- Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy: description of procedures, main differences
- Indications for sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy
- Preparing for research
- Contraindications to sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy
- Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy: painful or not
- Other bowel examination techniques
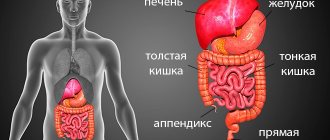
Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy are among the instrumental studies that allow you to examine and study the condition of the colon. Endoscopic diagnostics of the intestine can be performed as a separate manipulation or used as part of a comprehensive examination of the patient. How are sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy performed? Sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy - which is better? We'll talk about this in this article.
Colonoscopy
A diagnostic research method carried out to identify intestinal diseases using a special endoscope (colonoscope) is called “colonoscopy”. The main functions are to examine the inner surface of the intestine and diagnose possible pathologies.
When is it prescribed?
Indications for examination using colonoscopy are:
- discomfort and pain in the anus and abdominal cavity;
- purulent discharge from the rectum;
- the presence of mucus in the stool;
- difficult bowel movements alternating with loose stools;
- sudden weight loss of unknown nature while maintaining nutrition;
- presence of cancer in a family history;
- anemia of unknown etiology;
- elevated temperature;
- intestinal bleeding;
- traces of blood in the contents of the distal colon.
The procedure is also prescribed if there is suspicion of:
- disruption of the movement of contents through the intestinal tract;
- Crohn's disease;
- the presence of various neoplasms;
- UC (nonspecific ulcerative colitis).
During the inspection, the following actions are possible:
- tissue sampling for analysis when neoplasms of various etiologies are detected;
- removal of a foreign body;
- removal of abnormal tissue growths (polyps) and small benign tumors;
- restoration of patency during intestinal narrowing.
A colonoscopy examination may be prescribed before gynecological surgery. For people over 50 years of age, an annual examination is indicated for preventive purposes.
How is it carried out?
The colonoscopy procedure is impossible without complete preliminary cleaning of the gastrointestinal tract. You should start preparing for the study 3 days before it takes place. Exactly following the doctor’s recommendations will allow you to obtain reliable results and avoid difficulties during the examination.
Pre-cleaning includes two important stages:
- Following a special slag-free diet.
- Medicinal cleansing of the intestinal tract.
The study takes place in a specialized room. The examination is usually performed by an endoscopist surgeon.
Step-by-step colonoscopy:
- The patient, who first undresses to the waist, is placed on the couch on his left side with his knees bent and his legs pressed to his stomach.
- Anesthesia is administered.
- The specialist slowly and carefully moves the colonoscope deep into the colon, filling it with air to straighten the folds.
- The doctor, by palpating the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, controls the passage of the device through the bends of the rectum.
- During the entire procedure, a video is shown on the screen, which is carefully studied by the endoscopist.
- At the end of the study, gas is removed from the intestine, the endoscopic device is carefully removed and disinfected.
Patients who have undergone local anesthesia or sedation leave the clinic on the same day. The person being examined under general anesthesia is moved to a ward until the anesthesia wears off or left in a medical facility for several days under the supervision of specialists.
Videos of the procedure or photos of individual areas of the colon can be recorded on digital media. At the end of the examination, the doctor enters the data into a special document, gives the necessary instructions and writes a referral to a specialist for further treatment.
Contraindications
Colonoscopy is contraindicated in the following cases:
- acute myocardial infarction;
- diseases of the bronchial system;
- pulmonary and heart failure;
- severe circulatory disorders;
- peritonitis;
- pregnancy;
- penetrating damage to the walls of the colon;
- diverticulitis;
- ulcerative colitis;
- inguinal or umbilical hernia;
- general serious condition of the patient.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of colonoscopy include the following factors:
- this is one of the most accurate and informative ways to assess the condition of the intestine available to modern medicine;
- high visualization allows a specialist to detect even minor changes;
- Along with the examination, it is possible to carry out a number of therapeutic manipulations.
The advantage of colonoscopy is also considered that the examination allows:
- assess the condition of the mucous membrane and walls;
- determine the spread of pathologies;
- differentiate inflammatory processes in the intestines;
- takes a little time.
The disadvantages include:
- the complexity of the preparatory stage, the accuracy of which determines the reliability of the information obtained during the study;
- fear of the procedure, which usually causes anxiety and requires the patient’s psychological attitude;
- the need for anesthesia due to pain;
- the risk of a condition that aggravates the underlying disease.
