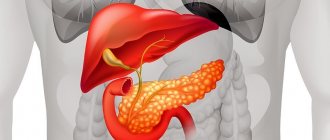
Pancreas and its role
The organ for the most part belongs to the exocrine type. Here the synthesis of enzymes that promote digestion occurs - they participate in the production of gastric juice, which is then sent to the duodenum. Inflammatory processes in this area often take a chronic form. This leads to the appearance of a focal formation of the pancreas provoked by pancreatitis.
The area of the gland where hormones are produced that regulate metabolic processes is of the endocrine type. These hormones include insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, pancreatic polypeptide, and ghrelin. They participate in glucose metabolic processes, regulate the production of glands, and influence the feeling of need for food. If pathology manifests itself in this area, the carbohydrate balance is disturbed, and tumors provoke intensive growth or suppression of hormone production.
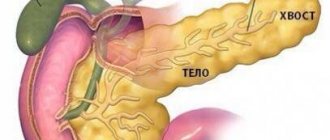
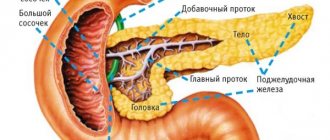
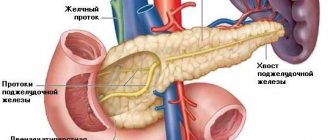
Important. The pancreas structurally includes several parts - the head, neck, body and tail. It is in the first part that most formations arise.
Characteristics of hepatic lesions
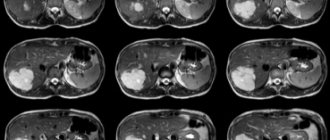
All volumetric neoplasms determined during computed tomography are divided depending on a number of parameters: density, structure, shape, contours, size, localization.
Density is the main characteristic of any tissue, measured on computed tomography in Hounsfield units. Based on density, foci can be hypodense, hyperdense, or isodense. Based on the density indicator, there is reason to assume what is in the structure of the lesion, whether there is fluid, blood, or soft tissue components.
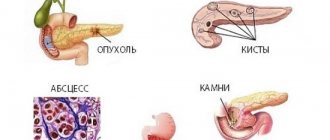
Cysts are divided into multi-chamber and single-chamber, they have or do not have visible walls, and contain bile. A foreign body or parasite, soft tissue or cystic component is determined inside.
With necrosis, there may be a heterogeneous structure; the duration of the pathological process is indicated by the identification of calcifications and lime.
Shape and contours
The shape of the formations is close to an elongated, irregular ball. Circuit:
- uneven or smooth;
- unclear or clear;
- visible along the entire perimeter or only in a limited area.
The formation is measured on an axial section; if a control study is necessary, a so-called marker lesion is selected. The dynamics of changes in the size of the lesion are assessed over time.
In order for the doctor to see the whole picture, the description of the computed tomography must indicate the location of the pathology. The outbreak may be located:
- deep in the liver;
- about with veins;
- near the gallbladder and ducts.
Such information suggests the etiology of the problem.
The number of pathological areas may vary. A solitary lesion in the liver is always single; with cancer there are many such altered areas. If one metastasis is detected, the doctor assigns stage M1 (according to the TNM measurement system).
But it must be remembered that multiple focal formations are not always metastases. The doctor will also need to conduct a differential diagnosis, carefully comparing all the available signs.
Features of contrast agent accumulation
The higher the accumulation of contrast agent, the better the tissue is supplied with blood. And vice versa, the slower the parenchyma accumulates contrast, the less developed the vascular network.
The more actively the tissue density decreases after completion of the administration of the substance, the more intense the blood flow in the affected areas of the liver.
Factors provoking pathology
Oncological diseases are often difficult to diagnose, and their causes are not fully understood. This is also typical for formations that arise in the head of the pancreas. The risk of developing the disease increases due to the following reasons:
- Heredity.
- Tobacco abuse. It contains many carcinogenic components that activate the development of cancer cells.
- Chronic pancreatitis causes disruptions in blood circulation and metabolic processes at the cellular level.
- Aging of the body. Older people suffer from frequent disruptions in the immune system, as a result of which malignant tumors occur more often.
- Diabetes mellitus in a long-term form. Due to the death of beta cells, foci of tumor formation arise.
- Excess weight, which acts as a provoking factor for hyperlipidemia and hypercholesterinemia. This causes lipodystrophy of the pancreas.
