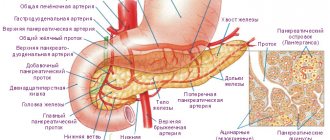
The importance of the pancreas in the body
The pancreas produces enzymes necessary for food processing. The purpose of the gland is to perform exocrine and endocrine functions.
In the first case, the gland produces digestive juices and enzymes that facilitate the digestion of proteins and fats. After food digested by the stomach enters the duodenum, the enzyme trypsin is produced, carbohydrates and fats are broken down, and gastric acid is neutralized in the small intestine. Thanks to its endocrine function, the pancreas produces insulin, which controls blood sugar levels, and other important hormones. The production of insulin occurs precisely when there is an increase in glucose in the blood, which is taken up by muscles and tissues to meet metabolic needs as a source of energy for cells. Low insulin production leads to increased glucose levels, the development of diabetes mellitus, and other diseases in the body.
The symptoms described above directly indicate problems with the pancreas, and this is a reason to consult a doctor and get diagnosed. You need to find the root of the problem and take measures to eliminate it, as well as sometimes unpleasant symptoms.
To understand why certain signs of problems with the pancreas occur, it is necessary to understand the importance of this organ in the body and what functions it performs.
As noted above, the pancreas is an organ of mixed secretion. Performing the function of an endocrine gland, it secretes three main hormones:
- insulin - reduces the concentration of glucose in the blood, facilitates its utilization by cells, increases protein synthesis and reduces the breakdown of fats;
- glucagon is the exact opposite of insulin, increases glucose levels, increases the breakdown of proteins and fats, which is why glucagon is also called a counter-insular hormone;
- somatostatin - suppresses the synthesis of pituitary hormones (somatotropic and thyroid-stimulating).
The exocrine pancreas is characterized by the production of the following enzymes:
- amylase - necessary for the absorption of carbohydrates, breaks down polysaccharides into monosaccharides (glucose and fructose);
- trypsin - breaks down proteins into amino acids;
- lipase - necessary for the absorption of fats.
From the main functions of the pancreas listed above, it follows that problems with it will primarily lead to digestive disorders. And with a longer course of the disease, disturbances in protein and carbohydrate metabolism also occur.
The main function of the pancreas is the secretion of pancreatic juice, which contains the most important food enzymes: trypsin, lipase, amylase, necessary for the processing of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. In addition, if the functioning of the pancreas is disrupted, it becomes impossible to transport the necessary elements formed after the breakdown of food to various organs.
The structure of the gland contains the so-called islets of Langerhans - clusters of cells that secrete insulin, glucagon and other vital hormones responsible for metabolic processes in the body. For example, insulin, by ensuring the penetration of glucose into cells, promotes its absorption and reduction of blood sugar.
Glucagon, on the contrary, is responsible for increasing sugar, preventing the development of hypoglycemia. In addition, the gland cells produce lipocaine, an element that prevents fatty degeneration of the liver. Moreover, the islets of Langerhans produce a polypeptide containing about 36 different amino acids, and it also controls the secretory function of the gland.
Common symptoms of pathology
Signs of pancreatic disease are caused by swelling and enlargement of the organ, stretching of the capsule, congestion, melting of tissue under the action of its own enzymes, infection with subsequent inflammation.
How intensely they are expressed depends on predisposing factors and the etiology of the disease. Any disease in its manifestations is associated with the same symptoms. Pain is the predominant symptom. They are localized in the upper abdomen, radiate to the interscapular region, left shoulder, back, and can become encircling.
Most often, an attack is associated with overeating fatty or fried foods or drinking alcohol.
Less commonly, the pain is dull and constant. Typically, the intensity decreases after applying cold and increases with a warm heating pad. The typical posture for patients is lying on their side with their knees drawn in. On palpation of the abdomen, severe pain is detected in the epigastric region, hypochondrium on the left, and Pasternatsky’s sign is positive (tapping on the lower back, usually used in the diagnosis of pyelonephritis).
