Do you need to immediately decide what a brain meningioma or arachnoidendothelioma is? Meningioma is a tumor originating from the arachnoid mater (arachnoid endothelium). The brain is surrounded by three membranes: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. Most researchers believe that extracerebral meningioma results from damage to cells by the dura mater, but many years of research have proven the opposite. The cell is a tumor derivative. Medicine first heard the term from an American-born neurosurgeon in 1922 - H.W. Cushing.
Meningioma in 95% of cases is a benign tumor, characterized by a slow growth rate. Sometimes the formation grows quickly after surgery with the subsequent possibility of relapse. The location varies. It is important to note that meningioma does not manifest itself in any way for a long time, demonstrating a long latent period.
At what age does it occur? In adults, the highest risk is at 40-45 years of age. As a rule, women are more exposed during a difficult period - menopause; rarely children, with the development of complications. Neurofibromatosis acts in this capacity.
What are the causes of the disease, risk factors?
The causes are radioactive and x-ray radiation. The source is microtrauma of the skull, brain, and spine. It has been proven that the occurrence of the disease is associated with genetics and hereditary predisposition.
Risk factors include: age from 40 to 70 years, female gender, work in enterprises with ionizing radiation and genetic diseases.
Localization, classification
Meningioma can look different, but it is always characterized by a round shape, dense consistency and attachment of the base to hard surfaces. In special cases, it can become calcified, becoming even denser.
Benign meningioma according to ICD 10 is assigned code C71, and malignant meningioma is assigned D33. Doctors distinguish a large number of types of tumors, because... it may have different composition and place of formation.
Localization
As a rule, the tumor is located on the superficial parts of the brain, but sometimes it can occur in other parts of the skull. This is especially true in cases where the meningioma is cancer. The location may be:
- Large hemispheres;
- Foramen magnum;
- Cavernous sinus;
- Tentorial tenderloin;
- Wings of the sphenoid bone;
- Cerebellopontine angle;
- Pyramid of the temporal bone;
- Parasagittal sinus.
It is quite difficult to detect the presence of a tumor in such places. For this reason, it is often found after a significant increase.
In 97% of cases, the neoplasm is benign.
Classification
Doctors distinguish a large number of types of meningioma. This is due to the variety of possible locations and features of the tumor. The main classification involves division into three degrees:
- Benign. The prognosis is almost always favorable, growth is slow, and easy to remove.
- Atypical. Requires high-quality control, grows rapidly, can grow into the medulla, and has a tendency to relapse.
- Malignant (papillary, anaplastic). Also called meningosarcoma, it grows very quickly, removal does not give the desired effect, there is a high probability of relapse.
Many additional species are also identified based on local characteristics. What types of meningioma are there?
- Falx - formed in the falx, characterized by convulsions and epilepsy, the patient can be partially paralyzed;
- Petrified type - the patient is especially tired, suffers from weakness and dizziness;
- Anaplastic - the causes of this type of meningioma are not precisely known, the disease is not detected symptomatically, and is malignant;
- Parasagittal - is distinguished by the appearance of hypertension, convulsions, there are problems with motor activity, the manifestation of which affects only the side of the body opposite to the side of brain damage by a tumor;
- Meningotheliomatous - the symptoms are extremely weak, and the tumor grows very slowly;
- Convexital meningioma of the temporal region - characterized by problems with hearing and speech;
- Meningioma of the frontal lobe - manifestations of this type of tumor affect the patient’s psyche, he cannot concentrate, is indifferent and passive, as the tumor grows he begins to show aggression, and may experience hallucinations and depression;
- Calcified meningioma of the parietal part - characterized by disturbances in spatial orientation, disruptions in associative thinking, and mental disorders;
- Cerebellar meningioma - can affect the tentorium or hemisphere, is characterized by disturbances in coordination of movements, problems with vision, the latter affecting only one eye;
- Meningioma of the tubercle sella is one of the safest types of the disease; such a tumor can be treated without surgery; negatively affects the vision of one eye.
There are other types of meningioma: fibrous, secretory, transitional, mixed, psammomatous, microcystic, metaplastic, lymphotic, chordoid, clear cell, rhabdoid. There are also separate types corresponding to the right or left side of the head. All of them are often not used when making a diagnosis.
Most types of tumors are treatable, giving patients a high chance of a full recovery.
Classification
A generally accepted classification of meningiomas has been created. According to the classification, 3 types are distinguished:
- Meningioma grade 1. The most common. They are described as slow-growing tumors. Often with favorable prognosis for recovery.
- Meningioma grade 2. Less common. The prognosis is rather unfavorable. The tumor is growing rapidly, relapse is not excluded.
- Meningioma grade 3. The possibility of encountering this species is no more than 1%. Described as having a poor prognosis, often affecting surrounding tissue. This is a petroclival area. This also includes three subtypes.
Another classification is histological. According to it, the following types of tumors are distinguished:
- Meningioma is standard and includes 9 subtypes:
- meningotheliomatous (ICD-O code: 9530/1);
- fibrous (ICD-O code: 9530/2);
- transitional (ICD-O code: 9537/0);
- psammomatous (ICD-O code: 9533/0);
- angiomatous (ICD-O code: 9534/0);
- microcystic (ICD-O code: 9530/0);
- secretory (ICD-O code: 9530/0);
- with many lymphocytes and asymmetry is present (ICD-O code: 9530/0);
- fibroplastic (ICD-O code: 9530/0).
- Atypical meningioma (ICD-O code: 9539/1), chordoid meningioma (ICD-O code: 9538/), clear cell meningioma. These types have 2 degrees of malignancy.
- Anaplastic meningioma (ICD-O code: 9530/3), rhabdoid (ICD-O code: 9538/3) and papillary (ICD-O code: 9538/3). Such tumors contain the third degree of malignancy. Localization – sphenopetroclival area in 50% of cases. What is an ICD-O code? Literally – international classification of oncological diseases, expansion of the classification of diseases. According to the provisions of the document:
- 0 – benign meningioma;
- 1 – the type has not yet been determined;
- 2 – stage zero cancer;
- 3 – malignant tumor without metastases.
What does such a formation on the head represent? This is a dense node, the shell is petrified, exhibits a round (oval), acute-angled shape. Cases have been recorded in which the tumor is fused with the meninges. Size from a couple of millimeters to fifteen centimeters. Color varies. A concomitant diagnosis is subependymoma.
How to treat meningioma?
As a rule, to eliminate this type of tumor, a complex treatment method is used in practice, consisting of two separate methods: radiation therapy and surgery. Brain meningioma is, as a rule, a benign tumor; therefore, chemotherapy as the most radical method will be the last type of treatment. It is prescribed only after surgery and radiation therapy show a negative result.
