Hypokinetic dyskinesia of the gallbladder is characterized by disturbances in the motility and tone of the organ and its ducts. According to statistical information, the disease is more often detected in women, which is associated with the characteristics (regular fluctuations) of hormonal levels. Dyskinesia often progresses against the background of various disorders: diabetes mellitus, gastritis, cholecystitis. The disease is a kind of “inconsistency”. The release of bile is irregular and can occur at inappropriate times. With this type of pathology, the sphincters of the receptacle do not contract sufficiently.
Characteristics of the pathology
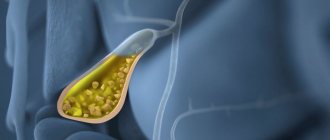
Bile is a specific fluid (secret) produced by the liver. It is actively used by the body to ensure food processing processes. The substance promotes the active absorption of fats and helps make the movement of the food bolus through the intestines as comfortable as possible. Before entering the intestines and performing its main function, bile passes through the ducts. The speed of its progress is different.
Biliary dyskinesia is diagnosed when problems with secretion are observed. In medical practice, dyskinesia is divided into two types: hypomotor and hyperkinetic. The latter is characterized by intense contraction with increased tone of the organ, while the sphincters of Oddi do not have time to work and open.
It is interesting that the symptoms of the pathologies are practically the same, but the hypomotor course is considered more complicated. The classic symptoms of gastrointestinal tract diseases are accompanied by others: belching, bitterness in the mouth, lightheadedness after eating. The risk of developing obesity increases, even in patients who do not have a predisposition to obesity initially.
Functions of the gallbladder
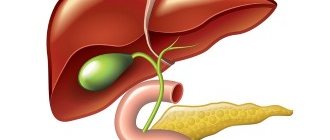
The gallbladder and the liver form the so-called biliary system. It is located directly under it and is a small oval, bag-shaped cavity (reservoir) with a volume of up to 70 cubic centimeters. The length of this organ in adults can reach up to 14 centimeters.
Main functions of the gallbladder:
- accumulation of bile produced by the liver around the clock;
- bringing it to the required consistency;
- delivery of this liver secretion to the duodenum when food enters the gastrointestinal tract.
Bile is a biological fluid that is involved in the breakdown of heavy animal fats and the release of necessary nutrients from foods entering the body.
The liver is responsible for the production of this fluid, from where it then enters the gallbladder through the common bile duct. There it accumulates, acquires the necessary consistency and, if necessary, is released into the digestive tract. This release occurs a short time after food enters the gastrointestinal tract.
Classification of the disease
Dysfunction of the gallbladder and its ducts can be secondary or primary, but the hypomotor type rarely manifests itself; more often it is diagnosed in conjunction with other pathologies. Primary hypomotor dyskinesia is provoked by the following factors:
- nervous overload;
- eating disorders;
- significant and prolonged abuse of alcoholic beverages;
- overeating combined with short-term food refusals;
- constant snacking on the go (fast food);
- sedentary lifestyle (hypodynamia);
- underweight;
- various diseases of allergic etiology.
Secondary hypotonic dyskinesia of the gallbladder is often provoked by existing diseases:
- various diseases of the digestive system;
- chronic pathologies affecting the abdominal organs;
- diseases of the pelvic organs (especially in women);
- disturbances in the functioning of the liver, gall bladder and its ducts;
- parasitic diseases, helminthic infestations;
- congenital structural abnormalities;
- endocrine disorders;
- prolonged course of bacterial processes.
These are just factors that slightly increase the likelihood of developing hypokinetic VA in adults. But, the prerequisites for the development of the problem can be created at the genetic level, even at the time of embryonic development. This feature makes it possible to explain the primary appearance of dyskinesia in children, when the risk of unfavorable factors is excluded.
How dangerous is the disease?
If the disease is not treated in adults, complications may occur. Most often, inflammatory process and cholelithiasis develop with JVP.
Violation of the tone and motility of the gallbladder leads to stagnation of secretions in the biliary tract and reflux - the release of bile into the stomach and esophagus. When an infection occurs, inflammation occurs, which is accompanied by acute symptoms - fever, paroxysmal pain, vomiting of bile contents.
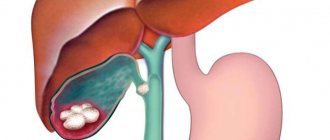
Another dangerous pathology is cholelithiasis - cholelithiasis.
