Pancreatic lipomatosis is a pathology in which normal cells are replaced by fat cells. Such changes negatively affect the performance of the organ. The situation is aggravated by the long asymptomatic period.
In fact, a person begins treatment when it is no longer possible to change something for the better using conservative methods. This article provides expert advice that will help you diagnose the disease in a timely manner and take adequate response measures.
Risk factors
Pancreatic lipomatosis is fatty pancreas.
Why some people develop lipomatosis and others do not is not known for certain.
However, ongoing statistical studies allow us to identify some risk factors, the presence of which may lead to the formation of unwanted fat cells in the pancreas.
The most common situations that provoke the development of lipomatosis are given below:
- history of acute pancreatitis;
- current chronic pancreatitis;
- frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- burdened heredity;
- current diabetes mellitus or chronic hepatitis;
- obesity;
- insufficient amount of thyroid hormones.
The fact that the factors mentioned above can provoke the development of lipomatosis does not mean that those who have these conditions will necessarily develop pancreatic obesity. However, in the absence of all these factors, the disease almost never develops.
Forms and degrees of pancreatic dystrophy
Depending on the nature of the changes that occurred in the pancreas, in medical practice the transformation is classified into several types.
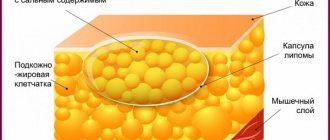
Diffuse changes are characteristic of muscle lipoma, lipid cells tend to grow along muscle fibers, the boundaries of normal and pathological tissue are washed away.
Nodular dystrophy is characterized by the formation of nodes that are localized symmetrically, they are surrounded by a specific capsule. Most often, many pathological nodules are formed. The mixed appearance combines the characteristics of the two previous forms.
Diffuse changes in the pancreas according to the type of fatty infiltration are classified according to the severity of the process. There are three degrees:
- First degree. Obesity has affected about 30% of the organ, with moderate impairment of its functionality. At this stage, the disease is not accompanied by any symptoms;
- The second degree is characterized by the spread of lipid tissue to 50-60% of the entire organ, and there is a disruption of the pancreas;
- Third degree – lipid tissue more than 60%. There are clear clinical manifestations of pathology, which are caused by digestive and endocrine insufficiency.
Many medical specialists do not support this classification, since often the first stage is much more complicated than the 2-3 stages of the disease.
Symptoms of fatty degeneration of the pancreas
An ultrasound will help identify the disease.
The main pathology of this disease is the replacement of parenchyma with fat cells. This process is extremely slow and can generally take several years or decades.
It can be discovered accidentally during ultrasound diagnostics of this organ. The first negative sensations appear only when a third of the organ becomes modified.
Then they begin to intensify, causing multiple symptoms. But despite all the versatility of the manifestation of symptoms, they are all a consequence of 2 global disorders:
- dysfunction of the pancreas;
- compression of healthy tissues of this organ and others that surround it.
Signs of pancreatic malfunction
Due to a decrease in the percentage of healthy, normally functioning tissues in relation to the affected ones, digestion is disrupted. Protein foods and everything fatty are especially difficult to perceive. A person experiences the following symptoms:
- nausea;
- stomach ache;
- flatulence;
- heaviness, bursting feeling in the stomach;
- frequent stools containing fat and other impurities.
Due to the disease, disruptions in the production of hormones occur. As a result, complex endocrinological disorders develop. This applies to a greater extent to carbohydrate metabolism. At the same time, glucose levels increase sharply.
If this pathological course is not stopped, then over time a person will develop diabetes.
Treatment of patients with fatty hepatosis
Liver treatment involves reducing body mass index. Losing weight by even 10% significantly reduces the fat content in the liver and physiological disorders, pain is also much less pronounced. This is achieved by a moderate, balanced diet (low fat, large amounts of cottage cheese, oatmeal and buckwheat) and light exercise, which is indicated for this disease. In severe cases, gastric surgery is prescribed, namely gastric bypass. But you can’t lose weight quickly: this can lead to fibrosis and necrosis of the liver.
Membrane-restoring medications (chophytol, Essentiale, α-lipoic acid), antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals will also help.
Compression of surrounding tissues
Abdominal pain is a sign of gastrointestinal dysfunction.
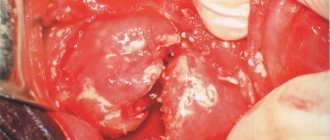
Fat cells can develop to fill a large space. As a result, adipose tissue grows, which takes up much more space than the healthy cells that precede it.