The disadvantages of the procedure include the risk of the following complications:
- end-to-end violation of the integrity of the intestinal walls;
- bleeding;
- reaction to sedatives;
- nausea;
- gagging;
- temperature increase;
- feverish condition;
- pain in the abdominal cavity.
The video explains the colonoscopy procedure. Filmed by the channel Live great!
Sigmoidoscopy
This is a method of endoscopic examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon. This procedure is similar to a colonoscopy, the only difference is the depth of examination of the intestines. If the pathology is located further than the limit of visibility of the device, colonoscopy will be more effective. Typically, sigmoidoscopy is used if it is not possible to thoroughly prepare for a colonoscopy.
When is sigmoidoscopy necessary?
Intestinal sigmoidoscopy is often performed in combination with other diagnostic methods. In our medical center, this diagnostic method is prescribed for the following pathologies:
- stool incontinence or constipation;
- suspicion of a tumor in the rectum;
- rectal bleeding;
- ileoanal anastomosis;
- suspected colon cancer.
For people who have a hereditary predisposition to colon polyposis, this endoscopic diagnostic method can be included in a routine preventive examination.
What you need to know about preparation
Preparation for a visual examination of the intestines consists of dietary restrictions and cleansing enemas. The patient is advised to stop eating and drink only water the day before the appointed date. At the time prescribed by the doctor, you need to do cleansing enemas, according to the recommendation of a specialist.
In some cases, the preparation procedure may be different. For example, if colitis is suspected, a cleansing enema is not performed. With this approach, assessing the condition of the intestinal mucosa is not difficult.
How does the procedure work?
After the patient assumes a left lateral decubitus position, the doctor will perform a digital examination of the rectum to ensure there are no contraindications. If sigmoidoscopy of the intestine is performed on a man, a preliminary digital examination will help to exclude prostatitis.
If there are no contraindications to the procedure, the doctor carefully inserts a sigmoidoscope into the patient’s anus to a depth of 60 cm. At the same time, the patient’s reaction is monitored: if pain occurs, the insertion of the sigmoidoscope is stopped
The doctor examines the intestinal mucosa as the sigmoidoscope advances. If small polyps are found, a tissue sample may need to be taken for testing. The endoscopist warns the subject about this.
In most cases, people have no consequences after sigmoidoscopy. Sometimes there may be some minor bleeding or discomfort after the biopsy that goes away quickly.
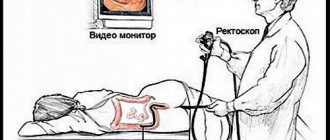
Rectoscopy
An endoscopic examination aimed at studying the condition of the intestine using a sigmoidoscope (rectoscope) is called sigmoidoscopy (rectoscopy). Inflammatory processes, all types of neoplasms in these organs are diagnosed and, if necessary, removed using this procedure.
When is it prescribed?
Diagnostic rectosigmocolonoscopy is performed for the purpose of a thorough examination of the intestinal mucosa. This procedure is prescribed to determine the correct treatment tactics.
With the help of such an examination it is possible to diagnose:
- rupture of the mucous membrane of the final part of the digestive tract;
- chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane with the formation of ulcerative processes;
- congenital malformations of the distal intestine.
In addition, sigmoidoscopy is indicated when symptoms occur:
- cutting, pain in the anorectal area;
- purulent inclusions and mucous discharge from the anus;
- bleeding;
- constipation;
- IBS (irritable bowel syndrome);
- hemorrhoids;
- pathologies of the pelvic organs;
- decreased hemoglobin levels in the blood due to iron deficiency of unknown etiology;
- chronic colitis, enterocolitis;
- severe symptoms of intestinal microflora disturbances for no apparent reason;
- causeless weight loss;
- alternation of loose stools and difficult bowel movements;
- uncontrollable urge to defecate;
- preparation for further intestinal examination;
- suspicion of polyps;
- possible pathological growth of the endometrium;
- presumptive oncopathology.
Therapeutic indications for the procedure include:
- removal of abnormal tissue growth (polyps);
- removal of foreign objects;
- stopping bleeding from blood vessels, ulcers, tumors.
Sigmoidoscopy is used to monitor and evaluate the state of the gastrointestinal tract after diseases of the digestive system, if there is a family history of a predisposition to pathologies in this area. The study helps diagnose rectocele, a disease associated with protrusion of the rectal wall, mainly in women.