Stones form in the bladder and bile ducts due to stagnant processes and changes in the chemical composition of the secretion. Stones can block the ducts, leading to obstructive jaundice. This condition requires surgical treatment.
How it manifests itself
There are certain clinical signs that suggest a problem. Their list is as follows:
- constant pain attacks, dull, bursting and aching in nature;
- severe pain in the right hypochondrium, which “spreads”; it is difficult to identify the source;
- discomfort becomes pronounced after eating, which is associated with stretching of the organ resulting from stagnation of bile;
- belching after eating;
- nausea ending with vomiting, the presence of bile in the erupting masses;
- bitterness in the mouth, which manifests itself actively in the morning and after meals;
- constant feeling of bloating, bursting pain;
- active release of gases with a foul odor;
- constipation, manifested due to the slow movement of the bolus of food through the body;
- obesity in patients (including children).
Interestingly, with hypokinetic dyskinesia, not only symptoms characteristic of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract appear.
Autonomic disorders are considered characteristic. Patients complain of bradycardia, hypotension, periodic dizziness, and increased sweating. The occurrence of these symptoms is associated with the lack of sufficient adaptation of the blood vessels and heart to stress; internal organs are faced with oxygen starvation.
Prevention and diet
The goal of the diet is to reduce the load on the liver. It is recommended to eat steamed food often, in small portions. When the pain intensifies, it is advisable to eat food in liquid form.
When the biliary system is reduced, the following are excluded from the diet:
- Absolutely all sausages.
- Sweets.
- Beef, pork.
- Eggs.
- Fresh vegetables, fruits and berries.
The following products have a beneficial effect on the body:
- low-fat kefir, yogurt,
- bird, fish,
- oil,
- vegetable soup,
- tea, coffee with milk.
Interesting fact: drinking coffee in the morning helps you forget about gallstones.
Diagnosis of the disease
You should report your suspicions of dyskinesia to a gastroenterologist, but an initial examination can be done by a general practitioner. The first appointment is an introductory one, it includes taking an anamnesis and a general examination of the patient, it is clarified when the first failures appeared and their possible causes are established.
Of course, the signs listed by the patient are not enough to determine an accurate diagnosis, so he is sent for an examination, including laboratory tests and instrumental methods. Main list:
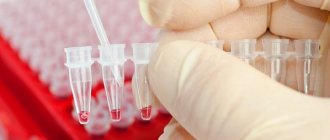
- general blood test and its biochemistry;
- urine analysis and coprogram;
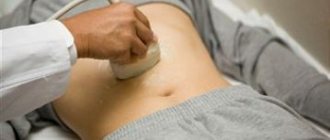
- Ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder;
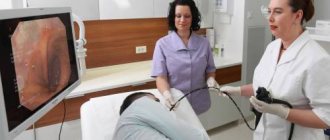
- gastroduodenal intubation;
- X-ray examination with a contrast reagent.
Treatment of gallbladder hypotension involves the use of special compounds that normalize the activity of the organ. To achieve lasting and noticeable results, it is important to normalize your mental state and constantly follow a diet. If the cause of dyskinesia is serious stress, you should consult a psychologist and select special sedatives.
Decoding the results
It is important to consider that the normal size of the organ may vary slightly depending on age. They will differ in older people and children, and the average volume of the gallbladder in an adult is about 40-80 ml.
Normal for adults
A healthy adult patient must have certain organ parameters, which include width, diameter, wall thickness and length.
The following are considered normal indicators:
- volume about 70 ml;
- wall thickness no more than 0.4 ml;
- organ length, about 6-10 cm;
- the width should not exceed 5 cm;
- the diameter of paired ducts is normally about 0.3 cm;
- the diameter of the main duct cannot exceed 0.7 cm.
Interestingly, in women over 40 years of age, gallbladder lesions are much more common than in men. Moreover, naturally overweight blondes often suffer from such diseases. In men, such pathologies are observed much later, and only under conditions of alcohol abuse and poor nutrition.
Find out the norms of the gallbladder from the video:
Norm for children
The normal size of the gallbladder in children varies depending on age. So, for newborns, the norm is considered to be a length of 3.4 cm and a width of 1.08 cm. From a month to five, the length should be 4 cm and the width should be 1.02.
A one-year-old child has a bladder length of 5.5 cm and a width of up to 1.07 cm. At 3 years old, these figures increase to 5 cm and 1.60 cm, respectively. For a 7-year-old child, the norm will be a length of about 7 cm and a width of no more than 3.70 cm. Children aged 10 years and older should have a length of the gallbladder of 7.7 cm, a width of about 3.7, and a diameter of up to 1. 4 cm.
