Fibroids are a benign tumor growing in the uterine myometrium (muscular layer of the organ). The age of the disease ranges from 20 to 70 years, but the majority of patients are from the middle age category.
Doctors believe that the main reason for the formation of uterine fibroids is changes in the patient’s hormonal levels.
After uterine fibroids have been diagnosed, the question arises about its size. After all, treatment depends on how many large tumors were discovered, what type they are, and their size in weeks. In order to determine the size of uterine fibroids in weeks, you need to do an ultrasound. It is believed that large fibroids, the size of which is more than 12-16 weeks (more than 6 cm or 60 mm), must be operated on without fail: such nodes are dangerous for the patient’s life, especially if there are many of them. Tumors less than 10-11 (2-6 cm or 20-60 mm) obstetric weeks are not subject to mandatory surgical intervention; they can be treated conservatively (medicines, physiotherapy, diet).
Features of the classification of the disease
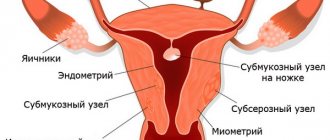
Myoma (leiomyoma, fibromyoma) of the uterus according to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) belongs to category D25. This code is assigned to all benign myometrial lesions, regardless of the size of the nodule. Division into groups is assumed only by tumor location:
- D0 – submucosal leiomyoma. This includes formations located in the submucosal layer, including on the stalk, deforming the uterine cavity;
- D1 – intramural leiomyoma. Nodes located deep in the muscle layer fall into this category;
- D2 – subserous leiomyoma. This group includes all tumors that are close to the outer layer of the uterus and protrude beyond the organ;
- D3 – unspecified leiomyoma. This code is set during the initial examination, when it is impossible to determine the location of the node.
The diagram shows the classification of types of fibroids depending on their location.
Traditionally, small fibroids are considered to be a node up to 25 mm in diameter with an enlarged uterus of up to 5-6 weeks. This can be a formation of any localization: located entirely in the muscle layer, on a pedicle in the uterine cavity, or extending beyond its limits. The exact size of fibroids is determined by ultrasound or MRI.
It is important to know
There is no such thing as a “normal fibroid size.” Normally, there should be no uterine tumor at all.
https://youtu.be/SVW3gtkg8uk
How big can these formations be?
The size of fibroids is one of the main parameters due to which effective treatment is prescribed. They can be calculated in millimeters (mm), centimeters (cm), and also weeks of pregnancy.
The size of the fibroid is its diameter (cm, mm). But also one of the criteria is the size of the uterus, which is calculated in weeks of pregnancy. That is, the size of the organ corresponds to its size at different stages of pregnancy.
According to these criteria, the doctor can determine the approximate size of the formation during a gynecological examination. This is explained by the fact that as the node grows, the uterus also increases in size. Despite the fact that there are many modern diagnostic methods, doctors today still use this method.
We can say that the tumor enlarges the uterine cavity, just like the embryo growing in it. The gestational age fully corresponds to the size of the organ in centimeters, that is, the height of its bottom.
What size does the uterus reach? At 8-9 weeks the uterus reaches 8-9 cm, 10-13 weeks - 10-11 cm, 14-15 - 12-13 cm, 16-17 - 14-19 cm, etc.
The diameter can only be determined using ultrasound, although this method also does not provide accurate numbers.
More accurate results are determined by MRI and CT.
Such modern methods can diagnose myomatous nodes, the diameter of which is only 5 mm.
Depending on the size, the following types of fibroids are divided:
- small;
- average;
- big.
Small tumor
Small fibromyoma is a tumor that is treated conservatively. The uterus can correspond to the size of up to 6 weeks of pregnancy, but no more. Small fibroids range in size from 15 mm to 25 mm.
The operation is performed only if the fibroid is of the submucous type, if there is torsion of the pedicle in the fibroid of the subserous type, or if there is a high probability of this.
Also, small nodes can be removed if the patient has been diagnosed with infertility or has developed anemia due to heavy bleeding.
Small formations of the interstitial type do not appear in any way.
Such myoma or fibromyoma often decreases significantly or disappears completely upon the onset of menopause.
But there may be situations when an operation during this period is necessary.
