Keratoconus is a term made up of two Greek words: “kerato” and “konos”, which are translated from Greek as “cornea” and “cone”. Actually, the name perfectly reflects the essence of the disease: with keratoconus, the cornea of the eye, due to degenerative changes, becomes thinner, and instead of the normal spherical shape, it takes on the shape of a cone.
As a rule, a similar problem occurs in teenage children, but sometimes keratoconus can be found in very young children, and even in people in their thirties. Typically, the transformation of a spherical cornea into a cone occurs rather slowly, taking several years. True, sometimes there are cases of rapid development of the disease.
The first mention of the disease dates back to the 18th century (B. Mohort, Taylor), but it was described in detail a century later, when the British ophthalmologist D. Nottingham isolated it from the group of other corneal ectasia in 1854. Treatment for keratoconus in those days was carried out by cauterizing the cornea with a solution of silver nitrate, after which a thick bandage was applied to the eye and drops were prescribed that caused miosis.
A little later, the Frenchman Eugene Calt began working on the manufacture of a special glass shell, which, when placed on the eye, would flatten the conical top of the cornea and correct its shape. This experiment is considered to be the first mention of the treatment of keratoconus with contact lenses.
Keratoconus - what is it? Description of the disease
Keratoconus is a degeneration of the eye due to which the cornea thins and changes its shape from a normal spherical to a cone-shaped one.
Keratoconus - what is it and how does the pathology differ from a healthy eye?
The first signs of the disease appear in people most often in adolescence. First, one eye is affected, and later symptoms appear in the second. Cases have been recorded in which keratoconus manifested itself in people after 25 years of age. Elderly people rarely encounter this disease.
The loss of elasticity in the cornea is affected by a decrease in the amount of keratin sulfate, collagen and total protein in the body, a lack of enzymes, and a decrease in the activity of antioxidants, which is why it easily stretches and takes on a different shape.
Symptoms of keratoconus
The initial sign of keratoconus is usually blurred vision, which cannot be corrected even with frequent changes of glasses. The identifying sign of this disease is the appearance of multiple phantom images, called monocular polyopia. This effect is especially common with visible objects of high contrast, for example, when viewing dark dots on a light background. In this case, instead of a single point, a person with keratoconus observes a picture with many chaotic images of it.
What does keratoconus of the eye look like: photo
How to avoid developing keratoconus?
Most often, the pathology progresses very slowly. In some cases, its development stops at a certain stage. The later ocular keratoconus appears, the better the prognosis for recovery and the slower the progression of the anomaly.
To minimize the risk of corneal curvature, it is necessary to promptly treat all diseases that can lead to pathology. Also protect your vision from injury and infection. Pay special attention to physical exercise and regularly visit your ophthalmologist for preventive examinations.
Causes
Many scientists have tried to find out what keratoconus is and what causes this disease. Doctors believe that the most correct explanation for this degeneration is hereditary enzymopathy, which manifests itself from adolescence.
Doctors find a connection between keratoconus and diseases such as:
- Leber congenital amaurosis;
- atopic dermatitis;
- Down syndrome;
- eczema;
- pigmentary retinopathy;
- keratoconjunctivitis;
- bronchial asthma;
- traumatic or viral keratitis;
- hay fever;
- Marfan syndrome, etc.
The use of corticosteroids is also responsible for the occurrence of corneal degeneration. The condition of the eye is also affected by the state of the environment. Dusty air, ultraviolet irradiation, and radiation are also causative agents of keratoconus, and microtrauma and mechanical stress on the eye contribute to progression.
Causes of keratoconus
Oddly enough, doctors have not yet come to a consensus on what causes the occurrence of keratoconus. Among the most common theories of origin are:
- Hereditary or genetic predisposition;
- Negative consequences after laser vision correction;
- Unfavorable ecology, influence of ultraviolet radiation;
- A consequence of improper selection of contact lenses, which cause injury to the cornea;
- Eye injury as a result of mechanical impact and even the habit of rubbing the eyes;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, hormonal dysfunction, disruptions in the metabolic process.
Another theory is that the cause of keratoconus is the consequences of previous infectious diseases, since in most cases it occurs in children with weak immunity. Some researchers associate the occurrence of keratoconus with mental trauma, stress and nervous experiences.
Symptoms
A patient with this disease who consults a doctor for the first time will complain of:
- deterioration of visual acuity;
- halos around light sources;
- rapid eye fatigue;
- increased sensitivity, irritation;
- duality in the eyes;
- three-dimensional letters when reading;
- itching and burning;
- Initially, visual acuity deteriorates in the evening, and then in daylight.
In acute keratoconus, the patient will complain of severe vision loss and severe eye pain. This type of disease lasts about three weeks, after which vision slowly improves. Acute keratoconus may be accompanied by corneal rupture and scarring.
Degrees of the disease
Depending on the cause, the pathology is divided into primary and secondary. Most often, destructive processes affect both eyes. Unilateral lesions are extremely rare, occurring in approximately 5% of all cases. Deformation of the cornea can be of the following type:
- Mastoid. The cone is increased to five millimeters, the change is in the center,
- Oval. The cornea protrudes by six millimeters, the deformation is directed downward,
- Globular. The cone size is more than six millimeters. The pathology affects the main part of the cornea.
| The disease can progress over fifteen years, and negative symptoms will increase. Since the signs of the disease are vague and identical to almost all existing eye pathologies, it is very difficult to detect in the early stages. |
Ophthalmologists distinguish several degrees of development of keratoconus:
- At the initial stage, the curvature of the cornea is less than forty-five diopters. Minor morphological changes are noted,
- At the second stage, ophthalmologists identify myopia or astigmatism, which is almost impossible to correct with glasses or contact lenses,
- Further, the deformation of the cornea increases and increases to fifty-two diopters. Microcracks appear on Descemet's membrane, through which moisture enters the cornea. The cone begins to become cloudy, at night the patient sees practically nothing,
- As the disease progresses, the curvature of the cornea increases. At this stage it is up to sixty-two diopters. The main part of the cornea becomes cloudy. Visual acuity decreases in the daytime, the number of points on the membrane increases. A slight bulge becomes visually noticeable,
- The severe stage of the pathology is characterized by a curvature of more than sixty-two diopters. The cornea becomes completely cloudy. The risk of rupture increases, which leads to loss of vision. Emergency surgery is required.