If the fat cells are distributed evenly throughout the pancreas, then this will not cause problems. The situation is worse when cells are collected in groups.
Then they start talking about lipoma - a benign tumor. There is nothing too scary about it, because it will not give metastases, which means it will not cause harm to neighboring organs.
Trouble will occur when the tumor develops to such a size that it begins to put pressure on the vessels, pancreatic ducts, and nerve endings. Such exposure will lead to pain, nausea, flatulence and other unpleasant symptoms.
Watch the video about the risk of developing diabetes and obesity:
Risk groups for developing the disease
The risk groups for developing the disease include the following patients with diagnosed pancreatitis:
- violating the diet prescribed by the attending physician;
- suffering from alcoholism;
- aged people;
- diabetics;
- people suffering from overweight and obesity;
- patients genetically predisposed to fatty infiltration of organs.
Since fatty degeneration is an irreversible process, it is very important for patients with pancreatitis to regularly consult a doctor and undergo clinical examinations. Regular monitoring and timely medical intervention will help avoid the development of the disease.
Nutrition for lipomatosis
There is an opinion in everyday life that reducing the amount of fat in the diet will help stop lipomatosis. This is a completely false statement.
Even completely stopping fat intake will not stop the degeneration of healthy cells into fat cells. The development of lipomatosis has nothing to do with nutrition. However, it is still better to exclude fats. This will have a beneficial effect on the body:
- relief of pancreas;
- getting rid of extra pounds.
Reducing the amount of incoming fat helps alleviate the condition; many signs of the disease recede and become less pronounced. In the absence of external manifestations of the disease, we can talk about preserved pancreatic functionality.
This means that all the ducts are functioning normally, they are not compressed by adipose tissue. With normal functioning of the pancreas, limiting fats in food will help you lose weight, but will not affect the further development of the disease.
Treatment of lipomatosis
Ibuprofen is a drug to relieve abdominal pain.
It is almost impossible to get rid of lipomatosis. The current treatment method goes in 3 directions:
Changing your lifestyle in the right direction will help improve the situation as a whole. With persistence and perseverance, you can achieve a lot.
The condition of patients seeking recovery improves even without additional medications. The basics of getting rid of pathology are giving up alcohol and other bad habits, normalizing your diet, and getting rid of excess weight.
To achieve good results, you need to be more active. The second important factor is diet. Following the nutritional principles outlined below will help get rid of many problems. The principles are:
- Fractional meals. The desired number of meals is at least 5, optimal is 6.
- Limit fat. Avoiding sweet, fatty foods.
- A general reduction in the calorie content of dishes, the desire to reduce the daily volume of incoming calories.
It is almost impossible to resolve the situation with medications. Taking medications only helps to get rid of unpleasant symptoms. To eliminate the severe consequences of pancreatic obesity, the following drugs are taken:
- Ibuprofen for pain relief.
- Pancreatin for correcting digestion.
- Loperamide to block diarrhea.
- Metoclopramide to relieve nausea.
- Mebeverine to relieve intestinal spasms.
Preventive actions
Proper nutrition is an excellent prevention of obesity.
Fatty degeneration of the pancreas can be prevented, but not cured.
Therefore, you need to follow a number of simple steps to maintain your health and not face the need to treat lipomatosis. Advice from experts on preventing this disease is as follows:
- Weight control.
- Quitting alcohol.
- Refusal of fatty foods.
- Eliminating stressful situations from life.
Smoking also weakens pancreatic function, so it is also better to give it up. After all, pancreatitis is a consequence of smoking, and lipomatosis develops from pancreatitis. To prevent the development of pancreatic obesity, it is necessary to keep the liver, kidneys and other internal organs in normal condition. It is especially important to maintain the normal functioning of the liver and biliary tract.
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Good afternoon, dear readers of my blog! Our topic today is such a dangerous disease as pancreatic obesity, which often does not manifest itself for quite a long time. And, meanwhile, it is fraught with the most serious troubles for the life of the body and, moreover, is irreversible.
What is its danger, what to do and what to do if you are diagnosed with it?
Folk remedies against obesity
Alternative medicine, like official medicine, offers various methods for treating diseases such as fatty infiltration of the pancreas. Treatment is based on the use of healing plant components.