Medium myoma and fibromyoma
An average myomatous node is diagnosed if the uterus is enlarged before 10-12 weeks of pregnancy. The diameter of such fibroids can reach from 40 mm to 60 mm.
In this case, the conservative method is indicated only if there are no symptoms of the disease, and also if there are no signs of active growth. In other cases, surgery is performed.
With medium-sized formations that are localized on the outer side of the uterine wall, the functioning of nearby organs may already be disrupted. Such nodes can provoke infertility, and spontaneous abortions often occur. This happens especially often if there are lesions of the cervix.
Large knots
If there is a large node, then the uterus has already reached a size comparable to 12-15 weeks of pregnancy, while the diameter of the myoma or fibroids can be 60 mm or more. At this stage of development, the myomatous node is removed during surgery. In this case, the location and type of tumor are unimportant.
Treatment of a large node may involve the use of complex drug treatment, and then surgery is prescribed. Medicines are needed to stop the rapid growth of the tumor.
When performing an operation to remove a large node, there is a risk of bleeding, and as a result, the doctor will be forced to remove the entire organ.
Since removal surgery is quite stressful for the reproductive organs, after it is carried out, medications are necessarily prescribed to normalize the condition and structure of the uterus, as well as to prevent relapse.
To do this, you need to normalize hormonal levels.
Causes of fibroids and leading risk factors
Both large and small leiomyomas develop according to the same scenario. It is important to understand: any benign tumor of the uterus was once in its infancy, but under the influence of certain factors it began to grow. Small nodes do not make themselves known in any way and are detected by chance during an ultrasound scan.
Small fibroids are often asymptomatic and do not affect the quality of life in any way, so they can only be detected by ultrasound.
There are several key aspects in the development of leiomyoma:
- Hormonal imbalance leading to the growth of myomatous node. In this case, a large role is given to estrogen as the main substance that stimulates the proliferation of tumor cells. Another female hormone, progesterone, also has a certain significance;
- Frequent ovulation and constant renewal of uterine tissue during the menstrual cycle triggers cell proliferation and leads to the appearance of fibroid rudiments;
- Injuries to the muscular layer of the uterus during childbirth, abortion and other instrumental interventions can provoke the growth of a benign tumor.
In the processes of occurrence of small myomatous nodes, changes in hormonal levels play an important role. At the initial stages of its development, the tumor is sensitive to the action of endogenous estrogen and progesterone. Over time, it gains the ability to autonomously proliferate. The further development of fibroids is not due to the influence of sex hormones, but to the influence of growth factors on it and the formation of new vessels.
On a note
Mitotic activity (ability to divide) in small fibroids is relatively low. But even a small tumor synthesizes proteins that inhibit the process of apoptosis - natural cell death. The formation gains the ability to grow uncontrolled - and a tumor forms. On average, the development of a neoplasm from a microscopic rudiment to a clinically significant formation takes 5 years.
Small myomatous nodes that have not yet become completely autonomous are better amenable to conservative treatment.
Myomatous nodes occur in women aged 25-35 years. By this period, various gynecological and somatic diseases accumulate in the patient’s body, provoking tumor growth. It is quite difficult to identify the mechanisms causing the growth of the node. But even without knowing the exact cause of the development of leiomyoma, we can assume the influence of certain factors on this process:
- No pregnancies or childbirths over the age of 30;
- Frequent abortions or miscarriages that injure the tissue of the uterus and provoke hormonal imbalance;
- Chronic inflammatory diseases of the reproductive organs;
- Difficult childbirth with tissue ruptures;
- The presence of other diseases of the uterus: hyperplastic process, endometriosis;
- Uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs.
Knowing the reasons for the development of fibroids, you can predict its appearance at a certain age and track the growth of the node using ultrasound.
Ultrasound examination allows you to monitor the tumor, changes in its size and the development of complications.
Indications for surgery
A woman, having heard that she has been diagnosed with uterine fibroids for 8 weeks, always tries to find out all the options and methods of treatment. Unfortunately, it is sometimes impossible to do without surgery.
Doctors have identified several indications when a tumor is definitely removed:
- Uterine fibroids 12 weeks (60 mm in diameter). Such a node threatens the health and life of the patient. Sometimes not one tumor is found, but several medium-sized nodes. When diagnosing multiple uterine fibroids 6 cm, excision of the tumor is mandatory and urgent.