Return to contents
Stages of keratoconus
There are many different classifications of the disease.
The most popular of them is the Amsler classification, which distinguishes 4 stages of keratoconus:
- Stage 1 is characterized by visual acuity of 1.0-0.5, irregular astigmatism. At this stage, it is possible to correct vision with cylindrical lenses;
- Stage 2 – visual acuity 0.4-0.1, more pronounced astigmatism is observed, but still correctable;
- Stage 3 is characterized by visual acuity of 0.12-0.02, thinning of the cornea and a change in its shape. For correction, hard lenses are used;
- Stage 4 – visual acuity 0.02-0.01. At this stage, correction is impossible due to the cornea taking a conical shape and becoming cloudy.
Classification
Keratoconus can be unilateral, when only one eye is affected, or bilateral.
Statistics show that about 95% of all cases of the disease occur in both eyes. Due to appearance:
- Primary, caused by genetic factors;
- Secondary, arising as a result of adverse environmental influences, surgical operations on the organs of vision, and the consequences of injuries.
According to the form of the disease:
- Acute;
- Chronic;
- With variable current.
Deviation of vision from the norm with keratoconus is divided into 3 stages:
- Weak, with a value of up to 40 diopters. During this period, slight morphological changes occur in the cornea of the eye, signs of astigmatism appear;
- Average degree, no more than 55 diopters. Cracks in the Descemet's membrane of the cornea form, allowing moisture to pass through from the anterior chamber. The apex of the cone takes on a cloudy outline, and the patient practically ceases to see in the dark;
- Severe, with a diopter value of more than 55. Visually, the unnatural shape of the cornea is already noticeable; it can become completely cloudy. Vision deteriorates sharply, the person sees poorly even during the day. If there is a high probability of corneal rupture, urgent surgery is required.
The level of corneal dystrophy can be:
- Moderate, with its thickness close to 0.5 mm;
- Medium, with a value of 0.4–0.5 mm;
- Over-permissible or close to rupture, with a thickness of less than 0.4 mm.
According to the degree of corneal deformation, the following forms are distinguished:
- Point dome. The pathology has a diameter of about 5 mm and is located in the center of the cornea;
- Oval dome shape. The cornea protrudes up to 6 mm, its deformation is localized below the center and sags;
- Ball-shaped deformation. The cone is more than 6 mm, the disease covers up to 70% of the cornea.
Diagnostics
At the initial stage, it is almost impossible for an ophthalmologist to immediately identify keratoconus, since the symptoms are similar to other eye diseases. It can only be diagnosed after a thorough and lengthy examination.
Procedures that need to be carried out include:
- interview and visual examination of the patient;
- refractometry, which helps determine myopia and astigmatism due to degenerative changes in the shape of the cornea. It determines the presence of a disease such as keratoconus, and what to expect from it at a certain stage. The patient's head is fixed on the refractometer stand and told to look at a far point in the machine;
- Diaphanoscopy using a light bulb to illuminate the eye helps determine the presence of a wedge-shaped shadow on the iris;
- Skiascopy helps to examine the refraction of the eye. With keratoconus, non-standard refraction of light is observed - the “scissors symptom”;
- ophthalmoscopy examines the optic nerve, retina, choroid using bright light that is reflected from the fundus of the eye;
- Keratotopography provides data on the anterior chamber of the eye and corneal thickness. The results make it possible to carefully plan the operation;
- photokeratometry – a computer examination that determines the presence of corneal deformation at the initial stage of keratoconus;
- biomicroscopy helps to examine the thinning of the cornea, the degree of opacification, the presence of cracks, and examine the deep anterior chamber. Using the procedure, the “Munsen sign”, hemosiderin deposits and Vogt stripes are observed;
- keratopachymetry determines the thickness of the cornea;
- Ultrasound of the eye.
Diagnosis of keratoconus
The beginning of detection of ocular keratoconus is the moment the patient contacts an ophthalmologist with a complaint of deteriorating vision. After the interview, the doctor measures visual acuity and eye refraction. If the presence of myopia or farsightedness is not confirmed, the examination of the patient will continue. The following diagnostic methods exist:
- Skiascopy. Using a special device (skiascope), the counter-movement of shadows specific to keratoconus, called the “scissors effect”, is determined;
- Keratometry is the most common diagnostic method in which the curvature of the cornea is determined;
- Refractometry. Using the technique, irregular astigmatism and myopia resulting from corneal deformations are detected;
- Computed tomography of the eye or ultrasound. These studies reveal changes in the tissues of the cornea, including scars on its surface.
In the later stages of the disease, its diagnosis is not difficult, since the pathology of the cornea is immediately visible without special devices. Only examinations are required to determine the extent of damage to the eye tissue. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, some additional examinations will be required from related specialists.
How to treat keratoconus - treatment methods
It is possible to treat keratononus with conservative methods in the early stages; in the later stages, surgical intervention is necessary.