Herbal medicine is not able to rid the patient of the disease, but it supports the functioning of the pancreas. The following herbal infusions are highly effective:
- valerian, St. John's wort, calendula and nettle;
- immortelle, mint and rose hips;
- corn silk, mint and fennel oil;
- grass grass, nettle, birch buds and calendula flowers;
- mint leaf, geranium, plantain, dill seeds and birch buds;
- primrose root, lungwort, mullein flowers, violet and raspberry leaf;
- flowers of meadowsweet, string, plantain, bergenia root and dandelion;
- bird cherry fruits, chamomile flowers, elecampane root, calamus and marshmallow.
Infusions are prepared quite simply - the components are crushed using a blender or meat grinder, and poured with boiling water. It is best to prepare this product in a thermos so that the liquid is infused for 8-10 hours. Most often, infusions and decoctions are taken 3-4 times a day, and the average duration of therapy is 10-12 weeks. After a 2-week break, taking the infusions can be continued according to the previously used regimen.
The advantage of herbal medicine is the possibility of using decoctions and infusions in combination with other medicines. But first it is better to consult with your doctor.
How is pancreatic obesity treated? How to identify symptoms and prescribe proper nutrition for hepatosis, infiltration or fatty involution? What kind of disease is this
Abuse of fatty foods, excess weight, addiction to alcohol and neglect of exercise lead to damage to liver cells, which begin to be replaced by fatty tissue. This phenomenon is called fatty hepatosis.
The pathology is serious and difficult to treat, and it also leads to deterioration in the functioning of other organs, in particular the pancreas. What are the true causes of fatty degeneration of the pancreas and liver is the topic of the article.
Fatty hepatosis is a lesion of liver cells, which gradually degenerate, and the entire parenchyma of the organ is filled with lipid (fat) cells. There is no such disease as fatty hepatosis of the pancreas; however, this disease is directly related to the degenerative changes in its tissues.
Fatty liver disease always occurs first. This process has a negative impact on the entire body, especially on the functioning of nearby organs.
As hepatocytes (liver cells) degenerate, pancreatic dysfunction worsens.
Over time, the tissues of the organ also begin to be replaced by fat cells, similar to fatty hepatosis, which is why this complication is often called fatty hepatosis in the pancreas.
Fatty infiltration of the liver and pancreas consists of cell degeneration, as a result of which the organs are affected by lipid formations. More often, the cause of this phenomenon is the excessive intake of fats in the body or their improper metabolism.
This happens in the following cases:
- The predominance of fats and simple carbohydrates in the daily menu.
- Improper use of glycogen by the body when fat reserves are actively accumulated in the liver.
- Delayed fat metabolism due to the influence of diabetes, alcoholism, impaired metabolism, obesity.
- Violation of somatotropic hormone synthesis.
- Impaired insulin resistance, which leads to abnormal penetration of fats from the blood into the liver.
- Liver diseases.
- Hyperlipidemia (increased lipid levels in peripheral blood).
- All gastrointestinal diseases (dysbacteriosis, colitis, pancreatitis, etc.).
- Endocrine dysfunction (hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency);
- Violation of the diet (fasting, strict diets).
- Drug intoxication.
- Regular intake of toxins (phosphorus, poisonous mushrooms, pesticides) into the body.
The sudden appearance of pain in the abdominal cavity is a sure sign of problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
Pain occurs because fat cells quickly fill the organ, actively displacing healthy pancreatic tissue, which leads to a slight increase in the organ.
However, in half of the cases, fatty infiltration of the organ proceeds slowly, so there is often no sign of pain.
The insidiousness of fatty hepatosis lies in its long asymptomatic phase. Often the diagnosis is made during a preventive ultrasound or at the time of diagnosing completely other pathologies.
In the early stages of hepatosis development, fatty infiltration of the liver and pancreas does not affect their functionality, so there are no obvious clinical symptoms. Or the symptoms are so insignificant that the patient wants to ignore them.
These include:
- Mild general weakness.
- Dryness and erosion in the oral cavity.
- Moderate nausea (usually in the morning).
- Irregular bowel movements.
When fatty infiltration of an organ worsens, more obvious signs appear:
- Pain in the hypochondrium, which can be described as pulling.
- Spontaneous vomiting, prolonged nausea.
- Dry skin.
- Flatulence and pain in the abdomen.
- Impaired defecation (mostly diarrhea).
- Apathy, anxiety.
- Hair loss.
- Skin rashes.
- Decreased vision.