It is important to note that the features of treatment are fundamentally different and directly depend on many different factors. The type of tumor, size, and location of the tumor influence what treatment the doctor will prescribe. Not all clinics have the necessary equipment to treat patients with radiation therapy or even more modern methods.
As a rule, treatment is first carried out, which is aimed at some reduction in the general swelling of the tissues surrounding the meningioma. After this, the main goal becomes the elimination of inflammatory processes occurring in the brain. A qualified specialist in this situation prefers to prescribe special drugs that are based on corticosteroids.
In the case where the tumor is accompanied by symptoms such as seizures, various anticonvulsants are used, whose goal is to eliminate this symptom. When meningioma appears in a certain place where it interferes with the normal circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, surgical intervention is performed to completely restore it.
Where is meningioma mainly located?
The most common lesion is the falx cerebri - 25%, the falx process. Less common in the posterior cranial fossa, and in the middle - 9%. If the cavernous sinus is affected, the functioning of the optic nerve is often affected. Sometimes localized on the wings of the sphenoid bone. A tumor of the tentorium cerebellum is known. Meningioma can form in one area or in several. It is worth adding that due to the fact that the arachnoid membrane covers the spinal cord, situations occur with its damage. In the spinal cord, this is the most common tumor that occurs on the right or left side.
Diagnostics
The slow growth of the tumor and vague symptoms significantly complicate the early diagnosis of meningioma. To make a diagnosis you will need:
- Neurologist's report. A complete neurological examination will reveal the slightest changes in the functioning of the nervous system. The doctor will carefully check all reflexes and, if necessary, refer you to other specialists for examination.
- Visualization of the tumor using CT or MRI with contrast. Tomography shows the presence of meningioma, the location and size of the tumor. MRI provides a more detailed picture and is more often used for diagnosis. In conclusion, the tomogram always clearly indicates the area of tumor localization. For example, “parasagittal meningioma” means that the tumor is visualized in the area of the sagittal sinus.
- Biopsy. Final confirmation of the diagnosis is possible only after histological examination of tumor tissue.
In some cases, the doctor may recommend additional tests (PET scan or angiography).
Life forecast
The chance depends on the location, grade of malignancy, type and subtype of tumor. If the neoplasm of the pia mater is benign, the prospect of relapse is extremely low, and after recovery no further treatment will be required. But it is very difficult to make a complete recovery by removing all formations: all brain surgeries are difficult and not always successful. For malignant tumors the situation is different; with a benign tumor there is a greater chance of living a long time.
Considering location, tumors located on the calvarium or pituitary gland have a low recurrence rate. 19% is allocated for those in the area of the cavernous sinus and where the falx is located. The highest percentage are tumors located on the frontal lobe, convexity surface (near the fornix). Multiple pathologies occur.
If you look at histology, for typical and benign formations the chances of relapse are 3%, for atypical ones - 38%. Speaking of malignant, it is 78%.
Meningioma on human brain
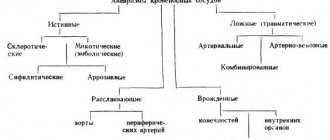
Classification of brain meningioma
Meningioma is formed from the arachnoid membrane, which covers the brain and spinal cord. Sometimes the tumor develops from the pia mater. It grows slowly, in 90% of cases it is a benign formation (not cancer). Most often found in the arachnoid membrane of the brain, less often in the spinal lining (spinal meningioma).
Tumors are classified according to location: for example, meningioma of the temporal region, tentorium cerebellum.
Malignant meningiomas are rare. As a rule, they grow quickly and metastasize to the brain, lungs and other internal organs. Some tumors are classified as atypical meningiomas. They can be called neither benign nor malignant, but they tend to malignize and develop into cancer.
https://youtu.be/ow5Cv5pk19M
Causes of meningioma
It is impossible to identify specific causes for the development of brain meningioma, but there are a number of factors that influence predisposition:
- Genetic pathology. The occurrence of a tumor is influenced primarily by genetics. This is due to the appearance of a defect in chromosome 22 and also provokes neuromas and neurofibromatosis type 2. In these diseases, peripheral nerves become affected. Studies have shown that the incidence of neoplasms in women is three times higher than in men. Guys more often develop tumors of a similar nature rather than meningiomas.
- Patients over 40 years of age and women are in the danger zone. Disruptions in the hormonal cycle determine the development of the tumor; therefore, tumor growth can increase during pregnancy.
- Ionized irradiation. Promotes the manifestation of a large number of intracranial tumors, including meningioma. According to research, however, lower radiation plays a major role in the appearance of various types of tumors.
- Traumatic brain injuries. This also affects the development of meningioma, which appears after injury, when increased proliferation of brain cells occurs due to the damage received.
Treatment methods
Treatment tactics for meningioma are always developed individually and depend on many factors. Taken into account:
- size and location of the tumor;
- tumor growth dynamics and aggressiveness;
- patient age and concomitant diseases;
- neurological symptoms.
In the presence of small, slow-growing tumors, the doctor may advise postponing treatment and observing the dynamics of growth if there are no neurological disorders. Typically, such tumors are found by chance during other studies. You will need to undergo a routine MRI and see a doctor regularly.
If the tumor grows and/or neurological symptoms are observed, the most effective treatment is surgery. The earlier the operation is performed, the better the future prognosis.
Either the entire tumor or part of it is removed if the meningioma is located too close to the brain or spinal cord. Therapy after surgery depends on whether all tissues of the formation were removed and what the cell biopsy showed.
If the benign tumor has been completely removed, no further specific treatment is required. If the tumor was not completely removed, it is either monitored or stereotactic radiosurgery (gamma knife) is used.
If the tumor is malignant, radiotherapy will be needed. Chemotherapy is rarely used and is only used if other methods have failed. Atypical meningioma is treated in the same way as malignant one.
Symptoms when meningioma appears
Cerebral meningioma is asymptomatic and slow in nature, so an experienced doctor can identify the tumor. When the formation acquires an impressive size, symptoms of meningioma appear. Symptoms depend on the anatomical location in the skull and brain. Divided into general and local characteristics.
- General: the first and most alarming symptom is constant and prolonged pain in the head. It can be dull, bursting, but also aching. Localization in the occipital and frontotemporal regions.
- Local are associated with the place where the meningioma presses. There are: paresis of the limbs (weakness, decreased sensitivity, convulsions), pain in the eyes, double vision or its absence, swelling of the face, hearing loss and the presence of olfactory hallucinations. Changes in behavior and mental fluctuations, atrophy of thinking, balance (gait becomes unsteady), and retching that goes away after vomiting are observed. There are dizzinesses and disturbances in eye pressure. The vagus nerve exerts pressure on the thoracic region. Damage along the trigeminal nerve is the cause of damage to the cerebellopontine angle.
