February 15, 2019 Last revised: December 18, 2019 Oral diseases
Oral leukoplakia is a chronic lesion of the mucous surfaces of the oral cavity or lips, with the process of keratinization of the epithelial layers and inflammation.
\
In rare cases, the pathology affects other mucous surfaces:
- nasal passages;
- areas of the esophagus and trachea;
- bladder and intestines;
- external parts of the genital organs.
The disease is more often diagnosed in middle-aged or elderly people. Pathology can degenerate into cancer.
Causes and risk factors
The disease, as a rule, occurs against the background of constantly acting external irritants (poorly fitted dentures, fillings, sharp edges of decayed teeth), in addition, oral leukoplakia can be caused by endogenous (internal) causes.
Risk factors include:
- immunodeficiency states;
- lack of vitamins and other essential substances in the body (unbalanced diet);
- constant consumption of too cold or too hot, hot, spicy foods;
- inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which help reduce the resistance of the mucous membrane to exogenous irritants;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- genetic factors;
- occupational hazards;
- malocclusion;
- constant electric currents of low strength and low voltage (if there are fillings and dentures made of different metals in the oral cavity);
- taking certain medications;
- iron deficiency in the body;
- endocrine disorders;
- viral infections (especially human immunodeficiency virus, papillomavirus);
- excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- exposure to ionizing radiation.
At risk are elderly patients who take a large number of medications from different pharmacological groups.
Oral leukoplakia can be caused by taking various medications.
The greatest damaging effect is the combination of several external (thermal, mechanical, chemical, etc.) and internal factors.
About 10% of all cases of oral leukoplakia become malignant, that is, they degenerate into oral cancer.
Possible complications
A frequent consequence of leukoplakia is a weakening of the body's protective functions. This complication is very dangerous, because the patient is exposed to all viruses and infections.
Doctors consider the most dangerous complication to be malignant degeneration of the damaged part of the oral mucosa.
Patients are registered and regularly invited to undergo examinations. This is a mandatory measure; leukoplakia can recur when specific factors appear.
Forms of the disease
Based on the nature of the pathological process, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- simple leukoplakia without cellular atypia;
- flat leukoplakia;
- soft leukoplakia Pashkov;
- leukoplakia of smokers (nicotine leukoplakia, Tappeiner's leukoplakia);
- verrucous leukoplakia;
- erosive leukoplakia.
Simple leukoplakia without cellular atypia has a latent course and in most cases does not malignize, i.e., does not degenerate into a malignant tumor.
The flat form of leukoplakia is most often diagnosed. In most cases, patients do not experience discomfort in the oral cavity or do not pay attention to the rough area that appears, so the disease is often discovered by chance during a routine examination.
In the mild form of oral leukoplakia, the lesions are localized mainly on the mucous membrane of the lips and cheeks, which is caused by constant biting of the oral mucosa. The mild form of leukoplakia is most often observed in young patients and children.
Leukoplakia of smokers develops against the background of active smoking. The lesion is a diffuse thickening of the mucous membrane of the palate; it rarely undergoes malignancy and, as a rule, disappears after the patient quits smoking.
The verrucous form of oral leukoplakia is formed from a flat one in the absence of adequate therapy, as well as with continued exposure to an irritating factor on the mucous membrane. It is distinguished by the appearance of nodules on the affected area (Latin verruca - wart). This form of leukoplakia is prone to malignant degeneration.
Erosive leukoplakia of the oral cavity develops from verrucous leukoplakia. The risk of malignancy in this form is the highest - in some cases, erosive leukoplakia is considered as the initial stage of the tumor process.
When is a hospital indicated?
In certain cases, therapy is only possible through surgery.
If there are no results from treatment measures, then patients are referred for surgical excision of pathological tissues. Surgery is performed for erosive or verrucous lesions.
We suggest you read: It hurts to press on a tooth under a crown
Reasons for removing affected areas are:
- rapid progression of the disease that cannot be treated;
- formation of ulcers and cracks;
- change in color of the affected area.
Radical excision is always performed if signs of malignancy develop.
Stages of the disease
Changes in the mucous membrane during oral leukoplakia occur in three stages:
- Violations of the correct ratio of cellular elements (discomplexation) in the basal and suprabasal layers of the epidermis, minor cellular atypia is possible.
- Spread of the pathological process to all layers of the epidermis, keratinization of the epidermal layer, parakeratosis of the epithelium.
- Thickening of the epithelial layer, cellular polymorphism, keratinization of the epidermis, parakeratosis with foci of erosion.