Deviation from the norm
Any deviations from normal values are a signal of the presence of a serious pathology. A large organ size indicates the development of cholelithiasis or acute cholecystitis, and a small one indicates hepatitis.
A sign of chronic cholecystitis is significant thickening of the walls of the organ. As a rule, all pathologies of the liver and gallbladder can be diagnosed using ultrasound, but in addition, the doctor prescribes a blood test, FGDS and a coprogram.
In addition, an upward deviation in size may indicate the development of oncology, dyskinesia, or liver damage. A deviation from the norm is considered to be an irregular shape of the bladder, an increase or decrease in size, scars and adhesions on the walls of the organ, and an uneven neck of the bladder.
Treatment methods
Treatment of the disease must be comprehensive. Dyskinesia is a problem of the gastrointestinal tract, therefore, like all other disorders of the digestive system, it requires adherence to a special diet. It is important to consider that drug correction alone will not be enough; results can only be achieved by following a diet, increasing activity and using physiotherapy.
Drug therapy
The basis of the drug regimen necessary for the treatment of hypotension of the gallbladder is choleretic drugs. They contain bile and help activate its production in the body. By taking them the following effect is achieved:
- the functioning of the gallbladder improves and is restored;
- digestive function is normalized;
- the processes of fermentation and decay in the esophagus and intestines are inhibited;
- bile secretion is improved due to the activation of the sphincters of Oddi;
- provides liver protection;
- the intensity of removal of harmful cholesterol increases.
The list of popular drugs in this group includes the following drugs: Cholenzym, Allohol, Holiver. Blind probing is used to cleanse the liver, bladder and ducts to restore contractility and restore gallbladder function. To carry out the procedure, vegetable oils, sorbitol or magnesia must be used. The principle of the method is to take these medications orally. After this, the patient lies down in bed and applies a warm heating pad wrapped in cloth to the liver area. The duration of the procedure is 1 hour. The possibility of using the technique should be discussed with your doctor, otherwise the condition will likely worsen.
Physiotherapy for patients
When the activity of the organ is reduced, the use of the following techniques is indicated:
- electrophoresis using drugs that increase smooth muscle tone;
- diadynamic therapy of the gallbladder;
- SMT therapy of the affected area;
- high frequency magnetic therapy.
Good results are achievable by providing spa therapy. Patients are recommended to rest in preventive sanatoriums once a year. Regular exercise from the exercise therapy complex will be beneficial.
ethnoscience
It is pointless to treat hypomotor dyskinesia with folk remedies. They can be used for a speedy recovery, after the acute phase and in combination with traditional therapy. On an ongoing basis, patients can use decoctions of peppermint and corn silk, which will help improve tone. The following recommendations are useful:
- regular consumption of pure green tea (without sugar or additives);
- visit to the steam room (bath or sauna);
- taking 1 tbsp unrefined olive oil. l every day before meals;
- drinking tomato juice.
The listed methods do not work equally well in each specific case. From the list presented, you need to choose one that is suitable for the patient and compatible with the treatment used.
Proper nutrition
It is important to saturate your diet with foods containing magnesium and plant fiber. The most useful in this regard is buckwheat. The diet may contain vegetables and fruits, vegetable oils, and dairy products.
It should be taken into account that the following products have a powerful choleretic effect:
- cream, sour cream and other fatty fermented milk products;
- black bread;
- butter and vegetable oils;
- a variety of vegetables and fruits;
- boiled eggs.
We have prepared an article with a detailed list of products that help restore the liver
Nutrition during an exacerbation should be as gentle as possible. It is better to remove all fatty foods from your diet. Avoid frying as a cooking method. Food should be steamed, and the basis of the diet should be cereals, vegetable soups and boiled lean meat.
Useful video
What symptoms indicate problems with the gallbladder can be found in this video.
The patient may not eat or drink before the examination, but the gastrointestinal tract may be reduced due to the fact that the patient is undergoing treatment with choleretic drugs. By increasing the tone of the muscle layer of the gallbladder, they promote its contraction and the secretion of bile. Taking such drugs even on the eve of the study can lead to collapse of the walls of the organ by the time of diagnosis. This is also not a sign of pathology, but to obtain reliable results, the study will need to be repeated.
