of the development of liver diseases is the fact that it contains a small number of nerve endings, so a person cannot always feel that something abnormal is happening to the organ. However, if the patient often complains of pain and heaviness in the liver area, bloating, metallic taste, nausea and bitterness in the mouth, such symptoms are an indication for an ultrasound, based on the results of which the doctor may prescribe a referral for a computed tomography scan.
Other indications for liver CT include:
- detection of organ enlargement for unknown reasons;
- the need to clarify the preliminary diagnosis, for example, cirrhosis or hepatitis;
- identification of pathological formations, the need to clarify their size and extent of distribution;
- suspicion of tumor diseases, the appearance of metastases;
- presence of disturbances in the functioning of liver vessels;
- conducting surgical interventions: surgeons prescribe CT scans before surgery, in preparation for it, and after it to assess its effectiveness;
- impaired blood flow and thrombosis in this part of the body;
- infectious and inflammatory processes, polycystic liver disease;
- chronic alcoholism, which, as is known, often provokes irreversible processes in the liver;
- previous abdominal injuries.
There are also situations where the potential risks of tomography are higher than the likely value of the data obtained in the process, or when, due to the nature of the human body, the information content of the study will be too low. In the presence of certain diseases and conditions, CT scanning can generally harm a person. Tomographic scanning of the liver is prohibited:
- for pregnant women and nursing mothers, due to the risk of exposure to the fetus;
- for children under 3 years of age, so as not to expose a very young body to x-rays;
- for diabetes mellitus, acute forms of bronchial asthma;
- in the presence of iodine intolerance, kidney or liver failure, if we are talking about computed tomography with contrast;
- in case of severe general condition of the patient, for example, if he is connected to life support devices;
- in diseases and pathologies associated with the manifestation of hyperkinesis: in such cases, the patient will not be able to ensure complete immobility during the scan, which is why the value of the resulting images will be almost zero.
For obese patients, liver CT remains questionable. On the one hand, it is known that ultrasound is practically uninformative for them, since it poorly visualizes the organ due to the presence of a pronounced subcutaneous fat layer. On the other hand, computer tomographs, in general, are simply not designed to weigh more than 140-180 kilograms. In such cases, the doctor decides at his own discretion how exactly the patient will be examined.
Contraindications
Like any other normal procedure, CT scan of the liver has some limitations and precautions in use, such as:
- Pregnancy, especially in the first trimester.
- Children under 16 years old. The procedure is prescribed extremely rarely, since radiation can have an unexpected effect on a fragile body.
- Increased sensitivity to x-rays, contrast, radiotracer.
- Severe pathologies and conditions. We are talking about cardiac and renal dysfunction, diabetes, myeloma, and thyroid problems.
Contraindications for examination
Computed tomography is attractive for its high information content and accuracy, but in some cases it cannot be performed:
- during lactation (if urgently necessary, take a break from breastfeeding);
- during pregnancy, in very serious condition;
- claustrophobia, epilepsy, mental disorders;
- severe diabetes mellitus;
- renal or liver failure (advanced stages);
- chronic thyroid diseases;
- allergy to iodine (serves as a contrast);
- too much weight (limit 150-180 kg depending on the characteristics of the device).
If the subject falls into this risk group, then another diagnostic option is selected for him, for example, ultrasound.
Preparation
The classical CT method does not require special preparatory measures. The exception is the technique with contrast. The condition for a successful procedure is to refuse food 6 hours before the start of the scan. You should take all existing health records with you to the tomography, and the doctor should be informed about existing pathologies, phobias (for example, fear of closed spaces), pregnancy, and lactation. To avoid any troubles, you should prepare yourself mentally for the procedure. If the patient is in a particularly nervous state, the doctor prescribes a sedative as preparation. If you experience an aversion to the contrast when taken orally, your doctor will allow you to dilute it with juice or tea.
Contraindications to CT
Tomography is excluded in case of serious disorders associated with the brain, throat, nose and neck, spine, reproductive system, mediastinum. The doctor may refuse this research method if a person has serious pathologies of the cardiovascular system, lymphatic flow and musculoskeletal elements.
In some cases, contrast is enhanced with an iodine-containing drug. This material is contraindicated in cases of thyroid disease, hyperglycemia, renal failure, complicated general condition, allergic reactions to contrast components. During lactation, breastfeeding is interrupted for 24 hours. Diagnosis is not carried out if the patient’s weight is unacceptable for the tomograph.
Due to radiation, CT scans are not performed on pregnant women or young children. Rays negatively affect rapidly growing tissues.
How do they do it?
The procedure is carried out in a special room with radiation protection. In a separate room there is a computer that reads data from the tomograph. The patient is placed on a special movable table in a supine position (on his back). The table slides inside the device, where the X-ray machines are mounted. To obtain the best and clearest images, the patient should lie still. Often the patient is secured with special belts. Sometimes you need to hold your breath for a while. The data obtained from CT is given to the patient within an hour.