The use of folk remedies
Folk remedies are recommended for use for leukoplakia only as an addition to the main treatment. Gargling with decoctions of medicinal herbs is most effective. Natural antiseptics are suitable for this purpose - dried flowers of St. John's wort, linden, calendula and chamomile.
They are brewed in the proportion of 1 tablespoon per glass of boiling water, filtered and rinsed in the mouth several times a day as prescribed by the doctor. Strongly brewed green tea has similar antiseptic and analgesic properties.
Sea buckthorn oil accelerates the healing process of tissues.
Important! In the fight against leukoplakia, it is strictly forbidden to cauterize damaged areas of the epithelium. Additional irritation of keratinized lesions is fraught with their malignancy.
Applications using rosehip and sea buckthorn oils successfully help with leukoplakia. Clean cotton swabs should be soaked in oil and applied to problem areas in the mouth. For the erosive-ulcerative variety of the disease, Kalanchoe juice is used in the same way.
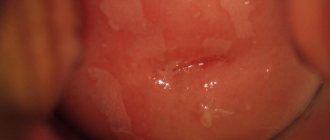
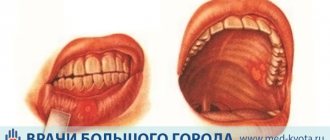
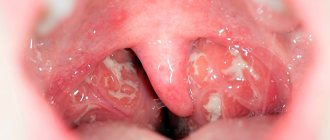
Symptoms of oral leukoplakia
The pathology usually debuts with a slight inflammatory process and/or swelling in a small area of the oral mucosa, which then evenly becomes keratinized. Foci of lesions in oral leukoplakia can be single or multiple. When they appear, patients may experience itching, burning, a feeling of tightness in the affected areas, and feel the rough area with the tongue. In some cases, the disease is asymptomatic for a long time, remaining unnoticed.
With simple leukoplakia without cellular atypia, a thin whitish film or white compaction with clearly defined contours is found on the affected area of the mucous membrane. The flat form of oral leukoplakia is usually not accompanied by unpleasant sensations; only in some cases the patient may complain of unusual dryness of the mucous membrane in a certain area. When the pathological area is located on the tongue, a weakening of taste sensations is noted.
In the mild form of the disease, densified whitish areas of the oral mucosa are observed. The damaged surface may peel off, in some cases the morphological element has a gray color, and when injured, erosions form.
Leukoplakia of smokers is manifested by lesions of the oral mucosa in the form of a dense white coating with red dots. The “plaque” is not removed; it is tightly fused to the underlying tissues.
With the verrucous form of the disease, patients complain of discomfort in the oral cavity. The affected area is compacted, has a characteristic white color, is raised above the surface of the mucous membrane, and is easily injured when eating solid food.
The erosive form of the disease is characterized by the formation of erosions and cracks in the area of leukoplakia. When the spots are localized in the corners of the mouth or on the side of the tongue, patients experience difficulty opening the mouth and eating. The eroded areas are painful, the pain intensifies when taking irritating foods and drinks.
Symptoms of oral leukoplakia that may indicate malignancy are:
- erosion of the surface of the spot, the occurrence of non-healing ulcers;
- the appearance of a compaction at the base of the morphological element;
- frequent bleeding of the affected area;
- rapid increase in the size of the lesion;
- enlarged lymph nodes on the affected side.
Drug therapy
Therapeutic measures taken for pathology depend on several factors.
This:
- form of the disease;
- speed of process development;
- size of lesions.
For moderate variants of the development of the disease, Leukogen or Batilol is indicated. If bacterial complications occur, when lesions appear on the skin, antibiotics are indicated: Ceporin, Ampicillin. Veroshpiron gives excellent results. This diuretic drug quickly reduces swelling.
Among the general effects, B vitamins and retinol acetate (vitamin A) are prescribed.
Vitamin B is administered orally or intramuscularly in the form of thiamine bromide. Vitamin A regulates the process of keratinization and increases the resistance of the membrane to irritating factors. The dosage is prescribed by the doctor. The duration of the course is 2 months.
If the form is flat, applications with vitamin A are effective. It must be applied at least 4 times during the day with a break of at least 30 minutes.
You can use sedatives, tincture of motherwort or valerian root.
It is strictly forbidden to use cauterizing agents, as they accelerate the process of malignancy.
If cellular atypia is not detected, a radical approach is excluded. The patient should only perform the procedures prescribed by the doctor and not skip scheduled testing.