Signs of neoplasms on the anterior surface of the brain are reduced to tremor. Patients experience prolonged headaches, pressure on the eyes, and the situation worsens in the morning and at night. Painful sensations do not have a specific localization, the pain is diffuse.
If the frontal lobe is affected, the person’s lifestyle and mental state changes. There is a tendency to aggressive, groundless and incomprehensible actions, and cannot soberly assess one’s actions and the situation as a whole. Associated symptoms: visual problems and disturbances in thinking ability, loss of olfactory sensitivity and seizures. The calcified area indicates a displacement of the formations relative to the initial location.
If pain occurs in the parietal or temporal region, there may be a lack of hearing, trouble with speech, when it is impossible to clearly express one’s thoughts in words or speech is poorly perceived by ear. Problems with the musculoskeletal system of the human body (paresis, paralysis) have been recorded. But it is worth remembering that the symptoms appear on the side opposite the arachnoid tumor from the tumor.
A disease on the cerebellum is dangerous due to impaired ability to balance, the appearance of a crooked gait with signs of intracranial pressure. If compression of the cerebral stem occurs, unpleasant pain may occur when swallowing, in the circulatory system, with breathing, and this is no less threatening for future life than the above symptoms.
Meningioma, located on the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone, has a detrimental effect on the visual nerve and optic chiasm, causes visual impairment, double vision or complete blindness, and affects the fatty tissue of the orbit. If the formation is located in or near the ventricles, with germination into other tissues, the cerebrospinal fluid pathways become clogged when excess cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the cranial cavity or in the area of the ventricles. This causes increased pressure in the skull. If communication between the ventricles and the subarachnoid space is impaired, shunt surgery will be required. In such a situation, physical exercise is prohibited.
If you have any symptoms, you should immediately consult a medical specialist for further examination and to identify the causes of certain symptom factors.
Symptoms
In most cases, the tumor grows very slowly and may not cause clinical symptoms for years. Symptoms depend on the location and appear when the tumor begins to grow into neighboring tissues: the brain or spinal cord, nerves, and blood vessels of the brain. This process is accompanied by compression of nearby organs.
The main signs of meningioma:
- vision problems, especially double, upside-down, or blurry images;
- headache attacks that become more frequent and severe over time;
- ringing in the ears, hearing loss;
- memory problems;
- lack of smell;
- epileptic seizures;
- weakness in the limbs.
Most symptoms develop gradually, which is why patients with meningioma ignore them for a long time. If at least one of the listed signs is observed, you need to go to an appointment with a neurologist.
Particularly alarming are the symptoms of visual impairment, memory and headaches, which are typical for meningioma of the frontal lobe of the brain.
Methods for diagnosing meningioma
Due to the slow development of the tumor and the possibility of no symptoms for a long period of time, timely diagnosis is difficult. Often, patients with nonspecific complaints are attributed to signs of aging. At the first manifestations of meningioma, it is necessary to undergo a full examination by a neurologist and an ophthalmologist. Doctors will determine the clinical picture and refer you for further examination. Hearing impairment is a reason to visit an ENT doctor.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) helps in identifying a malignant neoplasm, how much the tumor has fused with the meninges, and facilitates understanding in assessing the condition of nearby tissues. The study requires magnetic waves that provide a clear image and insight into the current situation in the brain. They are preliminarily sent for a CT scan.
- Computed tomography (CT) helps to visualize the extent of bone involvement and calcification associated with the tumor and, like MRI, allows you to see the tumor. This procedure is necessary for the general appearance of the brain.
- Positive emission tomography (PET) is not a common procedure due to its high cost and too little specificity. Allows you to identify the possible location of recurrent meningioma.
- Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) helps in determining the behavior as well as the chemistry level of meningioma.
- Angiography is performed to obtain data on the blood supply to the tumor; for this, a special injection is administered and with the help of it the vessels located in the human brain are visible. This is a method of preparation for surgery and a diagnostic method.
MRI of the head for humans
Despite all the listed methods for determining risk factors, the most reliable and accurate is a biopsy.
Doctors remove part of the tumor during surgery and perform a cytological examination to help understand the type and subtype. Less often, the operating doctor, when taking a tissue scraping, is able to immediately remove the tumor.
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed after a diagnostic examination, taking into account the location and symptoms of the disease. For benign forms of accessible localization, surgical intervention is usually performed. Other treatment methods: stereotactic radiotherapy and classical radiotherapy. Meningioma is unlikely to resolve on its own. But if treated correctly, its growth may slow down.
Non-surgical methods
If the tumor proliferates slowly, the oncologist may recommend monitoring the further development of the pathology. For meningiomas located in hard-to-reach parts of the brain, treatment is carried out without surgery, most often stereotactic radiotherapy. Chemotherapy is not used. Taking into account how long the therapeutic treatment lasts and what its results are, the doctor decides whether to continue conservative therapy or perform surgery.
Tablets and other forms of medication are prescribed after surgery to prevent the development of inflammatory processes and swelling of the brain matter.
The prognosis for life without surgery when diagnosed with meningioma affecting brain tissue depends on the location, degree of malignancy and intensity of tumor growth.
After totalectomy of a benign tumor, the likelihood of recurrence is low. However, complete removal of meningioma is fraught with difficulties if the tumor mass is located in hard-to-reach parts of the brain - in the area of the falx-tentorial angle, cavernous sinus, or at the base of the skull. The operation is difficult in multiple and petroclival forms.
Surgery
Indications for surgical intervention include rapid proliferation of modified cells, suspicion of a malignant form, severe neurological symptoms, which significantly worsen the patient’s quality of life. Surgical treatment of meningioma is performed in different ways:
- An operation to remove meningioma located in the brain, along with the intercellular matrix - connective tissue that ensures the delivery of nutrients to nerve cells and their mechanical support.
- Removal of the tumor followed by coagulation of the intercellular matrix.
- Resection of part of the tumor.
If a meningioma is diagnosed, surgery may be performed to decompress the surrounding brain structures. Surgical removal of meningioma is a radical method that has contraindications, including somatic diseases occurring in the decompensation stage (renal, acute heart failure, severe respiratory pathologies).
The operation is not performed if the patient has acute infectious diseases. The obstacle is the close communication of the neoplasm cells with nearby vessels, sinuses, and ducts through which the cerebrospinal fluid moves. The main contraindication for ectomy for meningioma affecting the brain is the growth of the tumor deep into the brain structures.
As an alternative to conventional surgery, the doctor will suggest stereotactic radiotherapy - exposure of degenerated nerve cells to ionizing radiation. Among the advantages of the method is access to hard-to-reach areas, when a conventional ectomy is associated with a high risk of brain damage.
Stereotactic radiosurgery involves high-dose irradiation of tumors up to 3 cm in diameter with high targeting accuracy. The procedure is carried out 1-2 times. The intervention is performed with special equipment (gamma knife). Stereotactic radiotherapy is a method of treating meningioma formed in the brain, which is based on irradiating degenerated tumor cells with low doses over several sessions.