- Weight loss or gain
- Frequent cold infections due to impaired immune function.
Most people turn to a therapist when it is no longer possible to tolerate all the symptoms of the disease. Unfortunately, at this stage the fatty infiltration is so extensive that treatment no longer brings good results.
Ultrasound often detects echo signs of diffuse pancreatic damage. This phenomenon indicates that the structure of the organ is disturbed and its size is increased. Hemorrhages and fibrous conglomerates of lipid cells may also be visualized.
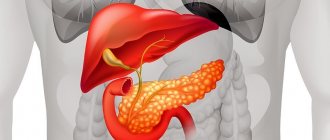
The liver and pancreas are tightly interconnected. If the body creates conditions for fatty infiltration of the liver, then sooner or later the pathological process affects the pancreas. However, timely treatment of one organ contributes to the rapid restoration of the function of another.
Pancreatic lipomatosis is a sluggish, progressive and in most cases asymptomatic disease. The pathology consists of a pathological accumulation of fat around the organ.
Over time, fat cells penetrate inside and lead to complete fatty infiltration of the pancreas.
This pathology has a similar development mechanism to liver hepatosis, since it is caused by the same reasons - obesity, consumption of fatty foods in large quantities, endocrine diseases.
Treatment of pancreatic hepatosis must begin with changing your usual diet. Not only the composition of the diet is subject to correction, but also the meal schedule and portion size. Note that diet is the main part of therapy.
The second part of treatment is taking medications. As a rule, treatment is symptomatic.
Antispasmodics (No-shpa and Papaverine) are prescribed for pain and spasms, and enzyme preparations (Mezim, Pancreatitn) are prescribed to improve food digestion.
To maintain liver function, hepatoprotectors are additionally prescribed - Heptpral, Essentiale, Karsil. If the disease is caused by pancreatic insufficiency, the endocrinologist may prescribe prescription insulin drugs.
In rare cases, when the pancreas is firmly enclosed in a fatty “cocoon”, surgery may be required. This operation is complex and can be life-threatening for the patient.
Considering the complexity of the disease and the high cost of treatment, it is better to practice prevention. Proper nutrition, maintaining a normal weight, a positive emotional background and exercise prevent fatty infiltration of the pancreas.
Diseases of the liver and pancreas are well treated with dietary nutrition:
- Meals must be taken at least 5 times a day, and portions should be of a modest size.
- The menu must exclude dishes that complicate digestion and contribute to weight gain - sweets, fatty and smoked foods, spices.
- Food is prepared in gentle ways - boiled, baked, stewed.
- Vegetables and meat are consumed pureed.
- It is prohibited to consume cold food and drinks.
- Limit the consumption of purine-containing foods (tomatoes, meat broth, offal) and salt.
- All dishes are prepared in accordance with dietary table No. 5.
- The duration of the diet is from two weeks to several years.
Fatty hepatosis can be cured with proper nutrition.
To allow the liver and pancreas to recover, the following products are excluded from the menu:
- Fish and meat (fatty types).
- Sauces and all marinades.
- Confectionery group of products.
- Legumes.
- Chicory.
- Alcohol.
- Hibiscus.
- Conservation.
- Stevia extract.
- Carbonated drinks.
- Puff pastry.
- Juices.
- Sushi.
- Sausages.
- Spices.
- Pancakes.
- Broths, except vegetable ones.
- Corn.
- Caviar.
- Milk and fermented milk products with a fat content of more than 1%.
- Mushrooms.
- Tomatoes.
- Eggplant.
- Offal.
- Sorrel.
- Waffles.
- Donuts.
- Sour berries and fruits without heat treatment.
- Barley grits.
- Green onions.
- Nuts and seeds.
- Coffee, green tea, cocoa.
- Ginger.
- Radish.
- Green pea.
- Raw cabbage.
In the menu for fatty hepatosis, it is useful to include some foods that improve digestion:
- Porridge - rice, buckwheat, semolina.
- Milk soups.
- Vegetable casseroles and stews.
- Kiseli.
- Low-fat fermented milk drinks.
To maintain the functioning of the gland, folk recipes are used:
- The seeds are removed from the pumpkin and the hole is filled with bee honey. After 14 days, the liquid is poured into a glass container and taken 45 ml per day.
- Half a glass of carrot juice is diluted with 100 ml of milk. Drink a drink every morning.
- Grains are extracted from apricot kernels and consumed daily in the amount of 5 pieces.