Causes of pathology in newborns
A contracted gallbladder in a newborn detected on ultrasound may be a consequence of previous feeding. If it is reliably known that the child is examined on an empty stomach, then a contracted gallbladder in an infant means possible biliary dyskinesia. This is a pathology in which the reflex secretion of bile is disrupted, which causes problems with the digestion and absorption of food, especially those high in fat.
Contracted gallbladder in adults - causes of pathology
The cause of a permanently contracted gallbladder may be the following diseases:
- Chronic cholecystitis. After each exacerbation of the disease, scar changes appear on the walls of the organ - the consequences of the inflammatory process. With a long course of pathology, cicatricial deformation of the bladder develops with the replacement of the organ cavity with connective tissue.
- Chronic cholangitis. Inflammation of the bile ducts leads to their fusion and cessation of the flow of bile into the bladder, which causes its collapse and subsequent deformation.
- Chronic calculous cholecystitis. In this disease, the inflammatory process is accompanied by the formation of stones that fill the organ cavity. In this case, the gallbladder loses its functional activity and is not able to act as a bile depot.
When it hurts on the left, a person involuntarily understands that it is more likely to worry the heart, above the navel - problems with the stomach, lower abdomen - worries the genitourinary system. The most common pathology of the right side is problems with the liver or biliary system. Almost every fifth person sees a diagnosis with the words - the gallbladder is contracted. But not everyone understands what this means. The purpose of the article is to provide the reader with complete, and most importantly understandable, information on this issue.
Bile is a secretion of the liver. It is formed in the gallbladder. If you imagine this organ as a slightly inflated balloon, then when you press it, the tail relaxes and air comes out through the hole. Our organ works in a similar way: when it contracts, the sphincter of Oddi opens and the yellow solution entering the duodenum begins to activate the processes of processing the food we take. Hypermotor form of dyskinesia is a pathology in which the hollow organ with bile is contracted, that is, the ball is constantly in a deflated state, which means that the procedure for supplying the yellow substance becomes uncontrollable.
In an adult, this part of the liver is in the form of an elongated pear, 5-14 cm long and 3-5 cm wide. The shape can vary due to deformation, the most unusual being kinks in the form of an hourglass and a boomerang. The size of the organ depends on the amount of yellow secretion inside. If normal functioning keeps its volume within 30-80 ml, then with bile retention it changes. The mucous membrane is covered with grooves and folds, which form the Lutkens-Martynov sphincter at the neck of the bile storage reservoir. As a fuse, it is responsible for the timely supply of bitter liquid.
Hormones and neuropeptides trigger the synthesis of yellow-green fluid for the functioning of important processes in the gallbladder:
- opening the intestines, disinfecting its mucous membrane;
- activation of fat decomposition: glycerin and acids;
- assimilation of necessary elements;
- conducting a safe digestion system.
Biliary dysfunction provokes other process disorders. When the gallbladder is contracted, problems with digestion of food, like a domino principle, overlap each other.
Dyskinesia in a child
According to leading experts, the main reason for the appearance of dyskinesia of the gastrointestinal tract in children is excessive susceptibility of the nervous system. Before the age of one year, the problem often arises due to developmental abnormalities at the embryonic stage or serious birth injuries. In most cases, special correction schemes are not used; it is believed that with age, children, provided they have the right diet and lifestyle, outgrow the disease.
In schoolchildren, dyskinesia develops due to the action of other factors. Most often these are stresses caused by problems in the family or school, so treatment always includes a consultation with a psychologist. It is very important to assess the level of emotional lability.
Often the prerequisites for development are created due to physical inactivity, and this is an equally important factor in recent years. The magnitude of its influence is difficult to overestimate, because children are increasingly abandoning outdoor games with peers in favor of social networks, and the famous pediatrician Dr. Komarovsky has spoken about this more than once.
The main task of parents is to detect the problem in time. Dyskinesia has no specific symptoms, and sometimes it can be latent. Dyskinesia can be detected by the following signs:
- persistent whitish coating on the tongue, present despite proper oral hygiene;
- yellowing of the sclera of the eyes;
- cracks on the lips and corners of the mouth;
- pale skin, it may become gray;
- heart rhythm disturbances.
At the age of up to 1 year, no special treatment is used; then, for hypomotor dysfunction, physical treatment methods are used. Physical therapy, massage, and water procedures are effective for children. Tonics help - herbal preparations that tone the entire body - infusions of ginseng or eleutherococcus.