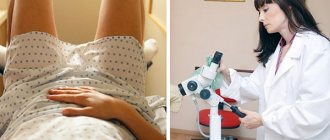
Diagnostics
Primary diagnosis of the disease is based on data obtained from the collection of complaints and anamnesis, as well as an objective examination. To confirm the diagnosis and determine the stage of the process, a biopsy is performed - a microscopic tissue sample is taken from the affected area, followed by histological examination.
A biopsy from the affected area can confirm oral leukoplakia
Differential diagnosis of pathology with candidiasis, lichen planus, systemic lupus erythematosus, syphilis and malignant neoplasm is necessary.
Leukoplakia of the oral cavity, as a rule, occurs against the background of constantly acting external irritants (poorly fitting dentures, fillings, sharp edges of damaged teeth).
Surgery
For radical treatment, a method is chosen to remove the affected area of the penis. The lesion can be removed in the traditional way - by circumcision, covering adjacent tissues. Also, in some cases, removal with liquid nitrogen is used, but doctors believe that this removal method leaves scars on the mucous membrane of the penis. If there is a suspicion of the development of a malignant process in the lesion, then a piece of the removed tissue is sent for histological examination.
Traditional methods of treating leukoplakia include the use of medicinal herbs such as St. John's wort and calendula. Tea tree and juniper essential oils are also used. But it is worth noting that before treating this disease with traditional methods, you need to consult with your doctor, since these methods are not suitable for everyone and can harm your health.
Treatment of oral leukoplakia
Treatment tactics for oral leukoplakia depend on the form and stage of the disease.
First of all, it is necessary to remove the source of constant irritation of the mucous membrane - replace a filling that has become unusable, adjust or replace dentures, and cure carious teeth. If there are endogenous factors influencing the development of oral leukoplakia, the underlying disease is treated. Measures are being taken to improve the health of the body and strengthen the immune system (quitting smoking, normalizing nutrition, etc.). In order to accelerate regeneration, the affected area of the mucous membrane is treated with an oil solution of vitamin A, rosehip oil, Karotolin or other drugs for local use that stimulate reparative processes. For the treatment of simple and mild forms of leukoplakia, these measures are usually sufficient.
The affected areas of the mucous membrane are lubricated with vitamin A or other agents that stimulate reparative processes
In verrucous and erosive forms of the disease, surgical excision of the morphological element may be required with mandatory histological analysis and subsequent clinical observation of the patient. In some cases, surgical removal may be replaced by cryodestruction.
Prevention of pathology development
Prevention of the development of leukoplakia must be carried out, since the disease can develop into malignant formations. Preventive measures are as follows:
- Boosting immunity. To strengthen the body's defenses, you should review your diet, follow a sleep and rest schedule, and spend enough time in the fresh air.
- Quit smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- When carrying out dental procedures, monitor the use of high-quality materials for implants and crowns.
- Visit your dentist regularly for preventive examinations.
The prevention and treatment of leukoplakia must be approached with all responsibility. Untimely elimination of pathology leads to serious consequences.
When visiting a doctor, a patient with diagnosed leukoplakia is registered for further monitoring of the development of the disease, since it can return again even with primary cure.
Basic examination methods for leukoplakia of the penis
Primary diagnosis consists of examining the affected areas; usually, after visualizing whitish spots, the doctor can assume the presence of leukoplakia.
However, additional laboratory tests are required to make an accurate diagnosis and determine treatment measures.
The doctor decides what tests are required in a particular case.
The basis of diagnosis is cytological and histological examination of the biopsy specimen.
To make a diagnosis, the following diagnostic measures are prescribed:
- Oncocytology - a smear of the affected areas is performed, after which the material is examined under a microscope. The study reveals the presence of atypical cells, but as a rule, during a smear, the cellular structures from the deeper layers remain unstudied, which does not always make it possible to detect atypia.
- Examination of a biopsy specimen is the most reliable method for identifying keratinized epithelial cells and atypia of basal cells. Such changes are the main sign of progressive pathology and indicate possible malignancy. In this case, the patient is referred to an oncologist.
- Smears for infections - required to identify chronic processes in the genitourinary area.
- Differential diagnosis is carried out with other diseases , in particular with sexually transmitted infections (fungal infection, syphilitic infection, Bowen's dermatosis, Queyra's erythroplasia, scleroderma).
- Additionally, the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system are examined.
Can penis cancer occur with leukoplakia?
The answer will be in the affirmative, since the processes occurring quite often become the cause of malignancy.
But it is possible to accurately identify atypical cells only with the help of a biopsy of a particle of the affected area.