It is possible to help organ cells recover faster in case of fatty hepatosis using herbal medicine.
What's under the stomach?
The pancreas is the same one that is located under the stomach, which is why it gets its name - an organ that is very important for the normal functioning of our body. What can I say, is there anything useless in our body?
Mother Nature got it all right, but not all the cogs always function as they should. Sometimes it even happens that it seems to us that everything is normal. But in fact, as in the case we are talking about today, you may not know for a long time that a failure has occurred somewhere. The failure is serious and can lead to irreversible consequences.
Unnoticed worker
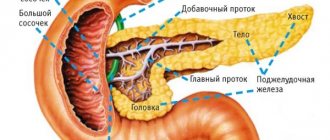
After all, this body is in charge of such incredibly important processes as
- secretion of most digestive enzymes - it helps digestion and absorption of nutrients
- the production of hormones, which makes it an important participant in the process of regulating carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism, in other words, metabolism.
- production of insulin, the lack of which provokes diabetes.
Failure in work
Sometimes all this activity begins to fail, and then fatty degeneration begins - pancreatic obesity, or lipomatosis.
What it is ? This is the name given to the process of replacing diseased or dead cells with adipose tissue. Cells damaged by the inflammatory process can no longer perform their functions, become weak, and die. And their place is taken by fat depots.
At the same time, outwardly these changes may not be noticeable for quite a long time and practically do not make themselves felt at all. At least until fat deposits begin to compress the tissue and interfere with the functioning of neighboring organs. Most often, the disease is detected by chance, during an ultrasound.
Misfortune never comes alone
The difficulty is that such a process of replacing healthy cells with fat is not isolated. Since our body is a single whole, the onset of a disease in one organ inevitably leads to problems in others. In this case, the liver most often suffers, which is also affected by the disease - fatty hepatosis - the degeneration of its cells into fatty deposits.
Symptoms and their absence
All these serious diseases may not manifest themselves for a long time. Only occasionally does slight fatigue, dry mouth appear, and small ulcers form on the oral mucosa.
But the stronger the disease, the more distinct its symptoms may be:
- vomiting, diarrhea, nausea
- flatulence
- pain in the right hypochondrium, often of a girdling nature
- in especially severe cases - weight loss
Looking for reasons
However, where and why does trouble come from? From metabolic disorders. But it is provoked by several reasons at once.
Lipomatosis is not a cause, but a consequence of pathological changes in this organ that occur in response to:
- pancreatitis, both acute and chronic
- alcohol abuse
- hepatosis (replacement of cells with fat) of the liver
- improper treatment of pancreatitis
- genetic predisposition
- the patient is overweight
It is worth noting that lipomatosis does not occur in everyone who suffers from pancreatitis. Most often, obese people face this problem. Therefore, those who have even been diagnosed with nutritional obesity should make sure that the pancreas is not attacked by fat deposits.
Stages of the disease
The disease is usually divided into 3 degrees.
- no more than 30% of the organ cells underwent changes
- organ tissues ranging from 30 to 60% are replaced by fat cells
- iron is more than 60% fat.
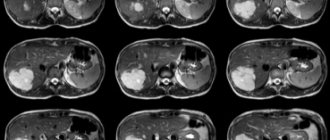
Only ultrasound can paint the final picture. It is there that you can see how crowded the fat deposits are and how hard they squeeze the gland. This examination allows us to diagnose this dangerous disease with 100% accuracy.
general characteristics
The pancreas performs the most important functions in the digestive system. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, the activity of the organ may be disrupted, and the tissues may undergo fatty degeneration.
This term hides a disease in which the process of replacing affected cells with adipose tissue occurs. Damaged cellular structures of the gland cannot cope with their functions and die. As a result, fatty elements take their place.
The danger of the pathological process lies in the fact that it is not localized for a long time in one organ; over time, other organs are affected.
In most cases, along with pancreatic obesity, fatty hepatosis begins, in which liver cells are replaced by fat.
To avoid going to the doctor later
As we know, it is better to prevent any disease than to treat it later. What to do in this case? What preventive measures exist to prevent pancreatic obesity?
- Do not abuse alcohol and do not smoke.
- Control your weight. Don’t miss the sneaking first degree of obesity, which is often mistaken for a harmless extra fold on the stomach.
- Do not overeat fatty foods.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle: spend more time outdoors, get enough sleep, avoid stress, eat right and provide your body with suitable physical activity.