Diagnosis of pancreatic diseases
Dyspeptic disorders with dull pain come first. They may be the first (initial) signs of damage to the pancreas, when a person, after drinking with a snack of meat dishes and spicy salads, each time develops diarrhea and vomiting.
Symptoms are initially mistaken for poisoning. But please note that none of those who took part in the feast were harmed. With repeated manifestations, the reason becomes clearer. A chronic process in the pancreas leads to persistent diarrhea, weight loss, and lack of appetite.
The patient feels aversion to food and smells. Feces during diarrhea contain a significant amount of unprocessed fat, and therefore have a characteristic foamy appearance with a shiny tint. Due to indigestion, the patient is bothered by heartburn and bloating. Damage to the endocrine function of the pancreas is suspected when the patient complains of constant hunger, desire to drink, and itchy skin.
Diseases in children
The most common causes of pancreatic problems are presented below:
- Pancreatitis is an inflammation of gland tissue, which can be acute or chronic. Most common in adults, rare in children.
- Neoplasms - benign and malignant tumors.
- Diabetes mellitus is the destruction of pancreatic cells involved in the synthesis of insulin, or impaired tissue sensitivity to insulin.
- Functional disorders of the gland - dysfunction of an organ in the absence of anatomical changes.
- Structural anomalies are a common cause of problems with the pancreas in a child.
Pancreatic problems in children can be either congenital or acquired.
Among congenital diseases the following pathologies are distinguished:
- ectopia of the gland;
- bifurcation of the pancreas;
- annular (ring-shaped) gland;
- congenital decrease in lipase activity (Sheldon-Reay syndrome);
- congenital amylase deficiency;
- isolated decrease in trypsinogen activity;
- generalized pancreatic insufficiency.
Among the acquired problems with the pancreas are:
- viral acute pancreatitis;
- cystic fibrosis;
- drug-induced pancreatitis;
- traumatic pancreatitis;
- pancreatitis in Henoch-Schönlein disease;
- pancreatitis due to excess nutrition.
Clinical manifestations and treatment of childhood pancreatitis are not fundamentally different from those in adulthood. The main thing in this case is to determine the cause of pancreatic inflammation and eliminate it.
Therefore, below we will analyze those problems of the pancreas that are specific to childhood.
For the first time, the classification of pancreatic diseases was adopted at an international conference of pancreatologists in 1963 and adjusted in 1983. In the latest version, two forms of chronic pancreatitis began to be distinguished - obstructive and non-obstructive.
There are several diseases that affect the pancreas:
- pancreatitis (acute, chronic, alcoholic, recurrent, purulent, hemorrhagic);
- cysts and pseudocysts of the pancreas;
- pancreatic steatorrhea;
- cystic fibrosis;
- pancreatic necrosis;
- malignant neoplasms;
- diabetes.
Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is an inflammatory-necrotic disease, which is a consequence of enzymatic autolysis (self-digestion) of the pancreas. The immediate cause of its occurrence is damage to healthy parenchyma cells by prematurely activated enzymes. Normally, they become active only when they enter the intestines.
Under the influence of a number of factors, the process of synthesis of digestive enzymes is disrupted; they are activated in the pancreas and digest the tissues of the organ. Moreover, enzyme substances can spread to nearby tissues and penetrate the systemic bloodstream, causing symptoms of general intoxication.
Symptoms of pancreatic disease in acute pancreatitis are:
- severe and constant pain in the upper abdomen, which can radiate to the back, chest, and intensifies when lying down, as well as after eating;
- nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief and does not stop;
- increased body temperature;
- yellowing of the skin.
During an attack, many patients are bothered by bloating, increased gas formation, and the appearance of small bruises in the abdominal area.
With timely treatment, acute pancreatitis is completely curable in 80% of cases, the remaining 20% are due to the chronic form of the pathology. Chronic pancreatitis has a long-term recurrent course and is characterized by a gradual change in the structure of the pancreas and a decrease in its functionality.
The development of pancreatitis is influenced by the use of hormonal and diuretic drugs, cholelithiasis and other factors. The first symptoms may appear only several years after the onset of the disease, but in the future it may worsen.