Acquired form
Most often, an S-shaped bend of the gallbladder is formed against the background of age-related changes in the body, during which the internal organs descend, changing their location and shape. Thus, they have a negative impact on neighboring structures. All this is clearly visible on ultrasound. Some patients learn that the gallbladder is S-shaped completely by accident, for example, during a routine examination.
The causes of the acquired anomaly are:
- Alternating systematic fasting and overeating.
- Chronic inflammation of the bile ducts.
- Poor nutrition.
- Regular overload of the abdominal muscles.
- Chronic pathologies of the digestive tract.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms.
- Spikes.
- Stones.
- Ductal dyskinesia.
- Increase in organ size.
- Weakened diaphragm.
- Chronic form of pericholecystitis.
Causes
- Poor nutrition. The child's body is very sensitive to food, since the stomach and other important organs that take part in digestion are not yet fully formed and are not ready for heavy loads.
- Thus, a child’s consumption of very fatty and fried foods can lead to the development of this disease. Parents do not always adhere to special diets and feed their daughters and sons exclusively steamed and boiled food. Most are of the opinion that after a year the baby can eat from the “common” table. This is a big mistake, since the baby’s body is not ready for such stress.
- Problems with the digestive organs. Very often, biliary dyskinesia accompanies diseases such as gastritis, pancreatitis, etc.
- Hepatitis. Today many children are carriers of this virus.
- Worms. As a rule, worms cause great damage to the child’s body, as they take all the necessary nutrients. And besides, due to its destructive actions, problems with the gallbladder may begin.
- Intestinal infection. When some kind of stick enters the baby’s body, it immediately develops, thereby provoking the appearance of symptoms such as nausea, weakness, and vomiting. The main symptom of intestinal infections is intoxication of the body, due to which the baby can suffer greatly. And an intestinal infection can provoke the development of complications, which, as a rule, are much more serious than the initial problem
- Problems with hormones. Often in childhood, hormonal disorders may appear, which are provoked by many factors. And because of such disorders, the likelihood that biliary dyskinesia may occur increases
- Nervous system disorders. The child’s nervous system is very vulnerable, and any emotional stress can provoke the development of problems that can later cause the development of other diseases.
- Physical exercise. Almost all pediatricians say that children should never be overloaded, especially physically, since their body is not designed and not ready for such stress.
- Fast growth. Sometimes the cause of the development of biliary dyskinesia can be the rapid growth of a child. This usually happens after 10 years, when the transition period begins. This happens most often in boys, because in 2-3 years they grow up and become about the same height as their parents. But the body does not always have time to adapt to such a change.
- Allergic reaction. Many people think that allergies are not scary, and they do not cause much harm to the body. But this is a serious misconception, since it can manifest itself in different ways, and it happens that the cause of simple peeling of the skin may not be a lack of water in the body, but an allergy. It is worth knowing that it all starts with the intestines, and often allergens penetrate other organs, provoking the development of serious complications. And, as a rule, parents do not pay attention to mild manifestations, although it is at this moment that unpleasant consequences can be prevented
- Congenital gallbladder defects
Traditional methods
If the symptoms are very pronounced, then treating the gallbladder with folk remedies will help. This is not the main therapy regimen, but only an auxiliary one. Decoctions and tinctures are brewed as a comprehensive remedy for treating kinks.
Experts recommend treating symptoms of deformity with valerian and hop cones (course of treatment from 3 weeks), corn silk, taken instead of the usual tea. St. John's wort is also effective, relieving spasms of the biliary system and strengthening blood vessels. These herbs should be taken under the strict supervision of a doctor. Before treating deformities, you should undergo a series of examinations. Gallbladder disease requires treatment in the form of a course of medications, therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy.
YouTube responded with an error: Daily Limit Exceeded. The quota will be reset at midnight Pacific Time (PT). You may monitor your quota usage and adjust limits in the API Console: https://console.developers.google.com/apis/api/youtube.googleapis.com/quotas?project=726317716695
Likely consequences
Typically, complications appear when the patient does not suspect that he has a disease for a long time and learns about it only during a routine examination. In such cases, the patient does not have any pronounced symptoms.
It is very important to start treatment of gallbladder inflection earlier, otherwise complications are likely to develop:
- inflammation;
- stone formation;
- blood flow disorders in the organs of the biliary system;
- penetration of bile into the abdominal cavity;
- pronounced signs of homeostasis;
- symptoms of intoxication;
- peritonitis;
- rapidly progressing esophagitis;
- weakened immunity;
- lethal outcome.