Conservative
At the initial stage, correction with glasses or lenses is possible, but it is important to consider that vision will rapidly deteriorate with a disease such as keratoconus, and that this is a disease that will require serious treatment over time.
Doctors recommend using drops such as taurine, taufon, retinol, Quinax, etc. 3 times a day. Patients are prescribed sea buckthorn oil. This helps improve metabolic processes in the body.
In addition, the patient is prescribed a course of antioxidants, vitamins, and immunomodulators. Among medical procedures, patients are recommended physical therapy (phonophoresis with tocopherol, magnetic therapy).
Crosslinking
Crosslinking has proven itself in the fight against keratoconus. The procedure involves removing the upper corneal epithelium and filling the damaged areas with a riboflavin solution. After this, the eye is irradiated with ultraviolet light and a treatment lens is placed on it.
Crosslinking in many cases helps prevent the development of the disease, in particular, it strengthens the cornea. After it is carried out, it is recommended to correct vision using glasses or contacts.
Lenses for keratoconus
There are a variety of lenses that can be used for keratoconus. Each is selected individually depending on the course of the disease, stage and structural features of the cornea. Semi-rigid lenses are mainly used.
Their peculiarity is that they are hard in the center, which helps compress the corneal cone, and soft at the edges. They bring air to the eyes very well. The soft part of the lenses is filled with tear fluid, thereby taking the desired shape and improving the refraction of light.
For those who are contraindicated with semi-rigid lenses due to their intolerance, ophthalmologists prescribe double-layer lenses . Such contraindications include clouding of the cornea and a pronounced apex of the cone. Contact lenses consist of two parts: the upper hard part and the lower soft part. This type of lens is very comfortable to wear and corrects vision well.
Scleral lenses, also recommended for keratoconus, have a large diameter, but are invisible to the eye. They do not allow dust and dirt to pass through. Due to the fact that the lenses completely cover the cornea, they do not injure the cone.
If semi-rigid lenses are intolerant, patients are prescribed hybrid lenses. This type is the most comfortable compared to all others due to the soft hydrogel edge. Thanks to this, they correct vision well. Initially, they were worn by people with normal conditions, but they provoked papillary conjunctivitis, corneal edema and the growth of pathological blood vessels.
What is keratoconus?
Keratoconus is a progressive non-inflammatory disease of the cornea, manifested in the form of protrusion of its central part with a normal level of intraocular pressure.
Due to the irregular shape of the cornea, light rays entering the eye are refracted with different strengths and cannot be focused at one point. Since there is no single focus, the image turns out fuzzy and distorted. The progression of keratoconus leads to clouding of the cornea and a significant decrease in visual acuity.
Causes of keratoconus
The exact etiological factor has not been established. There are several reasons, the combination of which can lead to the appearance of keratoconus:
- genetic predisposition;
- corneal injuries;
- endocrine disorders in common diseases;
- presence of allergic diseases;
- exposure to adverse environmental factors.
Genetic predisposition to the appearance of keratoconus is based on the presence of a genetically determined fermentopathy, which manifests itself under the influence of hormonal levels in adolescence. In this case, metabolic processes in the cornea are disrupted and its elastic properties are disrupted, leading to the formation of a protrusion.
Injuries, as well as constant exposure of the cornea to adverse environmental factors, for example, excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays, lead to an imbalance of enzymes in the cornea. An imbalance of enzymes triggers mechanisms of structural damage to the cornea, its thinning and protrusion. Long-term wearing of incorrectly fitted contact lenses can also trigger the development of keratoconus.
Keratoconus: degrees, forms and types of disease
Keratoconus of the cornea has several classifications that affect the tactics of observation and treatment.
There is a division of keratoconus into degrees, namely:
- Grade 1 is characterized by minimal changes in the cornea, not detected by biomicroscopy, and a slight decrease in visual acuity, which is corrected with glasses or contact lenses. Pachymetry is normal or slightly less than normal;
- 2nd degree – clinically manifested by pronounced astigmatism, but which can still be corrected. There are no biomicroscopic features. With pachymetry, the thickness of the cornea is 400-500 microns;
- 3rd degree - thinning of the cornea is observed, its protrusion occurs, the first biomicroscopic signs appear (Vogt's stretch marks, Kayser-Fleischer ring). Visual acuity sharply decreases, which cannot be corrected with glasses or conventional contact lenses;
- 4th degree - the cornea takes on a conical shape, the apex of the cone is thinned, vision is significantly reduced, clouding of the cornea, local edema of the stroma, and pronounced Vogt lines are determined. The thickness of the cornea is less than 370 microns.
By type, keratoconus is divided into:
- anterior (true) – the most common type. The anterior surface of the cornea undergoes structural changes;
- posterior – the topography of the posterior surface of the cornea is changed;
- latent – appears only after LASIK surgery;
- acute – occurs when Descemet’s membrane ruptures and aqueous humor penetrates the layers of the cornea;
- keratoglobus - the protrusion has a spherical shape.
There is also secondary keratoconus, or secondary keratectasia, which appears only after refractive surgery.
Important! Accurate determination of the degree and type of keratoconus plays a major role in choosing a treatment method.
Symptoms and diagnosis of keratoconus
Most often, both eyes are affected. Sometimes changes appear first in one eye and then in the other.
The main clinical manifestations of the disease are:
- decreased visual acuity;
- blurred image;
- double vision;
- the appearance of circles near light sources;
- lacrimation.
A decrease in visual acuity occurs due to changes in refraction. The progression of keratoconus leads to a change in the refractive power of the cornea and, consequently, a decrease in vision. Refractive errors are corrected only in the initial stages of the pathological process, and in advanced stages correction is impossible.