How can we determine in this case that there is something wrong with the pancreas? The clinical picture of chronic pancreatitis during exacerbation is almost the same as in the acute form, but the signs of pancreatic disease are less pronounced.
If inflammation of the pancreas is suspected, emergency hospitalization is required
An attack of acute or chronic pancreatitis requires prompt hospitalization and treatment. Before the arrival of doctors, it is strictly forbidden to take any medications other than antispasmodics and warm up the abdominal area. To alleviate the condition, you can give an injection of No-shpa and sit the patient so that his body is tilted forward.
After relief of acute symptoms, the patient is discharged and prescribed maintenance therapy. However, the transition of acute pancreatitis to the chronic stage is not excluded even if all medical prescriptions are followed. In this case, discomfort and heaviness in the abdomen, upset stool, nausea and pain will periodically occur. In addition, many patients complain of an aversion to fried and fatty foods.
Pancreatic necrosis
Pacreonecrosis is a complication of acute pancreatitis and is caused by a violation of the protective mechanisms of the pancreas from the destructive action of enzymes. Unlike pancreatitis, this disease mainly affects non-drinkers. However, in most cases, its development is caused by a single intake of large doses of alcohol in combination with a large meal.
As a result, the exocrine function of the pancreas sharply increases, its ducts expand and stretch, and the outflow of digestive juice slows down. Due to the overflow of the ducts, the pressure in them increases, which leads to swelling of the parenchyma and destruction of healthy gland cells.
The secreted enzymes are activated prematurely, which is the cause of self-digestion and the onset of large-scale necrosis. Active forms of lipases cause the death of fat cells, and elastases destroy the vascular wall. In addition, enzymes and fragments of decay of dead tissue penetrate the bloodstream, causing intoxication of the entire body.
Pain in the left upper hypochondrium, nausea and vomiting may indicate the development of pathological processes in the pancreas
Symptoms of problems with the pancreas in this case cannot be missed, since pancreatic necrosis is characterized by an acute and sudden onset. This allows patients to understand that the cause is food or drink.
First, a pain syndrome of a girdling nature appears, concentrated mainly in the left half of the abdomen. There is no pancreatic necrosis without pain, and the stronger the pain, the more severe the disease. It should also be noted that the pain gradually and quickly subsides, since the pathological process also extends to the nerve endings. If signs of intoxication persist, the prognosis is usually unfavorable.
Some time after the onset of pain, vomiting begins, which cannot be stopped. Vomit often contains bile and blood. To the question “what to do if pancreatic necrosis is suspected,” the answer is clear: call an ambulance.
In the vast majority of cases, patients require surgery to remove necrotic products and restore the outflow of enzymes. It is important to know that surgical intervention is not performed in the first five days due to the impossibility of assessing the degree of necrosis.
Cyst (pseudocyst)
A cyst is a pathological cavity in the parenchyma that has walls and liquid contents. It may appear as a result of an inflammatory process or traumatic injury to the pancreas.
Against the background of inflammation, so-called pseudocysts that do not have epithelium appear. When the patency of the ducts is disrupted, true or retention cysts are formed, in which an epithelial lining is present.
What symptoms will be accompanied by a cyst depends on many factors - location, size and causes of its occurrence. In case of problems with the pancreas of an inflammatory nature (pancreatitis), against which a cyst is formed, the most severe pain is observed. Over time, they become less pronounced and may even go away completely.
Why is the pancreas enlarged?
- nausea, vomiting;
- unstable stool;
- weight loss;
- yellowish pigmentation of the skin and eye sclera;
- swelling of the legs (due to compression of the portal vein cyst);
- urinary retention, partial intestinal obstruction.
What should you do if a cyst is found? Therapeutic methods are powerless in this case, and only surgery will help. And here there are two options: removal and drainage of the cyst. The choice of surgical tactics depends on the characteristics of the tumor.
Childhood diseases
The child may develop reactive pancreatitis, pancreatic insufficiency and diabetes mellitus. Pancreatic failure is usually congenital and difficult to treat. However, with proper nutrition and regular medical supervision, it is possible to maintain the digestive process at an acceptable level.