Stereotactic therapy gives a positive result. According to the results of observation within 10 years after treatment, the growth of benign forms is controlled in 95%. Malignant tumors recur more often. The stereotactic radiosurgery method can be used repeatedly. It is characterized by a low number of complications and a reduced rehabilitation period.
Folk remedies
Therapy with traditional medicine is ineffective against tumor formations localized in the brain area. It is recommended to take tinctures prepared from hemlock, clover and celandine after surgery in order to prevent relapses.
To prepare the tincture, take 20-50 g of plant flowers, pour in 0.5 liters of vodka, leave for 10 days in a dark place, and filter. For the first time, take 1 drop of hemlock tincture diluted in a glass of water. The procedure is repeated three times a day before meals. Gradually the number of drops increases to 40. Tinctures of clover and celandine are taken 1 teaspoon before meals.
Diet
Proper nutrition is of great importance in a comprehensive treatment program, so the patient is advised to adhere to a diet. Doctors recommend reducing the amount of fatty, smoked, and sweet foods in your diet. It is better to give up alcohol abuse and smoking.
Causes
The causes of brain meningiomas have been poorly studied, but with this type of tumor process the influence of a genetic factor is clearly visible. The onset of the disease is indirectly affected by:
- radiation therapy;
- breast cancer;
- female hormonal imbalances;
- head injury, often closed craniocerebral injury;
- harmful industrial emissions;
- consumption of nitrates from contaminated food;
- high radioactive doses;
- bad ecology;
- a history of inflammation of the brain, its membranes (brain abscesses, meningitis, etc.);
- age after 40 years.
Additional Recipes
There are several groups of plants that have a beneficial effect on the treatment of brain tumors:
- Celandine. This plant is taken as a basis in most folk methods of treatment. In order for the plant to have the most beneficial effect on the body, it can be collected independently and preferably away from the city. To prepare a medicine from celandine, you will need only 5 grams of this plant - that’s one tablespoon. The herb is placed in a bowl, poured with a glass of hot water, covered with a lid and left for 15 minutes. After cooling, the liquid is filtered through cheesecloth, after which the infusion is ready for use;
- Birch lye. Preparing the decoction is as simple as in the first case. You need to burn a small amount of birch firewood and collect the ash from it. Pour in 1 part ash to 5 parts water. The mixture must be boiled for 10 minutes, but it must be in a glass or clay container. It is not recommended to use metal utensils. Treatment with this decoction must be carried out according to a strict regimen. To do this, you need to dilute 8 teaspoons of the broth in milk or juice and drink it all in one sip. The solution is taken three to four times a day;
- Aloe. This plant has long demonstrated its great effectiveness in the treatment of various diseases. To treat meningioma with aloe, you need to take only a plant that is no more than three years old. It is in this case that we can hope for tumor resorption. To prepare a tincture from aloe leaves, you need to finely chop five leaves of the plant, put it in a jar and fill it with 200 mil of vodka. Infuse the solution in a dark place for 12-14 days, while shaking it every day. After preparing the solution, it should be taken three times a day, one tablespoon two hours before meals. It is worth noting that there may also be a side effect of this solution in the form of stomach upset. In this case, it is better to reduce the dose of the solution to 2 teaspoons 2 times a day;
- Carrot. Regular carrots have a very positive effect on the treatment of brain tumors, especially when it comes to meningioma. This product can be used both as therapy and for prevention. It is best to take fresh juice. It is recommended to take no more than 200 ml of fresh juice daily. It is best to take in the morning and evening, without using sugar or salt;
- Oak bark. Oak bark also has good results in the treatment of brain meningoma. To do this, take the bark from young branches, after which it must be thoroughly dried and finely chopped. After this, 1 tablespoon of bark is brewed in a glass of boiling water. You need to boil twice: after the first boil, turn off the heat, wait until the bubbles disappear from the surface of the solution, then turn on the heat again and bring the solution to the next boil. After cooking, the solution is poured into a jar, closed tightly and left to infuse for 3 hours. The decoction is used as a lotion on the head. They need to be kept for at least 2 hours. The entire course of therapy lasts a month, with lotions applied once a day.
Do not forget that sometimes treatment with folk remedies can harm your health and aggravate the overall situation. That is why before starting treatment it is necessary to consult with a specialist.
https://youtu.be/0vv_1J0Vm5Y
Clinics for the treatment of brain diseases
- Clinic Sofia. Moscow, st. Mitinskaya, house 17 building 4. Performs diagnosis and treatment of vascular diseases of the head and brain, all types of medical examinations.
- Department of Neurosurgery of the Federal State Institution at the National Medical and Surgical Center named after. N.I. Pirogova. Russia, Moscow, st. Nizhny Pervomaiskaya, 70. We analyze and treat all types of brain tumors. The latest technologies are used for analysis.
- Institute of Humanity RAS. Russia, St. Petersburg, Academician Pavlova St., 9. One of the largest centers where not only the diagnosis and treatment of meningiomas is performed, but also new methods are developed to combat the disease.
- Sheba Medical Center, Israel. A public hospital that has a rehabilitation department, a children's department and a general clinical clinic.
- Rambam Medical Services Center, Israel. The clinic is supported by government authorities and includes the Mayer MC, which provides all types of treatment for childhood diseases.
- Honey. Ichilov center, Israel. The second largest multidisciplinary clinic. There is a rehabilitation department, a heart institute, a general hospital and a maternity hospital.
- University Hospital Tübingen, Germany. Treatment abroad is possible using the latest drugs and technologies. This institute is developing new methods to combat brain tumors.
https://youtu.be/q8NTsgEbaKk
Histological forms of meningioma
Depending on the structure of the tissue, three types of tumors are distinguished, which characterize its malignancy.
| Malignancy grade | Proportion of all meningiomas | Characteristic | Histological variant of the tumor |
| 1st degree | Up to 92-95% | Benign in nature, absence of atypia and germination into surrounding tissues, slow growth, favorable prognosis, low percentage of relapses. | A typical tumor variant, including 9 subtypes: meningotelimatous, fibrous, transitional, psammomatous, angiomatous, microcystic, secretory, with an abundance of lymphocytes, metaplastic. |
| 2nd degree | Up to 4-5% | Atypical character, faster and more aggressive growth, higher percentage of recurrence, less favorable prognosis. | An atypical variant of the tumor, including 3 subtypes: atypical, chordoid, clear cell. |
| 3rd degree | About 1-3% | Malignant in nature, aggressive growth, accompanied by germination into surrounding tissues, high percentage of relapses, poor prognosis. | A malignant variant of the tumor, including 3 subtypes: anaplastic, rhabdoid, papillary. |
Removing meningoma without surgery
Basically, meningomas are benign tumors, and therefore do not require surgical intervention, since they do not affect internal organs and are not a threat to human life. In this case, treatment can be carried out without surgery. As for malignant tumors, in this case surgery is mandatory.