A particular condition that requires immediate treatment is acute keratoconus. It is characterized by sudden loss of vision, severe pain, swollen cornea and redness of the eye. If treatment is started late, corneal perforation is possible.
Diagnosis of keratoconus is based on the following examination methods:
- autorefractometry;
- pachymetry;
- computer keratotopography;
- biomicoscopy;
- confocal microscopy of the cornea.
Autorefractometry allows you to determine the average refractive power of the cornea in different meridians. If the difference between the readings in the two meridians is more than 1.4 diopters, then keratoconus can be suspected.
Pachymetry allows you to determine the thickness of the cornea in its different parts. The average thickness is 550 microns.
With keratotopography, a topographic map of the cornea is compiled. It reflects the refractive power of the cornea in all sections. Deviations in measurement parameters make it possible to identify keratoconus at the preclinical stage. As the disease progresses, keratotoporghaphy helps to assess the degree of increase in pathological changes.
Biomicroscopic examination is included in the diagnostic standard when visiting a doctor, but it allows you to determine the presence of only gross changes in the corneal stroma. Considering that the first biomicroscopic signs of keratoconus appear only at stage 3, during a routine medical examination in a clinic the doctor may not notice stages 1 and 2 of the disease.
Microscopy reveals changes at the cellular level and helps evaluate the morphological structure of the cornea. This way it is possible to identify the initial stages of the disease.
Surgery to treat corneal keratoconus
At the most advanced stages of the disease, the patient requires surgical intervention. One of these operations is keratoplasty aimed at restoring damaged areas of the cornea by transplanting a donor graft.
Depending on the size of the area that needs to be replaced, keratoplasty can be local, total, or subtotal. In relation to the layers that need to be restored, keratoplasty is divided into anterior layer-by-layer, posterior and through-layer.
The operation is aimed at restoring damaged areas of the cornea, improving transparency and visual acuity, as well as preventing the progression of keratoconus. It is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. The duration of the operation is about 40 minutes.
Cost of the operation
Prices for keratoplasty vary widely and depend on many factors. Sometimes you have to pay separately for the transplant and the surgeon. On average, a transplant costs about 98 thousand rubles, and an operation costs from 90 to 300 thousand rubles. and higher. When treating keratoconus, you should take into account all paid consultations with a specialist and the cost of the procedures performed. The final price largely depends on the type of locality and the prestige of the clinic.
After operation
After keratoplasty, the patient is given a protective bandage, which is recommended to be worn for 2-3 weeks. On average, the rehabilitation period lasts up to 1 year. Sutures are removed 6-12 months after the operation. The moment of suture removal depends on the structure of the eye. For a long time, the patient is contraindicated in physical activity and mechanical effects on the eye.
Doctors' observations show that in most cases, keratoconus stops progressing, vision improves, the cornea remains transparent, and the graft remains in place.
Contraindications
There are a number of contraindications in which the operation is prohibited. These include:
- poor patency of tear streams;
- relapse of lung and heart diseases;
- poor blood clotting;
- impaired intraocular pressure;
- inflammatory processes in the eye.
However, it is important to remember that not all contraindications are chronic, and after time has passed after getting rid of the disease, keratoplasty can be performed.
Keratoglobus and its manifestations
Disturbance in the distribution of cellular composition across the layers of the cornea changes the properties of each layer. In this case, the corneal stroma suffers the most. It is the thickest corneal structure and rich in cellular composition. Normally, it is quite strong, has no blood vessels and is transparent.
A pathological effect on its development is often exerted by genetic factors, in particular a violation of the synthesis of the fibrillar protein elastin, which is transmitted according to an autosomal recessive type of inheritance. Elastin is responsible for maintaining the shape, strength and regenerative ability of the cornea.
https://youtu.be/3XsfnNWNlyo
With its pathological production, the stroma loses all the properties described above and becomes easily extensible, which causes a gross change in the shape of the cornea. In most cases, its central sections become convex due to greater extensibility and thinning of the layers. The cornea takes the shape of a ball, becoming like a school globe.
The Greek scientist who first diagnosed this disease in 1907 had no choice but to designate this pathology as keratoglobus.
Clinical manifestations of keratoglobus may appear after the first six months of life. Usually, at the age of 6 months, with this disease, a child can see an unusually large cornea for an infant of the first year of life. But most often keratoglobus is detected at the age of six and older.
Patients with this corneal pathology will complain of decreased vision, double vision, and rapid visual fatigue. Teenagers suffer from headaches that do not have a specific nature and frequency of occurrence. Considering that the primary problem of keratoglobus is visual impairment, such patients in the vast majority of cases will turn to an ophthalmologist.
https://youtu.be/OGMYyJgXyX8
With keratoglobus, there is almost never any clouding of the cornea.
Among diagnostic measures aimed at timely detection of rare corneal pathologies, the main place is occupied by visometry with correction, biomicroscopy, autorefractometry and tonometry. Fundus examination (ophthalmoscopy) is an additional mandatory method of a comprehensive ophthalmological examination.
Checking visual acuity for keratoglobus reveals low levels and correction, with which certain difficulties arise. The fact is that due to the transformation of the shape of the cornea, its important ability, refractive, is lost. It changes so much that astigmatism, which most often appears with a spherical cornea, does not improve vision. And if a positive correction takes place, then vision improves slightly.
In milder cases, at the initial stages of development, refractive errors in the form of hypermetropia or myopia may be present, but visual acuity, taking into account the correction, also does not bring the expected effect. A visual examination of the eyeball in adolescence does not always reveal a gross change in the shape of the cornea; sometimes it is not even noticeable.