How is it carried out?
Before performing rectoscopy, it is necessary to collect information about the presence of diseases and allergic reactions in the patient, as well as medications taken. The examination is possible only 5-7 days after an X-ray of the gastrointestinal tract using barium, since it interferes with the examination of the mucous membrane.
The sigmoidoscopy procedure, like colonoscopy, requires preliminary preparation:
- 2-3 days before the procedure, you must begin following a certain diet;
- the night before and on the day of the study, you should avoid eating any food;
- to empty the intestines of contents, cleansing enemas are performed, which can be replaced by taking laxatives;
- Half an hour to an hour before the diagnosis, the patient is given a microenema.
The inspection includes the following steps:
- The patient is asked to undress to the waist and is placed on the examination table with his back or left side, with his legs bent at the knees. It is possible to use the knee-elbow position.
- The specialist examines the patient’s anus, assesses its condition and palpably examines the mucous membrane for the presence of feces, mucous and blood discharge.
- The sigmoidoscope is lubricated with Vaseline and carefully inserted into the anus to a depth of about 5 cm.
- Air is pumped into the intestines to straighten the folds of the mucous membrane. When moving the sigmoidoscope to a depth of 10–15 cm, the problematic area is reached – the natural curvature of the intestine. To prevent discomfort, the patient should relax as much as possible.
- The sigmoidoscope is removed using gentle rotational movements. In this case, the specialist carefully examines the rectal mucosa.
- Pathological areas found during examination are removed, or tissue is collected for further histological examination.
After the procedure is completed, the patient is left alone in the office for a short period of time, so as not to embarrass him during the period of gas leaving the intestines. The duration of the recovery process depends on the general condition of the patient and, as a rule, varies from 5 minutes to half an hour. If the patient feels well, he can immediately leave the clinic.
Advantages and disadvantages
Sigmoidoscopy is characterized by the following advantages:
- the procedure is relatively easy to perform and takes little time;
- the study is well tolerated and, as a rule, does not cause complications;
- examination allows you to study the condition of the objects under study with the possibility of conducting an accurate biopsy;
- The examination may be accompanied by therapeutic procedures, if necessary.
Flaws:
- the procedure makes it possible to study a short section of the colon and examine only the mucous membrane;
- in rare cases, perforation of the intestinal walls is possible.
Conclusion
Colonoscopy is a more informative research method. During the procedure, you can evaluate the condition of the entire large intestine and carry out therapeutic manipulations. Priority for sigmoidoscopy is given only if the doctor is sure that the lesion is localized in the lower parts of the digestive tract. Sigmoidoscopy and, if necessary, targeted examination of the distal part of the rectum are indicated.
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- How to check the intestines for oncology?
- Checking the intestines for diseases: physical, laboratory and instrumental methods
- What is anoscopy and how is it performed?
- How is capsule endoscopy of the intestine performed?
- Endoscopic methods for examining the intestine: description and preparation
- Preparation and performance of intestinal sigmoidoscopy
- Intestinal ultrasound or colonoscopy: comparison of techniques and their information content
- Irrigoscopy and colonoscopy: which test is better?
- MRI of the intestine and colonoscopy: which study is better?
- Checking the intestines without colonoscopy: alternative research methods
Main differences between colonoscopy and rectoscopy
The main difference between rectosigmocolonoscopy and colonoscopy is the depth of examination.
A comparison of research methods is reflected in the table.
| Feature name | Colonoscopy | Sigmoidoscopy |
| Main areas of research | Whole large intestine | Rectum and terminal part of the sigmoid colon |
| Depth of examination | up to 150 cm | up to 35 cm |
| Devices used | Flexible fiberoptic probe equipped with an illuminated camera and forceps for collecting material (colonoscope) | Rigid hollow metal instrument, with a lighting device and an air supply system (rectoscope, sigmoidoscope) |
| Necessity of anesthesia | The procedure is painful and requires anesthesia. | Typically, no anesthesia is required. |
| Type of suspected pathologies | Probable location of the disease in the colon | Suspicion of lower intestinal disease |
| Time of the study | 15-30 minutes | 5-15 minutes |
Indications for use
Before prescribing a diagnostic examination, the proctologist interviews and examines the patient, finds out the duration of the complaints, the time of onset, and provoking factors. Based on the data obtained, the level of damage is determined, which will be the main criterion for choosing between manipulations:
- rectum, lower parts of the sigmoid - sigmoidoscopy;
- overlying areas - colonoscopy.