- Pregnancy planning. Myoma at 9 weeks often causes infertility or early pregnancy failure. If you want to conceive, you must first remove the node, even if it is only 4 cm. Changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy can stimulate the growth of the tumor. If uterine fibroids are detected 5 weeks after conception, the doctor will recommend terminating or continuing the pregnancy according to indications.
- Risk of degeneration. If fibroids of 7 weeks have increased to 11 weeks in a few months, this may indicate the presence of atypical cells. To prevent the node from developing into cancer, it must be removed without fail.
- Pain syndrome and dysfunction of the pelvic organs. Subserous uterine fibroids of medium or large size can put pressure on the bladder or intestines, which causes constipation, urinary incontinence, etc. Constant pain and other negative manifestations of the tumor, such as heavy bleeding, are a direct indication for surgery.
Uterine fibroids at 9 weeks deserve special attention, as well as tumors of a different size if the tumor develops in a woman during menopause.
During menopause, estrogen is released in a smaller volume, so doctors often decide that surgery is not necessary, preferring a wait-and-see approach.
What to do if observation indicates tumor growth?
If the patient is not of childbearing age, the uterus is removed along with the node.
Will the tumor grow?
With regard to fibroids, the most exciting question remains the question of its uncontrolled growth or, on the contrary, regression. There are several stages in a woman’s life when a change in the size of the node is possible:
- Pregnancy. After conceiving a child, progesterone levels increase, which can lead to the growth of leiomyomas. It is known that only in 30% of women the tumor regresses or at least stabilizes in size during gestation. The rest of the expectant mothers experience a slight growth of the node (mainly in the first half of pregnancy, but no more than a quarter of the original value);
- Birth of a child and lactation period. It has been observed that breastfeeding for 6 months or more inhibits the growth of fibroids;
- Menopause. In many women, myomatous nodes regress with the onset of menopause due to a decrease in estrogen and progesterone levels. This applies to a greater extent to small tumors that are sensitive to the influence of endogenous hormones.
It is important to know
Small tumors are detected mainly before the age of 35 and in menopause. In the first case they are just beginning to grow, in the second they are already regressing. Myoma can resolve on its own only after menopause. During the reproductive period, the formation cannot completely disappear without treatment.
The growth of fibroids depends on the hormonal background of the woman. If there is an imbalance, intensive growth of nodes is observed.
It is also useful to read: Folk remedies in the treatment of uterine fibroids
Tumor growth
Taking hormonal drugs
To treat fibroids, it is important how quickly they grow. If over the course of a year the uterus has enlarged to 5 weeks or more, then this tumor is progressing. Its growth is affected by hormonal imbalance in the body. There are also the following reasons for the rapid development of this disease:
- a woman has not given birth until she is 30 years old
- gynecological pathologies
- sufficient number of abortions
- taking hormonal drugs
- long-term influence of ultraviolet radiation on the body.
Sometimes uterine fibroids grow to enormous sizes, the weight can be about 5 kg and 40 cm in diameter. This resembles late pregnancy.
Leading symptoms of the disease
Among all small-sized formations, clinically insignificant fibroids deserve special attention - nodes up to 2 cm in diameter. At this stage, the disease is asymptomatic. The menstrual cycle does not change, and only with submucous nodes can an increase in the volume and duration of menstrual flow be observed.
As leiomyoma grows to 2-2.5 cm, characteristic signs of the disease appear:
- Menorrhagia is prolonged and heavy menstruation. The duration of bleeding can be up to 7 days or more. This is mainly characteristic of submucosal nodes;
- Moderate nagging pain in the lower abdomen, lumbar region, perineum.
Heavy, prolonged periods are usually one of the first symptoms of fibroids.
Bloody discharge remains the leading symptom of fibroids at any age, including postmenopause. Uterine bleeding is not typical for small tumors. Heavy periods, turning into full bleeding, occur when fibroids are combined with endometriosis (adenomyosis) or endometrial hyperplasia. The latter option is more often detected during menopause.
It is important to know
Small fibroids primarily imply minimal severity of symptoms. If there is frequent and heavy bleeding, you need to look for another cause of the problem.