It will also be very useful to read a good book in which the principles of proper nutrition are laid out on the shelves. For example, the book by Svetlana Bronnikova, the first and so far only conscious nutrition trainer in Russia, psychologist and psychotherapist, specialist in the field of digestive problems, “Intuitive Nutrition. How to stop worrying about food and lose weight."
In it, Svetlana talks in a simple and understandable language to the widest range of readers about how to improve your diet in an ordinary, non-dietary way. As a result, reduce weight and thereby avoid problems associated with obesity.
What to remember
- Replacement of cells with fat depots in the pancreas is an almost imperceptible process, but dangerous and irreversible. The cause of the disease is a metabolic disorder.
- Diagnosis and treatment are possible only with a doctor.
- Disease prevention is a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition.
I wish you good health and see you in the next article!
Pancreatic obesity is a serious disease characterized by the replacement of tissue with fat cells. The pathology entails disruption of the activity of this organ, and also negatively affects other organs, and therefore requires urgent treatment.
Symptoms
Symptoms of pancreatic obesity do not appear immediately. The pathology can occur for a long time without clinical signs.
Therefore, the disease is often diagnosed completely by accident, when a person goes to the hospital for another disease or for a preventive examination.
Patients complain of the following symptoms:
- Pain in the abdomen that radiates down the abdomen.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Stool disorders, often in the form of diarrhea.
- Oily discharge in stool.
- Increased gas formation.
- Feeling of heaviness in the affected area.
Also, when the gland is obese, a sudden increase in blood sugar is observed.
Stages of the disease
There are three main stages of lipomatosis:
- At the first stage, changes affect no more than 30% of organ tissue.
- At the second stage, 30-60% of pancreatic tissues are mutant fat cells.
- At the most advanced stage of the disease, the organ consists of more than 60% fat.
This state of affairs is dangerous due to the consequences and complications of the disease. It contributes to the development of endocrine pathologies and increased blood sugar levels. As a result, diabetes mellitus may develop. Also, the process of obesity can spread to a neighboring vital organ - the liver. And provoke the development of hepatosis.
Causes
Pancreatic obesity can develop independently or against the background of other diseases.
Predisposing factors of pathology include the following:
- Damage to organ tissue.
- Pancreatitis.
- Gastritis occurring in a chronic form.
- Hepatitis.
- Diabetes.
- Weakened immunity.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Age-related changes.
- Uncontrolled use of medications, especially hormonal ones.
- Poor nutrition.
- Smoking.
- Alcohol abuse.
Most often, those people who suffer from obesity are those who tend to gain weight.
Prevention and prognosis
It is not possible to prevent the development of congenital pancreatic lipodystrophy, since it is caused by gene mutations. You can reduce the likelihood of developing such a rare acquired disease using the following preventive recommendations:
- complete renunciation of addictions;
- proper and nutritious nutrition;
- adequate use of insulin for diabetes mellitus in compliance with all rules established by the attending physician;
- taking only those medications prescribed by the clinician;
- use of personal protective equipment when working with chemicals and poisons;
- full treatment of those diseases that can lead to the occurrence of such a degenerative process.
The outcome of lipodystrophy is often uncertain, since it depends on the course of the disease, the etiological factor and the individual characteristics of the body of a particular patient. If you follow therapeutic recommendations, you can achieve a favorable prognosis for life.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, a comprehensive examination is necessary. During the diagnostic process, it is necessary to determine the degree of development of obesity, identify disturbances in the functioning of the affected organ, as well as concomitant diseases.
The following methods are used:
Laboratory testing of blood and urine.
- Ultrasound scanning.
- Endoscopy of the pancreas.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Based on the results obtained, a treatment regimen is prescribed.
Signs of the disease
At the initial stage, the pathology occurs secretly - there are no manifestations. The first symptoms appear in the second stage of the disease. The person clearly shows suspicious signs that affect the general well-being and digestive processes. A product that is not perceived by the diseased organ, taken orally, causes severe vomiting. Also, the presence of foreign seals on the body indicates the presence of a disease.
The pathology is characterized by the following signs:
- attacks of nausea while eating;
- increased gas formation in the small intestine;
- pain in the stomach area, moving to the chest or hypochondrium;
- belching after every meal.
With further progression of the disease, more serious symptoms appear:
- gagging after eating;
- severe painful spasms of a constant nature;
- pain during urination;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract - constipation or diarrhea;
- decrease in skin turgor and moisture;
- increased appetite, which leads to excess weight.