| Method | Medical indications | Patient's symptoms |
| Sigmoidoscopy | · detection of polyps, tumor formations; · identification of the source of bleeding; · exclusion of ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane. | · bursting feeling at the level of the rectum; · periodic constipation; · worsening hemorrhoids; · mucous, purulent discharge. |
| Colonoscopy | · clarification of the cause of intestinal obstruction, the level of the block; · confirmation of systemic inflammatory changes (Crohn's disease); · diagnostic search for the cause of severe abdominal pain in combination with anemia, bleeding while excluding extraintestinal pathology; · the need to take tissues of the formation for histological examination; · performing an operation in the form of excision of a polyp. | · weight loss, minimally elevated temperature, anemia; · feces mixed with blood, dark stools; · diarrhea, abdominal pain, mucous inclusions in stool; · constipation, impaired bowel movements, bloating. |
Which research method is better?
Despite a number of differences between colonoscopy and rectoscopy, these research methods are not usually opposed to each other. The doctor prescribes the examination that is most appropriate. In some cases, both procedures are carried out to obtain maximum information.
You can evaluate the difference between colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy and which research method is better based on several factors:
- Information content. When it comes to diagnostic value, colonoscopy wins. This procedure is intended for a thorough diagnosis of the mucous membrane from beginning to end of the colon.
- Soreness. From the point of view of the patient’s subjective feelings, colonoscopy is more painful. Sigmoidoscopy is accompanied by less discomfort. Sigmoidoscopy does not require anesthesia; anesthesia is administered only in some cases or, at the patient’s insistence, sedatives are used.
- Simplicity and ease of implementation. Colonoscopy takes two to three times longer than a sigmoidoscopy examination and requires more thorough preparation before it is performed.
Rectosigmoscopy
PREPARATION for rectosigmoidoscopy CARRIED OUT BY FORTRANS (in 1 shift - the study is performed in the morning)
3 days before the test, exclude fiber: fresh fruits and vegetables, berries, nuts. Avoid taking activated charcoal. On the eve of preparing FORTRANS in the evening, take a laxative, regardless of the nature of the stool - DUPHALAC 60 ml or castor oil 60 ml (2 bottles, take warm) On the day of taking FORTRANS at 14.00 - a light lunch, you can drink without restrictions; – FORTRANS 4 packets: dilute each packet with 1 liter of water at room temperature (boiled or mineral water, but without gases). Take all 4 sachets on the eve of the test from 15.00 to 19.00 (1 liter per hour), drink in GLASSES (a glass within 15 minutes). Take 1.5 - 2 liters of FORTRANS, wait for stool, then continue taking the solution. The solution can be drunk chilled and washed down with lemon juice (a few drops of juice per glass of water).
When performing a colonoscopy under anesthesia (according to indications), have with you the results of tests and examinations and their photocopies: ECG, general blood test, blood sugar
Please note that anesthesia is paid additionally in accordance with the price list in the amount of 3,500 rubles (optional).
PREPARATION for rectosigmoidoscopy, performed in the AFTERNOON (from 13.00 to 17.00).
3 days before the test, exclude fiber: fresh fruits and vegetables, berries, nuts. Avoid taking activated charcoal. On the eve of preparation with FORTRANS in the evening, take a laxative, regardless of the nature of the stool - DUPHALAC 60 ml or castor oil 60 ml (2 bottles, take warm) On the day of taking FORTRANS at 14.00 - a light lunch, you can drink without restrictions; FORTRANS package: dilute each sachet with 1 liter of water at room temperature (boiled or mineral water, but without gases). Take a sachet on the eve of the test from 18.00 to 20.00 (1 liter per hour), drink in GLASSES (a glass within 15 minutes). Take 1.5-2 liters of FORTRANS, wait for stool, then continue taking the solution. The solution can be drunk chilled and washed down with lemon juice (a few drops of lemon juice per glass of water). On the day of the study, take the remaining two liters of FORTRANS from 6.00 to 8.00.
When performing rectosigmoidoscopy under anesthesia (according to indications), have with you the results of tests and examinations and their photocopies: ECG, general blood test, blood sugar
Please note that anesthesia is paid additionally in accordance with the price list in the amount of 3,500 rubles (optional).