The growth of myomatous nodes is activated by the age of 35-40, when the performance of the ovaries decreases and their sensitivity to pituitary hormones decreases. Hormonal imbalances lead to tumor proliferation and the development of the following complications:
- Compression of the pelvic organs (bladder and rectum) with disruption of their function;
- The appearance of chronic pain in the lower abdomen or lumbar region;
- Acyclic bleeding;
- Infertility.
The larger the size of the fibroids, the more clearly it will manifest itself with corresponding symptoms.
Such complications are extremely rare with small tumors. For small formations, other conditions are relevant:
- Torsion of the tumor stalk. Occurs in submucous and subserous formations. It is characterized by the appearance of severe pain in the lower abdomen, nausea, vomiting, and tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall. Without treatment it ends in fibroid necrosis;
- Tumor necrosis. Tissue necrosis occurs when the node’s nutrition is disrupted and is accompanied by the appearance of severe cramping pain in the lower abdomen. Necrosis of fibroids can be provoked by pregnancy;
- Node infection. The natural result of necrosis left without treatment. Leads to an increase in body temperature and the appearance of other signs of intoxication;
- Birth of a myomatous node. Expulsion of the tumor is accompanied by severe cramping pain and bleeding.
All of these conditions are considered emergencies and require emergency surgical care. Conservative therapy for necrosis is possible only for special indications, when the risks of surgery are too high (for example, during pregnancy).
The presence of complications of fibroids in most cases requires emergency surgical treatment.
Signs of small uterine fibroids
The insidiousness of this type of myomatous neoplasm is that this pathological condition may not produce any clinical manifestations, gradually increasing in size. Small fibroids can be an accidental discovery during routine examinations or ultrasound examinations.
Sometimes such minor formations may appear:
- Minor nagging, aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- Increased volume of menstrual bleeding;
- Minor changes in the ovarian-menstrual cycle.
Pregnancy and uterine fibroids: are there any chances with small size nodes?
The prognosis for pregnancy with small leiomyoma is favorable. Reviews from women who have given birth and suffer from this pathology are very positive, although here everything depends on the location of the node:
- Small subserous fibroids do not interfere with conception and pregnancy and do not interfere with natural childbirth. With a subperitoneal location of the node measuring up to 2.5 cm, pregnancy proceeds without complications;
- Small interstitial tumors do not interfere with conception and implantation of the fertilized egg and have almost no effect on the course of pregnancy. With multiple nodes, the tone of the uterus may increase, which creates a threat of miscarriage or premature birth. With interstitial-submucous tumors growing towards the uterine cavity, impaired blood flow in the placenta and insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus are often recorded;
- Submucous fibroids growing in the uterine cavity can interfere with the conception of a child. Even a small formation acts as an intrauterine device and prevents sperm from meeting the egg. Implantation - the introduction of the fertilized egg into the wall of the uterus - is difficult, and the risk of miscarriage in the early stages is high. Gynecologists recommend getting rid of submucous fibroids before pregnancy, regardless of the size of the tumor.
Intramural nodes do not affect pregnancy, but submucosal nodes can deform the cavity and thereby prevent egg implantation.
Numerous reviews from women, both those who have undergone treatment for fibroids and those who have become pregnant without special therapy, indicate that formations up to 10-15 mm do not interfere with pregnancy. Childbirth with small fibroids occurs without complications and is usually carried out through the natural birth canal.
Abortion for small fibroids is carried out on a general basis: up to 12 weeks at the request of the woman. Small tumors are not included in the list of medical contraindications for pregnancy.
The question of the effectiveness of IVF for fibroids remains open. In vitro fertilization for nodes of any size may be ineffective due to impaired blood flow in the uterus and background hormonal changes in the woman’s body. And if there is no disagreement with the submucosal location of the tumor (submucosal formation of any size interferes with conception and gestation), then what about formations of other localization? Here the doctors were unable to reach a consensus. Russian gynecologists may refuse to perform the procedure on a woman with fibroids, in which case IVF is done after removal of the node. Foreign literature indicates that small fibroids that do not deform the uterine cavity do not interfere with pregnancy and cannot be an obstacle to in vitro fertilization. This issue is finally resolved after a complete examination of the patient and assessment of all risk factors.