- Irregular nutrition leads to overload of the gland and enzymatic deficiency.
- Excessive consumption of strong alcoholic beverages, which causes the death of groups of cells.
We also recommend viewing: Eating jam for pancreatitis
Complications
Complications of pancreatic cancer are diabetes mellitus, trophic disorders, functional disorders of the gallbladder, and malabsorption.
Metastases spread to the liver, lymph nodes, and lungs. Kidney and liver failure gradually develops.
In case of renal failure, the patient's diuresis is impaired, lethargy appears, a delirious state occurs, and death is possible. To combat this, hemodialysis is performed. When the liver is damaged, symptoms of jaundice, itchy skin, and bitterness in the mouth appear.
Types of formations of the pancreas
Focal formations of the pancreas can be benign and malignant. The former are characterized by a favorable prognosis for recovery, although they require surgical intervention. Malignant tumors can grow into neighboring organs and pose a threat to the patient’s life.
Pancreatic tumors can be classified into the following groups:
- epithelial;
- non-epithelial;
- pancreatic islet tumors:
- lymphoid type;
- metastatic;
- mixed;
- others.
Diagnostic measures
It is somewhat difficult to detect the presence of a tumor on the head of the gland. It is for this reason that diagnostics should only be comprehensive. Both laboratory and instrumental techniques are prescribed. The first stage of diagnosis is interviewing the patient and examining him. In addition, it is important for the doctor to clarify some points - the nature of the symptoms expressed, their intensity, whether any of the relatives had cancer (hereditary factor), etc.
The standard diagnostic plan includes the following methods:
- general clinical blood test;
- blood test for tumor markers;
- General clinical urine analysis;
- blood biochemistry;
- endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Ultrasound;
- CT and MRI;
- performing a biopsy. One of the most informative methods, as it makes it possible to clarify whether a benign or malignant tumor has formed.
Benign tumors
Such formations are characterized by slow development. In this case, the tissue is not damaged, and the tumor does not grow into nearby organs. The likelihood of metastases is practically absent.
Types of tumors
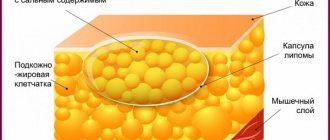
Multiple and single neoplasms localized in any part of the pancreas can form. When the epithelium of an organ is damaged, adenomas or cystadenomas appear, but connective tissues suffer from fibromas and lipomas.
Muscle tissue becomes the basis for the formation of leiomyomas, but lymphangiomas and hemangiomas are formed from tissues of the vascular type. The islets of the gland are susceptible to the action of insulinomas. In this case, due to neurogenic factors, neuromas and ganglioneurinomas appear.
The source of benign neoplasms is usually heredity. Bad habits, poor nutrition, and the environment have less influence on their origin.
Symptoms
In order not to miss the active development of a benign tumor, you should be attentive to the following signs:
- changes in hormonal balance, accompanied by lethargy, dizziness and headaches, anxiety, heavy sweating;
- pain in the left or right umbilical region, which is encircling or paroxysmal in nature with the possibility of spreading to the scapular area or arm;
- icteric manifestations, since the formations of the head compress the ducts;
- nausea and vomiting that occurs after eating and is a consequence of pressure on the duodenum.
The risk of such neoplasms should not be underestimated. They can degenerate into malignant ones or lead to bile intoxication. Against the background of the disease, pancreatitis develops and problems with the thyroid gland arise.
Important. An increase in the size of benign formations can provoke intestinal obstruction. However, if they are removed in time, a complete cure is possible.
Diagnostic features
Such tumors are detected at an early stage during regular medical examinations and examinations. They do not manifest themselves in the natural environment. To specify the diagnosis, ultrasound, CT, and MRI are performed. Blood is given for general analysis and biochemistry, and is also examined according to the criterion of an oncological marker.
We also recommend viewing: Pancreatic pulsation: causes, diagnosis and treatment
Treatment and rehabilitation
The only way to get rid of a diagnosed benign tumor is through surgery. If it occurs in the tail part of the gland, then partial resection is performed and a separate section of the organ is removed. Insulinoma can be eliminated using the desquamation method, when only the damage is removed.
The formation that has formed in the pancreas, and specifically on its head, is eliminated by pancreatoduodenal resection. During the operation, the duodenum is also removed. When the formations are small and located in the tail zone of the gland, and there is no risk of degeneration, doctors recommend performing a mini-invasive laparoscopy.