Symptoms of pancreatic insufficiency are periodic abdominal pain, undigested pieces of food in the stool, attacks of nausea and unstable stool.
Children's pancreatitis is usually mild; severe pancreatic lesions are extremely rare.
The most common disease of the pancreas in children is reactive pancreatitis, which occurs when other organs of the gastrointestinal tract are disrupted. As a rule, there are very specific reasons for its development:
- infectious pathologies - sore throat, flu, colds;
- parasitic infestations;
- abdominal trauma;
- unbalanced diet for a long period;
- congenital anomalies of the gallbladder;
- treatment with strong antibiotics.
Reactive pancreatitis can be suspected based on several symptoms. These include pain in the upper left abdomen, lack of appetite, light and loose stools, indigestion and a slight increase in body temperature.
Diabetes
Metabolic disorders in diabetes mellitus are caused by a deficiency in the production of insulin by the pancreas and an increase in glucose levels in the blood. The causes of its development may be autoimmune lesions of the pancreas, viral infections and intoxication with toxic substances (pesticides, some drugs, carcinogenic compounds).
Immediate treatment of pancreatitis
If symptoms of pancreatitis occur, it is recommended to immediately call an ambulance or take the person to the hospital yourself. The disease has no specific symptoms. Clinical manifestations are similar to signs of appendicitis and myocardial infarction, which only a doctor can exclude.
Before the ambulance arrives, the following steps must be followed:
:
- do not take food and drink, which further irritate the already inflamed tissues of the organ;
- take a lying position, relax, which helps reduce the intensity of pain;
- to reduce discomfort, you can apply a heating pad with cold water or any item from the refrigerator wrapped in cloth to the abdominal area (to prevent frostbite of the skin);
- It is prohibited to take medications, which distorts the clinical picture of the disease and causes an incorrect diagnosis.
In the first two days after the attack occurs, you need to fast, including only non-carbonated mineral water, weak weak tea or rosehip decoction in your diet. Bed rest is important.
To relieve an acute attack of inflammation, medications from the group of painkillers and antispasmodics that reduce the acidity of gastric juice are prescribed. If there are suspicions and after confirmation of the purulent process, they begin to take antibacterial agents.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, there is an abscess, or extensive pancreatic necrosis, surgery is performed. The abdominal cavity is washed using drainage. In severe cases, pancreatic resection is prescribed.
Therapy for chronic inflammation differs from treatment for the acute form of the disease. In this case, measures are taken to maintain the process of normal digestion of food. To do this, you need to take enzymes, but only after stopping the acute stage of the pathology. When the chronic process worsens, the patient is transferred to a special diet.
It is important to exclude stressful situations and maintain active physical activity.
Causes of disease development
If the functioning of the organ is disrupted, treatment is carried out, including medications and adherence to the correct diet. If you suddenly experience symptoms of a gland disease, and it is not possible to urgently seek medical help, you should fast to relieve the burden on the digestive tract and allow the organ to rest.
Despite the variety of origins of diseases of this organ, a number of main signs can be identified that are characteristic of any problem with the pancreas:
- Pain in the left hypochondrium, often girdling in nature and radiating to the back. The intensity of pain increases with a violation of the diet or palpation of the abdomen. Depending on the pathology, they can be of varying intensity, constant or cramping. Pain is the main symptom of problems with the pancreas in adults, which forces the patient to seek medical help.
- Dyspeptic manifestations. This group of symptoms develops with insufficiency of the exocrine pancreas, manifested by constipation and diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
- Decreased appetite, and as a result, weight loss and exhaustion of the body.
The remaining symptoms are more specific, so they will be considered in the context of individual diseases of this organ.
It is also worth noting that the signs of diseases may differ depending on the severity of the pathology and its cause, but they do not depend in any way on gender. Symptoms of pancreatic problems in women and men are the same.
Inflammation of the pancreas or pancreatitis is a common problem of digestive disorders in adults. This pathology can occur acutely or chronically. Acute pancreatitis in adults occurs due to alcohol abuse and poor diet. However, this problem can also occur in children.