IVF involves long-term use of hormonal drugs, but it is difficult to predict how this will affect the fibroids.
It is also useful to read: Periods with fibroids
Removal of fibroids
Surgery for fibroids
An ultrasound examination revealed that the nodes were enlarged; the doctor ordered a full examination of the patient to begin with. Then the operation is performed. There are the following types of surgical intervention: laparoscopy, laparotomy, strip surgery, hysteroscopy, hysterectomy.
Removal of fibroids 8 weeks. If the tumor begins to grow and has grown from a small to a medium stage and corresponds to a period of 8-9 weeks, it is recommended to undergo surgery. The type of operation used here is laparoscopy. This is the removal of fibroids through incisions made in the abdomen. After such an operation, there are no scars. The postoperative period lasts about two weeks.
For hard-to-reach and large nodes, hysteroscopy is done - making incisions through the vagina.
Removal of fibroids 10 weeks. You cannot delay removal. The operation is performed through an incision in the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. This rather serious operation to remove a benign tumor is called laparotomy. After it, a long rehabilitation is required.
Removal of fibroids 12 weeks. When a tumor of this size is diagnosed, surgery is performed immediately. As a last resort, hysterectomy is used - complete removal of the uterus. This operation is performed if no treatment is no longer effective. The rehabilitation period is about 2 months.
In case of a complex case, as well as widespread foci of the disease, a strip operation is performed.
Complete removal of the uterus for fibroids
The entire reproductive organ can be removed: if the size of the tumor has reached unacceptable levels, also if removal of the nodes is not possible. The main indicators for this are:
- late detected formation of nodes,
- uterine prolapse,
- prolonged blood loss,
- suspicion of a malignant tumor,
- increasing anemia.
Methods for early diagnosis of pathology
Scheme for identifying a uterine tumor:
- Gynecological examination. It is not indicative of small-sized fibroids, since the uterus is slightly enlarged (up to 5-6 weeks);
- Ultrasonography. On ultrasound, fibroids are visible as a hypoechoic formation located in the tissues of the uterus. The method allows you to accurately estimate the size, number and location of nodes. Distinctive echographic signs of fibroids help differentiate it from other gynecological pathologies. Ultrasound reveals fibroids ranging in size from 5 mm;
- Doppler ultrasound is an ultrasound diagnostic method for assessing blood flow in the vessels feeding the tumor. It is of great importance when choosing a treatment method;
- MRI. Carried out in doubtful situations to clarify the diagnosis;
- Hysteroscopy is an examination of the uterine cavity using endoscopic equipment. An indispensable method in the diagnosis of submucosal node;
- Laparoscopy is an examination of the uterus and pelvic organs through punctures in the abdominal wall. It is carried out to identify subserous nodes in controversial situations.
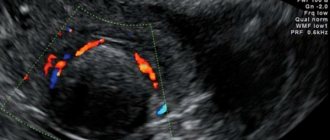
A photo of small uterine fibroids (12 mm) is presented below. This formation is not accompanied by symptoms and is detected accidentally during ultrasound examination.
Small myomatous node (12 mm) on ultrasound.
Causes
Experts call the main reason for the appearance of uterine fibroids an imbalance of sex hormones in a woman’s body - excess estrogen and lack of progesterone, as well as the development of hypergonadotropism. In addition, the following factors are noted that provoke the development of this disease:
- hereditary predisposition - every fifth woman was diagnosed with uterine fibroids in her family tree along the female line;
- late onset of first menstruation;
- absence of childbirth and breastfeeding in women over 30 years of age;
- previous gynecological manipulations and procedures (abortions, curettage);
- inflammatory and infectious processes in the genital organs;
- lack of meaningful sexual relationships;
- physical overload;
- psycho-emotional discomfort, stress;
- sedentary lifestyle.
Most often, such small myomatous nodes are discovered during gynecological examinations. Only in some cases, as the tumors grow, symptoms of uterine fibroids begin to appear. First of all, a woman experiences uterine bleeding, menstruation becomes heavy, often with blood clots. Many sick women have intermenstrual bleeding. In addition, the woman constantly feels discomfort, nagging pain in the lower abdomen. During menstruation, the intensity of pain increases significantly.