The ophthalmologist should be especially wary if a similar disease has already been encountered in the family history, and the patient has signs of low vision that is difficult to correct.
In children of the first year of life, there is a need for tonometry and measurement of intraocular pressure. This study allows us to exclude congenital glaucoma, since macrocornea is a sign of buphthalmos. If there are problems with correction, ophthalmologists perform autorefractometry with the keratometry function. The data from this examination reveal serious changes in the size of the cornea and refractive data (high myopia, the presence of complex astigmatism).
Biomicroscopy, which is an integral part of the ophthalmological examination, does not reveal any signs of dystrophic degeneration of the cornea, which is one of the diagnostic signs of keratoglobus. Ophthalmoscopy also reveals no pathological abnormalities in the fundus.
If there is a suspicion of the presence of a pathology in the shape of the cornea, the patient must be referred for an additional study - keratotopography, after which the final diagnosis will not raise doubts.
Keratoconus and pregnancy
For a long time, experts argued about the effect of pregnancy on keratoconus. Some argued that the best solution was a caesarean section, since natural childbirth puts a lot of strain on the eyes. In this case, the course of the disease may worsen.
The condition of the eyes with keratoconus may worsen due to the influence of hormones, as the tissues may swell. But it is still generally accepted that the disease and pregnancy do not affect each other in any way.
No harm will be done to the body if you initially prepare yourself for childbirth by performing gymnastics for pregnant women. Pregnant women are advised to understand the risks of keratoconus and what it is, and to perform exercises to strengthen the muscles.
Stages and classification of keratoconus
Keratoconus develops gradually, going through several stages. There are the following stages of disease formation:
- Changes in the cornea are minor. Nerve fibers become noticeable in the central zone. Cells lose their shape.
- Cracks appear on the posterior limiting membrane. The cornea begins to become cloudy and deformed.
- The turbidity reaches the membrane. The shape of the cornea, which gradually thins, resembles a cone.
- Significant damage to the membrane is detected. The cornea is completely clouded.
The degree of development of the disease indicates what method can be used to correct the disorders. In the initial stages, it is enough to wear lenses; subsequent spread of the disease forces one to resort to surgical intervention.
There are many classifications of keratoconus. Most often it is distinguished by the shape of the deformation of the contours of the cornea. It can be mastoid (affects up to 5 mm of the corneal area, located closer to the center), oval (5-6 mm lesion, displaced relative to the center to the bottom) and spherical (the cornea is damaged by 75% or more).
Marginal degeneration of the zona pellucida
It is important to distinguish marginal degeneration from keratoconus. It is a non-inflammatory process of thinning of the cornea. In this case, its lower edge is affected. The result of this manifestation is astigmatism, which can be corrected optically. Topographic examination of the cornea will help distinguish between keratoconus and marginal degeneration.
It is worth noting: If keratoconus occurs during pregnancy, it does not affect its course. However, it is advised to refuse natural childbirth, as it can cause progression of the disease.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is important to remember how to properly treat keratoconus and that this is a disease that cannot be cured with traditional medicine.
Folk remedies are used only for the purposes of prevention and strengthening of the body in order to avoid complications.
It is recommended to consume honey and other bee products. They strengthen the immune system and increase the overall tone of the body, cleansing it of toxins. Echinacea tea also has an immunoboosting function. From a decoction of chamomile, coltsfoot, and sage, you can make rinses and lotions for itching, burning and fatigue in the eyes.
It is necessary to remember what keratoconus is and what it can mean for the patient’s eyes. When the first symptoms appear, you need to go to the doctor and undergo all examinations, and not rely on self-medication. The sooner a problem is detected, the faster and safer it can be solved.
https://youtu.be/5_tW8cxNs7g
Treatment
There are two types of treatment for the disease, depending on the form of the pathology: conservative and surgical. Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely eliminate the curvature of the cornea with the help of medications, glasses and lenses.
Conservative therapy
The essence of treatment is the selection of effective medications and corrective optics. Doctors usually prescribe the following medications:
- Antibacterial medications (Tobrex, Floxal). They block the development of the disease and relieve inflammation,
- Antihypertensive drugs (“Timolol”, “Arutimol”). Reduce intraocular pressure,
- Non-hormonal drugs with anti-inflammatory effects (Naklof),
- Mydriatics (“Tropicamide”, “Mezaton”). Prescribed in acute form before surgery. Helps dilate the pupil
- Immunomodulators (Leukinferon). Correct and normalize the functioning of the body’s protective barrier,
- Hormonal drugs (Dexamethasone, Maxidex). They are prescribed when there is a malfunction of the endocrine system,
- To minimize the risk of perforation of the cornea, a pressure bandage is prescribed, on which sodium chloride ointment is applied at a concentration of 0.5%,
- To normalize metabolism, the doctor prescribes Quinax and Taufon eye drops.
Photodynamic therapy
Photodynamics is prescribed as an additional treatment. A unique substance, verteporfin (“Visudin”), which is highly photosensitivity, is injected into the patient’s circulatory system. It accumulates in the affected tissues, after which the eyes are exposed to laser beams that activate the action of the drug.
The procedure lasts twenty minutes and is carried out in specialized clinics under the supervision of an experienced doctor. The course of therapy is one month. The result of treatment is the blocking of destructive processes occurring in the visual apparatus.