Preparation for rectosigmoidoscopy with enemas (if there are symptoms of intestinal obstruction)
3 days before the test, exclude fiber: fresh fruits and vegetables, berries, nuts. Avoid taking activated charcoal. Do not have dinner the day before (light lunch at 14.00), you can drink without restrictions. At 16.00, take a laxative – 60 ml of castor oil (2 bottles, take warm). From 18.00, cleansing 1.5 liter enemas with water at room temperature at intervals of 1 hour until clean water (at least three). On the day of the study, do not have breakfast, you can drink, repeat cleansing enemas until you get clean water (at least two). When performing rectosigmoidoscopy under anesthesia (according to indications), have with you the results of tests and examinations and their photocopies: ECG, general blood test, blood sugar
Please note that anesthesia is paid additionally in accordance with the price list in the amount of 3,500 rubles (optional).
Preparation for anesthesia (narcosis) in the endoscopic department
Have with you:
- General blood analysis
- Blood test for sugar and urea
- ECG
The results are no more than 1 month old.
How much does research cost?
A sample of the cost of colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy services is presented in the table:
| Region | Cost of colonoscopy | Firm | Cost of sigmoidoscopy | Firm |
| Moscow | from 2900 rub. | "Trustmed Medical Center on Taganka" | from 1000 rub. | "Medical On Group - Balashikha" |
| Chelyabinsk | from 1000 rub. | "City Hospital No. 8" | from 400 rub. | "Polyclinic of Hospital No. 2" |
| Krasnodar | from 1600 rub. | "Railway Hospital" | from 700 rub. | "Family Health Clinic "City Clinic"" |
results
The results of the examination are assessed by an endoscopist or proctologist. The conclusion is issued to the attending physician, who interprets them. It is important to note that decoding should only be done by the attending physician. Under no circumstances should you engage in self-diagnosis or self-medication.
Two similar studies have the same indications and contraindications, methodology and interpretation of results. However, fibrocolonoscopy differs from colonoscopy in the devices used that can reduce the level of discomfort for a person. The modern version of the method is well tolerated by patients and does not lead to the development of complications.
Proctologist is a doctor who will understand
Proctological diseases belong to the category of those the presence of which a person is embarrassed to inform a stranger and prefers to turn a blind eye to the obvious symptoms of the disease or endure pain. Many people turn to a specialist only after ignoring the disease becomes impossible.
Because of this, the disease may progress, which will complicate further treatment. Instead of enduring pain and inconvenience, it is better to visit a doctor as soon as possible, because in some cases, the specialists of our center will help in getting rid of the problem in one visit. For example, anal papillomas or polyps can be painlessly removed in just one visit, after which the patient can return to their normal rhythm of life. Therefore, it is better to put aside the feeling of shame and contact our clinic.
Proctology in Moscow - trust the specialists
The effectiveness of treatment for diseases of this kind depends on three factors:
— the speed of a patient’s visit to a qualified proctologist;
— accuracy of diagnosis;
- providing competent and qualified treatment.
The first aspect depends entirely on the patient, the rest - on the medical institution to which the patient goes. We can confidently say that our center has at its disposal everything necessary to provide fast, high-quality and effective treatment. qualified proctologist will tactfully and delicately ask you about the signs of the disease. You can be sure that during the conversation you will not feel awkward or embarrassed. This will be followed by an examination by a proctologist , consisting of a doctor examining the condition of the anal canal and the adjacent perianal area, as well as conducting a rectal digital examination. Further diagnostics involve the use of the latest equipment available at our center. The following are used as diagnostic tools:
— rectoscope (allows you to study the condition of the rectum); An ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed;
- Oncological examinations are carried out.
This approach to the matter allows our specialists to accurately diagnose. Treatment methods for diseases of this kind, used in the network of our centers, also contribute to quick and painless treatment, upon completion of which the patient is able to return to normal life in a minimum number of visits to the proctologist . The combination of proven conservative treatment methods, an individual approach to the patient, and the use of original medicines known in proctology make it possible to speed up the healing process and minimize the discomfort associated with it.
Sigmoidoscopy is an examination of the cavity of the rectum and sigmoid colon using a flexible endoscope. It is often confused with colonoscopy. However, colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy have certain differences, the main one of which is the depth of the intestine at which the study is performed.
Often, sigmoidoscopy is performed when, for some reason, it is not possible to make thorough preparations and perform a colonoscopy. The latter is indicated if the location of the pathology in the intestinal lumen is deeper than the end of the sigmoid colon.