Today, the most common non-surgical treatment for meningioma involves the use of a unique system of focused and precisely aimed beams of radiation at the infected area. This beam destroys harmful cells without affecting healthy tissues that are located nearby. The effectiveness of this method is very high: approximately 95% of all meningomas stop growing after just one procedure and a short course of treatment, so the prognosis for life without surgery for the patient is very positive. There is a danger that with a disease such as brain meningioma, treatment without surgery can again resume the growth of infected tissue, but still the consequences after surgery can be much worse than without surgery.
Postoperative period
The rehabilitation program after removal of meningioma includes a set of measures aimed at restoring normal functions of the brain, organs and body systems. Main rehabilitation areas:
- Massage – classical and oriental.
- Physiotherapy.
- Physiotherapy.
- Water procedures (hydromassage, exercises in the pool, therapeutic baths).
- Taking angioprotectors and neuroprotectors.
Rehabilitation lasts approximately 1-6 months. The procedures are aimed at restoring nerve and muscle conduction. Often, rehabilitation is carried out in parallel with radiation therapy sessions (to destroy and suppress the activity of tumor cells after partial removal of the tumor).
Special individual classes are conducted to restore memory, motor activity, and speech after tumor removal. Doctors of narrow specialization work with patients - a physiotherapist, a speech therapist, a psychotherapist, and a rehabilitation specialist.
Symptoms of meningiomas.
Benign meningiomas can grow asymptomatically for many years and be an incidental finding during examination for other reasons.
Symptoms can be divided into two types - cerebral and focal.
General cerebral symptoms of meningiomas.
Often the only clinical manifestation of brain meningioma is general cerebral symptoms. This includes headache, dizziness and nausea. The only thing that can bother me is a headache.
Focal symptoms of meningiomas.
Focal symptoms are symptoms associated with loss of any functions of the nervous structures and depend on the location of the tumor.
For example, meningioma of the olfactory fossa can manifest itself as a dysfunction of the olfactory and optic nerves, that is, a violation of the sense of smell and vision. This meningioma can also lead to disruption of the psycho-emotional sphere, as it is located near the frontal lobes. In my practice, there have been cases where patients were observed by a psychiatrist for several years and meningiomas were detected only during a random examination.
Meningiomas of the middle cranial fossa (wing of the sphenoid bone and tubercle of the sella turcica), in addition to visual disturbances associated with compression of the optic nerves, can also manifest as oculomotor disturbances due to compression of the III (oculomotor nerve), IV (trochlear nerve) and VI (abducens nerve) cranial nerves. nerves involved in the movement of the eyeball.
Meningiomas of the posterior cranial fossa (petroclival, pyramid of the temporal bone, foramen magnum, subtentorial tentorium cerebellum) can lead to dysfunction of the brain stem and caudal group of cranial nerves, which is manifested by impaired swallowing, hoarseness, there may be taste disturbances, speech disturbances according to the type of dysarthria due to paralysis of the muscles of the tongue, paralysis of the facial muscles and impaired sensitivity on the face, there may also be hemiparesis (weakness) or hemihypesthesia (impaired sensitivity) in the arms and legs, that is, either in the arm and leg on the left, or in the arm and leg on the right. Often hemiparesis and hemihypesthesia are combined together, and this is due to compression and damage to the pathways from the brain to the spinal cord, which are located in the brain stem. In general, tumors located near the brain stem are extremely dangerous and, if decompensated with the development of edema, can lead to death, since the vasomotor and respiratory centers important for life are located in the brain stem.
With convexital meningiomas, depending on the location, focal symptoms manifest themselves in the form of disruption of the activity of various functional zones of the cerebral cortex. Moreover, if the source of damage, and in our case it is meningioma, is located on the left, then disturbances appear on the right and vice versa. There are also functional centers that are located only in the dominant hemisphere, that is, for right-handers on the left, and for left-handers on the right. This will be discussed below.
For the frontal lobe, these may be speech disorders such as motor aphasia, that is, when the patient cannot speak, paresis (weakness), and more often monoparesis in the limbs, when weakness appears in one arm or leg, psycho-emotional problems may occur. sphere.
With meningiomas of the temporal lobe, there may be sensory aphasia, when the patient does not understand speech addressed to him. It should be noted that the cortical centers responsible for speech are located on only one side for each person. Therefore, motor or sensory aphasia can only occur if the focus of damage to the cortical center is on the dominant side. Right-handers are on the left, and left-handers are on the right.
Meningiomas of the parietal lobe can cause sensory loss in the arm or leg, often in a monotype. Praxis may suffer. Praxis is automated, goal-directed action that is achieved through exercise and repetition. For example, the simple skill of tying shoelaces or making tea, the professional skill of driving a bus or operating on a patient, even the mechanical ability to write - all this is praxis. Violation of praxis is called apraxia. In addition, there may be tactile agnosia, that is, loss of the ability to identify objects and their characteristics by touch. For example, if a patient with his eyes closed is given an object in his hand, he will not be able to describe it and understand what it is, but if the object is simply shown, the patient will immediately answer what kind of object it is and what it is needed for.
The occipital lobe of the brain is the cortical analyzer of vision. Therefore, with meningiomas of the occipital lobe, vision suffers. Certain fields of vision may be lost. There may be a disorder of such a complex type of sensitivity as visual agnosia. For example, if you give a patient a writing pen in his hand, then by touch he will understand that it is a pen, but if you simply show it, the patient will only be able to describe its individual elements, but will not understand that it is a pen.
Any meningiomas, irritating the cerebral cortex, can cause an attack of epilepsy.
You also need to know that with decompensation with the development of edema and dislocation (dislocation) of the brain, headache, nausea, vomiting may suddenly appear, focal symptoms may sharply increase, and even depression of consciousness may occur, leading to coma.
Folk remedies
The use of folk remedies for brain meningioma makes the life prognosis more positive. Non-traditional treatment has a good preventive effect on the body after the main operation. The most effective:
- Celandine tincture - take one spoon daily. A third of the jar of flowers should be filled with vodka for 2 weeks, then strain and add another 2/3 of the jar of vodka;
- Clover tincture - take one spoon before meals. It is made by infusing 20 g of flowers in 0.5 liters of vodka for ten days;
- Hemlock tincture - crushed flowers and roots of the plant are used, which are infused in vodka for 3 weeks. They should be taken before meals, adding a drop of tincture to a glass of water, and the number of drops should be gradually increased to 40;
- Bee's jelly - take 250 g under the tongue 15 minutes before meals twice a day.
All remedies help reduce the risk of relapse and have a destructive effect on existing tumors. The duration of their administration is a month.