Lenses and glasses
Depending on the stage of the pathology, the following types of lenses are selected:
- Soft. They are usually prescribed at the initial stage of the disease. As the disease progresses, they are not effective because they “adapt” to the shape of the cornea,
- Two-layer. If hard ones are not suitable and severe clouding of the shell is detected, then doctors recommend using these optics,
- Scleral. They reduce the degree of pressure on the cornea because they rest on the sclera,
- Combined. Using soft and hard lenses at the same time gives a double result: absence of discomfort and vision correction,
- Rigid gas-tight. I correct the shape of the cornea and correct other anomalies that accompany keratoconus of the eye (astigmatism and myopia),
- Hybrid. The center of the product is made of hard polymer, and the edges are soft. This significantly increases the level of comfort when wearing lenses.
| In the initial stages of pathology, cylindrical glasses may be prescribed to improve visual acuity. Sidorenko eyepieces cope well with a similar task. This is a unique device that allows you to normalize blood circulation in the eyes and activate metabolism. |
Return to contents
Surgery for keratoconus
To eliminate it, pathologists most often resort to surgical intervention, since conservative therapy is unable to 100% eliminate the curvature of the cornea. The following types of operations are used:
- Penetrating keratoplasty. The essence of the procedure is a cornea transplant. During the intervention, the damaged element is removed and replaced with a donor implant,
- Epikeratophakia. Partial corneal replacement. The affected epithelial layer is removed and the donor layer is grafted onto
- Implantation. Installation of corneal rings and their elements,
- Thermokeratoplasty. Using pinpoint applications, the cornea is thickened,
- Radical keratotomy. Several microscopic incisions are made in the center of the cornea.
An individual type of intervention is selected for each patient. Surgery completely eliminates keratoconus, but in some cases there remains a risk of relapse.
Crosslinking and excimer laser correction
These two procedures are widely used in ophthalmology.
Crosslinking provides good but unstable results. Most often, after some time, the anomaly begins to progress again. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia; using a special device, the doctor removes the epithelial layer from the cornea and instills riboflavin (vitamin B2) into the freed area. It is then treated with ultraviolet rays.
The final stage of the operation is the application of an antibiotic and the installation of a special lens, which must be worn for four days after the intervention. The result of cross-linking is photopolymerization of the sling fibers; they begin to actively produce oxygen. Strong bonds are formed in collagen fibers, which become more resistant to mechanical stress and strengthen the cornea.
Excimer laser correction is carried out at the initial stages of the development of the disease, the effect of the operation is noticeable after a few days. In severe forms of pathology, they are used together with cross-linking. Most often, patients are prescribed LASIK or PRK. In the second case, the cornea is cleansed using a laser. Lasik helps correct the shape of the cornea.
Forecast
The prospects and prognoses for patients suffering from this eye disease are optimistic.
Keratoconus is not very dangerous. At the same time, it should be noted that the conical shape of the cornea significantly reduces visual acuity. Because of this, some objects may seem somewhat distorted to a person, and the lines may appear broken.
If you do not start to fight this problem in time, it will begin to progress in every possible way. As a result, a person may experience some problems when selecting optical correction devices.
Ultimately, the advanced stages of keratoconus threaten a person with thinning of the cornea, which will be accompanied by severe pain, and all this can lead to loss of vision!
https://youtu.be/bGMRiMqBQVE
How is eye disease such as keratoconus treated?
In the early stages of the disease, distortion of objects can be eliminated using cylindrical glasses. As the disease progresses, patients are advised to constantly wear contact lenses to improve clarity of vision. The selection of these optical products is strictly individual, since there is no single design suitable for all types and stages of keratoconus. The use of soft means of contact correction is limited, since they adapt to the distorted shape of the corneal surface and are therefore ineffective. In this case, ophthalmologists recommend using rigid gas-permeable lenses that are securely fixed and do not deform during use. This allows you to restore clarity of vision in case of this disease of the cornea of the eye.
Popular methods of treating the disease in the initial stages include cross-linking. It involves simultaneous instillation of riboflavin and exposure of the cornea to a special device (Seiler lamps). As a result, additional chemical bonds are created between its collagen fibers, forming a new structural framework. Another popular method, implantation of stromal rings, is a surgical approach to the treatment of keratoconus, aimed at introducing small arc-shaped elements from a material biocompatible with the structures of the eye into the cornea, creating a dense frame and helping to reduce intraocular pressure.
If the cornea is severely deformed, keratoplasty may be indicated. This is an operation during which sections of the shell are replaced with a special graft, which is located on its front layers or replaces them. For this purpose, special materials with increased survival rate are used. In addition, the treatment method using a femtosecond laser has become widespread. During this surgical intervention, a laser effect is applied to the structure of the cornea and its shape is changed. This method is considered one of the most gentle and effective, since it allows taking into account the slightest individual characteristics of the patient’s visual system.
The main methods of treating keratoconus:
- cross-linking (exposure to a Seiler lamp);
- keratoplasty;
- implantation of stromal rings;
- use of femtosecond laser;
- correction using rigid gas-permeable lenses (in the early stages).
If you use contact lenses, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the wide selection of products from world brands in the Ochkov.Net online store. With us you can buy your favorite products at a profit in just a few clicks!
Causes of keratoconus development - harmful factors and risk age
To date, the exact causes of the disease in question have not been established.
All methods of treating keratoconus today - types of operations for keratoconus, their pros and cons
Scientists put forward several theories about this:
- Hereditary-metabolic . The basis for the formation of this pathology is the presence of hereditary fermentopathy. Catalysts of the disease can be hormonal changes in the body, malfunctions of the immune system, some common diseases, etc.
- Ecological . The risk group in this case includes persons who are exposed to constant ultraviolet or radiation exposure. The first category includes those who live in mountainous areas or in the southern regions.