Chronic pancreatitis is most often a consequence of untreated acute pancreatitis. It occurs when a patient fails to seek medical help in a timely manner, the patient fails to follow a diet, and takes medication in bad faith.
Inflammatory processes in the gland occur due to blockage of the ducts, which leads to increased pressure in their channels. After a certain time, the ducts are damaged, and their contents, along with enzymes, are released into the blood, thereby injuring the pancreatic cells. The death of parts of the gland occurs (pancreatic necrosis). Enzymes accumulate in excess amounts in the blood (enzymemia), which has a toxic effect on internal organs.
The symptoms listed above should make the patient suspect that there is a problem with the pancreas, which requires immediate medical attention and, possibly, further hospitalization.
When diagnosing pancreatitis, the reference method is the laboratory determination of fecal elastase-1, an enzyme produced by the pancreas. A reduced concentration of this substance in feces indicates external pancreatic insufficiency. In addition, methods are performed to visualize this organ. Ultrasound diagnostics, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging are used.
Treatment and symptoms of pancreatic problems are inextricably linked. After all, pain relief and reduction of dyspeptic symptoms are task No. 1 in the treatment of pancreatitis.
To reduce pain, antispasmodics (Drotaverine, Papaverine) and analgesics (Analgin, Baralgin) are used. The use of narcotic analgesics for pancreatitis (Morphine) is strictly prohibited, as they cause spasm of the pancreatic ducts, which further prevents the outflow of secretions from the gland into the intestines.
It is also necessary to replace those enzymes whose synthesis is disrupted in the pancreas. For this purpose, enzyme replacement therapy is used. This is a separate group of drugs containing pancreatic enzymes (lipase, amylase, trypsin). These include “Creon”, “Pancreatin”.
Another link in the treatment of pancreatic problems is inhibition of the activity of enzymes that enter the bloodstream. For this purpose, the drug “Contrikal” is used.
Particular attention should also be paid to nutrition in diseases of the pancreas, but this will be discussed in the appropriate section.
Cystic fibrosis is a hereditary disease that can manifest itself either immediately after the birth of a child or several years later, depending on the severity of the disease. This pathology affects almost all organs and systems of the body.
It occurs due to a disruption in the exchange of chlorine between cells and the space around them, which leads to an increase in the viscosity of the secretion secreted by the gland. This secretion accumulates and clogs the pancreatic ducts, causing inflammation. This leads to severe exocrine insufficiency.
Diagnosis of the disease consists of determining sweat chlorides (typically increased), and ultrasound examination of the pancreas. Nowadays, genetic testing is becoming more common.
Symptoms of pancreatic problems and treatment are directly related to this disease. Enzyme replacement therapy and diet therapy, as with pancreatitis in adults, play an important role.
The multifunctionality of the pancreas makes it vulnerable to the development of various disorders, which are often caused by the person himself. Consumption of fatty and fried foods and alcoholic beverages leads to disruption of the gland and the appearance of negative symptoms.
Most often, the pancreas is subject to inflammatory and metabolic-dystrophic processes, as a result of which healthy cells die and the production of enzymes and hormones decreases. Problems with the pancreas affect the functioning of the body as a whole, and the patient is concerned not only with digestive and bowel problems.
Due to a deficiency or excess of hormones, glucose and cholesterol levels increase, vascular tone decreases, and the functions of the excretory system are disrupted. Pancreatic diseases can be caused by various reasons.
These include:
- heredity and congenital defects - kinks, hypoplasia, duct abnormalities;
- abdominal trauma;
- neoplasms;
- addiction to alcohol;
- unbalanced diet;
- intoxication;
- prolonged and severe nervous stress;
- past infections;
- the presence of systemic pathologies – hepatitis, cholecystitis, etc.
It must be said that the effect of alcohol on life expectancy is not as clear as is commonly believed. In people who drink daily, the organ can remain healthy, but for a teetotaler, taking even a single dose sometimes results in acute inflammation.