The last stage of the disease, preceding penile cancer, is characterized by several leading signs.
This is the formation of erosions, ulcers, rapid progression of the disease, an increase in the area of eroded areas, and thickening of keratinized areas of the penis.
Therefore, it is very important to seek help from a medical facility if any changes occur in the genital mucosa.
Methods for preventing leukoplakia
Good oral hygiene and stopping activities that damage and irritate the mouth are the easiest ways to treat and prevent leukoplakia.
Recommended ways to prevent leukoplakia and its complications include:
- Stop using tobacco products of any kind
- Avoid inhalation of smoke, including cannabis, cloves and tar
- Reducing or stopping alcohol consumption
- Routine dental examinations
- Avoiding abrasive dental hygiene products such as bleaches and rinses
- Use of dental devices such as dentures and braces
- Disinfection of wounds in the mouth
- Do not consume hot drinks or foods, wait until they cool down
- Avoiding candy or chewy products that have rough edges or cause mouth irritation
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet to avoid nutritional imbalances
- Avoid foods that cause allergic reactions
- Practice safe sex, including using a condom during oral sex
This article uses materials from Medical News Today magazine.
Is surgery to remove the foreskin necessary for leukoplakia of the penis?
The main predisposing factors in the development of pathology of the glans and prepuce of the penis are increased sweating and accumulation of smegma in the folds of skin around the head of the penis.
This leads to frequent accumulation of fungal and bacterial flora.
Therefore, sometimes the only correct solution is circumcision - removal of the foreskin.
The operation eliminates all of these factors.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia, the prepuce is excised completely or partially, depending on the extent of the lesions.
After the procedure, the spots remaining on the head of the penis are eliminated using the radio wave method, which allows you to completely get rid of the disease.
Complications after circumcision include decreased sensitivity of the head, less often bleeding or infection.
How is the treatment carried out?
After diagnosis, the doctor tells the patient in detail how the detected form of leukoplakia is treated. The first priority is to get rid of the irritating factor. First, the dentist examines the patient’s oral cavity and, having discovered a problem, begins to eliminate it. Interfering fillings must be replaced, chips on the teeth are ground down or the original shape of the crown is restored, if necessary, the patient is sent for bite correction or re-prosthetics, and so on.
If the provoking factor was a metabolic disorder, gastrointestinal disease or other internal pathology, then you will need to undergo a comprehensive examination of the body. Only after identifying the disorder and its treatment can we talk about the success of treatment.
Only a doctor can determine the cause of the pathology
Smoking patients, as well as those who like to drink strong alcohol, will need to say goodbye to their habits. To do this, the doctor can refer the person to a psychologist, psychotherapist, narcologist or other related specialists.
Treatment of leukoplakia with medications is aimed at eliminating symptoms and accelerating the healing of the mucous membrane:
- ulcerative formations and wounds are treated with antiseptics and agents that stimulate healing - “Solcoseryl”, “Stomatofit”,
- if pain bothers you (for example, with verrucous leukoplakia), blockades are indicated - Delagil, Khonsurid,
- help speed up tissue regeneration - “Retinol” (vitamin A in the form of an application), “Carotolin”, “Metacil”,
- to increase immunity, vitamin complexes, B vitamins, “Retinol” (inside), “Immunal” are prescribed,
- Taking sedatives, for example, tincture of valerian, can support the nervous system and psychological state of the patient.
As a rule, to treat a simple and mild form of the disease, the measures listed are sufficient to get rid of it (provided the provoking factor is eliminated). Other types of pathology at the initial stage can also be cured by conservative methods, but if they do not help or the disease has gone too far, they begin treatment in a hospital setting.
To remove leukoplakia in a hospital, one of the following methods is used:
- cauterization (coagulation) with a laser beam,
- thermal effects - dathermocoagulation,
- exposure to radio waves,
- cauterization with liquid nitrogen – cryodestruction,
- chemical exposure to drugs to eliminate warts, for example, “Condilin”,
- removal using current - electroexcision.
After the procedure, the patient is advised to treat the wound surface with antiseptic solutions, as well as agents intended for tissue regeneration.
Regardless of the form and location of leukoplakia, complex therapeutic measures are required. Treatment should begin with the elimination of provoking factors:
- traumatic dentures are removed from the oral cavity;
- you should stop smoking;
- eliminate vitamin A deficiency;
- treatment of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine and somatic diseases is carried out;
- anti-inflammatory and anti-infective therapy is mandatory.