- Hereditary . The disease in question is often associated with Down disease, Marfan syndrome, as well as with some other genetic diseases: - Ehlers-Danlos disease. - Leber's amaurosis. - Blue sclera syndrome. — Pigmentary retinopathy.
- Endocrine . Associated with dysfunction of the endocrine glands, which can occur against the background of the following conditions: - Hypo- or hyperthyroidism. - Addison's disease. — Metabolic disorders. — Errors in the functioning of the thymus gland.
- Immunological . In accordance with this theory, keratoconus can develop as a result of the following phenomena: - Pathological processes that are of an autoimmune nature: eczema, bronchial asthma, hay fever, etc. — Taking certain medications that negatively affect the functioning of the body’s defenses. An example of such medications are corticosteroids.
Recently, additional factors have appeared with which scientists associate the appearance of this eye pathology:
- Prolonged stay in a stressful situation.
- Frequent rubbing of eyelids with hands.
- Diseases of the visual organs arising from various causes.
- Regular stay in a dusty room: dust particles irritate and injure the mucous membrane of the eye.
- Consequences of laser vision correction.
- Inadequate diets that minimize the amount of fats and vitamins in the diet.
The concept of keratoconus in adults and children
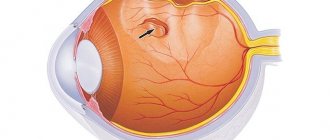
Keratoconus is a disease in which the cornea of the eye becomes thin and deformed. Normally, the cornea has the shape of a sphere. In the initial stages of keratoconus, it becomes thinner and its elasticity decreases sharply. Under the influence of intraocular pressure, the cornea protrudes forward and takes the shape of a cone. At the same time, vision deteriorates greatly: a person experiences double vision, severe myopia and astigmatism appear.
With keratoconus, the cornea takes on a cone shape
Depending on the shape the cornea takes, there are 6 types of keratoconus:
- pointed;
- blunt-topped;
- peaked;
- low-top;
- atypical low-top;
- atypical peaked.
Keratoconus was first diagnosed by the German physician B. Mohort, and his British colleague D. Nottingham described this disease in detail in 1854. Treatment in the 19th century consisted of cauterizing the cornea with silver nitrate and placing a tight bandage over the eye. Treatment of keratoconus with contact lenses began to be practiced only at the beginning of the twentieth century thanks to the developments of the French ophthalmologist E. Calt.
As a rule, at first the disease affects only 1 eye, but soon its “brother” also begins to see poorly. Decreased vision is poorly corrected with glasses, and patients are forced to constantly change them. In addition, they develop polyopia, when instead of a single object a person sees many copies of it. Keratoconus progresses slowly: it can take several years from the onset of the change to the cornea taking on an irregular shape. The rate at which vision deteriorates in different eyes may vary.
Most often, teenagers suffer from keratoconus, but sometimes this disease occurs in young children, and usually both eyes are affected at once.
Often the disease starts after the onset of puberty, but it happens that it affects middle-aged people or children. The impetus for the development of the disease can be various factors, from too much exposure to bright sun to diseases and injuries of the cornea. Young children can inherit keratoconus from their parents or develop as a complication of any eye diseases against the background of reduced immunity. As a rule, in children, keratoconus affects both eyes at once, and the disease develops much faster.
Surgeon Sergei Popov talks about the disease - video
Pathological changes
- The total amount of proteins decreases.
- Reduced density of collagen fibers.
- The number of non-protein components increases.
- A sharp decrease in the level of keratin sulfate.
- Decreased proteinase production leads to increased collagenolytic processes.
Keratoconus occurs during puberty in the form of slight astigmatism. There are three possible developments of the disease:
- stability phase (stationary). Progression stops completely or for a long time;
- rapid decline in vision (progressive). What is characteristic is that it never causes complete blindness without concomitant eye diseases;
- a sharp change from the phase of stability to worsening vision and vice versa.
With severe deformation and penetration of a large amount of intraocular fluid, partial rupture of the corneal layer is possible - corneal hydrocele. The process is reversible, and corneal clarity returns after 7-10 weeks.
Reviews about the treatment
Judging by reviews posted on the Internet, the best treatment method is surgery. Hard lenses are not suitable for everyone, much less helpful, but many patients report improved vision after surgery.
I strongly advise against wearing hard contact lenses; they contribute to the progression of keratoconus much faster. I ordered them in Almaty, gas permeable, I wore them for a month, it’s terrible, I don’t want the enemy to wear them. If possible, don't wear it. After all, lenses are beneficial to the doctors who prescribe and manufacture them; if you listen to them, the lenses will treat you and stop the progression.
Salgadin(Bishkek)
https://forum.ochki.net/viewtopic.php?p=31298
As a child, my vision was perfect; in my first year I began to notice a slight deterioration, which I did not pay much attention to. Later, while preparing for a session in the 4th year, I noticed that the text in the book seemed a little fuzzy, and there were double letters. I blamed this fact on stress. It was decided to postpone the trip to the doctor until better times. “I got so bad that I couldn’t see well, either up close or in the distance. It was decided that I needed to go to the doctor, who referred me for surgery. A week after this, near vision began to appear. And a month after the operation, vision in the operated eye was already 0.9–1.0 (100%). Now I see well, occasionally I take drops against dry eye syndrome.
Anitya
https://pikabu.ru/story/i_eshche_pro_samoe_dragotsennoe_nashe__zrenie_4510898
Using my own example, I can only say that this disease, keratoconus, is not so terrible and can be treated. I was offered a treatment method - implantation of rings - they did it, but it took a long time to take root. But in our case there is no choice, the main thing is to STOP THE PROCESS!!!!!! You have to try everything, but the body, of course, will resist!!!! As for unconventional methods of treatment, first of all you need to check the functioning of the liver; I have now included liver cleansing, because it is directly related to the organs of vision. I plan to do a liver cleanse 2 times a year, and then intensive vitamin nutrition for the liver.