After surgery, you should follow a diet, excluding fatty, salty, sweet or starchy foods from your diet. The duration of this regime is at least 1 year. At the same time, enzymes are prescribed and physical activity is limited.
Important. To eliminate the risk of a hernia, the patient is prescribed to wear a support belt. You should undergo regular ultrasound examinations for 2 years.
It is quite difficult to eliminate the risk of developing pathology. There are no specific methods of prevention, especially since the role of heredity is high. However, a balanced diet, exclusion of alcoholic beverages from the menu and therapy for pancreatitis can reduce the risk of the disease.
Therapeutic diet
Regardless of the cause of swelling, diet should be an integral part of therapy. With its help, the load is removed from the gastrointestinal tract and, in particular, the pancreas. In addition, therapeutic nutrition allows you to speed up the process of tissue healing and relieve inflammatory processes.
Like most therapeutic diets, nutrition for swelling of the gland involves avoiding harmful foods, introducing healthy and neutral foods into the diet, as well as rules for preparing and eating dishes. The list of prohibited products includes:
- fast food;
- fresh flour and confectionery products, sweets, baked goods;
- sour fruits, berries and vegetables;
- fatty fish, meat and broths made from them;
- semi-finished products, sausages;
- alcohol and carbonated drinks;
- pickled products;
- canned meat and fish;
- mushrooms.
You should also avoid seasonings and large amounts of salt and sugar.
The list of permitted products includes:
- cereals and cereal soups, porridges;
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- boiled, baked and steamed non-sour vegetables and fruits;
- weak tea;
- lean fish and meat;
- crackers and dried light bread;
- decoction of rose hips, currants.
Rules for preparing and eating dishes:
- Any of the listed products should not be fried or baked with large amounts of fat. Allowed to boil, cook with steam, bake without oil.
- Optimally fractional meals. It is recommended to eat food five to six times a day at regular intervals.
- Overeating is strictly prohibited. The maximum serving size is two hundred - two hundred fifty grams.
- The last meal should be taken no later than one to two hours before bedtime.
- The first two to three days after the onset of the attack, the patient is advised to fast. Further, light pureed soups are allowed. Coarser foods can only be introduced gradually.
- Following a diet is necessary to prevent relapse of the disease.
Each patient with diseases of the digestive system is prescribed a special diet. It allows you to normalize the amount of enzymes produced and alleviate the patient’s condition.
Doctors recommend adding the following foods to your diet:
- Low-fat fermented milk products. These are kefir, natural yogurt without additives, fermented baked milk and products containing cottage cheese.
- Porridge. Buckwheat and rice are best suited. You can also eat oatmeal porridge.
- Steamed vegetable dishes. Seasonal produce: squash, pumpkin, cauliflower and broccoli. Vegetables that are found in the store all year round: beets, potatoes and carrots.
- Fruits. Patients with pancreatic diseases are recommended to eat baked apples and pears.
Approximately 80% of the total diet should consist of foods and dishes prepared in a double boiler.
It is recommended to avoid the following products:
- Nuts;
- Sweet drinks;
- Beans and peas;
- Mushrooms;
- Sausage and smoked meats;
- Fatty fish;
- Canned foods;
- Alcoholic drinks;
- Fast food.
If possible, avoid fried and spicy foods. Eating too much fat can change the amount of enzymes produced and worsen the patient's condition.
The presence of large amounts of sweets in the diet will negatively affect the condition of the pancreas.
It is highly not recommended to add sour fruits, especially citrus fruits, to food. It's better to make do with baked apples and pears.
Also, patients with pancreatic edema need to completely eliminate salt from their diet. Excess table salt can cause fluid retention in body tissues, which will greatly complicate the treatment of the disease.
Another piece of advice would be to switch to fractional meals. You need to eat often and in small portions so that the digestive system copes with its functions effectively.
Malignant tumors of the gland
The formation of a head in the pancreas of a malignant type is a serious problem that is very difficult to cure. At the same time, the level of bile patency in the ducts, as well as in the duodenum, drops sharply. A tumor can grow into the stomach if it initially affects the body of the gland. Tail tumors often spread to the vascular system of the spleen, and the tumor begins to cover the entire pancreas.