There are many methods for examining the pancreas that allow you to comprehensively assess the condition of the organ and establish an accurate diagnosis. Diagnosis of pancreatic diseases is carried out by a gastroenterologist and includes a physical examination, a patient interview, as well as instrumental studies and laboratory tests.
Based on existing complaints and physical signs, the patient may be prescribed:
- hemogram to assess the qualitative and quantitative composition of blood;
- biochemical blood and urine tests;
- glucose test with or without exercise;
- blood test for enzyme levels;
- coprogram (stool analysis);
- test for tumor markers.
Instrumental examination methods:
- FGS;
- X-ray;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- endoultrasonography;
- CT, MRI;
- biopsy of pancreatic tissue.
In rare cases, ERCP is prescribed - an endoscopic procedure necessary to identify stones, tumors and protein accumulations in the ducts of the gland.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor prescribes treatment, which can be either conservative or surgical. You can read about how to treat pancreatic diseases here. Be healthy!
Symptoms and treatment of pancreatic tumor
Adelina Pavlova
General nurse. More than 40 years of working experience. Retired copywriter.
More about the author
Last updated: October 11, 2019
Preventing Disease Symptoms
In most cases, the presence of symptoms of pathology of the stomach and pancreas is the result of an incorrect lifestyle. To warn them, you need to:
- limit consumption of fatty foods;
- do not overeat;
- give up alcoholic beverages;
- eat more vegetables and fruits;
- eat small meals 4-6 times a day;
- move more;
- promptly treat cholecystitis and other infectious diseases;
- prevent toxic substances from entering the body;
- prevent stress;
- exercise;
- stop smoking;
- drink more clean water;
- take vitamins.
In order to prevent symptoms of diabetes, you need to eat less sweets and periodically take a blood test for glucose. Diet is both a therapeutic and preventive measure. If you have symptoms of pancreatic diseases, you should contact a gastroenterologist. Ignoring complaints can lead to complications (diabetes mellitus, chronicity of the process, tissue necrosis, sepsis, peritonitis, phlegmon, abscess).
How to treat pancreatic diseases in men or women? What are the signs, symptoms of the disease and treatment with medications, proper diet, doctor’s advice.
What affects the condition of the pancreas?
Alcohol takes precedence among the negative factors that can lead to disruption of the pancreas. Abuse of alcoholic beverages leads to an inflammatory process, as a result of which the gland tissue degenerates. By the way, there is no direct connection between the duration of alcohol abuse and the development of the disease.
Also among the causes leading to the disease, concomitant diseases should be highlighted, for example, the presence of gallstones, infections or injuries. In addition, the development of the disease can be triggered by taking certain medications or allergic reactions, including to food or household chemicals.
Unfavorable factors, the presence of which can lead to illness, are frequent stressful situations or depression, during which the process of juice secretion changes.
What are the dangers of pancreatic dysfunction?
The most common disease among adults is pancreatitis, an inflammatory process in the pancreas that can occur in acute or chronic form. In acute pancreatitis, the pancreatic cells literally “melt”; as the inflammatory process progresses, it affects deeper tissues, necrosis develops, and the structure and functions of the organ are disrupted.
In the chronic form, the disease is not so aggressive, but irreversible changes occur in the gland itself, the cells of which are replaced by connective tissue, and the production of digestive enzymes becomes impossible. As a result, intestinal pathologies develop; diabetes mellitus is also one of the most common. In addition, the development of serious diseases such as cysts, abscesses and even pancreatic cancer cannot be ruled out.
Statistics
The variety of diseases of this small organ, which is also an endocrine gland, alarms doctors in different countries with a 4-fold increase in prevalence over the decade, almost 2-fold among adolescents. And also a severe outcome: mortality from pancreatic necrosis stubbornly remains at 90% in some regions.
Analysis of the situation draws attention to the increased connection between pancreatic diseases and alcoholism among people of working age, and with cholelithiasis in patients over 65 years of age.
The prevalence of cases of pancreatic dysfunction has not been calculated, since this type of lesion occurs against the background of other underlying diseases of the digestive, nervous and endocrine systems.