How is a CT scan performed?
The examination is carried out under the supervision of a radiological technician. A medical opinion is given by a doctor - surgeon, therapist or infectious disease specialist.
Before the procedure, jewelry and clothing are removed and a disposable gown is put on.
A tomograph for examination is a device in the form of a ring with a table. The patient is placed in it. A separate piece of equipment rotates, examining the necessary areas of the body from the inside. The images are captured layer by layer. During the procedure, a slight hum or clicking sound is heard. The patient must be completely relaxed so that he does not move.
CT scan with contrast of the liver
The indicator substance allows you to obtain more accurate images of soft tissues to identify the condition of blood vessels, the lymphatic system, and detect tumors. When using contrast, before entering the table, the patient is injected or given an indicator substance to drink. Subsequently, the contrast will be removed naturally some time after the CT scan. To make this happen faster, it is recommended to drink more fluid - on the second day the body will completely get rid of the indicator.
Is it possible to do a CT scan of the gallbladder?
The computed tomography method does not always detect gallstone disease. Therefore, this study is prescribed when it is not possible to resort to other diagnostic procedures or in order to clarify the diagnosis. The build and anatomical features of the patient are the determining factor when choosing examination tools.
There is a restriction on performing a CT scan of the gallbladder, which shows that this method is unsafe for health. The recommended frequency of the procedure is no more than once every 3 or 4 months. The primary purposes of computed tomography are:
- Diagnosis of stones and their difference from tumor-like processes of benign and malignant nature.
- Determination of the type of jaundice (hemolytic, mechanical or parenchymal).
If the clinical picture of the disease is atypical, then tomography is recommended. This study allows you to accurately determine whether there is thickening of the walls, changes in shape, and see structural changes in the organ better than with ultrasound. However, identifying purulent processes using CT is difficult, since bile and pus have an equal absorption coefficient.
The use of contrast makes it possible to visualize inflammatory changes. However, this examination is additional for cholecystitis and helps to obtain data for the correct choice of subsequent treatment tactics.
Possible risks
Radiation exposure during tomography is minimal, but should not be overused.
CT involves irradiating the body, but a single use will not lead to consequences. But despite the minimal doses, frequent procedures are not recommended due to the ability of radiation to accumulate in tissues. Therefore, if it is necessary to repeatedly monitor the patient’s condition, CT is replaced by alternative methods, for example, ultrasound. Frequent CT scans are fraught with cancer.
Adverse reactions to the use of contrast agents are possible, although the risk of occurrence is minimal. The diagnostic room always has emergency medications to normalize the patient’s condition in case of an unexpected allergic reaction. To exclude side effects, it is recommended to prepare for creatinine blood tests before the procedure. If the patient has underlying pathologies, the procedure is performed in the presence of an anesthesiologist who can help in an emergency.
Stages of preparation for the examination
The procedure is performed quickly, it is important to prepare for the study in advance. Preparing for CT:
- Before the study, it is necessary to do a general blood and urine test and undergo ultrasound diagnostics in order to determine whether the procedure is contraindicated.
- For a couple of days, it is important not to allow yourself to eat flour, smoked products, spicy and fatty foods, and other foods that increase gas formation. With increased gas formation, the intestines put pressure on other organs, which can cause distortion of the examination results.
- It is forbidden to eat immediately before the test. The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach. It is important that 7-8 hours pass after eating. Doctors also recommend taking a laxative or doing an enema to cleanse the body.
- It is advisable for the person being examined to wear clothes that do not restrict movement. Before the procedure, you must remove jewelry.
- It is important for the patient to be relaxed. Anxiety leads to unnecessary movements, which will not allow you to take a high-quality image.
Recommendations
When a contrast agent is administered, the patient may experience a metallic taste in the mouth, nausea, dizziness, and a feeling of heat throughout the body. If symptoms become severe, you should tell your doctor right away. After completing the procedure, it is advisable to drink a lot of clean water to quickly cleanse the body of the contrast agent.
Accuracy and influencing factors
The quality of the results obtained during computed tomography of the liver is influenced by recent examinations using a barium-based contrast agent or a special intensifier. This substance may not yet be completely eliminated from the body and will give false results when exposed to X-rays. Metal objects in the form of surgical clamps in the peritoneum can interfere with the normal course of liver examination.
There are a number of examinations similar to tomography in terms of the safety of the procedure and the quality of the results.
Differences between CT and MRI
MRI is magnetic resonance imaging; the test is prescribed as often as CT.
The capabilities of the two examinations differ, since the devices use different types of radiation. It cannot be said that one method is better. For some diseases, only MRI is prescribed. Computed tomography provides accurate results when examining internal organs, so it is necessary to assess the condition of the liver. MRI is mainly used to visualize cartilage, muscle tissue, and brain structures.