Symptoms
At later stages of development of malignant neoplasms, signs appear, which, however, can be a manifestation of other diseases:
- regular pain in the stomach, becoming more pronounced at night;
- loss of appetite, lack of cravings for meat dishes, coffee or fatty foods;
- rapid reduction in body weight;
- insomnia and weakness;
- enlarged gallbladder;
- manifestations of thrombotic disorders of peripheral veins;
- jaundice;
- digestive problems, heaviness in the stomach;
- bleeding, manifested by blackening of stool;
- thirst and dry mouth;
- skin itching;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
We also recommend viewing: Why diseases occur in the pancreas: symptoms and treatment methods
Diagnosis and prognosis
To make a diagnosis, the following instrumental diagnostic methods are used:
- Ultrasound – volumetric neoplasms larger than 20 mm in size are determined with a high degree of accuracy;
- CT scan, which evaluates the location of the tumor, its dimensions and shape, as well as the presence of metastases and the risk of germination;
- MRI helps detect small tumors and assess the spread of formations;
- Positron emission tomography - plays an important role in diagnosing cancer-type tumors;
- Irrigographic and x-ray examination of the stomach. X-rays provide information about the degree of deformation of organs and are performed using contrast.
- Performing gastroscopy;
- Taking a biopsy using fibrogastroduodenoscopy and oral cholangiopancreatography.
Malignant changes detected at early or late stages are difficult to treat, and the prognosis is usually unfavorable. The pancreas responds poorly to chemotherapy courses, is not subject to surgical manipulation, and the tumor quickly spreads to other organs.
Diagnostic methods
Only an examination can detect a tumor.
Even despite the presence of symptoms (which may characterize another pathology), the following studies are carried out:
- Ultrasound. This is a safe and highly informative method. Such a study allows us to determine the presence of an inflammatory process, reactive changes in the pancreas, and its condition. An ultrasound examination can detect a tumor whose size exceeds 2 cm. In addition, the study gives an idea of the level of echogenicity. The examination determines the condition of tissue such as pancreatic parenchyma. Ultrasound can reveal its structural changes.
- CT. The examination provides a description of the size, location of the pathology, and involvement of adjacent organs. The study is quite reliable when detecting a tumor from 3 cm. However, CT is associated with x-ray radiation. Therefore, it is not recommended to carry it out often.
- MRI. The high information content of the method is combined with less stress on the body.
- Biopsy. This is the most reliable diagnosis of oncology. A specific area of the tumor is taken for examination, which is carefully examined under a microscope. The required material is collected in two ways. Under ultrasound guidance, a special needle is inserted into the tumor area. The endoscopic method can be used. A special thin tube is inserted into the patient's mouth.
- Blood test. In oncology, an increase in a certain substance is detected in it. However, this characteristic may be a symptom of other diseases.
Leading cancer center in Germany
Take advantage of all your options against cancer
Neuroscience is not our only goal.
Have you discovered hypodense formation of any organ? Do not despair. You can go to Germany for treatment, find out what specific pathology you have and choose the optimal treatment for your disease.
Coming to Germany to treat hypodensity formations, you get a unique opportunity to make an accurate diagnosis as early as possible and select the most effective treatment. Contact us for advice. We make appointments for diagnostics every day during business hours.
Rare diseases
- Better clinics in Germany
- Only specialized doctors
- Individual approach
- Quick Feedback
- Medical secrecy
- Interaction with the client
- Customer support 24/7
- Refund of payment in case of refusal of the clinic
- Legal responsibility of a doctor
- Medical translation of statements
- Independent opinion of several doctors
- 100% confidentiality
What types of treatment does EMEX Medical provide in Germany?
The German medical company EMEX Medical GmbH provides the widest possible range of services related to treatment in Germany. We cooperate with clinics that specialize in treating a variety of areas: cardiology, gastroenterology, ophthalmology, surgery, oncology, orthopedics. In addition, treatment in Germany is available not only to adults, but also to children - taking into account all age characteristics. Of course, before starting treatment it is necessary to undergo diagnostics - German doctors will professionally handle this using the latest diagnostic procedures and technologies. If you want not only to receive high-quality treatment and diagnostics in Germany, but also to take preventive measures for yourself related to preventing possible complications of diseases to which you are predisposed, contact the team of EMEX Medical professionals. Still have questions? Our center's consultants will be happy to provide all the necessary information regarding treatment in Germany, as well as organizational procedures. To do this, use the feedback button located on our website.