A sign of small uterine fibroids can be a woman’s infertility and frequent miscarriages. This is due to the fact that the myomatous node often interferes with the attachment of the fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus, acting as a kind of “contraceptive coil”.
Treatment tactics for small benign uterine tumors
Do fibroids need to be treated? For small nodules, wait-and-see tactics are justified in the following situations:
- The disease is asymptomatic: it does not lead to disruption of the menstrual cycle, is not accompanied by chronic pelvic pain, and does not cause complications;
- The myomatous node does not prevent pregnancy and the birth of a child on time.
Dynamic monitoring of fibroid growth is indicated: ultrasound monitoring every 6 months, regardless of the presence of complaints.
Indications for fibroid therapy:
- The appearance of obvious symptoms of the disease;
- Development of complications: necrosis, torsion of the leg, etc.;
- Suspicion of sarcoma;
- Combination of fibroids with other gynecological pathology with the development of a complete clinical picture;
- Infertility or miscarriage;
- In terms of preparation for IVF.
If there is a small tumor and there are no complications, you can limit yourself to ultrasound monitoring of the development of the tumor.
Treatment of small uterine fibroids is predominantly conservative. Drug therapy includes taking hormonal drugs that affect tumor growth. Under the influence of hormones, fibroids decrease in size, unpleasant symptoms of the disease go away, and the chances of successfully conceiving a child increase.
You can treat fibroids up to 3 cm in size with various drugs:
- Combined oral contraceptives (Regulon, Rigevidon, Klayra, Yarina, Marvelon, Novinet, Zhanin, etc.) are used for formations 1.5-2.5 cm in diameter. Prescribed mainly to women under 35 years of age. The course of treatment is from 3 months;
- The use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (Buserelin, Lucrin Depot, etc.) is one of the most effective methods of drug therapy for fibroids. These drugs reduce the size of the node by up to 60% within 3 months. Priority is given to depot forms of the drug (one injection every 28 days);
- Progesterone receptor modulators (Esmiya). Prescribed daily in a course for 3 months. Effective for a combination of fibroids and endometriosis.
Progesterone preparations (Duphaston, Utrozhestan) are rarely used. According to the latest data, gestagens enhance the growth of the node, so their use in the treatment of the disease is not justified.
When treatment with hormonal drugs is stopped, node growth may resume.
It is important to know
Your doctor will tell you what medications to take for uterine fibroids. It is prohibited to independently take any hormonal drugs, as well as biologically active supplements with phytoestrogens. Uncontrolled use of medications is dangerous to health!
At home, many women practice herbal treatment, which, according to reviews, stabilizes hormonal levels. It is impossible to cure fibroids with folk remedies, but it is quite possible to boost immunity and improve general condition with herbal medicines.
On a note
Estrogen-containing drugs (Femoston and others), including those used to eliminate the signs of menopause, are prescribed with caution for fibroids, since this may activate the growth of the node.
Surgical treatment for small fibroids is practically not carried out. The doctor will decide after examination whether the tumor needs to be removed.
Indications for surgery:
- Submucous uterine fibroids, interfering with conception and gestation;
- Development of complications: tumor necrosis, leg torsion, etc.;
- Suspicion of sarcoma.
Surgical removal of a small tumor is carried out only when indicated.
The choice of treatment method will depend on the location and number of nodes:
- Hysteroresectoscopy is used for submucosal tumors. The node is removed using endoscopic equipment through the vagina;
- Laparoscopic myomectomy is practiced for interstitial and subserous tumors. The tumor is removed through punctures in the abdominal wall;
- Uterine artery embolization is the treatment of choice for multiple fibroids. Regression of myomatous nodes is achieved by stopping blood flow in the feeding vessels.
Treatment
When treating benign tumors of the uterus that are small in size, conservative therapeutic methods are used, aimed at stopping their activity that causes intensive growth and stabilizing the size of their cell nuclei. For this purpose, a low dose of oral contraceptive drugs is used to normalize the hormonal balance, as well as the introduction of an intrauterine system to restore the functioning of the ovaries; surgery is not performed in case of small fibroids.