The most frequently detected diseases are acute pancreatitis (3.5–4 per 1000 people), chronic pancreatitis accounts for up to 9% of all gastrointestinal diseases. At the same time, mortality from pancreatitis in all developed countries remains at the level of 25–35%.
Cancer is detected in 10 cases per 100 thousand population. It is considered a rare disease, but is dangerous due to the difficulties of diagnosis and the lack of radical treatment.
How to recognize pancreatitis and what are its main symptoms?
Pain sensations can be either dull and pulling, or cutting; the nature of the pain depends on the volume of the lesion, the presence of edema or necrosis, and the involvement of surrounding tissues in the process. Often the pain can be girdling, radiating to the hypochondrium, behind the sternum, collarbone or back - this is due to the location of the main focus of the pathology.
Nausea, vomiting, stool disorders that appear at the onset of the disease and are associated with errors in diet. With intense manifestations, dehydration is possible; in severe cases, disruption of the heart and the development of multiple organ failure cannot be ruled out.
Skin changes
Pallor and jaundice appear as a result of compression of the bile ducts due to swelling of the gland, cyanosis of the skin of the abdomen is caused by poor circulation, etc. In acute pancreatitis, subcutaneous nodules up to 3 cm in size, petechiae on the buttocks can be detected, and the presence of rashes on the skin may indicate a chronic form.
First signs
Often the first sign is pain around the belly button (in the upper abdomen). Its intensity depends on the extent to which inflammation is expressed; it is for this reason that during the acute course of the disease the pain is very pronounced.
With pancreatitis, the pain is girdling in nature and is reflected throughout the back and abdomen. Often the pain is quite severe and long-lasting. Painful spasms can also intensify after eating, drinking, and when lying down. It is possible to relieve pain by not eating food and applying ice to the stomach.
In addition, the first signs may be heaviness in the abdomen, gas formation, and nausea. This disorder may be accompanied by vomiting, which does not bring any relief; it occurs in acute and chronic pancreatitis.
The causes of pancreatic diseases can be:
- Ingestion of significant quantities of fatty, fried and spicy foods.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Pregnancy period (early period after childbirth).
- Injury in the abdominal area.
- Gallbladder diseases.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Ulcer.
These are the basic causes of pain, but folk therapy for the gland will be a good help if you follow all the principles and carry out systematic procedures.
Is it possible to maintain the health of the pancreas?
The pace of today's life dictates its own conditions; snacking instead of a full lunch, dry meals, excess fried or smoked meats, failure to observe the optimal break between meals, etc. have become the norm. The situation is aggravated by the stress that awaits us at literally every step. With such a lifestyle, the disease will not keep itself waiting.
As a preventive measure, unfavorable factors that can provoke the disease should be excluded. Regular and adequate physical activity will help combat inactivity. What if you don’t have enough time to play sports? Even walking can easily replace going to the gym.
And most importantly, remember!
Overeating leads to many problems; excess weight is the cause of many diseases, including the pancreas. In addition, one of the most common pathologies today, cholelithiasis, causes pancreatitis in 25% of cases. But by adhering to the basics of a healthy diet, you can prevent disruption of the digestive system.
If any signs of trouble appear, do not waste time on self-medication; only timely and competent help from specialists will help you avoid long and grueling treatment!
Oksana Matiash, general practitioner
Illustrations: Anastasia Leman
How is pancreatic disease treated?
A comprehensive examination to clarify the disease usually requires hospitalization. All pancreatic diseases are treated in a hospital setting. Sometimes a council of doctors comes to the conclusion that an urgent operation is necessary.
Treatment of an acute attack in a hospital provides the patient with motor rest; for this, bed rest is prescribed. The three important components of the basic treatment are cold, hunger and rest.
For the first 2 days, fasting is recommended, the body's strength is maintained by intravenous infusions of saline solution, and the introduction of plasma substitutes. It is allowed to drink up to 6 glasses a day of decoctions of medicinal herbs.