A simple form of the disease, in which no atypical cells are detected, does not require radical treatment. In this case, alternative medicine methods are effective:
- Herbal infusions. Calendula and St. John's wort are used to treat the genital organs. The herbs are mixed in equal parts, brewed, left for 20 minutes, and filtered. The affected areas are washed daily. St. John's wort heals the mucous membrane, calendula relieves itching and inflammation. Medicinal herbs (St. John's wort, calendula, chamomile, knotweed, horsetail, eucalyptus, yarrow) are used to make infusions and douches to treat affected tissues of the vulva and cervix.
- Sunflower oil. Lubricating the affected areas, tampons with refined sunflower seed oil relieve inflammation, painlessly help fight the disease, and promote the regeneration (restoration) of damaged tissues.
- Candles. Used to treat lesions of the cervix. They are prepared using cocoa butter. Melt 100 g of the product in a water bath. Add 2-3 drops of juniper and tea tree essential oils, 10 drops of vitamin A. Pour in 0.5 tablespoons of propolis and calendula tinctures. Mix the medicinal composition thoroughly, pour into special molds, and allow to harden in the refrigerator. Place candles before bedtime for 8-10 days. If necessary, repeat the treatment course after 7 days.
Surgery is widely practiced to treat leukoplakia. Its purpose is to remove affected areas of tissue. Surgical treatment methods include:
- Diathermocoagulation. With the high effectiveness of the method, there is a high probability of developing complications - bleeding, reproductive dysfunction, and others.
- Cryodestruction. An effective and safe method based on cauterization of affected areas with liquid gases. The disadvantage of this method is the rough scars that remain after the procedure.
- Laser coagulation (or radio wave method). A simple method that eliminates the risk of bleeding and damage to healthy tissue and does not require anesthesia. The operation is performed in an outpatient setting. Painlessness and bloodlessness are the undeniable advantages of this method. The duration of healing depends on the degree of damage to the mucous membranes. In some cases, surgical excision of the inflamed tissue along with the area of the affected organ is performed, which entails reconstructive plastic surgery.
Leukoplakia is a disease that affects the skin, mucous membrane of the mouth and genitals. As a result of thickening and increasing the degree of keratinization of the epithelium, plaques and white plaque appear.
The exact causes of leukoplakia are unknown, but a number of external and internal factors influence the likelihood of the disease.
External factors for the occurrence of leukoplakia:
- Poor quality food products;
- Severe environmental pollution;
- Lack of clean drinking water;
- The emergence of new strains of viruses and bacteria.
Various damage to the skin and mucous membrane can also provoke the appearance of leukoplakia:
- Thermal or chemical burn;
- Mechanical damage (scuffs, cuts, bruises, abrasions, etc.);
- Frostbite;
- Galvanic injury is an electric shock.
In addition, leukoplakia is often observed against the background of hormonal imbalances.
The risk group includes patients over 30 years of age; leukoplakia is extremely rare in children and elderly people.
DTK is a treatment method using electric current. The electrode with which the procedure is performed is a small loop or “button”. It is pressed against the affected area of the cervix and a small electrical shock is applied.
This method is considered quite effective - 70% of cases are completely cured, but it is quite painful. In addition, it cannot be used in nulliparous women, since the cervical canal may subsequently become closed. The disadvantages of this method include: the possibility of bleeding and a rather long rehabilitation period.
The only advantages that can be noted are the low cost and the possibility of performing the procedure at any gynecologist - the necessary equipment is available in almost every hospital.
Cryodestruction
Cryodestruction is a treatment using liquid nitrogen. As a result, crystals form in damaged cells, which completely destroy their structure.
The duration of the procedure does not exceed 10 minutes. The treatment is effective in 94% of cases. Patients who have undergone cryotherapy note that the procedure is painless and bloodless. In addition, there are no scars after cryodestruction, so this method can be used to treat leukoplakia in nulliparous women.
Laser therapy
In private clinics, the procedure for treating leukoplakia using a special laser is gaining popularity.
Laser therapy is a non-contact method of influencing affected areas. As a result of laser exposure, diseased cells dry out, all moisture evaporates from them, which leads to their complete destruction. During laser therapy, patients experience no pain, no bleeding or scarring. Full recovery takes 2 to 3 weeks. This method is suitable for both women who have given birth and women who have not given birth.
Radio wave method
One of the most advanced and popular methods of treating cervical leukoplakia is exposure to radio waves, under the influence of which intracellular fluid evaporates. The procedure is painless and bloodless. The recovery period is short, characterized by rapid healing and absence of scars.