This video will tell you a little more about the difference and features of these two studies.
Alternatives
There are many similar CT techniques. All of them are interchangeable, but are more often prescribed in combination, especially in complex cases. Radiation scanning is often used when the accuracy of other diagnostic techniques is not up to par. Among non-radiation techniques, only MRI can be compared in terms of information content with CT, as it is the same fast and accurate way to diagnose pathologies of the liver, blood vessels and bile ducts. Less commonly, CT is replaced by conventional X-rays or ultrasound, which are lower in cost per examination. For a comprehensive examination of the liver and body, we recommend the latest development of nuclear medicine - PET CT, which examines pathological changes in real time.
Which is better - ultrasound or CT scan of the liver?
But which is better: ultrasound or CT scan of the liver? Ultrasound is often used due to its accessibility and lack of health risks. If we consider the issue in relation to pregnant women, then ultrasound is allowed without restrictions. CT cannot be used at any stage of pregnancy, as the magnetic field can have a teratogenic effect on the unborn child. And in terms of the amount of information obtained, CT is significantly inferior to ultrasound research.
Benefits of using liver CT:
- high resolution: during diagnosis, the doctor receives layer-by-layer images, the thickness of which is less than 0.5 mm;
- reduction of study duration;
- high quality of received images;
- obtaining images of the heart and coronary vessels as quickly as possible (with the risk of developing circulatory disorders, even a minute of delay can cost the life of a sick person);
- the ability to obtain images in several dimensions at once;
- excellent visibility of scanned objects, high clarity of each image;
- minimal number of contraindications (pregnancy, breastfeeding, excess body weight);
- excellent informativeness of the method in cases of suspected blockage of coronary vessels;
- minimizing the risk of adverse reactions;
- affordable cost of research.
Classification of computed tomography
Doctors divide clinical equipment depending on the nuances of the task and the design of the device. There are three types:
- Step-by-step research (classical technique) - during the test, the transforming table is moved inside the tunnel with slow movements, sensors record readings and simulate an image. To create a new cut, the couch must be in constant motion. The photo shows the desired section in section.
- Spiral analysis (SCT) - the workplace moves at a constant pace, and the X-ray emitter independently describes a trajectory in a circle of a certain area. The installed detectors will record vibrations that have penetrated into the anomalous area. The survey takes much less time compared to the first method and shows detailed and specific summary information.
- Multislice tomography (MSCT) is a multilayer assessment of the condition, which stands out from others due to the location of the clamps. They are placed in several lines.
Decoding the received data
Diagnostic results in the form of images, diagrams of liver segments and transcripts are provided on film and CD.
The attending physician assesses the condition of the liver, identifies abnormalities, diagnoses the disease and prescribes appropriate treatment. If the readings are normal, the bile and hepatic ducts are located in areas of low density. When contrast is used, they are distinguished from surrounding tissues and vessels. Compared to other internal organs, the liver is more dense. On the device you can see the portal vein; the vessels are characterized by a linear and rounded shape, as well as lower density. The gallbladder has the same characteristics; the parenchyma is homogeneous.
With pathology, the contours of the liver change noticeably. The primary tumor can be detected by round formations, including stones. The presence of a benign tumor is indicated by the presence of an area with low density. The liver is enlarged and has uneven edges, and the bile flows are dilated.
- Distorted indicators can be obtained if the person was moving at the time of diagnosis.
- Also, incorrect data can be obtained if a woman is pregnant or there are metal inserts on clothing.
- Among the substances used the day before, barium and bismuth can reduce the accuracy of the study.
This is a very accurate and detailed technique, so it is used both in the early and late stages of the development of pathology. Volumetric images allow you to identify the disease and determine the causes of its occurrence. The procedure is painless, so it is actively practiced in cancer centers and hospitals.
The price of the procedure is 5-8 thousand rubles, the cost depends on the city and the prestige of the clinic. Contrast agent is paid separately. There are also less expensive alternatives for liver testing.
- Ultrasound irradiates internal organs using ultrasound. This method diagnoses mild illnesses, since the rays quickly dissipate and do not allow accurate readings to be obtained. Such research costs no more than a thousand rubles.
- MRI, which uses magnetic atomic resonance to obtain a good three-dimensional image of an internal organ, is considered more accurate. Radiation is not used here, so the technique is used to study children and pregnant women; it can be done quite often. The diagnostic price is 10 thousand rubles.
- The most expensive is positron emission tomography, the cost of which reaches 50 thousand rubles. Electrons and positrons are introduced into the body in the form of a contrast agent. But PET is one of the most accurate methods for detecting disease.
For diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract, you should consult a gastroenterologist. Cardiovascular disorders in the liver area are detected by a cardiologist, and metastases by an oncologist.