Svetlana (Kazakhstan)
https://forum.ochki.net/viewtopic.php?p=31298
Prevention and prognosis
To date, there are no specialized measures aimed at preventing the development of such a disease. General prevention of keratoconus includes:
- early identification and complete elimination of those disorders leading to a similar type of deformation of the cornea of the eye;
- preventing microtrauma of the cornea;
- use of protective equipment when working in a dusty room;
- taking only those medications prescribed by the attending physician, with strict adherence to the daily dosage and duration of treatment;
- Regular visits to an ophthalmologist, which will make it possible to detect pathology in the early stages and avoid surgical intervention.
The disease has a relatively favorable prognosis, which is achieved due to the slow progression of the pathological process. In some situations, stabilization of the condition and the absence of development of pathology can occur at any stage of its course. In addition, a similar disease is characterized by the fact that the older age keratoconus occurs, the slower its progression and positive outcome will be.
Disability and keratoconus are quite compatible concepts. Disability threatens the patient only in cases of development of the main complication of the pathology - blindness.
Signs of a thinning cornea
The symptoms of keratoconus look quite vague and do not allow a person without specific education and the help of an ophthalmoscope to determine that the cause is precisely this disease, and not many others that are similar. Typically patients note:
- Decreased vision. The symptom is classic - it becomes more difficult to see objects that are in the distance. See objects that are located nearby, too. Night vision is especially affected: in twilight and darkness the patient ceases to navigate quite quickly.
- Multiplicity of forms. Double objects are common in ophthalmic practice. But objects that are duplicated many times are already a classic symptom of keratoconus. This is most noticeable if the patient looks at the book. Each letter there will be repeated several times, in a random order around the original. If the patient remembers how the letters were located once, he will be able to make sure that their position does not change over time.
- General discomfort. Appears in the later stages, when vision decreases greatly. The patient begins to feel uncomfortable with bright light, both sunlight and lamp light, and headaches appear, which are caused by the constant need to squint. Itching may occur in the affected eye.
At the same time, there is no pain, except for headaches, with keratoconus. And the process of vision loss occurs so slowly that a person who is not accustomed to monitoring his health can only notice it when he is unable to navigate the street.
Prognosis and possible complications
The later in life keratoconus occurs, the more favorable its prognosis. As a rule, the disease progresses no more than 10 years from the date of the first symptoms. After this, it stops at one of the stages and often manifests itself only as weak vision.
When contacting specialists, eye functions are successfully restored with the help of contact lenses. In the initial stages, vision may improve to 1.0. In advanced cases, conservative treatment can also help: sometimes it is possible to achieve an increase in visual acuity to 0.5–0.6.
Sometimes treatment does not have the desired effect, and vision remains weak. In this case, it is possible to register a disability of group II or III on the basis of significant visual impairments leading to limitation of life activities.
If left untreated, the most common complication of the disease is acute keratoconus with pain and a sharp deterioration in vision. However, even if this condition is not treated, after 1.5–2 months it goes away on its own: the fog from the eyes disappears, and vision may become even better than it was before the exacerbation.
In the most severe case (at the terminal stage of the disease), a corneal rupture may occur, which sometimes leads to complete blindness. In this case, an urgent operation to transplant donor material is indicated.
Stage I (first degree)
- Myopia and a weak degree of myopic astigmatism are detected (possibly with a plus or zero sphere);
- K-index <= 48 D;
- no biomicroscopic signs;
- A “protrusion spot” or a characteristic pattern on computer topography is revealed - bow-tie;
- Pachymetry readings are normal or slightly less than 500-550 microns.
Advantages of treating keratoconus at the MGK clinic
Thanks to the use of the most modern diagnostic equipment from the world's leading manufacturers, the clinic's specialists can diagnose keratoconus at the earliest stages of the disease, which allows the use of more gentle treatment methods and minimized costs. After conducting a detailed diagnosis, the doctor not only draws up a complete picture of the state of the visual system, but also determines the indications for a particular treatment method, and can also predict the outcome of treatment.
If there are indications for cross-linking, the procedure is performed on an outpatient basis on a one-day basis. At the same time, according to indications, laser vision correction can be performed to eliminate refractive errors (myopia and astigmatism). The installation of stromal rings is also performed on an outpatient basis, under local drip anesthesia. After the operation, each patient receives detailed recommendations to speed up the rehabilitation period; the doctor also draws up a schedule of follow-up visits to conduct follow-up preventive examinations.
The highest level of theoretical training and extensive practical experience of our specialists guarantees the achievement of the best treatment results.
The clinic employs Professor Alexey Yurievich Slonimsky, one of the most authoritative specialists in the treatment of patients with various corneal pathologies, a recognized leader in the field of end-to-end corneal transplantation for keratoconus, and the author of a monograph on keratoconus. Professor Slonimsky Yu.B. - Member of the Board of the Russian Society of Ophthalmologists. Among fellow ophthalmologists, Yuri Borisovich is a recognized authority in the field of treatment of patients with severe corneal pathology.
Operations are also performed by a surgeon of the highest category, the chief physician of the clinic, Fomenko Natalya Ivanovna, who has successfully performed more than 12 thousand operations of various categories of complexity.
The operations of cross-linking and installation of stromal rings (kera-ring) are carried out by Yuri Ivanovich Kishkin, Candidate of Medical Sciences, and other clinic specialists.