When treating with any of the above methods in the postoperative period, doctors recommend maintaining sexual rest for at least 1.5 months, not taking hot baths, not visiting saunas and baths, and not lifting weights.
Within 10 days after the manipulation, vaginal discharge may appear.
To prevent cervical leukoplakia, first of all, you need to carefully observe personal hygiene; it is recommended to use a barrier type of contraception to avoid STDs, and regularly consult a doctor.
The term "erythroplakia oralis" is used to describe intraoral lesions similar to those on the glans penis in Queyre's erythroplasia.
Some of them are scattered or mixed with leukoplakia plaques and are described as mottled erythroplakia.
Histology. The white color of leukoplakia is the result of hydration of the thickened stratum corneum. Histologically, about 80% of oral leukoplakia lesions are benign and manifest as hyperkeratotic or parakeratotic thickening of the stratum corneum, acanthosis and chronic inflammatory infiltrate. Of the remaining 20% of cases, 17% have varying degrees of dysplasia or carcinoma in situ, and 3% have invasive squamous cell carcinoma.
In case of cancer in situ, along with moderate acanthosis, pleomorphism and nuclear atypia are detected. The nuclei appear large, hyperchromic, and irregular in shape. There is a loss of stratification and vertical anisomorphy, leading to a disordered arrangement of cells. In some cases, incomplete keratinization with the presence of dyskeratotic cells in the keratinization is detected; lower parts of the epidermis, accumulation of nuclei in the basal layer and abnormal downward proliferation of the epithelium.
Leukoplakia of any form and location requires complex treatment. It consists in eliminating the factors that provoked the development of leukoplakia and associated disorders. This includes: freeing the oral cavity from metal dentures, quitting smoking, eliminating hypovitaminosis A, treating gastrointestinal pathologies, treating endocrine and somatic diseases, as well as infectious and inflammatory processes.
Simple leukoplakia without cellular atypia often does not require radical therapeutic measures. But such patients must be observed and periodically examined. Detection of basal cell hyperactivity and cellular atypia during histological examination is an indication for removal of the leukoplakia lesion in the near future.
Removal of affected areas of the mucosa can be carried out using a laser or radio wave method, by diathermocoagulation and electroexcision (excision with an electric knife). The use of cryodestruction is undesirable, since after exposure to liquid nitrogen, rough scars remain on the mucous membrane. In some cases, surgical excision of not only the mucous membrane, but also the area of the affected organ (urethra, vagina, bladder) is required, which entails reconstructive plastic surgery. Signs of malignant transformation of leukoplakia are an indication for radical surgery followed by x-ray therapy.
Localization of leukoplakia on the laryngeal mucosa requires microlaryngosurgical surgery. Coagulation of the affected areas of the bladder mucosa is possible during cystoscopy. In the treatment of bladder leukoplakia, the introduction of ozonated oil or liquid, as well as ozone gas, into the bladder has been successfully used. However, in case of persistent disease, resection of the bladder is required.
Timely and adequate treatment of leukoplakia gives a positive result. However, the occurrence of relapses of the disease cannot be excluded. Therefore, the patient needs further observation. You should be careful when using traditional methods of treatment and thermal procedures. They can contribute to the malignant transformation of leukoplakia and aggravate the course of the disease.
How to distinguish scleroderma from penile leukoplakia?
Some forms of scleroderma are much more similar to leukoplakia than other pathological processes.
Therefore, most patients try to distinguish these diseases on their own.
The differences between lichen sclerosus (one of the forms of scleroderma) and leukoplakia of the penis are as follows:
- with lichen, plaques or papular rashes appear at the beginning, accompanied by atrophy of the affected areas; with leukoplakia, the first signs are the appearance of a whitish or grayish film;
- lichen sclerosus is accompanied by severe itching and dryness of the mucous membranes, burning; with leukoplakia in the early stages there are no other symptoms besides plaque;
- rashes with lichen have clear boundaries, which is absent with leukoplakia.
Each of the diseases can trigger the development of cancer of the penis.
Differences between ring-shaped scleroderma and leukoplakia of the penis:
- this form of scleroderma is the most dangerous and affects not only the head and foreskin of the penis, but also quickly spreads to the urethra; white spots appear, the skin becomes thinner, in most cases there is a narrowing of the prepuce, which prevents the head from coming out;
- scleroderma often leads to tears of the prepuce during intimate contact.
But despite the existing differences between leukoplakia and other similar diseases, a doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis only after carrying out diagnostic measures.