Treatment of fibroids involves an individual selection of medications, depending on the characteristics of the patient’s condition, her age, plans for children, symptoms of the disease, tumor size and the number of nodules. Today, the following methods are used to treat myomatous formations of this nature:
- Hormonal agents that can normalize hormonal levels, reduce the production of female hormones and cause artificial menopause, which stops tumor growth.
- The use of special contraceptives that stop the growth of myomatous nodes.
- The use of a special Mirena hormonal device, which allows the required amount of hormones to be delivered directly to the uterus.
- Bringing a course of vitamin therapy designed to maintain the body's defenses.
- The use of dietary nutrition aimed at eliminating benign formations.
- Using electrophoresis with sodium or potassium iodide, which leads to a reduction in the production of sex hormones and a decrease in inflammation.
- Carrying out magnetic therapy to enhance the effectiveness of hormonal medications taken.
- Baths containing radon, which reduce estrogen production.
The formed tumors, when carrying out the most effective conservative therapy, decrease in size and stop their development, however, their center is not able to completely disappear. The result of treatment is the absence of pathological symptoms and growth of nodes, and the treatment process is considered successful if the tumor does not increase over a long period of time.
How to live with fibroids?
Lifestyle with leiomyoma involves a number of restrictions:
- It is not recommended to visit the sauna, take a steam bath, or sunbathe in the open sun or in a solarium too often. The effect of thermal procedures on the growth of fibroids has not been proven, but it is not worth provoking tumor proliferation;
- Heavy physical activity should be avoided and training that involves impact on the abdominal muscles and pelvic organs should be avoided. It is not recommended to pump up the press with this pathology;
- Massage sessions should be gentle, without stimulation of the abdominal muscles, lower back, and pelvic organs;
- Taking any medications must be agreed with your doctor. Some medications provoke the growth of nodes;
- You should not expose your body to stress. It is believed that chronic nervous tension stimulates tumor proliferation.
There are no significant contraindications for small fibroids. A woman can play sports, but without fanaticism, lead a normal lifestyle, but not overexert herself. A diet with a reduced amount of fats and carbohydrates will be beneficial - excess weight provokes tumor growth. If you have any doubts, it would be a good idea to consult your doctor.
Useful video about uterine fibroids and minimally invasive treatment options
Classification
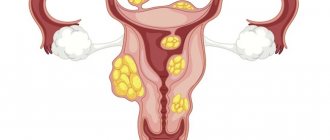
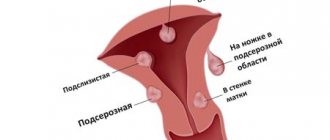
Small myomatous nodes of the uterus can be in different parts of the organ. Doctors classify them by location and size. The location of the tumor can be:
- submucous - with the direction of growth inside the uterine tissue;
- subserous - with the direction of growth outward;
- interstitial - growing in the muscles of the uterus.
The size of fibroids is determined by ultrasound examination. It is set according to the diameter and the correspondence of the diameter to the obstetric weeks.
- A five-week tumor is up to five centimeters.
- Seven weeks - from six centimeters.
- Ten - thirteen weeks - ten centimeters.
- Eighteen to nineteen - from sixteen to twenty centimeters.
- Twenty-four weeks – twenty-three to twenty-eight centimeters.
- Thirty-two weeks – twenty-nine – thirty-three centimeters.
- Forty weeks and above – thirty-five centimeters.
Fibroids lasting up to five weeks are considered small.
At what size is it necessary to remove fibroids?
There are situations when it is necessary to remove even small fibroids. What are the indications for surgery:
- Rapid tumor growth;
- Severe pain and bleeding;
- Fibroids are located under the mucous layer of the uterus;
- Risk of degeneration into a cancerous tumor;
- Submucosal fibroid;
- Difficulty conceiving;
- Nodular necrosis.
Thanks to surgical intervention, it is possible to prevent the risk of serious complications, including uterine cancer.
What not to do
A woman with uterine fibroids should know what can and cannot be done with this disease. Contraindications for uterine fibroids:
- lifting weights weighing more than three kg;
- excess physical labor;
- stressful situations;
- abortion;
- excess fluid intake;
- intensive massage and warming;
- oral contraception without a doctor's prescription.
All these factors provoke the growth and development of a small myomatous node, and its further transformation into a malignant tumor.