How to diagnose a tumor
https://youtu.be/Q8RhTaHKCL8
It is not easy to identify a tumor; if suspicious symptoms appear, you should visit a specialist (neurologist or neurosurgeon) who will prescribe the necessary diagnostic procedures. Visual acuity, hearing, spatial coordination will be checked, and ophthalmoscopy will be performed. Later, the doctor will refer the patient for the following studies:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) detects the presence of cancerous objects even of a few millimeters.
- MRI can also monitor the results of surgical treatment and detect possible relapse of the disease.
- CT scan. The level of malignancy is determined by the introduction of a contrast agent.
- Oncology has the property of accumulating contrast substance in its tissues.
- Taking blood for the presence of tumor markers.
- A spinal tap may be needed to look for cancer cells in the cerebrospinal fluid.
- A biopsy is taken during or after surgical removal of the object.
- Positron emission tomography is necessary to detect possible recurrence of the disease.
- Angiography determines the condition of blood vessels.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of the disease depend on the location of the tumor. The closer to the cerebral cortex the space-occupying lesion is located, the more often the disease manifests itself as convulsive seizures.
With the parasagittal localization of the tumor, there are no symptoms of impaired liquor dynamics, since with this location there is no compression of the liquor-conducting tract. Considering that meningioma grows for a long time, the clinical picture manifests itself in advanced, advanced stages.
Moreover, symptoms caused by compression and displacement of the brain come to the fore. Most often, the cranial nerves are affected, oculomotor disturbances appear, and double vision appears.
Useful to know: What to do if you are diagnosed with stage 4 brain cancer, how long do you live with this disease?
When the tumor is located between the inner surfaces of the frontal lobes, in the projection of the anterior third of the superior longitudinal sinus, the first symptoms appear 10-15 years after the start of tumor growth and proceed very mildly.
Disturbances in liquorodynamics come to the fore, which is manifested by arterial hypertension syndrome.
There is a headache accompanied by vomiting at the height of pain. Symptoms gradually develop indicating a displacement of the brain from front to back in the cranial cavity.
https://youtu.be/5M9K7VUcMHw
If the meningioma is located in the anterior cranial fossa, where the olfactory and optic nerves pass, then a disorder of smell, vision, and psyche develops. Mental disorders are manifested by elements of the frontal psyche, which is characterized by euphoria, flat jokes, sexual disinhibition, a tendency to antisocial behavior, and a gradual decrease in intelligence.
The optic nerves are compressed by a large tumor, therefore, they are the last of all the above symptoms to occur. A decrease in vision develops on the affected side due to atrophy of the optic nerve from pressure.
When meningioma begins to grow in the area of the tubercle of the sella turcica, visual disturbances develop first and can be significant, since the optic chiasm is located in this area. Considering that this area contains the diencephalic gland and the pituitary gland, symptoms of damage to these areas may develop.
Hypothalamic-pituitary damage is characterized by a violation of thermoregulation, water, salt, mineral, fat, and protein metabolism. Endocrine organs and endocrine glands suffer, hormone production is disrupted, sleep and wakefulness are affected.
Common symptoms include increased appetite, arterial hypertension, arrhythmia, difficulty breathing, a feeling of interruptions in heart function, sexual dysfunction in the form of early menopause, and impotence.
to contents ^
Features in pregnant women
Meningioma is rarely observed during pregnancy. They appear more often at the base of the brain and are characterized by active growth, which quickly leads to a deterioration of the condition.
More often, the symptomatic picture of the disease begins to appear in the third trimester, or up to 8 days after birth. Many studies prove the hormonal dependence of the tumor process.
Meningioma of a pregnant woman can be recognized by histological examination by its special hypervascular structure. They grow due to greatly changed blood flow and a shift in the hormonal background of the female body. Pregnancy may be a contraindication if there has been a history of tumor excision, or if a residual tumor is detected.
Treatment options for meningiomas
The most effective treatment for benign meningioma is surgery.
As mentioned above, the approach to treating meningioma is largely determined by its location, size, and rate of progression. In some cases (especially for “accidentally” discovered meningiomas with no clinical symptoms), even a wait-and-see approach is possible, that is, no treatment as such. Meningioma can be small and grow very slowly. If the attending physician decides on a wait-and-see approach, then CT or MRI monitoring of the tumor becomes mandatory, that is, systematic repetition of these examinations so as not to miss the moment when the tumor begins to grow.
CM. SEE ALSO: Signs of a brain tumor
Since meningiomas are most often benign, surgical methods are most widely used for their treatment. That is, the tumor is simply removed. Moreover, the more radically the tumor is removed, the better the prognosis for the patient. Ideally, the neurosurgeon should strive to remove as much tumor tissue as possible. However, unfortunately, this is not always possible. After all, the tumor may be located in functionally significant areas of the brain or simply cannot be completely removed (for example, it grows into the optic nerve). Neurosurgeons adhere to the following principle regarding the removal of meningiomas: the surgical treatment performed should not increase the neurological deficit in the patient. Simply put, if after the operation the patient’s arm or leg fails, which makes him deeply disabled, then there can be no talk of total removal. Therefore, in each specific case, they try to find a middle ground: to remove the tumor as much as possible, and not cause even more harm to the patient.
The most radical operation is considered to be one in which it is possible to remove all the tumor tissue, part of the dura mater at the site of initial growth and the affected bone. In this case, the percentage of tumor recurrence is close to zero.
If the meningioma recurs over time, repeat surgery may be necessary. According to statistics, the five-year survival rate of patients operated on for meningioma is 92%. The probability of recurrence with complete removal of a benign tumor over the next 15 years is 4%.
Another treatment option for meningiomas is stereotactic radiosurgery. Stereotactic radiosurgical techniques are based on targeted irradiation of meningioma tissue from different angles. In this case, calculations are made so that only the tumor tissue is exposed to maximum radiation, while nearby normal tissues are exposed to minimal radiation. This treatment method is used in cases where the meningioma is located near vital structures of the brain, which the neurosurgeon cannot get to. It is also possible to independently use stereotactic radiosurgery for small meningiomas (up to 3.5 cm in diameter). Sometimes surgical tumor removal is combined with radiosurgical techniques (if radical tumor removal is impossible) or in case of recurrence after surgical treatment.
Standard radiation therapy is now used less and less. Indeed, with this method of treatment, the rays destroy not only the tumor tissue, but also nearby healthy tissue.
Rehabilitation and prognosis
In medical practice, there is such a term as the five-year survival rate of patients after undergoing surgical interventions to remove tumors. This indicator is influenced by both the structure and size of the brain meningioma, as well as the patient’s age and initial state of health. Rehabilitation after meningioma removal is also important.