The disease often occurs with the active development of type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus. Fatty pancreas causes insulin deficiency, which leads to the disease.
The symptoms present in lipomatosis resemble the development of pancreatitis, which sometimes makes diagnosis difficult. The pathology is easily diagnosed at the initial stage, so doctors recommend undergoing annual scheduled examinations at the clinic. If you have the first suspicious symptoms, you should immediately contact your doctor and get tested - this will allow you to start treatment early and increase the chances of a full recovery.
Treatment
Treatment of pancreatic obesity is carried out in a complex way. The following methods are used:
- Diet food.
- Medications.
- Folk remedies.
- Surgical intervention.
It takes a lot of time to combat pathology, it may take several months.
Medicines
To normalize the functioning of the pancreas and digestive system as a whole, as well as to eliminate symptoms, medications are used.
The following drugs are prescribed:
- Enzymes that help cope with the feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
- Antiemetics.
- Painkillers.
- Medicines against diarrhea.
- Vitamin complexes to strengthen the immune system.
If necessary, the treating doctor prescribes insulin treatment.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine methods are a good additional aid in the treatment of obesity. They are safe for health and help enhance the effect of the main therapy.
You need to choose folk remedies together with your doctor:
- Make a mixture of equal amounts of the following plants: mint, chamomile, rowan fruits. Separate 10 g, pour into a thermos and pour boiling water. Let it brew for 30 minutes. Take half a glass 4 times a day.
- Pass the celery root through a blender and squeeze out the juice. Drink the resulting product one tablespoon before each meal. You can also prepare a decoction based on this plant. To do this, pour a large spoonful of celery roots into a glass of boiling water and let stand for 60 minutes. Take the resulting decoction a day, dividing into 4 doses.
- Pour a large spoonful of crushed birch leaves into a liter of boiling water and leave to steep for 12 hours. Before taking, separate 100 ml of infusion and add a tablespoon of honey. Take twice a day.
The patient is also recommended to have a massage. To do this, the patient lies down, the specialist smears the problem areas with honey and massages them with his palms. The duration of the procedure is 15 minutes. Then the body is wrapped in cling film, kept for another 20 minutes and washed off.
Nutrition
The diet is based on the following principles:
- Fractional diet, that is, eat often, but little by little.
- Avoid snacking at night.
- Reducing the caloric content of food.
- Increased protein, fiber, vitamins and minerals.
- Cooking food by stewing, boiling, baking, but not frying.
Dietary nutrition for pancreatic obesity is one of the main stages of treatment.
The following is excluded from the diet:
- Fast food.
- Confectionery.
- Fatty and fried foods.
- Sweet carbonated drinks.
- Smoked meats.
- Marinated and salted dishes.
- Mayonnaise.
- Coffee.
The menu should include fruits, vegetables, berries, dairy products, dried fruits, lean meat and fish, cereals, natural juices, herbal infusions.
Diet for fatty infiltration
If a fatty infiltrate is detected in an organ, then it requires mandatory unloading, since it is capable of fully performing its functions. If we talk about the pancreas, then the following basic principles of food consumption should be adhered to:
- Meals should be fractional - 5-6 times a day in small portions.
- The amount of fatty foods in the diet should be minimal.
- It is better to give preference to low-calorie foods
Patients suffering from obesity are recommended special nutrition according to dietary table No. 5. In this case, a number of products are prohibited:
- fish, meat, offal with high fat content;
- smoked meats, marinades, sauces - mayonnaise, ketchup;
- hotly seasoned dishes;
- preserved products;
- fatty dairy products;
- fried food;
- confectionery and sweet dishes.
Important information: Symptoms of pancreatic insufficiency
It is advisable to include the following dishes on the menu:
- vegetables - fresh, boiled or steamed;
- soups cooked in vegetable broth without meat with fresh herbs;
- milk soups;
- low-fat cottage cheese;
- cheese with low fat content;
- steam omelettes;
- vegetable casseroles;
- oatmeal, buckwheat, rice and semolina porridge, as well as these cereals as a side dish;
- low-fat fermented milk products: yoghurt, kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk.
The diet also involves reducing salt intake to 6-10 g per day. An important aspect of treatment when a fatty infiltrate forms is maintaining a normal drinking regime. On average, it is recommended to drink about 2 liters of water per day. Among the methods of processing food, steaming, stewing and baking in the oven are preferable.