The attending physician immediately prescribes:
- injections of painkillers;
- injections of antispasmodics, usually Baralgin, Platyfillin, No-Shpa, Drotaverine, Acetaminophen, Ibuprofen;
- injections of anticholinergics, it is always Atropine.
During the day, a heating pad with ice is applied to the epigastric zone several times for ½ hour. Oral medication is prescribed in the absence of vomiting. Here the choice of medication is up to the doctor.
Must be assigned:
- antihistamines;
- antibiotics;
- insulin-glucose drugs;
- anabolics;
- vitamins.
At the first stage of an acute illness, antacid medications help well. They are used in the form of gels, suspensions, and neutralize acidic environments well - Almagel, Phosphalugel. Reduce acid production in the stomach: Contraloc, Omez, Omeprazole, Gastrozol, Proseptin, Otsid.
In hospital settings, H2 blockers are prescribed: Ranitidine, Famotidine, Acidex, Zoran, Gasterogen, Pepsidin.
Medications that reduce the synthesis of pancreatic enzymes are administered through intravenous drips. As a rule, these are Trasylol, Contrical, Gordox, Aprotinin. To avoid dehydration during the fasting period, salt and electrolyte solutions are administered via droppers in doses selected by the doctor in accordance with the patient’s condition, with the presence of concomitant pathologies.
When acute symptoms are relieved, the patient begins to receive gentle nutrition and take enzyme tablets - Creon, Mezim, Pancreatin, Panzinorm, Festal, Enzistal - as prescribed by the doctor.
Enzymes restore the functioning of the digestive tract and allow you to switch to a gentle diet. Effective enzyme preparations are Contrikal and Aprotinin. They reduce the synthesis of enzymes and facilitate digestion.
However, common enzymes are produced based on pork protein; if you are allergic to pork, they cannot be used so as not to cause intestinal obstruction.
In this case, doctors have herbal preparations in their arsenal, produced from rice fungus or papain: Unienzyme, Somilaza, Pepfiz.
The course of treatment with enzymes is long; they are taken by the sick person throughout his life as supportive agents, even in the stage of remission of the disease. Patients themselves determine where the gland hurts, and adhere to the diet strictly. Even with dietary nutrition, enzymes are required.
To stimulate pancreatic secretion, Pilocarpine, Morphine, vitamin A, and magnesium sulfate are prescribed. Histamine and Atropine are used to reduce secretion. When the disease leads to diabetes, the doctor includes insulin medications in the course of treatment.
Isolated enzyme deficiency
Pancreatic problems in children can occur due to an isolated deficiency of one of three enzymes: lipase, trypsin or amylase.
Lipase deficiency is characterized by diarrhea and fatty stools. When diagnosed using a coprogram, a large amount of undigested fat in the stool (steatorrhea) is determined. The amount of fecal elastase-1 also decreases.
An isolated disorder of amylase production is possible, which is characterized by the presence of diarrhea with undigested starch (amilorrhea). Trypsin deficiency is also possible, causing diarrhea with protein inclusions (creatorrhoea). Malabsorption of protein leads to a decrease in its amount in the body (hypoproteinemia), which contributes to the development of massive edema.
This pathology, fortunately, is quite rare, but it is worth knowing and remembering when diagnosing problems with the pancreas in children.
Diet therapy
Special attention should be paid to diet when treating pancreatic diseases. When treating diseases of this organ, patients are recommended to eat the following dishes:
- White bread;
- light soups with vegetable broth;
- lean types of meat: rabbit, chicken, turkey, lean pieces of beef, steamed, boiled or baked;
- vegetables in any form, except fried;
- dairy products;
- vegetable fats - vegetable oil, a small amount of butter is allowed;
- no more than one egg per day;
- among sweets, only fruit, compote, and honey are allowed;
- among drinks, preference should be given to tea and rosehip infusion.
When correcting nutrition for problems with the pancreas, the following foods are prohibited:
- fatty meat and fish;
- fried foods;
- smoked dishes;
- smoked meats and spices;
- baked goods, sweets, chocolate;
- alcohol.
Following this diet in combination with drug treatment will help get rid of problems with the pancreas!