Of course, quality care, a balanced diet, support and attention from relatives and friends - all this improves the prognosis and increases the chances that meningioma will remain a thing of the past and will not recur. As a rule, control tomography of the brain is required at 1-3-6 months, and then every six months.
If the process is benign, the chances of recovery are high. If meningioma is malignant, even if it is completely and timely removed, the probability of relapse remains 55–75%. However, experts urge not to give up and fight for every day of a fulfilling life.
Meningioma can be defeated. The main condition for success is to seek the advice of doctors at the slightest change in well-being, especially if headaches have become frequent and intense, and subsequently, when the diagnosis of meningioma is confirmed, to follow all the recommendations of the attending physician.
Description of the disease
Many people have at least once seen such tumors on the skin, but not everyone knows what a hemangioma in the liver is, why it is dangerous, what such a tumor looks like, and how its signs appear. A benign focal formation in the liver can pose a great threat, so anyone who is concerned about their health, and especially those who are faced with this disease, needs to know general information about a benign liver tumor.
https://youtu.be/YwpI0wLvPgo
The neoplasm in most cases is diagnosed in old age, but this does not mean that it was not present there throughout life. The liver does not react in any way to the tumor if it does not increase in size, therefore, as a rule, there are no symptoms. And only when the patient begins to worry about the liver due to an enlarged tumor, he turns to the doctor and learns about his pathology.
Meningioma falx
A tumor growing from the greater falciform process of the brain is called falx meningioma. Over time, the tumor grows into the sagittal venous sinus, resulting in impaired venous circulation and intracranial hypertension. The growth of the tumor causes the following negative symptoms: epileptic seizures, impaired sensitivity and motor activity of the legs, pelvic disorders.
Meningioma: photo
Tar and liver
- 1 Useful properties and composition
- 2 Use of Tar for the treatment of liver cirrhosis
- 3 Tar water against dropsy
- 4 Treatment of opistrochiasis
- 5 Harm and contraindications
Our readers successfully use Leviron Duo to treat the liver.
Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here... Birch tar has long served as an indispensable assistant. In the domestic sphere, it was used as glue, lubricant for shoes and armor. Healers, finding it a powerful cleanser and disinfectant, used it in the treatment of worms, skin diseases and wounds. The usefulness of tar for the liver was especially noted. Covering a wide range of effects on the body, tar is still used today in cosmetology and medicine.
Tar, which has antiseptic properties, can help the liver remove toxins and eliminate inflammation.
Useful properties and composition
Tar is an oily, viscous liquid with a pungent odor. A product obtained from a light layer of birch bark (by dry distillation). It has analgesic, antiseptic and absorbable properties, since it is rich in useful elements and organic acids (phytoncides, betulin, guaiacol, creosol, xylenol, resinous substances, etc.). Traditionally used to treat:
- skin injuries and diseases (bedsores, burns, psoriasis, skin itching, eczema, seborrhea, fungal infections, neurodermatitis);
- digestive system (stomach upset, erosive and inflammatory processes, intestinal ulcers, cirrhosis);
- respiratory system (bronchial asthma, tonsillitis);
- urinary system (urolithiasis, urethritis);
- infectious and parasitic diseases (anthrax, lice, worms, scabies mites).
The list of diseases is endless, but it is worth considering some of them in more detail.
Return to contents
Application of Tar for the treatment of liver cirrhosis
Tar is used to cleanse the body as a whole, but it is especially useful for liver cirrhosis. The disease is chronic and difficult to treat. The main factors predisposing to cirrhosis are considered to be alcoholism, viral hepatitis, poor nutrition, toxic and parasitic lesions. To support the liver affected by cirrhosis, you should take the product orally, following the recipe: in 1 tbsp. l. add a drop of tar to fresh sour cream and take a teaspoon of honey. The regimen for taking such a medicine must be strictly followed:
- 1st day – 1 drop;
- 2nd day – 2;
- so on in an increasing manner until the 10th day.
From the 11th – we reduce the amount of tar drop by drop per day. Then you need to take a break. With a new exacerbation, the course is repeated according to the same scheme. To make the treatment more effective, the water should be replaced with oatmeal broth (put 1 tablespoon of cereal into 1 glass of boiling water and leave for several hours). If during treatment your health worsens, weakness, allergic reactions occur (itching, redness, irritation of the mucous membranes), then treatment should be stopped immediately and consult a doctor.
Return to contents
Tar water against dropsy
Dropsy has long been eliminated with a solution of tar and water.
In medicine, there are diseases that are caused by more serious illnesses. Such diseases include ascites, popularly called dropsy of the abdomen. It occurs as a consequence of malfunctions of the cardiovascular system, more often with cirrhosis of the liver and kidney disease. Due to dysfunction of the abdominal cavity and the accumulation of excess fluid in it, in people with this disease the stomach resembles a barrel. For dropsy of the abdomen, traditional medicine advises drinking tar water. To prepare it you need:
- add 500 grams of pure tar to 4 liters of cold water;
- mix and close the container, putting it in a dark place for 2 days;
- drain the water from the container, being careful not to shake the mixture;
- Store refrigerated in a tightly sealed container.
It is necessary to drink on an empty stomach, an hour and a half before meals and before bedtime for two months according to the scheme: 6 days of intake - 3 days of break - 6 days of intake - 3 days of break, etc. At the end of the cycle there is a break (one to two months ).
Return to contents
Treatment of opistrochiasis
Tar is an invariably effective remedy in the treatment of opistrochiasis, a disease that affects the liver and pancreas. The causative agents are trematodes (feline fluke and Siberian fluke), parasitize the liver, gall bladder and pancreas of humans, wild and domestic animals that are infected by eating raw, unprocessed or poorly processed fish infected with helminth larvae. To prepare a remedy for parasites, you need to add tar (1 drop) to warm milk (1 tablespoon) and take it in the morning on an empty stomach 30 minutes before breakfast. The procedure is repeated every day, increasing the concentration of the medicine drop by drop. Having reached 20 drops, you need to move towards a decrease. After a 10-day break, the cycle repeats. The course lasts 40 days. During treatment, it is better to replace ordinary water with mineral water.
Return to contents
Harm and contraindications
Tar can deplete the skin and is contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women.
Tar is undoubtedly a miracle cure. But he can be dangerous. Having dismissed the obviously undesirable use in case of individual intolerance, it is worth remembering the following nuances.
- Private external use of tar exposes the skin to premature aging and can cause rashes and irritation.
- Medical studies have shown that the product contains carcinogenic substances. Therefore, thoughtless consumption will cause serious harm to the body.
- Tar is contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women, since the carcinogenic substances included in the composition have a detrimental effect on the growing body, and the odor of the product can develop a tendency to allergies.
In order for tar to be beneficial, it should be used carefully: for external use, mix with cosmetics, and it is advisable to take either tar water orally, or mix the medicinal liquid with other products, lowering the concentration. And in no case should you exceed the dosage or arbitrarily extend the treatment time!
https://youtu.be/UJKv5XJUi6Q
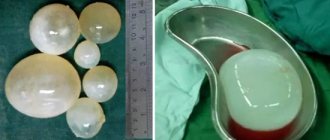
About seven percent of the world's population are faced with liver hemangioma, since this organ has a good blood supply. Hemangioma is a benign vascular neoplasm that can form on any part of the body where there are blood vessels, be it the skin or internal organs. The average age of people who develop a vascular node varies from thirty to fifty years, but in fact even a child can get sick.
In women, the development of tumors is diagnosed five times more often than in men, which may be due to the effect of estrogens on the body, which provoke tumor growth. Hemangioma almost never becomes malignant, but without medical intervention it can cause other serious complications, such as rupture and bleeding, even leading to death. Signs of hemangioma are mild or absent, so it can be detected on ultrasound during diagnosis in gastroenterology or during examination for other pathologies, for example, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or gall bladder cancer.
In rare cases, children may develop hemangioma before birth. In this case, it is usually random and goes away during the first years of life. Surgical treatment of hemangioma is carried out if there is a potentially dangerous large formation. For asymptomatic small tumors, non-invasive or minimally invasive methods of treating hemangiomas in the liver are selected.
Diet
For people suffering from meningioma, nutrition is of particular importance. By avoiding certain foods, the patient will be able to slow down the growth of the tumor and reduce the risk of its development. A healthy lifestyle is the best prevention of the development of meningioma, both for those already suffering from it and for healthy people.
The diet should consist of the most healthy and safe food. It is important to exclude from it fatty and smoked foods, meat broths, and all fast food. It is also not recommended to drink alcoholic beverages or smoke cigarettes. One of the best nutrition options for meningioma is a raw food diet. It is not suitable for everyone, but it almost always gives a positive result.
Parasagittal meningioma
Parasagittal meningioma is located in the occipital, parietal or frontal part along the longitudinal midline. Often this tumor is accompanied by a pathological increase in the content of bone matter in the bone tissue. Parasagittal meningiomas, growing in the frontal part of the head, cause:
- increased intracranial pressure;
- development of congestive optic discs in the fundus;
- severe nausea and vomiting, headache;
- epileptic seizures.
Parasagittal meningioma of the parietal region of the head is characterized by sensory disturbances and epileptic seizures. Meningioma of the occipital region is characterized by increased intracranial pressure and hallucinations.
Forecast, risks
In most cases, the prognosis for recovery is positive. After removal of a benign tumor, patients recover completely in almost 100% of cases. A significant risk of relapse is present only with malignant meningioma. Patients with such a tumor recover after surgery only in 25% of cases.
It is also important to consider that even a small remnant of a benign tumor that could not be removed can grow again. Moreover, everything may be fine for a long time, but after a few months the meningioma will begin to grow. In case of relapse, repeated surgery is prescribed.
Risks
There are other dangers too. Resected brain meningiomas cause complications after surgery that can be very serious. The following problems are possible:
- Infection;
- Large blood loss;
- Loss of vision, hearing;
- Brain swelling;
- Paralysis;
- Re-growth of the tumor at an accelerated pace.
The patient requires close medical supervision during the postoperative period. Therefore, he remains in the hospital for several days.
Rehabilitation
After surgery, the body needs time to fully recover. Therefore, the patient undergoes special rehabilitation, which can last up to six months. The exact duration depends on the person's condition. Complex therapy includes:
- Acupuncture – helps restore sensation in the limbs;
- Taking pharmacological agents – maintain the patient’s condition, reduce the risk of complications;
- Exercise therapy classes restore motor functions and help strengthen the immune system.
Additionally, special treatment methods may be prescribed that take into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
All procedures must be carried out regularly so that the person has the maximum chance of a full recovery.
Symptoms and signs
When the tumor is small, there are no symptoms or signs. The neoplasm is most often discovered accidentally. If the tumor grows to five or seven centimeters, then the manifestation of the disease will be the appearance of minor pain in the right hypochondrium. When the tumor size is ten centimeters, vivid symptoms appear.
We recommend reading Pheochromocytoma of the adrenal gland - causes and treatment
The main symptoms of liver hemangioma with which people go to the doctor are the following:
- painful sensations, mainly in the right hypochondrium, which are dull and aching in nature;
- sensations of constriction in the stomach, duodenum and all adjacent structures;
- dyspeptic symptoms - diarrhea, bloating, nausea, vomiting, heaviness in the stomach even after eating a small amount of food;
- jaundice and its signs - discolored stool, concentrated urine, yellowing of the skin and sclera.
Occasionally, sudden intense pain may occur, which may indicate tumor infarction, necrosis, or bleeding. In case of such pain, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible; it is best to call an ambulance. Basically, symptoms and treatment depend on the morphological appearance of the tumor and its size.
Treatment of meningioma
Among the many factors that determine the choice of treatment, the leading ones can be identified:
- size of meningioma;
- histological variant of the tumor;
- location of education;
- symptoms;
- general condition of the patient;
- the patient's ability to tolerate treatment.
Patients diagnosed with meningioma may be offered several treatment options.
| Treatment method | Characteristic |
| Surgical removal | Since most arachnoidendotheliomas are benign, surgery is the main treatment method. The scope of the operation and its final result largely depend on the proximity of the tumor to functionally important brain structures and the degree of involvement of vascular formations and nerves in the process. In case of complete removal of the meningioma, a cure is practically ensured and the likelihood of relapse is significantly reduced. But with some meningiomas, radical surgery is not always possible. This applies to cases where vital brain structures and blood vessels are affected. Although the primary goal of surgery is to remove the tumor, it is equally important to improve or preserve the patient's neurological function. In case of a high risk of complications during radical surgery, partial removal of the tumor with subsequent dynamic observation is possible. |
| Radiation therapy | The technique using conventional radiation therapy is practically not used to treat most types of meningiomas due to low efficiency. It is possible to use stereotactic irradiation (focusing the radiation flux on a specific target) for the treatment of tumors localized in areas that are difficult to remove surgically or adjacent to functionally important brain structures. The combination of stereotactic radiotherapy with a surgical method is also used. In this case, the part of the tumor remaining after surgical treatment is subject to irradiation. This tactic reduces the risk of relapse. |
| Endovascular embolization | X-ray surgical intravascular procedure, which consists of selective blockage of blood vessels with special emboli, which stops the flow of blood to the tumor. It is sometimes performed before surgical removal of a meningioma to reduce the risk of bleeding. For patients with absolute contraindications to surgery, the method can be considered as the main treatment. |
Most meningiomas require surgical treatment.
Chemotherapy is not used to treat benign meningiomas.
Not all patients require emergency surgery. Observation under MRI and CT control may be recommended for patients who: